News
The very real challenge of a Tesla Pickup Truck

Call it the Tesla Truck, the Tesla Pickup Truck, or the Tesla-150, but CEO Elon Musk has made it clear as revealed in the company’s Master Plan, Part Deux that the electric carmaker plans to make a pickup and heavy-duty truck. In fact, he couldn’t be clearer: he stated in the past that plans call for something to compete with the best-selling light-duty vehicle on American roads: the Ford F-150. This precludes the idea of a small or mid-sized Tesla truck and says that Musk seems to be clearly aiming for a full-sized offering.
 A full-sized electric truck seems like a lark to most truck owners and enthusiasts. I live in the heart of truck country, Wyoming, where pickup trucks equal passenger cars in numbers on the road and range from half-ton F-150s, 1500s, and Silverados to heavy-duty and diesel-driven duals. Although many enjoy scoffing at the wannabe cowboys who buy a big, shiny pickup and drive it to the office and back every day – never seeing dirt or any load larger than an IKEA furniture set – the core truck buyer and, indeed, the majority of truck owners do not fit that stereotype.
A full-sized electric truck seems like a lark to most truck owners and enthusiasts. I live in the heart of truck country, Wyoming, where pickup trucks equal passenger cars in numbers on the road and range from half-ton F-150s, 1500s, and Silverados to heavy-duty and diesel-driven duals. Although many enjoy scoffing at the wannabe cowboys who buy a big, shiny pickup and drive it to the office and back every day – never seeing dirt or any load larger than an IKEA furniture set – the core truck buyer and, indeed, the majority of truck owners do not fit that stereotype.
In general, truck owners fall into three categories: weekend warriors, offroaders, and workhorses. The weekend warrior uses a truck to tow toys (boats, RVs, what have you) and occasionally haul household construction goods for home improvement. The offroader buys the TRD, Pro-4X, and similar packages and spends a lot of time getting mud, dirt, and tree branches stuck on the truck (this would be my personal category, for the record). Finally, the workhorses are those who buy a truck to work with, either as a commercial vehicle or as a personal working machine – these include farmers, ranchers, commercial haulers, tradesmen, and so forth.
Traditionally, the largest truck market are the weekend warriors. These are the folks who buy a truck because they want to haul the family and their playthings around. They tow boats, jet skis, haul camping stuff, tote gear to the game, tailgate, and otherwise use their truck mostly as a recreational vehicle that may or may not be their everyday driver. Next to that market, and not as small as some might expect, are the workhorse buyers. These are the people who buy trucks to work with them and rely on them to get any of a number of jobs done. Most importantly to the industry, these are the repeat buyers – the ones who buy, trade-in and buy again (rinse, repeat). Where I live, for example, it’s not unusual for a rancher to buy a new truck every two or three years. Trading in a machine that will have over 100,000 miles on it is not unusual either. That’s 30,000-50,000 miles driven in only one year. For reference, as a commercial over-the-road driver, I put a little over 100,000 miles per year on my rig. Surveys of the truck market nationally show that in the traditional truck strongholds of the West, including Texas on up to the Dakotas and over to the coast, that kind of mileage is not unusual for the working pickup.
So let’s assume that Tesla plans to make a truck that will sell on the traditional pickup truck market in competition with the best-sellers from Ford, GM, and Ram. We can assume they won’t be doing a hard-core off-road package, but will aim for a 4×4 market in order to appeal to most truck buyers. Here’s a bullet list of criteria for a mainstream Tesla Truck offering, based on the most common features of a mainstream full-size pickup truck today:
- V8-like performance including roughly 400 hp and 380 lb-ft
- Extended and four-door cab offerings
- Cargo bed size of 5.5 feet with option for 7 feet
- Towing capacity of about 10,000 pounds
- Payload capacity of 1/2 ton to 3,000 pounds
- 4×4 capability
- Driving range, under load, of at least 150 miles
- Conventional styling and appeal
Those criteria make up the most common things truck buyers ask for. The recent revamp of the Toyota Tundra, for example, was mostly about style since the previous-generation Tundra was dated and didn’t look like a “beefy truck,” as one friend put it. This may be laughed at by the Teslarati, but it’s akin to the Model S having been designed to look like the Volkswagen Thing rather than the beautiful Euro-styled sedan it is. So don’t scoff.
Now that we have those basic requirements, let’s look at what Elon and Tesla would have to accomplish to make that happen.
For starters, the current powertrain in the Model S or Model X would not be sufficient. If put under load, towing a trailer for example, and with the aerodynamics of a pickup, the current powertrain would be lucky to achieve half the range required. Anyone who doubts this need only consider how much work went into Bob Lutz’ never-selling VIA truck and its plug-in hybrid powertrain, which together only produce marginal range when trailering at capacity. That’s an ICE (internal combustion engine) and electric drivetrain combined. Remember also that every pound of batteries added has a net-reduced benefit to the overall range of the vehicle as it also adds weight. Since Tesla isn’t currently using and hasn’t made a lot of noise about eventually using high-tech, high-density, bleeding-edge lithium batteries to lighten the battery’s weight, we can assume that the current Panasonic cells are what would power a Tesla Truck if it were made in the near future.
