

News
Tesla’s race to full self-driving under pressure as GM Cruise gets $2.25B investment
In a press release on Thursday, General Motors announced that SoftBank would be investing $2.25 billion in the automaker’s self-driving unit, GM Cruise Holdings LLC. The Detroit-based auto giant would also be investing an additional $1.1 billion into its self-driving division. These investments are aimed at boosting the unit’s capability to reach commercialization at scale by next year.
GM Chairman and CEO Mary Barra lauded the additional investments into the company’s self-driving unit. Barra noted in the press release that the support from SoftBank adds an “additional strong partner” as the automaker pursues its “vision of zero crashes, zero emissions, and zero congestion.”
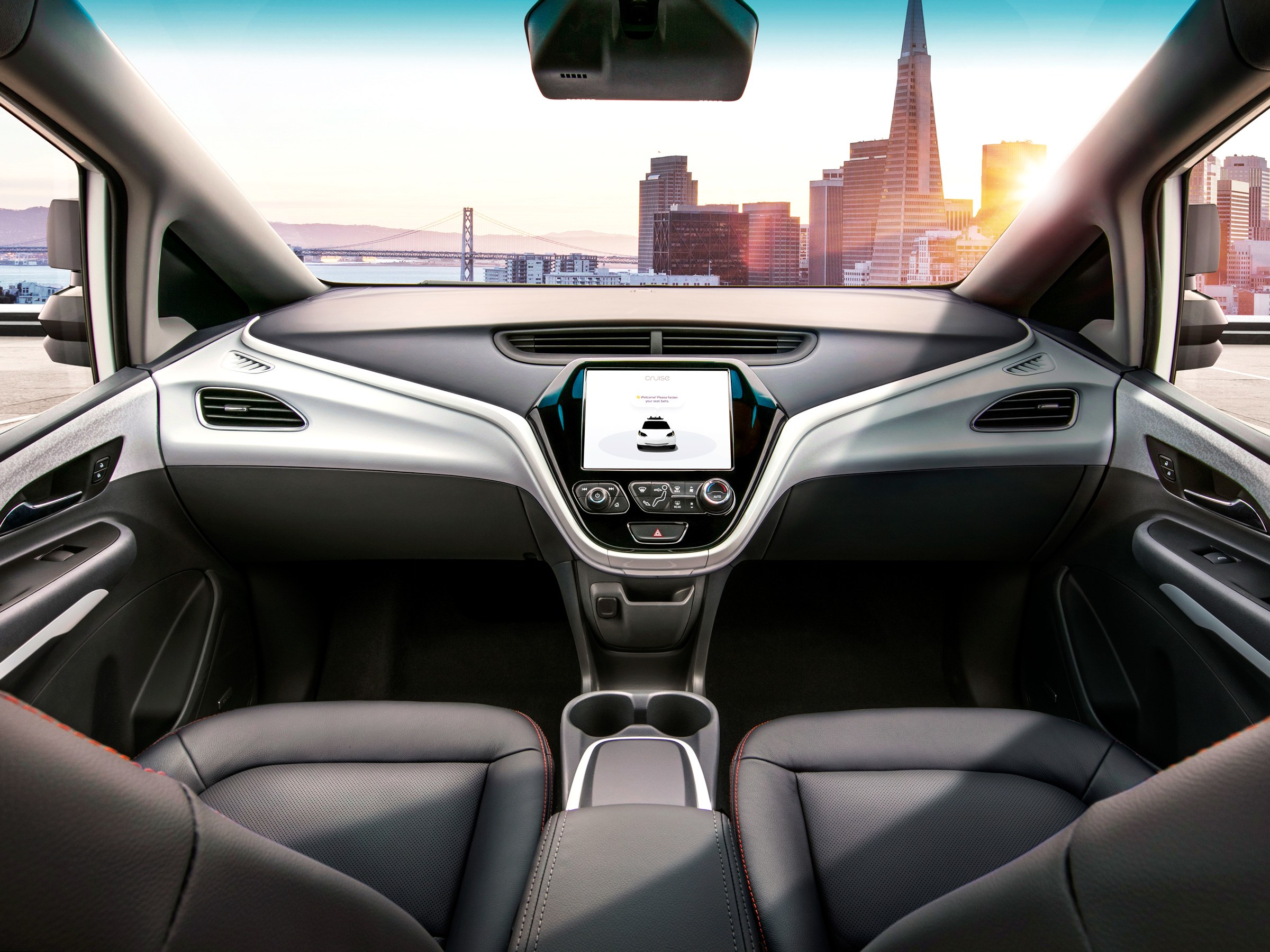
GM Cruise currently operates a fleet of autonomous Chevy Bolt EVs in San Francisco that provide autonomous ride-hailing services to its employees. Plans are also underway to develop a Chevy Bolt EV variant that is specifically designed to be fully autonomous, with the vehicle not having pedals or a steering wheel.
SoftBank’s $2.25 billion investment into GM Cruise will be made in two tranches. SoftBank Vision Fund will first invest $900 million at the closing of the transaction. Once GM Cruise’s autonomous vehicles are ready to hit the market, Vision Fund will release the second tranche of $1.35 billion. This will ultimately result in SoftBank Vision Fund commanding a 19.6% stake in GM Cruise.
The new investment brings GM Cruise’s valuation close to $11.5 billion. The investment also brings to light the arguable undervaluation of Tesla’s Autopilot system, which has been on the consumer market for several years and has more than 150,000 vehicles from around the world that’s collecting data.
Still, GM Cruise’s new financial backing puts tremendous pressure on Tesla, which has seen its fair share of scrutiny as it steadily improves its Autopilot software in the public eye. Despite having collected reservation deposits for its Full Self-Driving capability that is yet to be released, Autopilot continues to improve and pacing toward full autonomy, according to CEO Elon Musk.
During the Q4 2017 earnings call, Musk addressed the delays in the company’s planned coast-to-coast autonomous drive. The exhibition, which was set for December 2017, did not pan out, although Tesla could have accomplished the coast-to-coast trip, according to Musk. However, doing so would have required far too much “specialized code” that would only be fully effective on a particular route. During the earnings call, Musk stated that Tesla would likely conduct the autonomous coast-to-coast drive sometime this year.
One notable difference between Tesla and GM Cruise, and Google’s Waymo is the Tesla’s opposition to the utilization of LiDAR technology – a common fixture on self-driving cars. Instead of LiDAR, Tesla’s electric cars rely on a series of cameras, radar, and ultrasonic sensors to collect data on a vehicle’s surroundings. LiDAR, which is used in GM Cruise’s Chevy Bolt EVs and Waymo’s autonomous vehicles, boasts high spatial precision. Inasmuch as LiDAR can measure distances well, however, it performs poorly in bad weather.
Ultimately, Tesla’s ace-in-the-hole in the increasingly competitive self-driving car market could be its neural net and sharing of fleet data. There are roughly 150,000 AP2.0 vehicles on the road today, with each one providing valuable data to Tesla’s deep neural networks. Akin to the human brain, the more data that is available to train the neural network, the better its performance would be.
Ultimately, Tesla’s neural net could be the difference-maker when the company goes all-in and competes in the self-driving race. Until then, however, the electric car maker could soon be taking a backseat to companies like GM Cruise and Waymo, both of which are accelerating their efforts at rolling out consumer-ready autonomous vehicles in the near future.
News
Tesla UK sales see 14% year-over-year rebound in June: SMMT data
The SMMT stated that Tesla sales grew 14% year-over-year to 7,719 units in June 2025.

