

Space
NASA’s next Mars rover will pave the way for humans
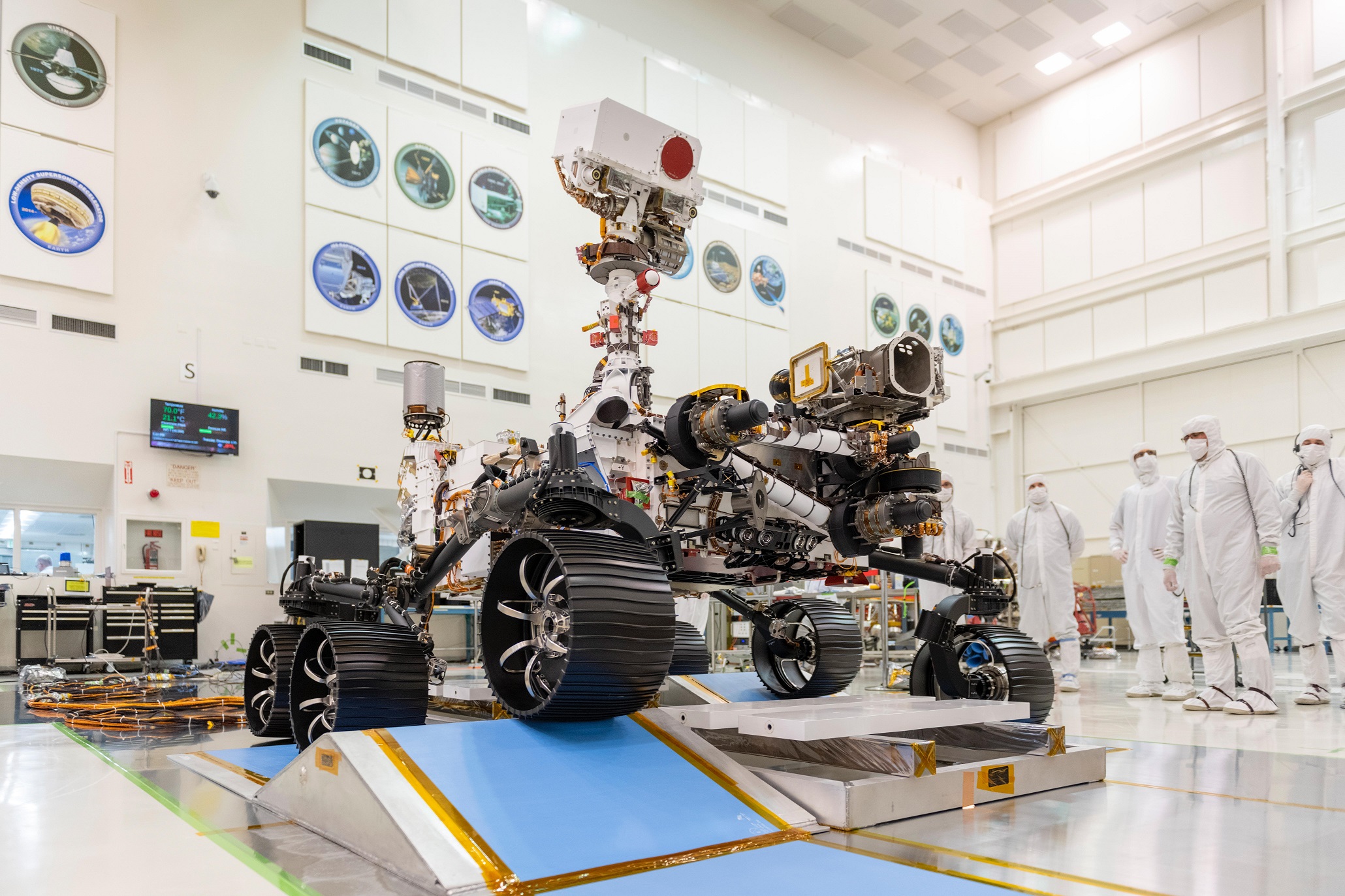
NASA’s Mars 2020 rover is scheduled to land on the red planet in February 2021, and when it does, it will touch down in Jezero Crater, the site of an ancient lake that existed 3.5 billion years ago. The next generation rover, which will get an official name soon, will build on the success of the robotic explorers who came before it by collecting the first samples of Mars for a future return to Earth.
