SpaceX
DeepSpace: A critical juncture for SpaceX, Blue Origin, ULA, other players

This is a free preview of DeepSpace, Teslarati’s new member-only weekly newsletter. Each week, I’ll be taking a deep-dive into the most exciting developments in commercial space, from satellites and rockets to everything in between. Sign up for Teslarati’s newsletters here to receive a preview of our membership program.
A high-pressure competition between all four major US launch providers – SpaceX, ULA, Blue Origin, and Orbital ATK (now NGIS) – is about to head into its most critical stage, a period of 60 days allotted for interested parties to submit their completed proposals. According to the US Air Force (USAF), the final request for proposals (RFP) could come as early as March 29th, giving the four aforementioned companies until May 28th to complete their proposals.
All things considered, the growing pressure and some of the USAF’s strategy behind the program – known as Launch Service Procurement (LSP) Phase 2 – has raised significant questions that remain largely unanswered and lead to a few mild bouts of strife or unhappiness from contract competitors. Most notably, Blue Origin – having just won a USAF development contract worth $500M – has repeatedly requested that the USAF and Department of Defense (DoD) delay the RFP and contract awards until 2021, according to Space News’ Sandra Erwin. Meanwhile, a lack of clarification from the USAF means that it’s unclear whether the strategy behind launch contract awards (LSP) will end up contradicting or undermining a partially connected development program known as Launch Service Agreements (LSA) that saw the USAF award ~$2B to three providers (excluding SpaceX) between 2018 and 2024.
Battle of the Acronyms: LSP vs. LSA
- Recently rebranded by the US military as the National Security Space Launch (NSSL) program, LSP Phase 1 and 2 and LSA are the latest major procurement initiatives begun under the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) program, spun up in the 1990s to provide a firmer foundation for the commercial launch of military spacecraft after the 1986 Shuttle Challenger disaster pushed most satellites off of the platform.
- Phase 2 of the EELV program has been ongoing for several years and will culminate with the procurement of 25+ launch contracts (LSP) from two providers no earlier than 2020. The USAF’s Launch Service Agreements are also a major strategic feature of Phase 2, nominally seeing the military branch contribute major funding to assist in the development of three separate launch vehicles (New Glenn, Vulcan, and Omega) with the intention of ultimately certifying those rockets for EELV (now NSSL) launches.
- LSA also saw the USAF award several tens of millions to SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Aerojet Rocketdyne to develop capabilities centered around advanced, new rocket engines (BE-4, AR-1, and Raptor), but the latest phase of LSA is valued at least several times higher than its earlier engine-specific awards.
-
- Oddly, the purpose of LSA was – at least on the cover – to effectively ensure that the Air Force had multiple (more than two) providers and thus preserve a healthy, competitive military launch market. A senior leader specifically stated that “the goal of [LSA] is to make sure [the US military has] a competitive industrial base.”
- Aside from an initial $181M awarded to Blue Origin, ULA, and Orbital ATK (now Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems, NGIS) in 2018 and 2019, the remaining funding – up to $320M for Blue Origin’s New Glenn, $610M for NGIS’ Omega, and $785M for ULA’s Vulcan – would be dispersed to each provider between 2020 and 2024.
- However, an odd and controversial bit of language behind the coming five-year launch services procurement (LSP) initiative would completely cut off funding to LSA awardees in the event that they fail to be awarded launches from the latest LSP.
- Additionally, the LSP awards are strictly meant – apparently very intentionally – to be distrubuted among two launch providers, despite a minimum at least four being able (SpaceX) or required (ULA, Blue, NGIS) to enter a bid.
- In other words, this guarantees that either one or two of the three LSA awardees would have the vast majority of their supposedly awarded development funding cut off after FY2020, four years early.
- Oddly, the purpose of LSA was – at least on the cover – to effectively ensure that the Air Force had multiple (more than two) providers and thus preserve a healthy, competitive military launch market. A senior leader specifically stated that “the goal of [LSA] is to make sure [the US military has] a competitive industrial base.”
