
Space
NASA data points to Mars underground water source at Arcadia Planitia site
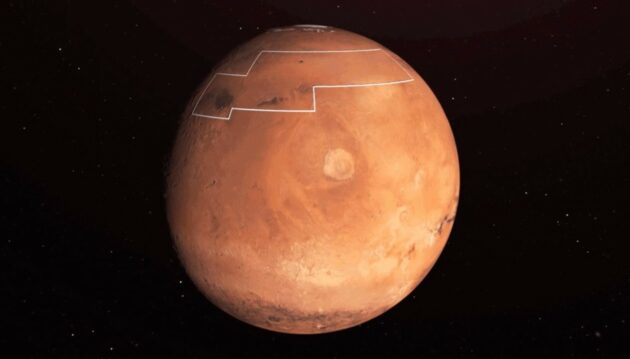
Mars’s Arcadia Planitia may be hiding buried treasure. A new global map indicates that the region could be harboring a supply of water, mere inches below its surface.
Armed with fresh data from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and the Mars Odyssey spacecraft, researchers identified a promising landing spot for future astronauts. The region is located in the planet’s Northern Hemisphere, and has an ample stash of water ice making it an ideal location for any potential human mission to Mars.
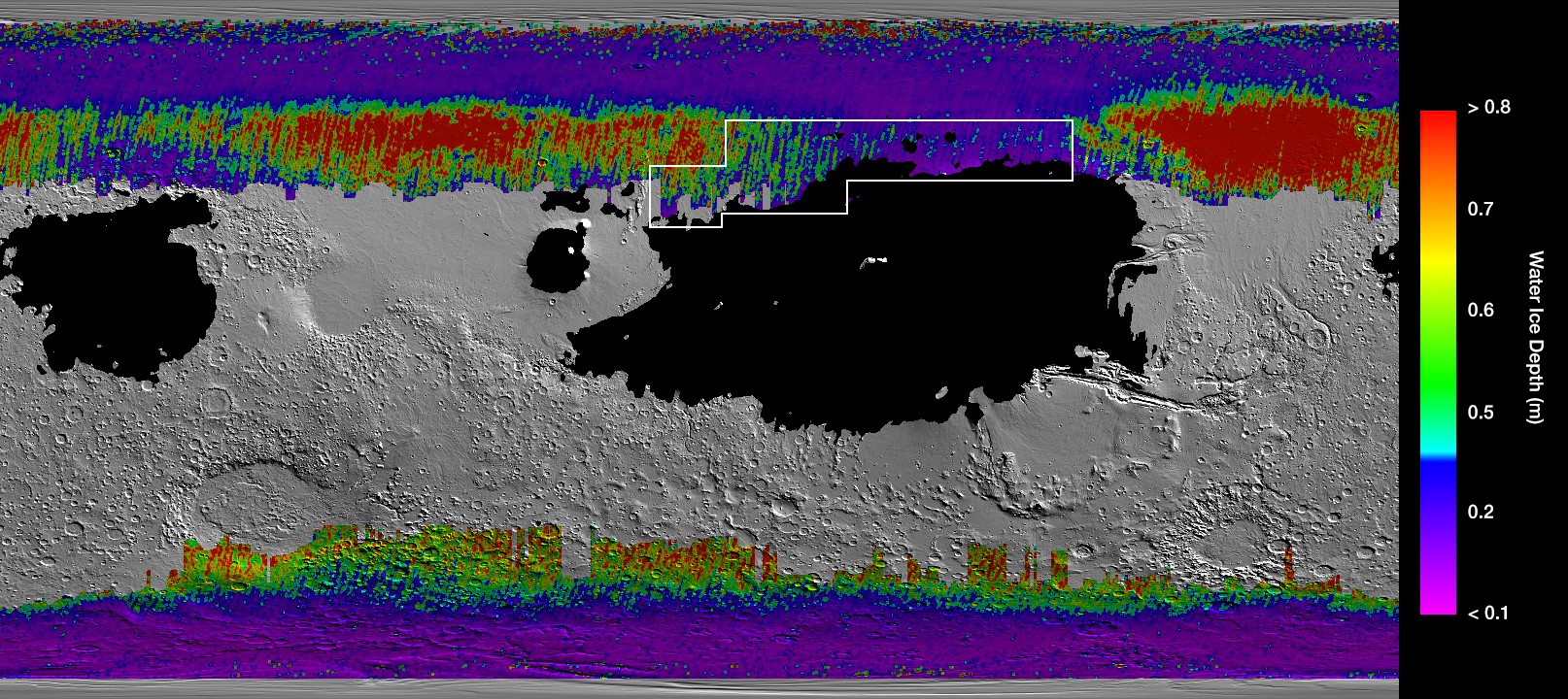
A new paper published in Geophysical Research Letters on Dec. 10 details a treasure maps of sorts, pointing to places where researchers believe water ice lurks as little as an inch (2.5 centimeters) below the surface.
