News
DeepSpace: Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin banter about the fine print of suborbital tourism

Welcome to the sixth edition of our new newsletter, DeepSpace! Each Tuesday, I’ll be taking a deep-dive into the most exciting developments in commercial space, from satellites and rockets to everything in between. If you’d like to receive DeepSpace and all of our newsletters and membership benefits,
Just shy of two months into 2019, the new year has been marked by a distinct focus on human spaceflight. Most of that focus has centered (as it should) on the relatively imminent launch debut of both SpaceX’s Crew Dragon and Boeing’s Starliner, crewed spacecraft designed and built to carry astronauts into orbit for NASA.
However, beyond SpaceX and Boeing, a considerable amount of noise is being made about the labors and relative progress of companies like Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic, both primarily focused on building a suborbital tourism market with their New Shepard and SpaceShipTwo launch vehicles. Coming as no surprise from companies aiming to create a sustainable market for a very expensive consumer product, both products have been dragged through a torturous maze of marketing hype in a process that has not really done the serious endeavor of human spaceflight any favors.
The Shepard and the Ship
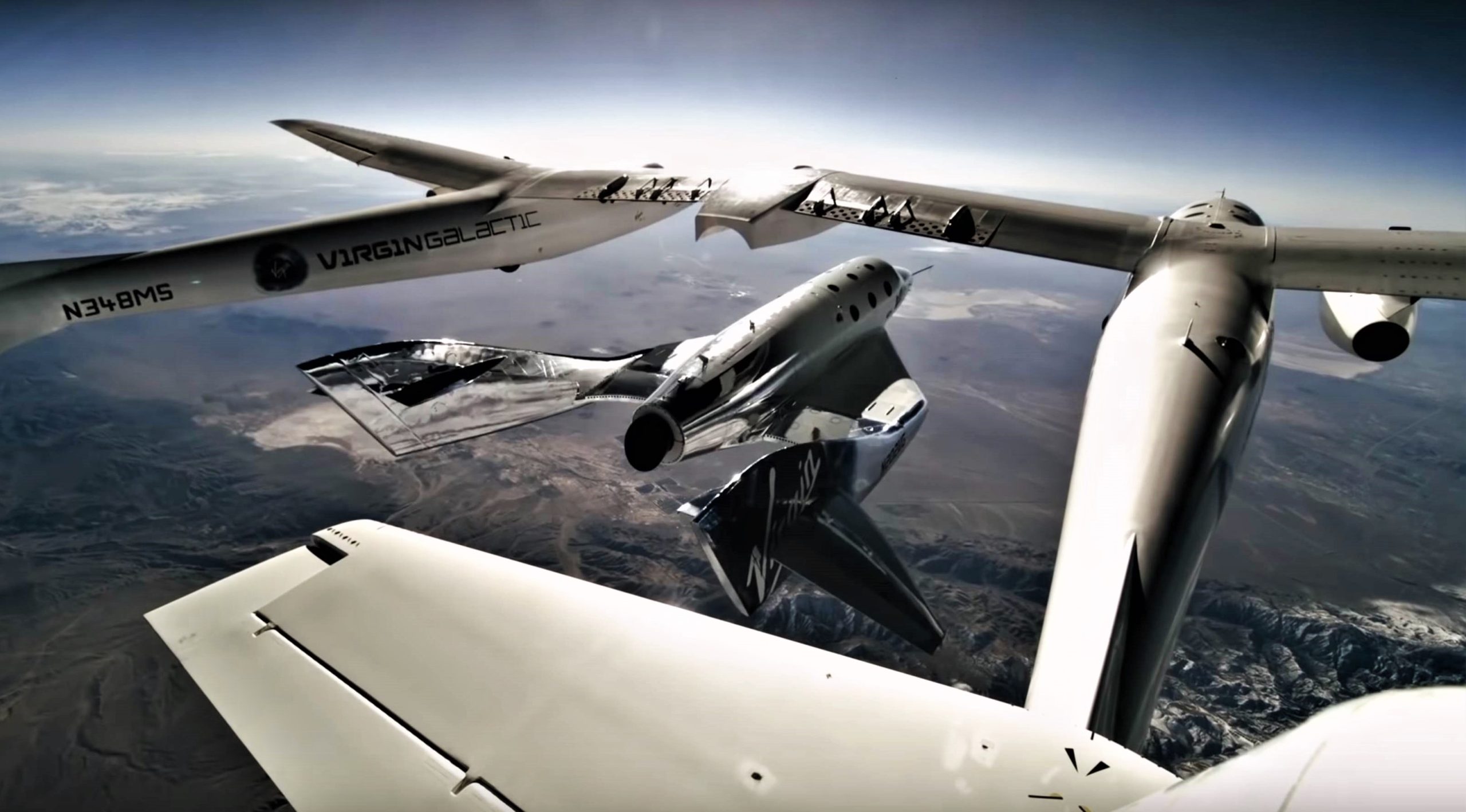
- Virgin Galactic’s launch vehicle provider The Spaceship Company has been working to develop a suborbital platform to launch humans since the early 2000s, incorporated after billionaire Paul Allen funded a group of companies that ultimately won the Ansari X Prize in 2004.