Tesla’s sales in the United Kingdom rose in June, climbing 14% year-over-year to 7,719 units, as per data from the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders (SMMT). The spike in the company’s sales coincided with the first deliveries of the updated Model Y last month.
Model Y deliveries support Tesla’s UK recovery
Tesla’s June performance marked one of its strongest months in the UK so far this year, with new Model Y deliveries contributing significantly to the company’s momentum.
While the SMMT listed Tesla with 7,719 deliveries in June, independent data from New AutoMotive suggested that the electric vehicle maker registered 7,891 units during the month instead. However, year-to-date figures for Tesla remain 2% down compared to 2024, as per a report from Reuters.
While Tesla made a strong showing in June, rivals are also growing. Chinese automaker BYD saw UK sales rise nearly fourfold to 2,498 units, while Ford posted the highest EV growth among major automakers, with a more than fourfold increase in the first half of 2025.
Overall, the UK’s battery electric vehicle (BEV) demand surged 39% to to 47,354 units last month, helping push total new car sales in the UK to 191,316 units, up 6.7% from the same period in 2024.
EV adoption accelerates, but concerns linger
June marked the best month for UK car sales since 2019, though the SMMT cautioned that growth in the electric vehicle sector remains heavily dependent on discounting and support programs. Still, one in four new vehicle buyers in June chose a battery electric vehicle.
SMMT Chief Executive Mike Hawes noted that despite strong BEV demand, sales levels are still below regulatory targets. “Further growth in sales, and the sector will rely on increased and improved charging facilities to boost mainstream electric vehicle adoption,” Hawes stated.
Also taking effect this week was a new US-UK trade deal, which lowers tariffs on UK car exports to the United States from 27.5% to 10%. The agreement could benefit UK-based EV producers aiming to expand across the country.
News
Tesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
Despite being on the market longer than many of its rivals, the Tesla Model 3 continues to set the bar for vehicle safety.