Researchers are trying to narrow down the best places for astronauts to land and this discovery puts Arcadia Planitia near the top of the list. Data also shows that because this is a temperate region, basked in plenty of sunlight, it wouldn’t be difficult to uncover the watery bounty.
“You wouldn’t need a backhoe to dig up this ice. You could use a shovel,” lead author Sylvain Piqueux, who studies planetary surfaces at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California, said in a statement.
The Mars we see today is a barren, desert world, devoid of water deposits on its surface. That’s because any liquid water that might trickle on its surface evaporates very quickly. Mars’s once ample atmosphere, eroded over time, stripped away by solar particles, resulting in the thin atmosphere we see today.
As a result, any liquid water on the surface would evaporate immediately when exposed to the thin atmosphere.
That doesn’t mean that Mars is completely devoid of any water on its surface. There’s plenty of water trapped in ice caps at the Martian poles. However, this is a viable solution for human missions as the polar regions are too cold and dark to be viable options for landing. And NASA hopes that future human missions will be able to rely on what they call “in-situ resource utilization”, meaning relying on the resources in a given area.
The new map was created by combining data from two long-running Martian spacecraft: NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and Mars Odyssey. Each orbiter used onboard heat-sensitive instruments to detect the ice since buried ice changes the temperature of the surface. To corroborate their findings, the scientists cross-referenced their work with other data — like ice seen in radar instruments and Mars Odyssey’s gamma-ray spectrometer, a tool designed to spotting water ice deposits.

Water is a precious commodity and thanks to this new data, NASA is hoping that future missions can land near Arcadia Planitia and use its resources instead of having to travel to the poles and hauling water back.
The agency hopes that this map will also identify other promising areas. See it’s not just water that the map is locating, it’s also other valuable resources. When broken down into its components (hydrogen and oxygen), astronauts could not only get water to drink, but could also make rocket fuel, thus decreasing the load they would need to haul from Earth.
News
SpaceX Ax-4 Mission prepares for ISS with new launch date
SpaceX, Axiom Space, and NASA set new launch date for the Ax-4 mission after addressing ISS & rocket concerns.