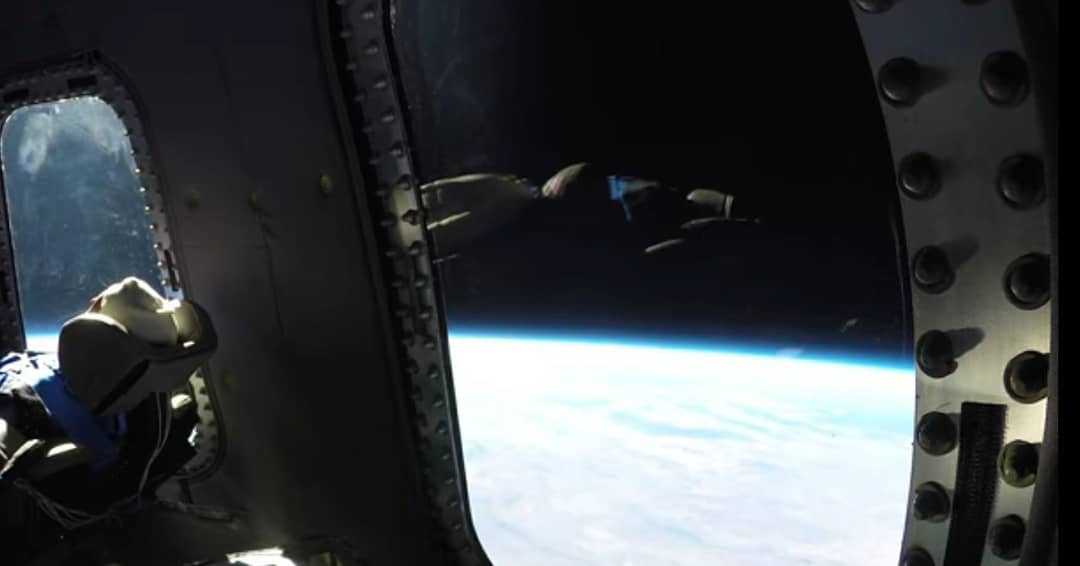
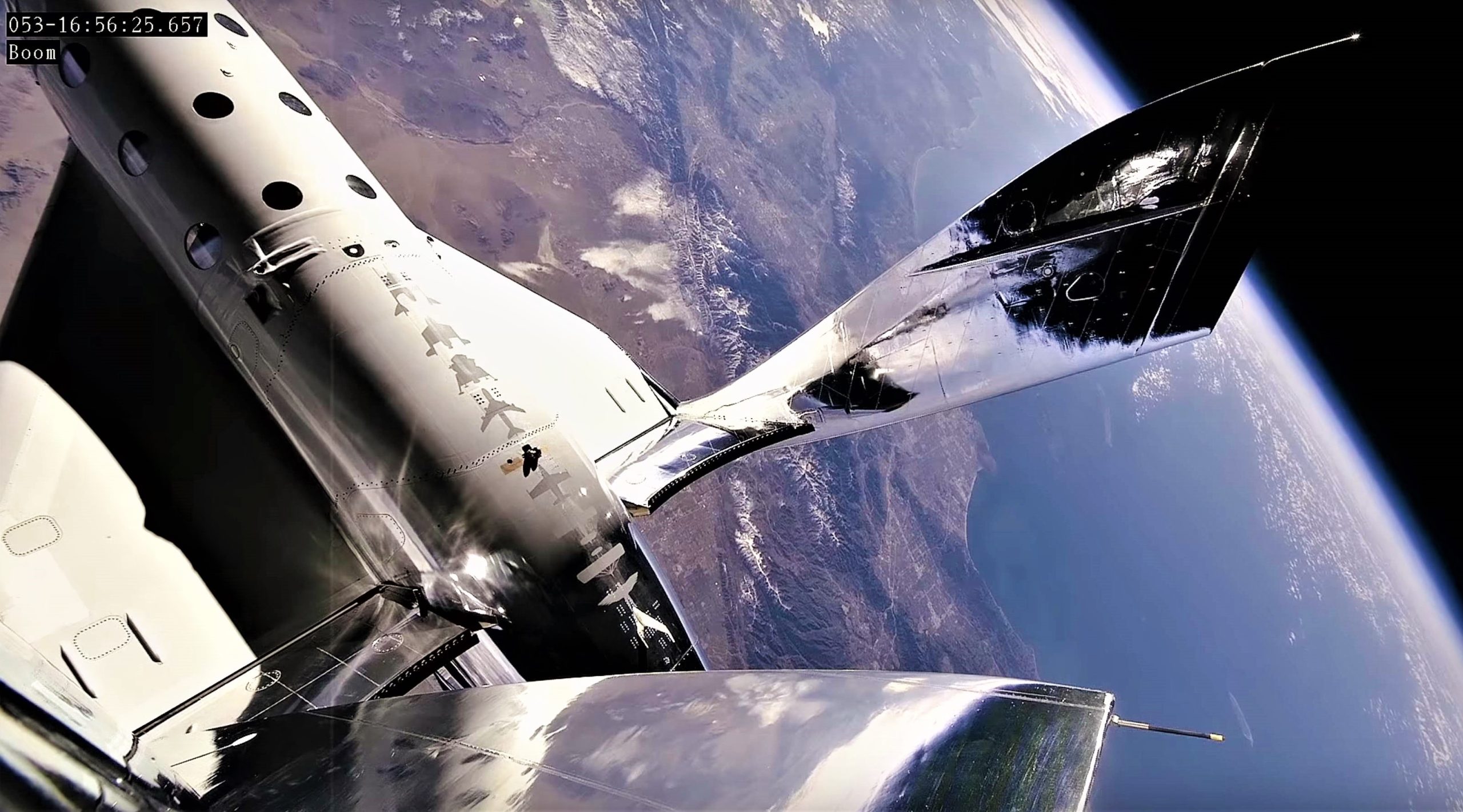
- The Virgin/TSC approach involves a carrier aircraft (Known as White Knight Two) and a much smaller rocket plane (SpaceShipTwo) that is carried up to ~30,000 feet (9 km) before dropping and igniting its engine.
- SpaceShipTwo is meant to reach a maximum altitude of around 300,000 feet (~90 km) at a top speed of roughly Mach 3 (1000 m/s, 2200 mph) before gliding back to land on the same runway.
