Investor's Corner
Manufacturing Expansion Provides 2015 Narrative for Tesla
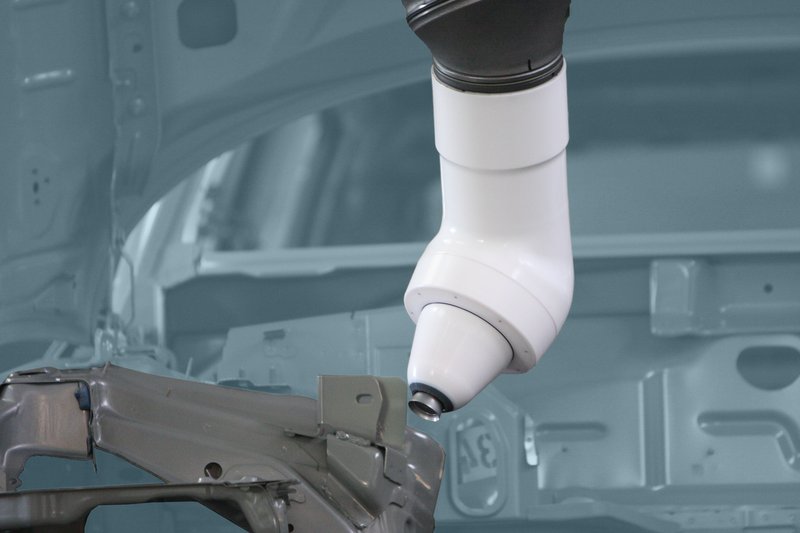

Tesla’s supercharging buildout receives its share of publicity these days as the company builds out an electric highway for multiple countries. However, Tesla’s massive manufacturing expansion resonates as the underlying narrative for Tesla in 2015 for investors, along with a very important Model X release.
Part of investors’ fascination with Tesla is the lack of legacy costs and perceived future advantage in electric car production over traditional automakers at scale. Another big advantage for Tesla over traditional automakers is the evolution of manufacturing technology and software, and the lack of legacy control or operation architectures as an obstacle. Sophisticated industrial networking at the factory floor can communicate with SAP level enterprise business layers and drive efficiencies now. Things have changed.
Over the last ten years, factory manufacturing has integrated higher processing speeds for machinery equipment and added a lot of sensors. Everybody has read or heard about the the Internet of Things, but in the factory space it’s known as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). This sensor explosion has been evolving quickly for manufacturers since the 2008 downturn.
However, it’s been a struggle for legacy manufacturers and automakers. That’s why the Fremont plant expansion for the Model X and Model 3 is really advantageous for Tesla. They have a clean manufacturing slate.
So what’s happening in Fremont? Just four months ago, German-based Durr AG announced that it had shipped its 9,000 robot to the Fremont plant. In the release, Durr said that as many as 100 paint, 48 handling and 26 sealing robots went to Tesla’s recently finished paint center, as Musk refers to it.
The paint center has two sealing, primer and top coat lines, which can paint as much as 500,000 bodies per year. That’s the key number.
“This is quite a huge capital cost for us and the new paint center is actually set up to be able to do 10,000 cars a week,” says Musk at a recent shareholder meeting. “So, this paint center is intended to be able to match the 2020 production level (500,000/annually) that includes the Model 3.”
Musk also mentioned that the new Lathrop, Calif. castings and machining center for the Model S will allow Tesla “to expand our vehicle capacity and allocate more space for vehicle final assembly.”
Tesla recently carved out more room at its Fremont plant for its SX body production line. The SX line will be able to switch to the either the Model X or S vehicle, depending on demand. “The new line will have more automation and greater flexibility and we should be able to do three times more than we’re able to do in the current body line,” says Musk.
Of course, this is just the car side. The Tesla Gigafactory is another component to meet future demand for its car and energy side of the business. Just last week around 8 pm eastern time on Friday, Tesla quietly announced that it took out a credit line of “$500M, five-year, credit facility via five banks and it has the option to increase the credit facility’s size to $750M.”
Most investors would admit there’s a good deal of risk in this strategy. However, Elon Musk and his talented team know this is the only strategy to enable high-volume manufacturing for a mass-market electric car. So the rest now comes down to execution.
*Below is an interesting car assembly application via ABB robotics, see video below. Love to see a Tesla video like this, enjoy!
Elon Musk
Tesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
Jim Cramer is now speaking positively about Tesla, especially in terms of its Robotaxi performance and its perception as a company.

