Investor's Corner
Tesla’s ‘Alien Dreadnought’ factory takes a step forward with structural cable patent
When Elon Musk envisioned the Model 3 production line, he saw a factory that was so automated; it looked like it was literally out of this world. In later statements, Musk shared Tesla’s internal name for the automated factory – Alien Dreadnought – a reference to the fascinating, intricate extraterrestrial motherships that are a trope of classic sci-fi franchises. Musk also noted that the Alien Dreadnought should be operational sometime in 2018.
The Model 3 production ramp would eventually teach Elon Musk that his timeline for the Alien Dreadnought was far too optimistic. Since starting the production of the electric car, Tesla has been met with bottleneck after bottleneck in both the Fremont factory and Gigafactory 1. While Tesla was eventually able to find a system that balances robot and human work to effectively ramp the Model 3, Musk would later admit that Tesla overreached when it came to the automation of its production lines. In a post on Twitter, Musk candidly noted that human workers are still underrated.
Yes, excessive automation at Tesla was a mistake. To be precise, my mistake. Humans are underrated.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) April 13, 2018
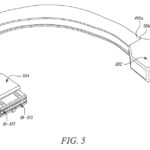
While Elon Musk’s Alien Dreadnought factory might be coming later than expected, the company appears to be paving the way for even more automation in its factories. A recently published patent on Thursday, for one, outlines a structural cable design that is fully optimized for automated manufacturing. In the discussions of the patent, Tesla described the rationale of a structural cable that is rigid by design.
“The structural cable according to the present disclosure is a cable with structural integrity that may be manipulated into place by a robotic arm as part of an automated process while providing reliable data connections to its desired location. As part of the form manipulation, the structural cable preferentially allows manipulation into different geometries allowing for placement that avoids obstacles, and that can be performed in a reproducible manner so as to be implemented as part of an automated process.”
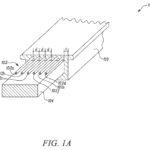
Tesla notes in its patent that traditional cables, due to their non-rigid nature, are best installed by human hands, which connect the appropriate connectors to their respective ports during the production process. The electric car maker notes that this is due to the cables lacking “sufficient structural integrity and rigidity to be easily picked up, moved, and placed by a robotic arm,” as well as their inability to be formed into pre-determined shapes.
“Because traditional cables are not rigid, they may not be easily formed into different shapes and routed to a pre-determined location amidst tight spatial constraints. Routing traditional, flexible cables during manufacturing, for example to connect different components during automobile manufacturing, typically cannot be automated and therefore require humans to place by hand. Such manual placement is time-consuming, tedious, and costly. Hence, there is a need for a structural cable that overcomes the aforementioned drawbacks.”
Tesla’s designs for its structural cable design as outlined in the newly-published patent. [Source: Patentscope]
Tesla intends to work around these compromises by using a rigid structural cable, which could be easily picked up and installed automatically by a robotic arm. By using such components, Tesla would be able to optimize the level of automation in its facilities even further.
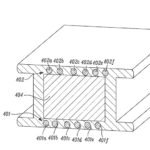
“An advantage of this flat cable configuration with known geometries and wires/conductors spaced at known dimensions (and preferably collinear) is that the process of connecting the flat wires/conductors to connectors may be automated through, for example crimping, traditional soldering, or laser soldering. In a specific implementation, encased wires are held on a flat conveyer or with a robotic arm, and the wires are stripped using a stripping attachment so as to preserve the wire spacing. The robotic arm (or another robotic arm) may then pick up a connector and crimp the connector to the wires by pressing down (or utilizing an appropriate tool).”
It should be noted that while Elon Musk’s Alien Dreadnought factory is delayed, the company’s production lines are already heavily automated. Back in the Q1 2018 earnings call, for one, Elon Musk noted that Tesla was able to reduce the time it takes to produce Model 3 battery packs by 94%, from seven hours per unit to under 17 minutes per pack. Tesla has since improved its production lines in the Fremont factory and Gigafactory 1, and this Q4 2018, the company intends to optimize its operations even further. Gigafactory 1, for example, is expected to receive new battery cell assembly lines from Panasonic this quarter. New Grohmann machines, which are expected to improve production, are also expected to go online in the Nevada facility this Q4 as well.
The full text of Tesla’s patent for its structural cables could be accessed here.
Investor's Corner
Tesla could save $2.5B by replacing 10% of staff with Optimus: Morgan Stanley
Jonas assigned each robot a net present value (NPV) of $200,000.