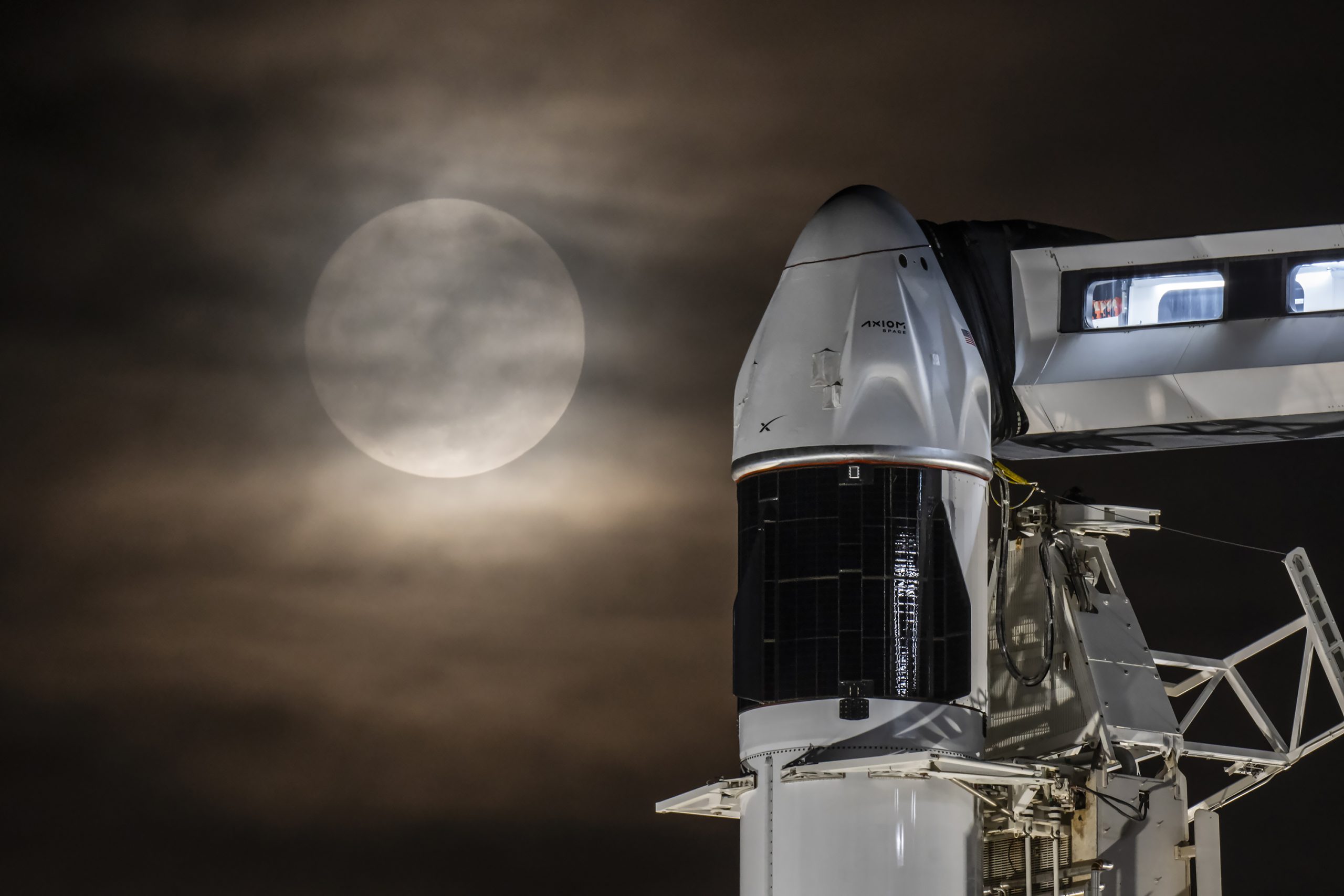

SpaceX is preparing for a new launch date for the Ax-4 mission to the International Space Station (ISS).
SpaceX, Axiom Space, and NASA addressed recent technical challenges and announced a new launch date of no earlier than Thursday, June 19, for the Ax-4 mission. The delay from June 12 allowed teams to assess repairs to small leaks in the ISS’s Zvezda service module.
NASA and Roscosmos have been monitoring leaks in the Zvezda module’s aft (back) segment for years. However, stable pressure could also result from air flowing across the hatch seal from the central station. As NASA and its partners adapt launch schedules to ensure station safety, adjustments are routine.
“Following the most recent repair, pressure in the transfer tunnel has been stable,” a source noted, suggesting the leaks may be sealed.
“By changing pressure in the transfer tunnel and monitoring over time, teams are evaluating the condition of the transfer tunnel and the hatch seal between the space station and the back of Zvezda,” the source added.
SpaceX has also resolved a liquid oxygen leak found during post-static fire inspections of the Falcon 9 rocket, completing a wet dress rehearsal to confirm readiness. The Ax-4 mission is Axiom Space’s fourth private astronaut trip to the ISS. It will launch from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on a Falcon 9 rocket with a new Crew Dragon capsule.