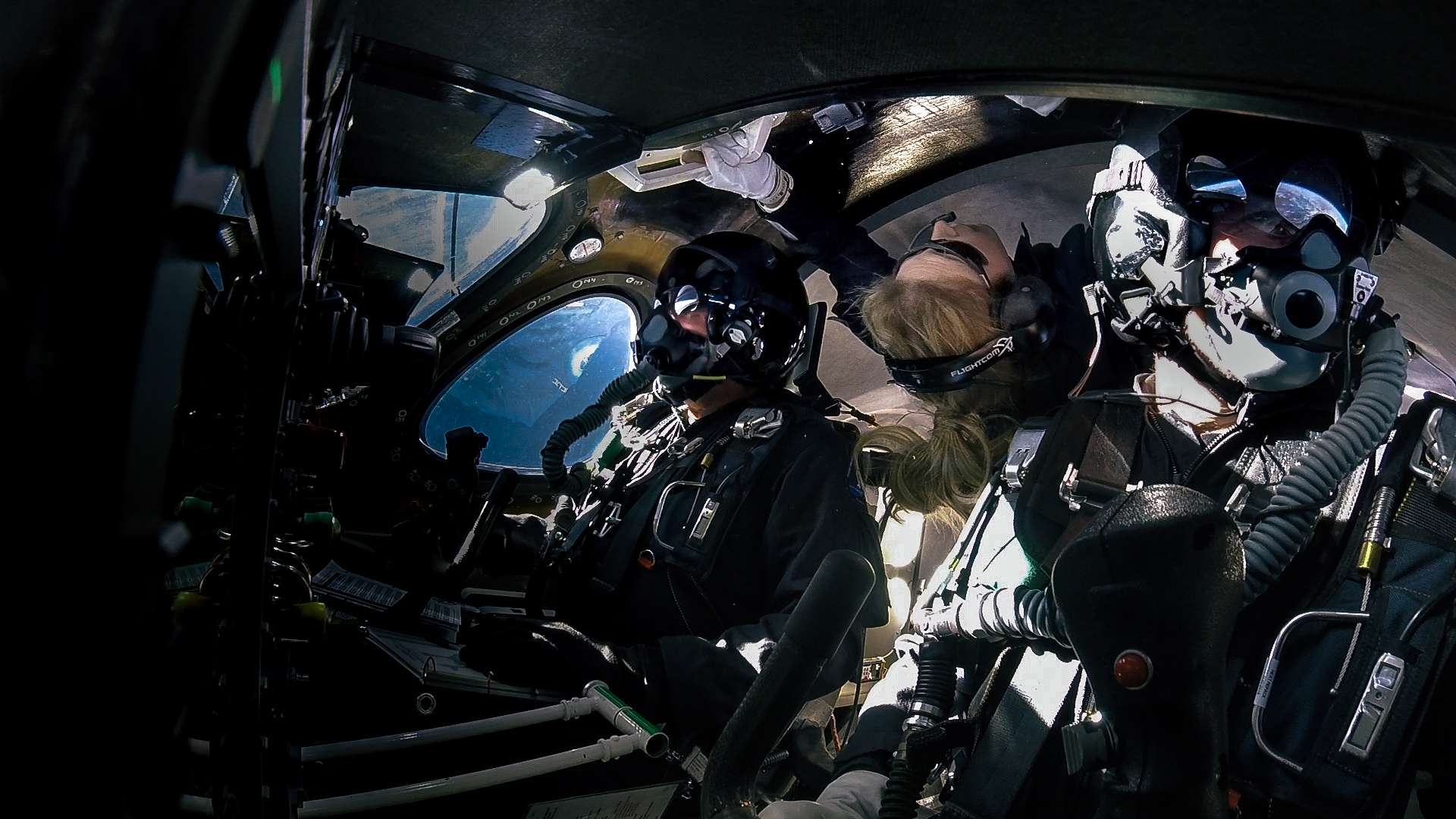
- In 2014, a combination of bad aeronautical design and pilot error triggered the in-flight failure of the first SpaceShipTwo, killing one of its two pilots. A member of the NTSB board that investigated the failure stated that Scale Composites (one of TSC’s parent companies) “put all their eggs in the basket of the pilots [flying the vehicle] correctly.”
- In a February 2019 video, Virgin Galactic CEO George Whitesides noted that “many aircraft are moving to being less piloted over time [but] our vehicle really is piloted to space.”
- SpaceShipTwo most recently launched on February 22nd.
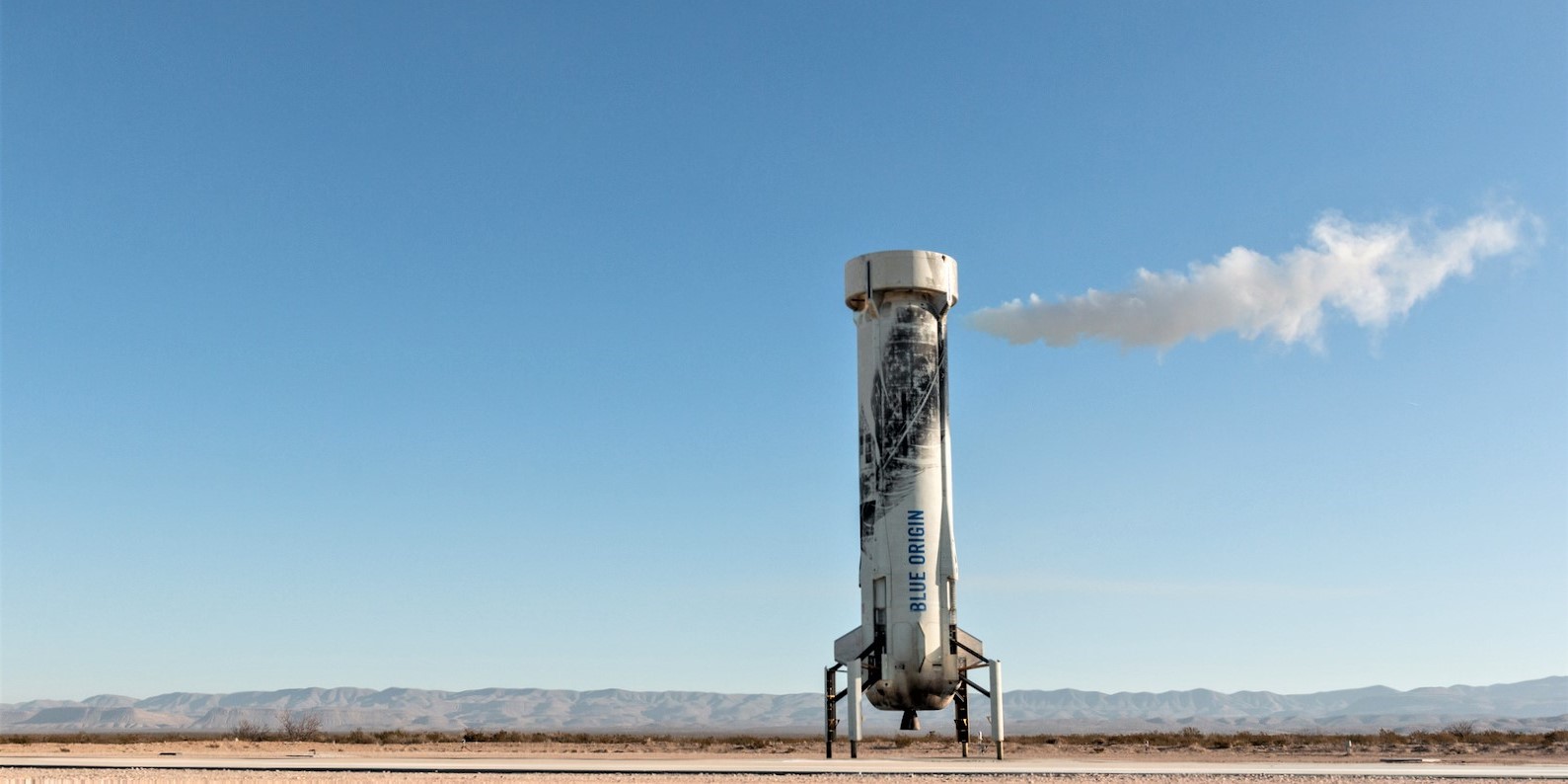
- Blue Origin has yet to launch an actual human on New Shepard, a small, reusable single-stage rocket designed to loft a separate passenger capsule to approximately 100 km (330,000 ft).
- New Shepard has conducted ten launches since its 2015 debut, most of which saw the crew capsule and booster approximately reach that nominal 100 km apogee and nine of which concluded with a successful landing of the rocket’s booster.
- Capable of carrying up to six passengers, the Crew Capsule features a built-in abort motor that has been successfully tested, as well as a parachute system for a relatively soft landing at end-of-mission.


“Spacecraft” and “astronauts”
- Aside from the generally impressive technology itself and the undeniable challenges and risks of launch humans on fueled rockets, both Blue Origin’s New Shepard and Virgin Galactic’s SpaceShipTwo exist – albeit with different weights – to cater to a new market, suborbital or “space” tourism.
- While NASA is taking advantage of the opportunities to test small experiments with both vehicles as a partial platform, the real goal of both vehicles is to routinely launch paying customers.
- While Blue Origin has yet to announce ticket pricing, Virgin Galactic has priced their offering at $250,000 per person. In both cases, the end result will likely be a six-figure sum in return for an experience that should last no more than 10-60 minutes from start to finish, excluding buildup from screening and whatever training is deemed necessary.
- In other words, short of cases involving charity, tickets on New Shepard and SpaceShipTwo will almost indefinitely be reserved for less than 1% of humanity, those with income around $1M or more per year. This is by no means a bad thing and is, in fact, a proven first or second step in the direction of democratizing exotic or expensive technologies like air travel, computers, and even electric cars (namely Teslas).
- However, both companies are laser-focused on branding their vehicles as spacecraft and their passengers as astronauts, with Virgin Galactic being the worst offender in this regard.