- Despite continued protests from a number of stakeholders, the USAF has refused to budge from its decision to simultaneously A) create a duopoly, B) defeat the purpose of LSA awards, and C) mass-award ~25 launch contracts to two providers in 2020, anywhere from 12-24 months prior to the planned inaugural launches of all three LSA-funded rockets.
- Without cost-sharing development funds from the USAF and a chance of winning more than a handful of US military launch contracts between now and the late 2020s, it can be all but guaranteed that an LSA funding cutoff will either indefinitely pause or slow to a crawl a given provider’s development of their proposed launch vehicle.

A rocket and a hard place
- This sticky situation thus offers up a few potential ways that this badly-designed (or entirely dishonest) military launch development and procurement strategy will end up by the end of 2020. One way or another, the current strategy as it stands will end up providing two (or one, given that SpaceX will not receive LSA funding) companies with several years of development funding and at least five years of bountiful, guaranteed launch contracts.
- The four providers and two LSP slots available offer a set range of possible alternate realities, limited by political barriers that would, say, almost invariably prevent the USAF from severely harming ULA by cutting off the vast majority of the company’s only real source of income for 5+ years.
- ULA and SpaceX win: This maintains the status quo, wholly invalidating the point of using LSA funds to ensure “a competitive industrial base.” NGIS likely cancels/freezes all Omega development with no chance of competing in commercial markets. Blue Origin owner Jeff Bezos could significantly delay New Glenn’s readiness for military missions if he fails to invest an additional $500M in infrastructure. Likeliest result: a marginally competitive duopoly.
- ULA wins, SpaceX loses: Having just certified Falcon 9 – and nearly Falcon Heavy – for high-value military launches and awarded SpaceX a total of 10 launch contracts (9 yet to be completed), the USAF could effectively spit in SpaceX’s face and award ULA and Blue Origin or NGIS LSP’s 25+ launch contracts.
- It’s hard to exaggerate just how much of a slight this would be perceived as by SpaceX and its executives, CEO Elon Musk in particular. The USAF would be risking the creation of a major political enemy, one which has already demonstrated a willingness to take the federal government to court and win. The USAF/DoD would effectively be hedging their bets against an assumption that SpaceX’s nine present military launch contracts will sate the company and ensure that SpaceX indefinitely remains a certified EELV/NSSL provider.
- In this eventuality, either Blue Origin or NGIS would lose LSA funding and the prospect of almost any military launch contracts until the late 2020s. For NGIS, this would likely kill Omega.
- At the end of the day, it’s sadly conceivable that the USAF/DoD may end up awarding LSP contracts to ULA (effectively a politically-forced hand) and NGIS, the latter assuring Omega’s survival. The military would thus be assuming that the political fallout created with SpaceX and Blue Origin would not be enough to severely harm their relationships, while also assuming that their much stronger commercial prospects and independent funding sources would ensure that each provider remains certified and willing to compete for future NSSL/EELV launches.
Regardless of what happens, the contradictory ways the USAF/DoD have structured their LSA and LSP programs seems bizarrely intent on creating major headaches and potential problems where that could easily be avoided with extraordinarily simple changes, namely removing the inexplicable cap and allowing three or more companies to win some of the ~25 LSP launch contracts).
Mission Updates
- The second launch of Falcon Heavy – the rocket’s commercial debut – is still scheduled to occur as early as April 7th.
- After Falcon Heavy, Cargo Dragon’s CRS-17 resupply mission is firmly scheduled for April (April 25th), while the first dedicated Starlink launch is now NET May 2019.