“This is the first flight for this Dragon capsule, and it’s carrying an international crew—a perfect debut. We’ve upgraded storage, propulsion components, and the seat lash design for improved reliability and reuse,” said William Gerstenmaier, SpaceX’s vice president of build and flight reliability.
The Ax-4 mission crew is led by Peggy Whitson, Axiom Space’s director of human spaceflight and former NASA astronaut. The Ax-4 crew includes ISRO astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla as pilot, alongside mission specialists Sławosz Uznański-Wiśniewski from Poland and Tibor Kapu from Hungary. The international team underscores Axiom’s commitment to global collaboration.
The Ax-4 mission will advance scientific research during its ISS stay, supporting Axiom’s goal of building a commercial space station. As teams finalize preparations, the mission’s updated launch date and technical resolutions position it to strengthen private space exploration’s role in advancing space-based innovation.
News
Starlink India launch gains traction with telecom license approval
Starlink just secured its telecom license in India! High-speed satellite internet could go live in 2 months.

Starlink India’s launch cleared a key regulatory hurdle after securing a long-awaited license from the country’s telecom ministry. Starlink’s license approval in India paves the way for commercial operations to begin, marking a significant milestone after a three-year wait.
The Department of Telecommunications granted Starlink a Global Mobile Personal Communication by Satellite (GMPCS) license, enabling it to roll out its high-speed internet service. Local reports hinted that Starlink plans to launch its services within the next two months. Starlink India’s services are expected to be priced at ₹3,000 per month for unlimited data. Starlink service would require a ₹33,000 hardware kit, including a dish and router.
“Starlink is finally ready to enter the Indian market,” sources familiar with the rollout plans confirmed, noting a one-month free trial for new users.
Starlink’s low-Earth orbit satellite network promises low-latency, high-speed internet that is ideal for rural India, border areas, and hilly terrains. With over 7,000 satellites in orbit and millions of global users, Starlink aims to bridge India’s digital divide, especially in areas with limited traditional broadband.
Starlink has forged distribution partnerships with Indian telecom giants Reliance Jio and Bharti Airtel to streamline deployment and retail logistics. However, the company still awaits spectrum allocation and final clearances from India’s space regulator, IN-SPACe, and national security agencies before its full launch, expected before August 2025.
India’s satellite internet market is becoming increasingly competitive, with Starlink joining rivals like OneWeb and Jio Satellite Communications. While Starlink positions itself as a premium offering, its entry has sparked debate among domestic telecom operators over spectrum pricing.
Local reports noted that other players in the industry have raised concerns over the lower regulatory fees proposed for satellite firms compared to terrestrial operators, highlighting tensions in the sector.
Starlink India’s launch represents a transformative step toward expanding internet access in one of the world’s largest markets. Starlink could redefine connectivity for millions in underserved regions by leveraging its advanced satellite technology and strategic partnerships. As the company navigates remaining regulatory steps, its timely rollout could set a new standard for satellite internet in India, intensifying competition and driving innovation in the telecom landscape.
Elon Musk
SpaceX to decommission Dragon spacecraft in response to Pres. Trump war of words with Elon Musk
Elon Musk says SpaceX will decommission Dragon as a result of President Trump’s threat to end his subsidies and government contracts.