- Aside from literally calling its 600+ prospective customers “Future Astronauts”, Virgin Galactic uses every chance it gets to hammer home its claim that SpaceShipTwo is a commercial spacecraft and its pilots true licensed, “wing”-ed astronauts.
- While passengers are not eligible for official FAA ‘astronauts’ wings’, it appears that Virgin will continue to market its passenger experience as one where customers will get to ‘travel to space’ and more or less become astronauts.
- Blue Origin describes its commercial offering as a “reusable suborbital rocket system designed to take astronauts and research payloads past the Kármán line – the internationally recognized boundary of space.”
- Both Blue and Virgin flights offer about ~4 minutes of weighlessness between launch and landing.
- Virgin Galactic Makes Space for Second Time in Ten Weeks with Three On Board
- For context, Alan Shepard – the US test pilot and namesake of New Shepard – was launched to an altitude of almost 190 km (120 mi) for what was recognized as the first US “spaceflight” and spent something like 5-10 minutes in microgravity and above the Karman Line (100 km).
- Used as a rough measure for a sort of fixed, arbitrary boundary between “Earth” and “Space”, reasonable arguments have been made in the last few years that the 100 km Karman Line could more accurately be placed around 70-90 km, in which case Virgin Galactic might actually be technically correct when saying that SpaceShipTwo and its passengers are traveling to space.
- Fewer than 570 humans in all of history have visited space (> 100 km), around 99.5% of which were astronauts that reached orbit. To call pilots of a spaceplane as distinctly suborbital as SpaceShipOne “astronauts” is palatable, particularly given the risks they face as test subjects and test pilots.
- However, to even hinting that tourists riding New Shepard or SpaceShipTwo to altitudes of ~80-100 kilometers are astronauts would do an immense disservice to those that pushed the limits of technology, risked their lives, or even died in pursuit of orbital spaceflight, the only kind of spaceflight with any significant utility.
- Much like cruise ship customers are not under the impression that they are coming along to ‘become sailors’, suborbital tourists are not astronauts. That being said, it’s not inaccurate to describe the experience they will have the privilege of being part of as something truly extraordinary, given that they will become one of a very select few humans to have actually launched on a rocket or seen the exaggerated curvature of Earth’s limb against the blackness of space.
- SpaceX’s first attempted orbital launch of Crew Dragon – a spacecraft designed to transport astronauts to and from the International Space Station – is set to occur as early as 2:49 am EST/07:49 UTC on March 2nd.