The Tesla Model 3 has been named the safest new car on sale in 2025, according to the latest results from the Euro NCAP. Among 20 newly tested vehicles, the Model 3 emerged at the top of the list, scoring an impressive 359 out of 400 possible points across all major safety categories.
Tesla Model 3’s safety systems
Despite being on the market longer than many of its rivals, the Tesla Model 3 continues to set the bar for vehicle safety. Under Euro NCAP’s stricter 2025 testing protocols, the electric sedan earned 90% for adult occupant protection, 93% for child occupant protection, 89% for pedestrian protection, and 87% for its Safety Assist systems.
The updated Model 3 received particular praise for its advanced driver assistance features, including Tesla’s autonomous emergency braking (AEB) system, which performed well across various test scenarios. Its Intelligent Speed Assistance and child presence detection system were cited as noteworthy features as well, as per a WhatCar report.
Other notable safety features include the Model 3’s pedestrian-friendly pop-up hood and robust crash protection for both front and side collisions. Euro NCAP also highlighted the Model 3’s ability to detect vulnerable road users during complex maneuvers, such as turning across oncoming traffic.
Euro NCAP’s Autopilot caution
While the Model 3’s safety scores were impressive across the board, Euro NCAP did raise concerns about driver expectations of Tesla’s Autopilot system. The organization warned that some owners may overestimate the system’s capabilities, potentially leading to misuse or inattention behind the wheel. Even so, the Model 3 remained the highest-scoring vehicle tested under Euro NCAP’s updated criteria this year.
The Euro NCAP’s concerns are also quite interesting because Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) Supervised, which is arguably the company’s most robust safety suite, is not allowed for public rollout in Europe yet. FSD Supervised would allow the Model 3 to navigate inner city streets with only minimal human supervision.
Other top scorers included the Volkswagen ID.7, Polestar 3, and Geely EX5, but none matched the Model 3’s total score or consistency across categories. A total of 14 out of 20 newly tested cars earned five stars, while several models, including the Kia EV3, MG ZS, and Renault 5, fell short of the top rating.
Elon Musk
Why Tesla’s Q3 could be one of its biggest quarters in history
Tesla could stand to benefit from the removal of the $7,500 EV tax credit at the end of Q3.

Tesla has gotten off to a slow start in 2025, as the first half of the year has not been one to remember from a delivery perspective.
However, Q3 could end up being one of the best the company has had in history, with the United States potentially being a major contributor to what might reverse a slow start to the year.
Earlier today, the United States’ House of Representatives officially passed President Trump’s “Big Beautiful Bill,” after it made its way through the Senate earlier this week. The bill will head to President Trump, as he looks to sign it before his July 4 deadline.
The Bill will effectively bring closure to the $7,500 EV tax credit, which will end on September 30, 2025. This means, over the next three months in the United States, those who are looking to buy an EV will have their last chance to take advantage of the credit. EVs will then be, for most people, $7,500 more expensive, in essence.
The tax credit is available to any single filer who makes under $150,000 per year, $225,000 a year to a head of household, and $300,000 to couples filing jointly.
Ending the tax credit was expected with the Trump administration, as his policies have leaned significantly toward reliance on fossil fuels, ending what he calls an “EV mandate.” He has used this phrase several times in disagreements with Tesla CEO Elon Musk.
Nevertheless, those who have been on the fence about buying a Tesla, or any EV, for that matter, will have some decisions to make in the next three months. While all companies will stand to benefit from this time crunch, Tesla could be the true winner because of its sheer volume.
If things are done correctly, meaning if Tesla can also offer incentives like 0% APR, special pricing on leasing or financing, or other advantages (like free Red, White, and Blue for a short period of time in celebration of Independence Day), it could see some real volume in sales this quarter.
You can now buy a Tesla in Red, White, and Blue for free until July 14 https://t.co/iAwhaRFOH0
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 3, 2025
Tesla is just a shade under 721,000 deliveries for the year, so it’s on pace for roughly 1.4 million for 2025. This would be a decrease from the 1.8 million cars it delivered in each of the last two years. Traditionally, the second half of the year has produced Tesla’s strongest quarters. Its top three quarters in terms of deliveries are Q4 2024 with 495,570 vehicles, Q4 2023 with 484,507 vehicles, and Q3 2024 with 462,890 vehicles.
-

 Elon Musk5 days ago
Elon Musk5 days agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-
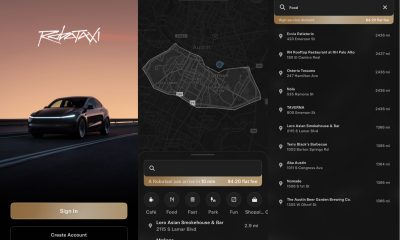
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoSpaceX and Elon Musk share insights on Starship Ship 36’s RUD
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoWatch Tesla’s first driverless public Robotaxi rides in Texas
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoWatch the first true Tesla Robotaxi intervention by safety monitor
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla has started rolling out initial round of Robotaxi invites
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla to launch in India in July with vehicles already arriving: report


