But the new rover will also lay the groundwork for future human exploration by testing new technologies.
The Mars 2020 rover, which looks nearly identical to the Curiosity rover that landed in 2012, will begin its mission exploring Jezero Crater. The six-wheeled rover is equipped with a suite of instruments designed to help it look for signs of life called biosignatures.
Artist rendition depicting the early Martian environment (right) versus the Mars we see today (left). Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center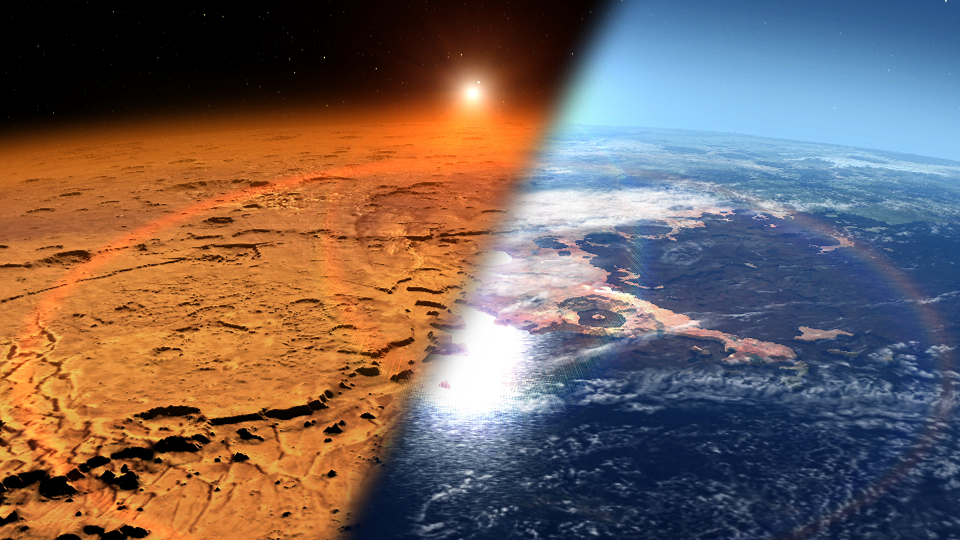
NASA believes that Mars was habitable sometime in its past. The inhospitable desert-like planet we see today was not always the case. Mars’ once ample atmosphere eroded over time, stripped away by solar particles, resulting in the thin atmosphere we see today.
But so far, we haven’t been able to detect any real signs of ancient life yet. The rover’s team thinks that its specialized suite of instruments will change that.
The twin Mars Exploration Rovers (Spirit and Opportunity) were tasked with finding evidence of water, and they were successful right out of the gate. The Mars Science Laboratory (aka Curiosity) was designed to understand habitability and if the conditions were right for life. Now, the Mars 2020 rover will take that one step further and search for actual signs of life.

Artist rendition depicting the early Martian environment (right) versus the Mars we see today (left). Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
The 2020 rover will do so by drilling into its surroundings and extracting samples that will be returned to Earth at a later time. Returning the samples is a challenge that NASA is already starting to tackle. The agency estimates that the earliest it can send a mission to fetch the rover’s samples would be some time around 2026 or 2027.
In the meantime, 2020 will be busy sciencing the heck out of Mars to search for microbial life as well as testing out technologies that future human missions will rely on.
Here’s how four of those instruments will work.
Terrain Relative Navigation
Landing on Mars is tricky. To date, only about half of the missions attempted have successfully touched down on the red planet. The 2020 rover will be equipped with a specialized feature to help it avoid any potential hazards in the landing zone.
Past missions, like Curiosity, needed a landing spot that was free of debris (like rocks, boulders, etc). But 2020 will be able to navigate around them. That’s because the rover is equipped with a unique lander vision system. This system take pictures during the parachute descent stage. It then compares those images to an onboard map.