- This is the first truly serious date, thanks to the successful completion of a critical pre-launch review conducted by NASA and SpaceX.
- The second launch of Falcon Heavy could occur as early as late March
- Aside from DM-1 and Falcon Heavy Flight 2, it’s unclear what SpaceX mission will happen next, although a West Coast launch (the Radarsat Constellation Mission) is a strong candidate.
Mission Updates |
Photos of the Week:
After successfully sending the world’s first commercial lunar lander on its way to the Moon and placing Indonesian communications satellite PSN-6 in a high-energy Earth orbit, Falcon 9 B1048 completed its third launch and landing and returned to port on February 24th. The booster’s fourth mission, a Crew Dragon in-flight abort test, will likely destroy B1048, making this its last successful recovery. (c. Tom Cross)



News
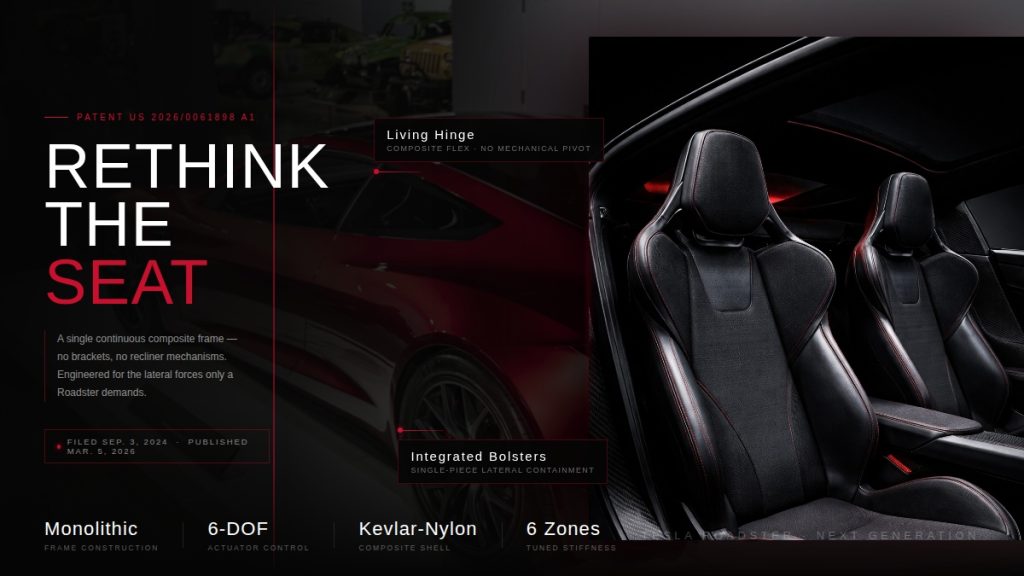
Tesla Roadster patent hints at radical seat redesign ahead of reveal

A newly published Tesla patent could offer one of the clearest signals yet that the long-awaited next-generation Roadster is nearly ready for its public debut.
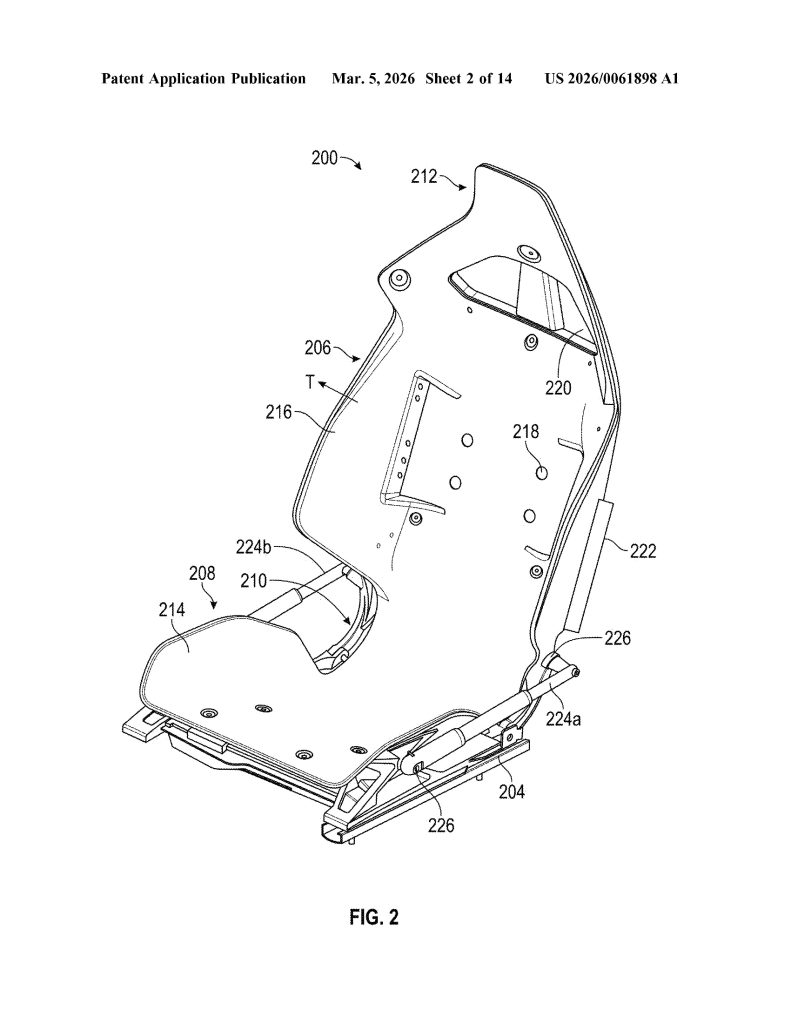
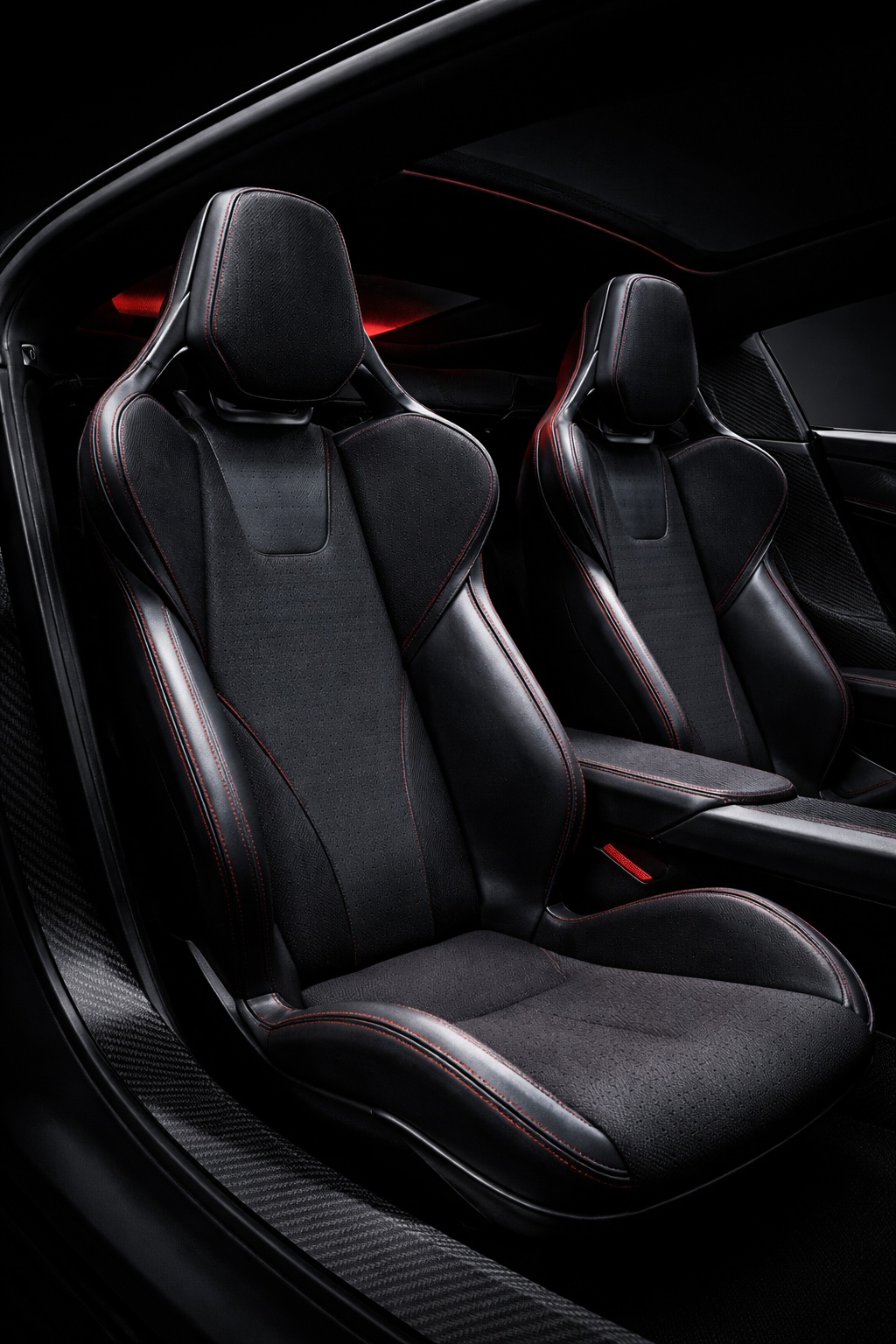
Patent No. US 20260061898 A1, published on March 5, 2026, describes a “vehicle seat system” built around a single continuous composite frame – a dramatic departure from the dozens of metal brackets, recliner mechanisms, and rivets that make up a traditional car seat. Tesla is calling it a monolithic structure, with the seat portion, backrest, headrest, and bolsters all thermoformed as one unified piece.
The approach mirrors Tesla’s broader manufacturing philosophy. The same company that pioneered massive aluminum castings to eliminate hundreds of body components is now applying that logic to the cabin. Fewer parts means fewer potential failure points, less weight, and a cleaner assembly process overall.
Tesla ramps hiring for Roadster as latest unveiling approaches
The timing of the filing is difficult to ignore. Elon Musk has publicly targeted April 1, 2026 as the date for an “unforgettable” Roadster design reveal, and two new Roadster trademarks were filed just last month. A patent describing a seat architecture suited for a hypercar, and one that Tesla has promised will hit 60 mph in under two seconds.
The Roadster, originally unveiled in 2017, has been one of Tesla’s most anticipated yet most delayed products. With a target price around $200,000 and engineering ambitions to match, it is being positioned as the ultimate showcase for what Tesla’s technology can do.
The patent was first flagged by @seti_park on X.