To tow a trailer at 7,000+ pounds would require an enormous amount of energy and to do so for a long range like truck owners would expect (e.g. to the lake and back) would be a feat. It’s not insurmountable, of course. There’s little doubt that Tesla’s engineers couldn’t overcome this obstacle, but it will be a huge one.
Matching V8-like performance would not be difficult – the Model S and Model X already does this and with the inherent strengths of an electric motor, namely torque from zero, the numbers actually required would be smaller than those needed for the gasoline equivalent.
Next comes another problem – off-road. With the problems the Model S has had in the past with undercarriage breaches on the highway, it’s easy to see concern when going fully off the road. Even the best of dirt roads are rough. Putting an under-pan, as Tesla has done may or may not work well with a truck. Skid plates are not unusual for trucks, of course, but they rarely run past the front engine compartment. Most of the safety is addressed by lifting components high up into the framing to minimize exposure. With a big, long, heavy battery pack, though, this is problematic. A skid plate may do the trick, but this would at the very least be a big marketing hassle for Tesla if nothing else.
Another big roadblock is going to be the price tag. In order to compete with the F-150 and its brethren, the Tesla Truck would need to sell at around the $30,000-$40,000 mark at entry-level. Truck buyers would probably be willing to pay a premium of $8,000, even $10,000 on the truck if the expected fuel savings are big and obvious. Yet even that premium markup is going to be a problem for Tesla because, well, unless of course the pickup will be based off the Model 3. This is where the Gigafactory could possibly pay off, but at this point, that is only an idea that is likely to become reality, but until it is, we have no idea how real its cost-savings in terms of dollars per kWh will be.
Finally, for sake of space, we have not even mentioned dealership woes. The top truck markets are well outside of Tesla’s best markets for the Model S and Model X. Some of those markets, such as Texas, are off limits to Tesla’s direct sales entirely. Yet if that’s overcome, there’s also marketing. Not only are pickup truck buyers exceedingly brand loyal (just ask Toyota and Nissan how easy it is to penetrate the full-sized market), but they’re finicky as well.
The conclusion? Tesla could likely, eventually, field a full-sized pickup truck capable of competing with the F-150, but the challenges are huge. Just as Elon likes ’em. Will they do it? Good question, but it’s fair to say that if they do, they may be treading on the thin crust of a deep, deep lake.
Feature image via Topspeed
Elon Musk
Tesla begins expanding Robotaxi access: here’s how you can ride
You can ride in a Tesla Robotaxi by heading to its website and filling out the interest form. The company is hand-picking some of those who have done this to gain access to the fleet.

Tesla has begun expanding Robotaxi access beyond the initial small group it offered rides to in late June, as it launched the driverless platform in Austin, Texas.
The small group of people enjoying the Robotaxi ride-hailing service is now growing, as several Austin-area residents are receiving invitations to test out the platform for themselves.
The first rides took place on June 22, and despite a very small number of very manageable and expected hiccups, Tesla Robotaxi was widely successful with its launch.
Tesla Robotaxi riders tout ‘smooth’ experience in first reviews of driverless service launch
However, Tesla is expanding the availability of the ride-hailing service to those living in Austin and its surrounding areas, hoping to gather more data and provide access to those who will utilize it on a daily basis.
Many of the people Tesla initially invited, including us, are not local to the Austin area.
There are a handful of people who are, but Tesla was evidently looking for more stable data collection, as many of those early invitees headed back to where they live.
The first handful of invitations in the second round of the Robotaxi platform’s Early Access Program are heading out to Austin locals:
I just got a @robotaxi invite! Super excited to go try the service out! pic.twitter.com/n9mN35KKFU
— Ethan McKanna (@ethanmckanna) July 1, 2025
Tesla likely saw an influx of data during the first week, as many traveled far and wide to say they were among the first to test the Robotaxi platform.
Now that the first week and a half of testing is over, Tesla is expanding invites to others. Many of those who have been chosen to gain access to the Robotaxi app and the ride-hailing service state that they simply filled out the interest form on the Robotaxi page of Tesla’s website.
That’s the easiest way you will also gain access, so be sure to fill out that form if you have any interest in riding in Robotaxi.
Tesla will continue to utilize data accumulated from these rides to enable more progress, and eventually, it will lead to even more people being able to hail rides from the driverless platform.
With more success, Tesla will start to phase out some of the Safety Monitors and Supervisors it is using to ensure things run smoothly. CEO Elon Musk said Tesla could start increasing the number of Robotaxis to monitors within the next couple of months.
Elon Musk
Tesla analyst issues stern warning to investors: forget Trump-Musk feud

A Tesla analyst today said that investors should not lose sight of what is truly important in the grand scheme of being a shareholder, and that any near-term drama between CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump should not outshine the progress made by the company.
Gene Munster of Deepwater Management said that Tesla’s progress in autonomy is a much larger influence and a significantly bigger part of the company’s story than any disagreement between political policies.