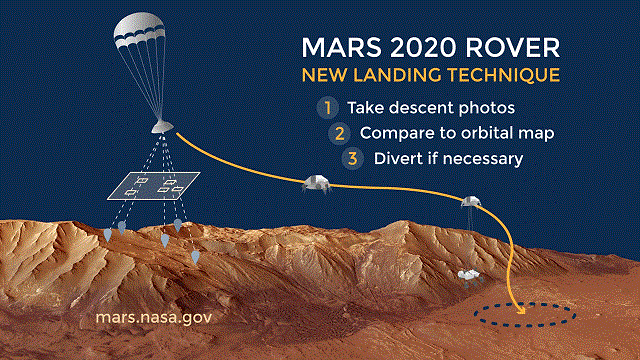
A view of how the terrain-relative navigation works. Credit: NASA/JPL_Caltech
The computer matches the map (which is created from orbital imagery), to create a guide that can identify landmarks such as craters and mountains.
The system then ranks landing sites based on safety, and can even identify a hazard. The Mars 2020 mission will be the first to test out this new system. If all goes well, it will be used on future missions, including human missions to Mars and even the moon.
MOXIE
Astronauts traveling to Mars will need oxygen to breathe and to use as rocket fuel. However, hauling it with the other cargo is expensive and not a viable solution. The Mars 2020 rover is equipped with an instrument on called the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE for short).
MOXIE will convert carbon dioxide (a gas that’s abundant on Mars) into the oxygen, which astronauts can use as needed. 2020 is equipped with a small, prototype version of the equipment needed for future human missions.
The team will study how the experiment performs and use that data to scale up the technology to use on subsequent missions. But how will it work?
MOXIE can only run for a few hours at a time, and only about once a month. (That’s because the system uses a full day’s worth of rover power each time it runs.) Humans use about 20 grams per hour of oxygen and MOXIE can only produce about half of that.
In order to support a crew of 4-6 astronauts and be able to generate propellant, future iterations of MOXIE will need to produce about 200 times that amount of oxygen.
MEDA
The Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer, aka MEDA, is a suite of sensors designed to study the Martian weather, as well as dust and radiation and how they change over the Martian seasons.
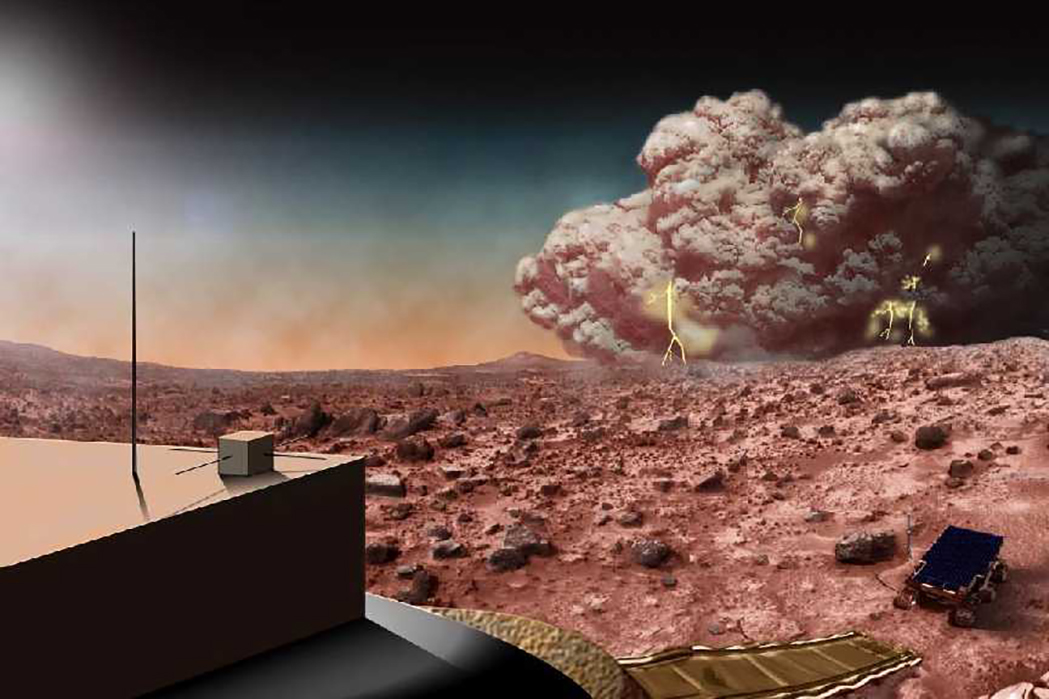

NASA is trying to better understand dust storms and other Martian weather phenomenon. Credit: NASA
Day and nighttime temperatures on Mars can fluctuate by as much as 80 or 90 degrees. MEDA will help scientists track those changes as well as measure radiation from the surface, to understand how much the sun heats the air. This solar heating causes changes in the Martian wind and can help scientists better understand the Martian water cycle.