Tesla Roadster Monolithic Seat: Feature Highlights via US Patent 20260061898 A1
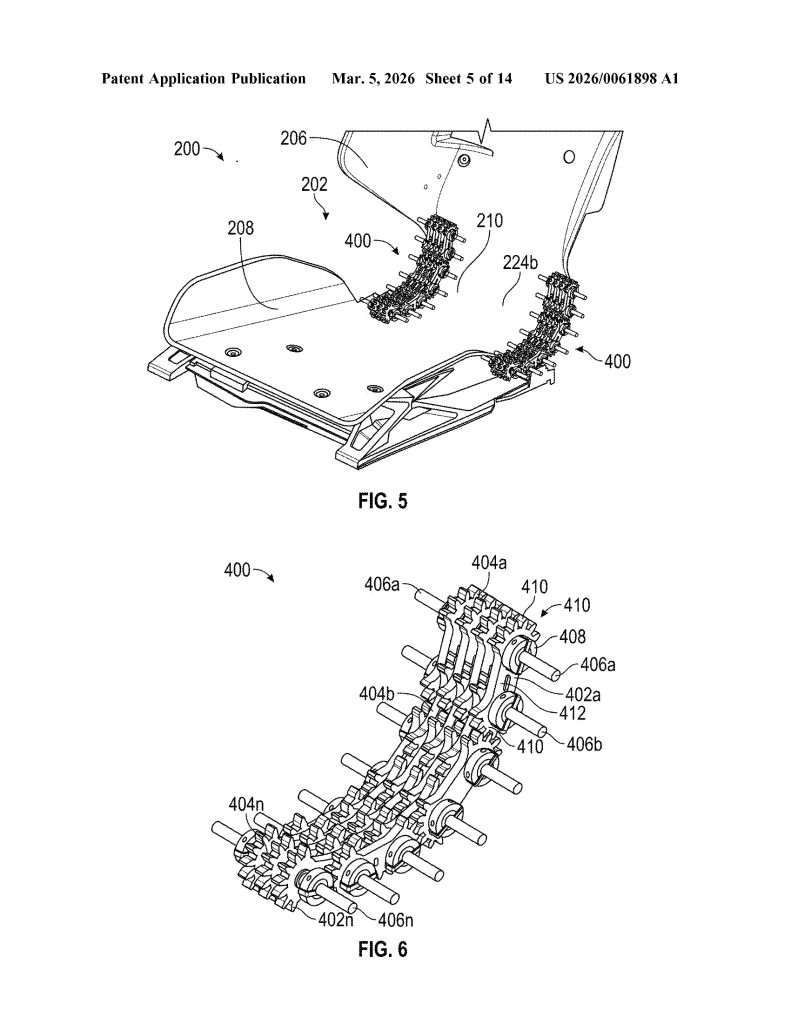
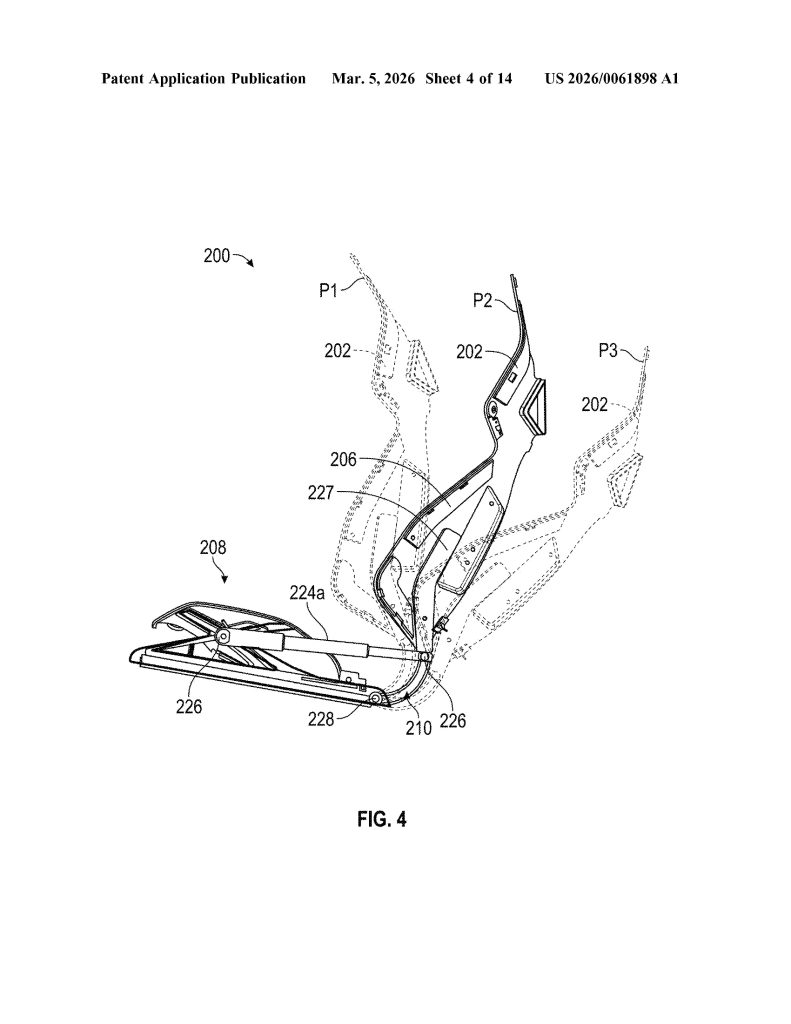
- Single Continuous Frame (Monolithic Construction). The core invention is a seat assembly built from one continuous frame that integrates the seat portion, backrest portion, and hinge into a single component — eliminating the need for separate structural parts and mechanical joints typical in conventional seats.
- Integrated Flexible Hinge. Rather than a traditional mechanical recliner, the hinge is built directly into the continuous frame and is designed to flex, and allowing the backrest to move relative to the seat portion. The hinge can be implemented as a fiber composite leaf spring or an assembly of rigid linkages.
- Thermoformed Anisotropic Composite Material. The continuous frame is manufactured via thermoforming from anisotropic composite materials, including fiberglass-nylon, fiberglass-polymer, nylon carbon composite, Kevlar-nylon, or Kevlar-polymer composites, enabling a molded-to-shape monolithic structure.
- Regionally Tuned Stiffness Zones. The frame is engineered with up to six distinct stiffness regions (R1–R6) across the seat, backrest, hinge, headrest, and bolsters. Each zone can have a different stiffness, allowing precise ergonomic and structural tuning without adding separate components.
- Linkage Assembly Hinge Mechanism. The hinge incorporates one or more linkage assemblies consisting of multiple interlocking links with gears, connected by rods. When driven by motors or actuators, these linkages act as a flexible member to control backrest movement along a precise, ergonomically optimized trajectory.
- Multi-Actuator Six-Degree-of-Freedom Positioning System. The seat uses four distinct actuator pairs, all controlled by a central controller. These actuators work in coordinated combinations to achieve fore/aft, height, cushion tilt, and backrest rotation adjustments simultaneously.
- ECU-Based Controller Architecture. An Electronic Control Unit (ECU) and programmable controller manage all seat actuators, receive user input via a user interface (touchscreen, buttons, or switches), and incorporate sensor feedback to confirm and maintain desired seat positions, essentially making this a software-driven seat system.