Tesla investors will be shocked by analyst Jim Cramer’s latest assessment of the company.
When it comes to Tesla analysts, many of them are consistent. The bulls usually stay the bulls, and the bears usually stay the bears. The notable analysts on each side are Dan Ives and Adam Jonas for the bulls, and Gordon Johnson for the bears.
Jim Cramer is one analyst who does not necessarily fit this mold. Cramer, who hosts CNBC’s Mad Money, has switched his opinion on Tesla stock (NASDAQ: TSLA) many times.
He has been bullish, like he was when he said the stock was a “sleeping giant” two years ago, and he has been bearish, like he was when he said there was “nothing magnificent” about the company just a few months ago.
Now, he is back to being a bull.
Cramer’s comments were related to two key points: how NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang describes Tesla after working closely with the Company through their transactions, and how it is not a car company, as well as the recent launch of the Robotaxi fleet.
Jensen Huang’s Tesla Narrative
Cramer says that the narrative on quarterly and annual deliveries is overblown, and those who continue to worry about Tesla’s performance on that metric are misled.
“It’s not a car company,” he said.
He went on to say that people like Huang speak highly of Tesla, and that should be enough to deter any true skepticism:
“I believe what Musk says cause Musk is working with Jensen and Jensen’s telling me what’s happening on the other side is pretty amazing.”
Tesla self-driving development gets huge compliment from NVIDIA CEO
Robotaxi Launch
Many media outlets are being extremely negative regarding the early rollout of Tesla’s Robotaxi platform in Austin, Texas.
There have been a handful of small issues, but nothing significant. Cramer says that humans make mistakes in vehicles too, yet, when Tesla’s test phase of the Robotaxi does it, it’s front page news and needs to be magnified.
He said:
“Look, I mean, drivers make mistakes all the time. Why should we hold Tesla to a standard where there can be no mistakes?”
It’s refreshing to hear Cramer speak logically about the Robotaxi fleet, as Tesla has taken every measure to ensure there are no mishaps. There are safety monitors in the passenger seat, and the area of travel is limited, confined to a small number of people.
Tesla is still improving and hopes to remove teleoperators and safety monitors slowly, as CEO Elon Musk said more freedom could be granted within one or two months.
Investor's Corner
Tesla gets $475 price target from Benchmark amid initial Robotaxi rollout
Tesla’s limited rollout of its Robotaxi service in Austin is already catching the eye of Wall Street.

Venture capital firm Benchmark recently reiterated its “Buy” rating and raised its price target on Tesla stock (NASDAQ: TSLA) from $350 to $475 per share, citing the company’s initial Robotaxi service deployment as a sign of future growth potential.
Benchmark analyst Mickey Legg praised the Robotaxi service pilot’s “controlled and safety-first approach,” adding that it could help Tesla earn the trust of regulators and the general public.
Confidence in camera-based autonomy
Legg reiterated Benchmark’s belief in Tesla’s vision-only approach to autonomous driving. “We are a believer in Tesla’s camera-focused approach that is not only cost effective but also scalable,” he noted.
The analyst contrasted Tesla’s simple setup with the more expensive hardware stacks used by competitors like Waymo, which use various sophisticated sensors that hike up costs, as noted in an Investing.com report. Compared to Tesla’s Model Y Robotaxis, Waymo’s self-driving cars are significantly more expensive.
He also pointed to upcoming Texas regulations set to take effect in September, suggesting they could help create a regulatory framework favorable to autonomous services in other cities.
“New regulations for autonomous vehicles are set to go into place on Sept. 1 in TX that we believe will further help win trust and pave the way for expansion to additional cities,” the analyst wrote.
Tesla as a robotics powerhouse
Beyond robotaxis, Legg sees Tesla evolving beyond its roots as an electric vehicle maker. He noted that Tesla’s humanoid robot, Optimus, could be a long-term growth driver alongside new vehicle programs and other future initiatives.
“In our view, the company is undergoing an evolution from a trailblazing vehicle OEM to a high-tech automation and robotics company with unmatched domestic manufacturing scale,” he wrote.
Benchmark noted that Tesla stock had rebounded over 50% from its April lows, driven in part by easing tariff concerns and growing momentum around autonomy. With its initial Robotaxi rollout now underway, the firm has returned to its previous $475 per share target and reaffirmed TSLA as a Benchmark Top Pick for 2025.
Elon Musk
Tesla blacklisted by Swedish pension fund AP7 as it sells entire stake
A Swedish pension fund is offloading its Tesla holdings for good.

Tesla shares have been blacklisted by the Swedish pension fund AP7, who said earlier today that it has “verified violations of labor rights in the United States” by the automaker.
The fund ended up selling its entire stake, which was worth around $1.36 billion when it liquidated its holdings in late May. Reuters first reported on AP7’s move.
Other pension and retirement funds have relinquished some of their Tesla holdings due to CEO Elon Musk’s involvement in politics, among other reasons, and although the company’s stock has been a great contributor to growth for many funds over the past decade, these managers are not willing to see past the CEO’s right to free speech.
However, AP7 says the move is related not to Musk’s involvement in government nor his political stances. Instead, the fund said it verified several labor rights violations in the U.S.:
“AP7 has decided to blacklist Tesla due to verified violations of labor rights in the United States. Despite several years of dialogue with Tesla, including shareholder proposals in collaboration with other investors, the company has not taken sufficient measures to address the issues.”
Tesla made up about 1 percent of the AP7 Equity Fund, according to a spokesperson. This equated to roughly 13 billion crowns, but the fund’s total assets were about 1,181 billion crowns at the end of May when the Tesla stake was sold off.
Tesla has had its share of labor lawsuits over the past few years, just as any large company deals with at some point or another. There have been claims of restrictions against labor union supporters, including one that Tesla was favored by judges, as they did not want pro-union clothing in the factory. Tesla argued that loose-fitting clothing presented a safety hazard, and the courts agreed.
(Photo: Tesla)
There have also been claims of racism at the Fremont Factory by a former elevator contractor named Owen Diaz. He was awarded a substantial sum of $137m. However, U.S. District Judge William Orrick ruled the $137 million award was excessive, reducing it to $15 million. Diaz rejected this sum.
Another jury awarded Diaz $3.2 million. Diaz’s legal team said this payout was inadequate. He and Tesla ultimately settled for an undisclosed amount.
AP7 did not list any of the current labor violations that it cited as its reason for
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla confirms massive hardware change for autonomy improvement
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla features used to flunk 16-year-old’s driver license test
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla China roars back with highest vehicle registrations this Q2 so far
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla dominates Cars.com’s Made in America Index with clean sweep
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Grok integration will be more realistic with this cool feature