Understanding the current weather patterns and environment could also lead to a better understanding of Mars’s history and shed light on how it transitioned from a warm, habitable planet into the dusty, cold desert we see today.
RIMFAX
The Mars 2020 rover will be equipped with a ground-penetrating radar instrument: Radar Imager for Mars’ Subsurface Experiment, or RIMFAX.
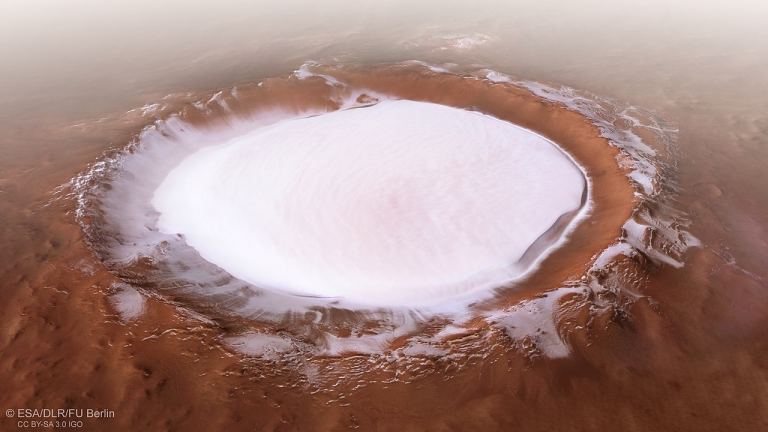

The Korolev crater on Mars as seen by Mars Express. Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin
Scientists hope that RIMAX will help them study the history of Jezero Crater by peering below the surface. With the instrument’s help, scientists will be able to look at subsurface rock and ice. To date, only orbital observations have been made of the Martian polar ice, but this will increase our understanding of the planet’s inner geology.
The Mars 2020 rover is scheduled to launch in July of 2020, and will land on the Martian surface six months later. If all goes according to plan, we may finally be able to answer the question of whether or not Mars once hosted life.

News
SpaceX shades airline for seeking contract with Amazon’s Starlink rival

SpaceX employees, including its CEO Elon Musk, shaded American Airlines on social media this past weekend due to the company’s reported talks with Amazon’s Starlink rival, Leo.
Starlink has been adopted by several airlines, including United Airlines, Qatar Airways, Hawaiian Airlines, WestJet, Air France, airBaltic, and others. It has gained notoriety as an extremely solid, dependable, and reliable option for airline travel, as traditional options frequently cause users to lose connection to the internet.
Many airlines have made the switch, while others continue to mull the options available to them. American Airlines is one of them.
A report from Bloomberg indicates the airline is thinking of going with a Starlink rival owned by Amazon, called Leo. It was previously referred to as Project Kuiper.
American CEO Robert Isom said (via Bloomberg):
“While there’s Starlink, there are other low-Earth-orbit satellite opportunities that we can look at. We’re making sure that American is going to have what our customers need.”
Isom also said American has been in touch with Amazon about installing Leo on its aircraft, but he would not reveal the status of any discussions with the company.
The report caught the attention of Michael Nicolls, the Vice President of Starlink Engineering at SpaceX, who said:
“Only fly on airlines with good connectivity… and only one source of good connectivity at the moment…”
CEO Elon Musk replied to Nicolls by stating that American Airlines risks losing “a lot of customers if their connectivity solution fails.”