Tesla’s (NASDAQ:TSLA) near-term outlook may be clouded by political controversies and regulatory headwinds, but Morgan Stanley analyst Adam Jonas sees a glimmer of opportunity for the electric vehicle maker.
In a new note, the Morgan Stanley analyst estimated that Tesla could save $2.5 billion by replacing just 10% of its workforce with its Optimus robots, assigning each robot a net present value (NPV) of $200,000.
Morgan Stanley highlights Optimus’ savings potential
Jonas highlighted the potential savings on Tesla’s workforce of 125,665 employees in his note, suggesting that the utilization of Optimus robots could significantly reduce labor costs. The analyst’s note arrived shortly after Tesla reported Q2 2025 deliveries of 384,122 vehicles, which came close to Morgan Stanley’s estimate and slightly under the consensus of 385,086.
“Tesla has 125,665 employees worldwide (year-end 2024). On our calculations, a 10% substitution to humanoid at approximately ($200k NPV/humanoid) could be worth approximately $2.5bn,” Jonas wrote, as noted by Street Insider.
Jonas also issued some caution on Tesla Energy, whose battery storage deployments were flat year over year at 9.6 GWh. Morgan Stanley had expected Tesla Energy to post battery storage deployments of 14 GWh in the second quarter.
Musk’s political ambitions
The backdrop to Jonas’ note included Elon Musk’s involvement in U.S. politics. The Tesla CEO recently floated the idea of launching a new political party, following a poll on X that showed support for the idea. Though a widely circulated FEC filing was labeled false by Musk, the CEO does seem intent on establishing a third political party in the United States.
Jonas cautioned that Musk’s political efforts could divert attention and resources from Tesla’s core operations, adding near-term pressure on TSLA stock. “We believe investors should be prepared for further devotion of resources (financial, time/attention) in the direction of Mr. Musk’s political priorities which may add further near-term pressure to TSLA shares,” Jonas stated.
Investor's Corner
Two Tesla bulls share differing insights on Elon Musk, the Board, and politics
Two noted Tesla bulls have shared differing views on the recent activities of CEO Elon Musk and the company’s leadership.

Two noted Tesla (NASDAQ:TSLA) bulls have shared differing views on the recent activities of CEO Elon Musk and the company’s leadership.
While Wedbush analyst Dan Ives called on Tesla’s board to take concrete steps to ensure Musk remains focused on the EV maker, longtime Tesla supporter Cathie Wood of Ark Invest reaffirmed her confidence in the CEO and the company’s leadership.
Ives warns of distraction risk amid crucial growth phase
In a recent note, Ives stated that Tesla is at a critical point in its history, as the company is transitioning from an EV maker towards an entity that is more focused on autonomous driving and robotics. He then noted that the Board of Directors should “act now” and establish formal boundaries around Musk’s political activities, which could be a headwind on TSLA stock.
Ives laid out a three-point plan that he believes could ensure that the electric vehicle maker is led with proper leadership until the end of the decade. First off, the analyst noted that a new “incentive-driven pay package for Musk as CEO that increases his ownership of Tesla up to ~25% voting power” is necessary. He also stated that the Board should establish clear guidelines for how much time Musk must devote to Tesla operations in order to receive his compensation, and a dedicated oversight committee must be formed to monitor the CEO’s political activities.
Ives, however, highlighted that Tesla should move forward with Musk at its helm. “We urge the Board to act now and move the Tesla story forward with Musk as CEO,” he wrote, reiterating its Outperform rating on Tesla stock and $500 per share price target.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk has responded to Ives’ suggestions with a brief comment on X. “Shut up, Dan,” Musk wrote.
Cathie Wood reiterates trust in Musk and Tesla board
Meanwhile, Ark Investment Management founder Cathie Wood expressed little concern over Musk’s latest controversies. In an interview with Bloomberg Television, Wood said, “We do trust the board and the board’s instincts here and we stay out of politics.” She also noted that Ark has navigated Musk-related headlines since it first invested in Tesla.
Wood also pointed to Musk’s recent move to oversee Tesla’s sales operations in the U.S. and Europe as evidence of his renewed focus in the electric vehicle maker. “When he puts his mind on something, he usually gets the job done,” she said. “So I think he’s much less distracted now than he was, let’s say, in the White House 24/7,” she said.
TSLA stock is down roughly 25% year-to-date but has gained about 19% over the past 12 months, as noted in a StocksTwits report.
Investor's Corner
Cantor Fitzgerald maintains Tesla (TSLA) ‘Overweight’ rating amid Q2 2025 deliveries
Cantor Fitzgerald is holding firm on its bullish stance for the electric vehicle maker.

Cantor Fitzgerald is holding firm on its bullish stance for Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA), reiterating its “Overweight” rating and $355 price target amidst the company’s release of its Q2 2025 vehicle delivery and production report.
Tesla delivered 384,122 vehicles in Q2 2025, falling below last year’s Q2 figure of 443,956 units. Despite softer demand in some countries in Europe and ongoing controversies surrounding CEO Elon Musk, the firm maintained its view that Tesla is a long-term growth story in the EV sector.
Tesla’s Q2 results
Among the 384,122 vehicles that Tesla delivered in the second quarter, 373,728 were Model 3 and Model Y. The remaining 10,394 units were attributed to the Model S, Model X, and Cybertruck. Production was largely flat year-over-year at 410,244 units.
In the energy division, Tesla deployed 9.6 GWh of energy storage in Q2, which was above last year’s 9.4 GWh. Overall, Tesla continues to hold a strong position with $95.7 billion in trailing twelve-month revenue and a 17.7% gross margin, as noted in a report from Investing.com.
Tesla’s stock is still volatile
Tesla’s market cap fell to $941 billion on Monday amid volatility that was likely caused in no small part by CEO Elon Musk’s political posts on X over the weekend. Musk has announced that he is forming the America Party to serve as a third option for voters in the United States, a decision that has earned the ire of U.S. President Donald Trump.
Despite Musk’s controversial nature, some analysts remain bullish on TSLA stock. Apart from Cantor Fitzgerald, Canaccord Genuity also reiterated its “Buy” rating on Tesla shares, with the firm highlighting the company’s positive Q2 vehicle deliveries, which exceeded its expectations by 24,000 units. Cannacord also noted that Tesla remains strong in several markets despite its year-over-year decline in deliveries.
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk3 days ago
Elon Musk3 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 Elon Musk18 hours ago
Elon Musk18 hours agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla’s Omead Afshar, known as Elon Musk’s right-hand man, leaves company: reports
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”