Photo of the Week:

SpaceX CEO Elon Musk offered a glimpse of a 1650 Kelvin (2500ºF/1400ºC) test of Starship’s metallic heat shield, simulating mid-range temperatures such a shield’s windward side might experience during an orbital-velocity reentry.(c. Elon Musk/SpaceX)
News
SpaceX launches Ax-4 mission to the ISS with international crew
The SpaceX Falcon 9 launched Axiom’s Ax-4 mission to ISS. Ax-4 crew will conduct 60+ science experiments during a 14-day stay on the ISS.
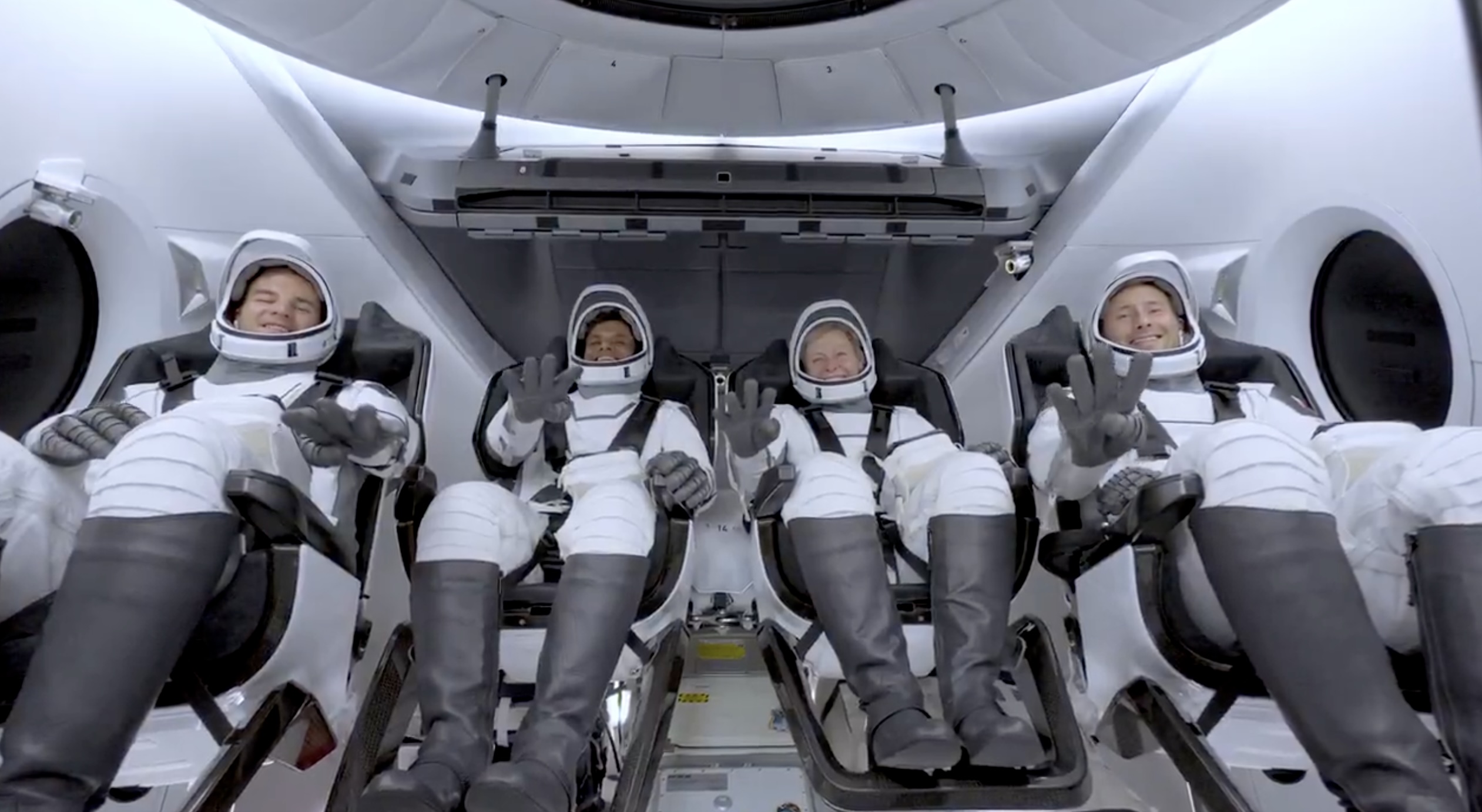

SpaceX launched the Falcon 9 rocket kickstarting Axiom Space’s Ax-4 mission to the International Space Station (ISS). Axiom’s Ax-4 mission is led by a historic international crew and lifted off from Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A at 2:31 a.m. ET on June 25, 2025.