American Airlines will lose a lot of customers if their connectivity solution fails
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) December 14, 2025
There are over 8,000 Starlink satellites in orbit currently, offering internet coverage in over 150 countries and territories globally. SpaceX expands its array of satellites nearly every week with launches from California and Florida, aiming to offer internet access to everyone across the globe.
Currently, the company is focusing on expanding into new markets, such as Africa and Asia.
News
Tesla hints at Starlink integration with recent patent
“By employing polymer blends, some examples enable RF transmission from all the modules to satellites and other communication devices both inside and outside the vehicle.”

Tesla hinted at a potential Starlink internet terminal integration within its vehicles in a recent patent, which describes a vehicle roof assembly with integrated radio frequency (RF) transparency.
The patent, which is Pub. No U.S. 2025/0368267 describes a new vehicle roof that is made of RF-transparent polymer materials, allowing and “facilitating clear communication with external devices and satellites.”
Tesla believes that a new vehicle roof design, comprised of different materials than the standard metallic or glass elements used in cars today, would allow the company to integrate modern vehicular technologies, “particularly those requiring radio frequency transmission and reception.
Tesla has recently filed a US patent application on integrating RF transparent materials into the roof structure.
“facilitating clear communication with external devices and satellites”
Tesla fleet is getting @Starlink connectivity integration soon. LFG @Tesla @elonmusk… pic.twitter.com/bLa8YtPLd1
— Chansoo Byeon (@Chansoo) December 9, 2025
Instead of glass or metallic materials, Tesla says vehicles may benefit from high-strength polymer blends, such as Polycarbonate, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, or Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate.
These materials still provide ideal strength metrics for crashworthiness, stiffness for noise, vibration, and harshness control, and are compliant with head impact regulations.
They would also enable better performance with modern technologies, like internet terminals, which need an uninterrupted signal to satellites for maximum reception. Tesla writes in the patent:
“By employing polymer blends, some examples enable RF transmission from all the modules to satellites and other communication devices both inside and outside the vehicle.”
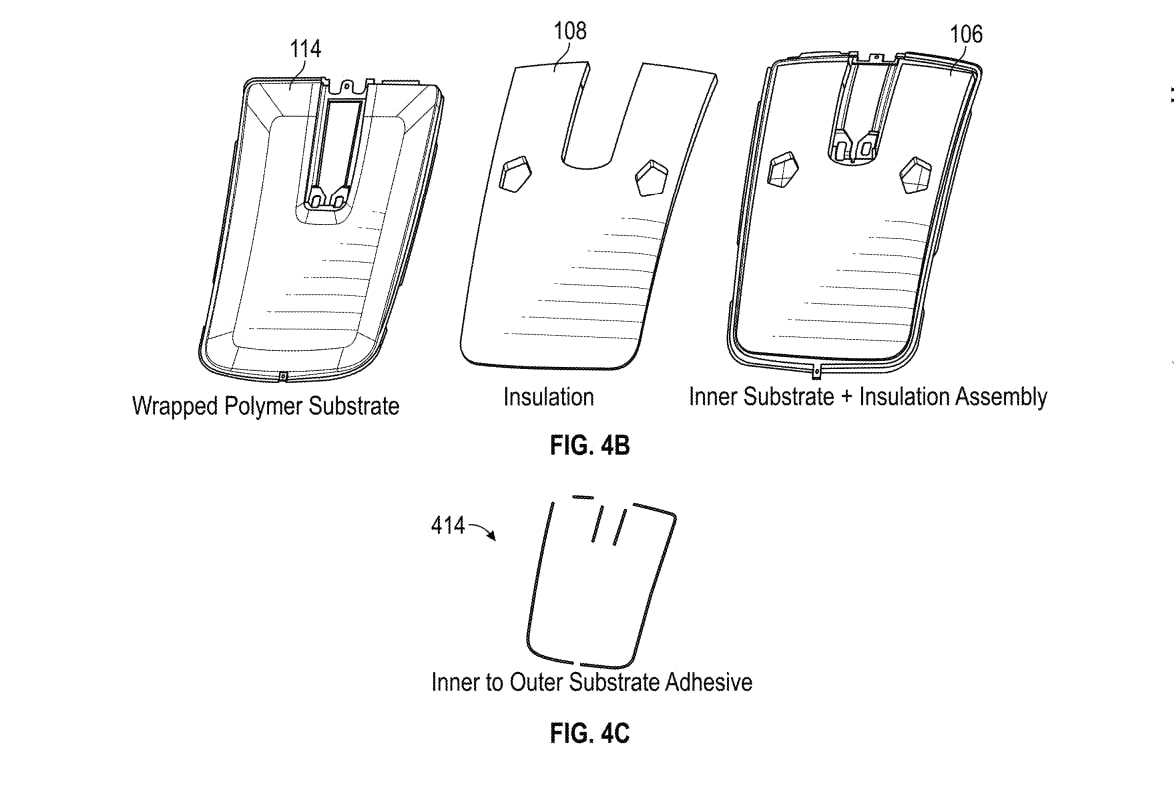
One of the challenges Tesla seems to be aware of with this type of roof design is the fact that it will still have to enable safety and keep that at the forefront of the design. As you can see in the illustration above, Tesla plans to use four layers to increase safety and rigidity, while also combating noise and vibration.
It notes in the patent that disclosed examples still meet the safety requirements outlined in the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS).
Starlink integrated directly into Tesla vehicles would be a considerable advantage for owners. It would come with a handful of distinct advantages.