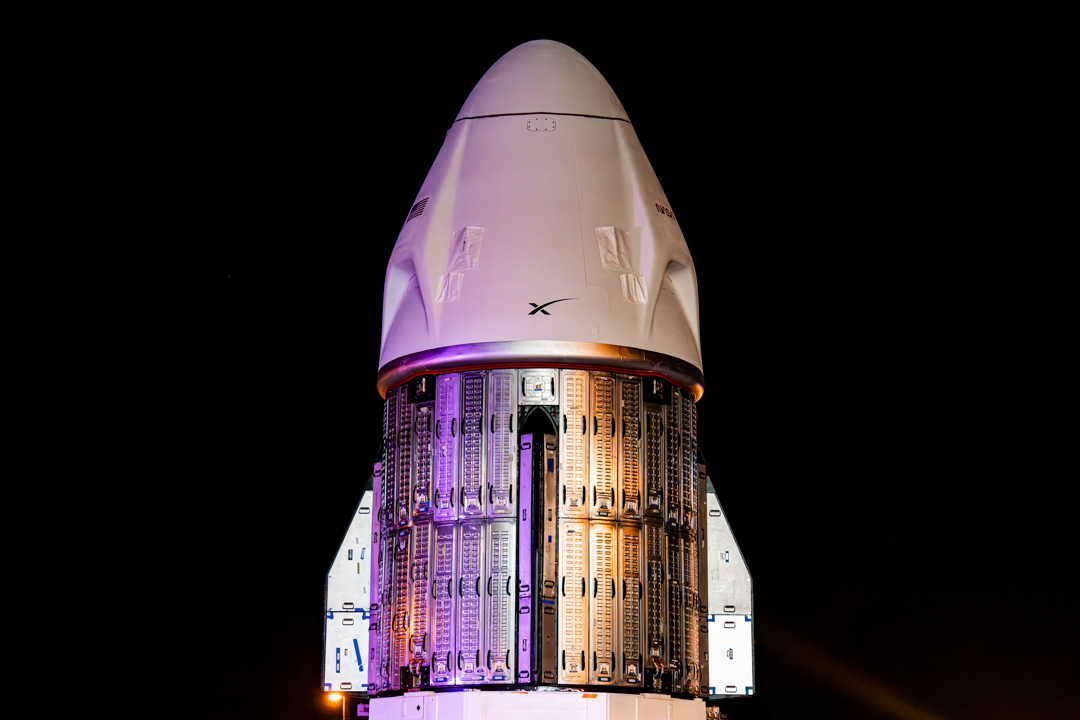
SpaceX will decommission its Dragon spacecraft in response to the intense war of words that President Trump and CEO Elon Musk have entered on various social media platforms today.
President Trump and Musk, who was once considered a right-hand man to Trump, have entered a vicious war of words on Thursday. The issues stem from Musk’s disagreement with the “Big Beautiful Bill,” which will increase the U.S. federal deficit, the Tesla and SpaceX frontman says.
How Tesla could benefit from the ‘Big Beautiful Bill’ that axes EV subsidies
The insults and threats have been brutal, as Trump has said he doesn’t know if he’ll respect Musk again, and Musk has even stated that the President would not have won the election in November if it were not for him.
President Trump then said later in the day that:
“The easiest way to save money in our Budget, Billions and Billions of Dollars, is to terminate Elon’s Government Subsidies and Contracts. I was always surprised that Biden didn’t do it!”
Musk’s response was simple: he will decommission the SpaceX capsule responsible for transporting crew and cargo to the International Space Station (ISS): Dragon.
🚨 Elon says Dragon will be decommissioned immediately due to President Trump’s threats to terminate SpaceX’s government contracts https://t.co/XNB0LflZIy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) June 5, 2025
Dragon has completed 51 missions, 46 of which have been to the ISS. It is capable of carrying up to 7 passengers to and from Earth’s orbit. It is the only spacecraft that is capable of returning vast amounts of cargo to Earth. It is also the first private spacecraft to take humans to the ISS.
The most notable mission Dragon completed is one of its most recent, as SpaceX brought NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams back to Earth after being stranded at the ISS by a Boeing Starliner capsule.
SpaceX’s reluctance to participate in federally funded projects may put the government in a strange position. It will look to bring Boeing back in to take a majority of these projects, but there might be some reluctance based on the Starliner mishap with Wilmore and Williams.
SpaceX bails out Boeing and employees are reportedly ‘humiliated’
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoWatch the first true Tesla Robotaxi intervention by safety monitor
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla Robotaxi rollout proves that Elon Musk still delivers, even if it’s late
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI welcomes Memphis pollution results, environmental groups push back
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk commends Tesla team on successful Robotaxi launch
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk confirms Tesla Optimus V3 already uses Grok voice AI




