The Ax-4 crew is set to dock with the ISS around 7 a.m. ET on Thursday, June 26, 2025. Axiom Space, a Houston-based commercial space company, coordinated the mission with SpaceX for transportation and NASA for ISS access, with support from the European Space Agency and the astronauts’ governments.
The Ax-4 mission marks a milestone in global space collaboration. The Ax-4 crew, commanded by U.S. astronaut Peggy Whitson, includes Shubhanshu Shukla from India as the pilot, alongside mission specialists Sławosz Uznański-Wiśniewski from Poland and Tibor Kapu from Hungary.
“The trip marks the return to human spaceflight for those countries — their first government-sponsored flights in more than 40 years,” Axiom noted.
Shukla’s participation aligns with India’s Gaganyaan program planned for 2027. He is the first Indian astronaut to visit the ISS since Rakesh Sharma in 1984.
Axiom’s Ax-4 mission marks SpaceX’s 18th human spaceflight. The mission employs a Crew Dragon capsule atop a Falcon 9 rocket, designed with a launch escape system and “two-fault tolerant” for enhanced safety. The Axiom mission faced a few delays due to weather, a Falcon 9 leak, and an ISS Zvezda module leak investigation by NASA and Roscosmos before the recent successful launch.
As the crew prepares to execute its scientific objectives, SpaceX’s Ax-4 mission paves the way for a new era of inclusive space research, inspiring future generations and solidifying collaborative ties in the cosmos. During the Ax-4 crew’s 14-day stay in the ISS, the astronauts will conduct nearly 60 experiments.
“We’ll be conducting research that spans biology, material, and physical sciences as well as technology demonstrations,” said Whitson. “We’ll also be engaging with students around the world, sharing our experience and inspiring the next generation of explorers.”
SpaceX’s Ax-4 mission highlights Axiom’s role in advancing commercial spaceflight and fostering international partnerships. The mission strengthens global space exploration efforts by enabling historic spaceflight returns for India, Poland, and Hungary.
News
Starlink Cellular’s T-Mobile service to grow with third-party app data
From Oct 2025, T-Satellite will enable third-party apps in dead zones! WhatsApp, X, AccuWeather + more coming soon.

Starlink Cellular’s T-Mobile service will expand with third-party app data support starting in October, enhancing connectivity in cellular dead zones.
T-Mobile’s T-Satellite, supported by Starlink, launches officially on July 23. Following its launch, T-Mobile’s Starlink Cellular service will enable data access for third-party apps like WhatsApp, X, Google, Apple, AccuWeather, and AllTrails on October 1, 2025.
T-Mobile’s Starlink Cellular is currently in free beta. T-Satellite will add MMS support for Android phones on July 23, with iPhone support to follow. MMS support allows users to send images and audio clips alongside texts. By October, T-Mobile will extend emergency texting to all mobile users with compatible phones, beyond just T-Mobile customers, building on its existing 911 texting capability. The carrier also provides developer tools to help app makers integrate their software with T-Satellite’s data service, with plans to grow the supported app list.
T-Mobile announced these updates during an event celebrating an Ookla award naming it the best U.S. phone network, a remarkable turnaround from its last-place ranking a decade ago.
“We not only dream about going from worst to best, we actually do it. We’re a good two years ahead of Verizon and AT&T, and I believe that lead is going to grow,” said T-Mobile’s Chief Operating Officer Srini Gopalan.