- Airbag-Integrated Bolster Deployment System. The backrest bolsters (216) are geometrically shaped and sized to guide airbag deployment along a specific, pre-configured trajectory. Left and right bolsters can have different shapes so that each guides its respective airbag along a distinct trajectory, improving occupant protection.
- Ventilation Holes Formed into the Backrest. The continuous frame includes one or more ventilation holes formed directly into the backrest portion, configured to either receive airflow into or deliver airflow from the seat frame — enabling passive or active thermal comfort without requiring separate ventilation components.
- Soft Trim Recess for Tool-Free Integration. The headrest and backrest portions together define a molded recess, specifically designed to receive and secure a soft trim component (foam, fabric, or cushioning) directly into the continuous frame, eliminating the need for separate attachment hardware and simplifying final assembly.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk’s xAI plans $659M expansion at Memphis supercomputer site
The new building is planned for a 79-acre parcel located at 5414 Tulane Road, next to xAI’s Colossus 2 data center site.

Elon Musk’s artificial intelligence company xAI has filed a permit to construct a new building at its growing data center complex outside Memphis, Tennessee.
As per a report from Data Center Dynamics, xAI plans to spend about $659 million on a new facility adjacent to its Colossus 2 data center. Permit documents submitted to the Memphis and Shelby County Division of Planning and Development show the proposed structure would be a four-story building totaling about 312,000 square feet.
The new building is planned for a 79-acre parcel located at 5414 Tulane Road, next to xAI’s Colossus 2 data center site. Permit filings indicate the structure would reach roughly 75 feet high, though the specific function of the building has not been disclosed.
The filing was first reported by the Memphis Business Journal.
xAI uses its Memphis data centers to power Grok, the company’s flagship large language model. The company entered the Memphis area in 2024, launching its Colossus supercomputer in a repurposed Electrolux factory located in the Boxtown district.
The company later acquired land for the Colossus 2 data center in March last year. That facility came online in January.
A third data center is also planned for the cluster across the Tennessee–Mississippi border. Musk has stated that the broader campus could eventually provide access to about 2 gigawatts of compute power.
The Memphis cluster is also tied to new power infrastructure commitments announced by SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell. During a White House event with United States President Donald Trump, Shotwell stated that xAI would develop 1.2 gigawatts of power for its supercomputer facility as part of the administration’s “Ratepayer Protection Pledge.”
“As you know, xAI builds huge supercomputers and data centers and we build them fast. Currently, we’re building one on the Tennessee-Mississippi state line… xAI will therefore commit to develop 1.2 GW of power as our supercomputer’s primary power source. That will be for every additional data center as well…
“The installation will provide enough backup power to power the city of Memphis, and more than sufficient energy to power the town of Southaven, Mississippi where the data center resides. We will build new substations and invest in electrical infrastructure to provide stability to the area’s grid,” Shotwell said.
Shotwell also stated that xAI plans to support the region’s water supply through new infrastructure tied to the project. “We will build state-of-the-art water recycling plants that will protect approximately 4.7 billion gallons of water from the Memphis aquifer each year. And we will employ thousands of American workers from around the city of Memphis on both sides of the TN-MS border,” she said.
News
Tesla wins another award critics will absolutely despise
Tesla earned an overall score of 49 percent, up 6 percentage points from the previous year, widening its lead over second-place Ford (45 percent, up 2 points) to a commanding 4-percentage-point gap. The company also excelled in the Fossil Free & Environment category with a 50 percent score, reflecting strong progress in reducing emissions and decarbonizing operations.

Tesla just won another award that critics will absolutely despise, as it has been recognized once again as the company with the most sustainable supply chain.
Tesla has once again proven its critics wrong, securing the number one spot on the 2026 Lead the Charge Auto Supply Chain Leaderboard for the second consecutive year, Lead the Charge rankings show.
NEWS: Tesla ranked 1st on supply chain sustainability in the 2026 Lead the Charge auto/EV supply chain scorecard.
“@Tesla remains the top performing automaker of the Leaderboard for the second year running, and increased its overall score by 6 percentage points, while Ford only… pic.twitter.com/nAgGOIrGFS
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) March 4, 2026
This independent ranking, produced by a coalition of environmental, human rights, and investor groups including the Sierra Club, Transport & Environment, and others, evaluates 18 major automakers on their efforts to build equitable, sustainable, and fossil-free supply chains for electric vehicles.
Tesla earned an overall score of 49 percent, up 6 percentage points from the previous year, widening its lead over second-place Ford (45 percent, up 2 points) to a commanding 4-percentage-point gap. The company also excelled in the Fossil Free & Environment category with a 50 percent score, reflecting strong progress in reducing emissions and decarbonizing operations.
Perhaps the most impressive achievement came in the batteries subsection, where Tesla posted a massive +20-point jump to reach 51 percent, becoming the first automaker ever to surpass 50 percent in this critical area.
Tesla achieved this milestone through transparency, fully disclosing Scope 3 emissions breakdowns for battery cell production and key materials like lithium, nickel, cobalt, and graphite.
The company also requires suppliers to conduct due diligence aligned with OECD guidelines on responsible sourcing, which it has mentioned in past Impact Reports.
While Tesla leads comfortably in climate and environmental performance, it scores 48 percent in human rights and responsible sourcing, slightly behind Ford’s 49 percent.
The company made notable gains in workers’ rights remedies, but has room to improve on issues like Indigenous Peoples’ rights.
Overall, the leaderboard highlights that a core group of leaders, Tesla, Ford, Volvo, Mercedes, and Volkswagen, are advancing twice as fast as their peers, proving that cleaner, more ethical EV supply chains are not just possible but already underway.
For Tesla detractors who claim EVs aren’t truly green or that the company cuts corners, this recognition from sustainability-focused NGOs delivers a powerful rebuttal.
Tesla’s vertical integration, direct supplier contracts, low-carbon material agreements (like its North American aluminum deal with emissions under 2kg CO₂e per kg), and raw materials reporting continue to set the industry standard.
As the world races toward electrification, Tesla isn’t just building cars; it’s building a more responsible future.