Munster appeared on CNBC‘s “Closing Bell” yesterday to reiterate this point:
“One thing that is critical for Tesla investors to remember is that what’s going on with the business, with autonomy, the progress that they’re making, albeit early, is much bigger than any feud that is going to happen week-to-week between the President and Elon. So, I understand the reaction, but ultimately, I think that cooler heads will prevail. If they don’t, autonomy is still coming, one way or the other.”
BREAKING: GENE MUNSTER SAYS — $TSLA AUTONOMY IS “MUCH BIGGER” THAN ANY FEUD 👀
He says robotaxis are coming regardless ! pic.twitter.com/ytpPcwUTFy
— TheSonOfWalkley (@TheSonOfWalkley) July 2, 2025
This is a point that other analysts like Dan Ives of Wedbush and Cathie Wood of ARK Invest also made yesterday.
On two occasions over the past month, Musk and President Trump have gotten involved in a very public disagreement over the “Big Beautiful Bill,” which officially passed through the Senate yesterday and is making its way to the House of Representatives.
Musk is upset with the spending in the bill, while President Trump continues to reiterate that the Tesla CEO is only frustrated with the removal of an “EV mandate,” which does not exist federally, nor is it something Musk has expressed any frustration with.
In fact, Musk has pushed back against keeping federal subsidies for EVs, as long as gas and oil subsidies are also removed.
Nevertheless, Ives and Wood both said yesterday that they believe the political hardship between Musk and President Trump will pass because both realize the world is a better place with them on the same team.
Munster’s perspective is that, even though Musk’s feud with President Trump could apply near-term pressure to the stock, the company’s progress in autonomy is an indication that, in the long term, Tesla is set up to succeed.
Tesla launched its Robotaxi platform in Austin on June 22 and is expanding access to more members of the public. Austin residents are now reporting that they have been invited to join the program.
Elon Musk
Tesla surges following better-than-expected delivery report
Tesla saw some positive momentum during trading hours as it reported its deliveries for Q2.

Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA) surged over four percent on Wednesday morning after the company reported better-than-expected deliveries. It was nearly right on consensus estimations, as Wall Street predicted the company would deliver 385,000 cars in Q2.
Tesla reported that it delivered 384,122 vehicles in Q2. Many, including those inside the Tesla community, were anticipating deliveries in the 340,000 to 360,000 range, while Wall Street seemed to get it just right.
Tesla delivers 384,000 vehicles in Q2 2025, deploys 9.6 GWh in energy storage
Despite Tesla meeting consensus estimations, there were real concerns about what the company would report for Q2.
There were reportedly brief pauses in production at Gigafactory Texas during the quarter and the ramp of the new Model Y configuration across the globe were expected to provide headwinds for the EV maker during the quarter.
At noon on the East Coast, Tesla shares were up about 4.5 percent.
It is expected that Tesla will likely equal the number of deliveries it completed in both of the past two years.
It has hovered at the 1.8 million mark since 2023, and it seems it is right on pace to match that once again. Early last year, Tesla said that annual growth would be “notably lower” than expected due to its development of a new vehicle platform, which will enable more affordable models to be offered to the public.
These cars are expected to be unveiled at some point this year, as Tesla said they were “on track” to be produced in the first half of the year. Tesla has yet to unveil these vehicle designs to the public.
Dan Ives of Wedbush said in a note to investors this morning that the company’s rebound in China in June reflects good things to come, especially given the Model Y and its ramp across the world.
He also said that Musk’s commitment to the company and return from politics played a major role in the company’s performance in Q2:
“If Musk continues to lead and remain in the driver’s seat, we believe Tesla is on a path to an accelerated growth path over the coming years with deliveries expected to ramp in the back-half of 2025 following the Model Y refresh cycle.”
Ives maintained his $500 price target and the ‘Outperform’ rating he held on the stock:
“Tesla’s future is in many ways the brightest it’s ever been in our view given autonomous, FSD, robotics, and many other technology innovations now on the horizon with 90% of the valuation being driven by autonomous and robotics over the coming years but Musk needs to focus on driving Tesla and not putting his political views first. We maintain our OUTPERFORM and $500 PT.”
Moving forward, investors will look to see some gradual growth over the next few quarters. At worst, Tesla should look to match 2023 and 2024 full-year delivery figures, which could be beaten if the automaker can offer those affordable models by the end of the year.
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-
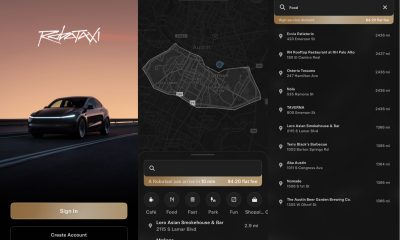
 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla Robotaxis are becoming a common sight on Austin’s public roads
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoSpaceX President meets India Minister after Starlink approval
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Grok 3 partners with Oracle Cloud for corporate AI innovation
