T-Mobile unveiled two promotions for its Starlink Cellular services to attract new subscribers. A free DoorDash DashPass membership, valued at $10/month, will be included with popular plans like Experience Beyond and Experience More, offering reduced delivery and service fees. Meanwhile, the Easy Upgrade promotion targets Verizon customers by paying off their phone balances and providing flagship devices like the iPhone 16, Galaxy S25, or Pixel 9.
T-Mobile’s collaboration with SpaceX’s Starlink Cellular leverages orbiting satellites to deliver connectivity where traditional networks fail, particularly in remote areas. Supporting third-party apps underscores T-Mobile’s commitment to enhancing user experiences through innovative partnerships. As T-Satellite’s capabilities grow, including broader app integration and emergency access, T-Mobile is poised to strengthen its lead in the U.S. wireless market.
By combining Starlink’s satellite technology with strategic promotions, T-Mobile is redefining mobile connectivity. The upcoming third-party app data support and official T-Satellite launch mark a significant step toward seamless communication, positioning T-Mobile as a trailblazer in next-generation wireless services.
News
Starlink expansion into Vietnam targets the healthcare sector
Starlink aims to deliver reliable internet to Vietnam’s remote clinics, enabling telehealth and data sharing.

SpaceX’s Starlink expansion into Vietnam targets its healthcare sector. Through Starlink, SpaceX seeks to drive digital transformation in Vietnam.
On June 18, a SpaceX delegation met with Vietnam’s Ministry of Health (MoH) in Hanoi. SpaceX’s delegation was led by Andrew Matlock, Director of Enterprise Sales, and the discussions focused on enhancing connectivity for hospitals and clinics in Vietnam’s remote areas.
Deputy Minister of Health (MoH) Tran Van Thuan emphasized collaboration between SpaceX and Vietnam. Tran stated: “SpaceX should cooperate with the MoH to ensure all hospitals and clinics in remote areas are connected to the StarLink satellite system and share information, plans, and the issues discussed by members of the MoH. The ministry is also ready to provide information and send staff to work with the corporation.”
The MoH assigned its Department of Science, Technology, and Training to work with SpaceX. Starlink Vietnam will also receive support from Vietnam’s Department of International Cooperation. Starlink Vietnam’s agenda includes improving internet connectivity for remote healthcare facilities, developing digital infrastructure for health examinations and remote consultations, and enhancing operational systems.
Vietnam’s health sector is prioritizing IT and digital transformation, focusing on electronic health records, data centers, and remote medical services. However, challenges persist in deploying IT solutions in remote regions, prompting Vietnam to seek partnerships like SpaceX’s.
SpaceX’s Starlink has a proven track record in healthcare. In Rwanda, its services supported 40 health centers, earning praise for improving operations. Similarly, Starlink enabled remote consultations at the UAE’s Emirati field hospital in Gaza, streamlining communication for complex medical cases. These successes highlight Starlink’s potential to transform Vietnam’s healthcare landscape.
On May 20, SpaceX met with Vietnam’s Ministry of Industry and Trade, announcing a $1.5 billion investment to provide broadband internet, particularly in remote, border, and island areas. The first phase includes building 10-15 ground stations across the country. This infrastructure will support Starlink’s healthcare initiatives by ensuring reliable connectivity.
Starlink’s expansion in Vietnam aligns with the country’s push for digital transformation, as outlined by the MoH. By leveraging its satellite internet expertise, SpaceX aims to bridge connectivity gaps, enabling advanced healthcare services in underserved regions. This collaboration could redefine Vietnam’s healthcare infrastructure, positioning Starlink as a key player in the nation’s digital future.
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla confirms massive hardware change for autonomy improvement
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla China roars back with highest vehicle registrations this Q2 so far
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla features used to flunk 16-year-old’s driver license test
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla dominates Cars.com’s Made in America Index with clean sweep
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Grok integration will be more realistic with this cool feature