Initially, the inclusion of Starlink would completely eliminate cellular dead zones, something that is an issue, especially in rural areas. Starlink would provide connectivity in these remote regions and would ensure uninterrupted service during road trips and off-grid adventures.
It could also be a critical addition for Robotaxi, as it is crucial to have solid and reliable connectivity for remote monitoring and fleet management.
Starlink’s growing constellation, thanks to SpaceX’s routine and frequent launch schedule, will provide secure, stable, and reliable internet connectivity for Tesla vehicles.
Although many owners have already mounted Starlink Mini dishes under their glass roofs for a similar experience, it may be integrated directly into Teslas in the coming years, either as an upgrade or a standard feature.
Investor's Corner
SpaceX IPO is coming, CEO Elon Musk confirms
However, it appears Musk is ready for SpaceX to go public, as Ars Technica Senior Space Editor Eric Berger wrote an op-ed that indicated he thought SpaceX would go public soon. Musk replied, basically confirming it.

Elon Musk confirmed through a post on X that a SpaceX initial public offering (IPO) is on the way after hinting at it several times earlier this year.
It also comes one day after Bloomberg reported that SpaceX was aiming for a valuation of $1.5 trillion, adding that it wanted to raise $30 billion.
Musk has been transparent for most of the year that he wanted to try to figure out a way to get Tesla shareholders to invest in SpaceX, giving them access to the stock.
He has also recognized the issues of having a public stock, like litigation exposure, quarterly reporting pressures, and other inconveniences.
However, it appears Musk is ready for SpaceX to go public, as Ars Technica Senior Space Editor Eric Berger wrote an op-ed that indicated he thought SpaceX would go public soon.
Musk replied, basically confirming it:
As usual, Eric is accurate
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) December 10, 2025
Berger believes the IPO would help support the need for $30 billion or more in capital needed to fund AI integration projects, such as space-based data centers and lunar satellite factories. Musk confirmed recently that SpaceX “will be doing” data centers in orbit.
AI appears to be a “key part” of SpaceX getting to Musk, Berger also wrote. When writing about whether or not Optimus is a viable project and product for the company, he says that none of that matters. Musk thinks it is, and that’s all that matters.
It seems like Musk has certainly mulled something this big for a very long time, and the idea of taking SpaceX public is not just likely; it is necessary for the company to get to Mars.
The details of when SpaceX will finally hit that public status are not known. Many of the reports that came out over the past few days indicate it would happen in 2026, so sooner rather than later.
But there are a lot of things on Musk’s plate early next year, especially with Cybercab production, the potential launch of Unsupervised Full Self-Driving, and the Roadster unveiling, all planned for Q1.








