News
NASA and SpaceX probably can’t terraform Mars but that doesn’t matter
In recent weeks, a great deal of exaggerative noise has been spread wide about the supposed impossibility of making the planet Mars more Earth-like and hospitable, a concept known as terraforming. The reality is quite a bit different, especially within the context of any SpaceX or NASA-driven human outposts or colonization attempts.
Triggered by comparatively reasonable research just published by two experienced planetary scientists, much of the hyperbolic media coverage that followed failed to properly frame the true challenges of terraforming the Red Planet.

Keeping the cart behind the horse
Before anything else, it’s critical to take a step back from the idea of terraforming and consider the simpler facts of any human presence on Mars. First, the rationale for a permanent human presence on Mars is largely independent of the environmental conditions on the planet – it’s a huge help to have basic resources available in situ (on site), but the difficulty of surviving in a given non-Earth environment is immaterial to the human desire to both explore and survive.
Assuming we humans really do want to ensure that a subset of ourselves can independently survive any truly global catastrophe on Earth, be it natural or artificial, we will find a way to do so in even the harshest of environments. Living on Mars would be downright luxurious compared to life aboard the International Space Station, thanks largely to ~1/3rd Earth gravity, accessible natural resources to replenish consumables, an Earthlike day and night cycle, considerably more forgiving temperature extremes, and much more.
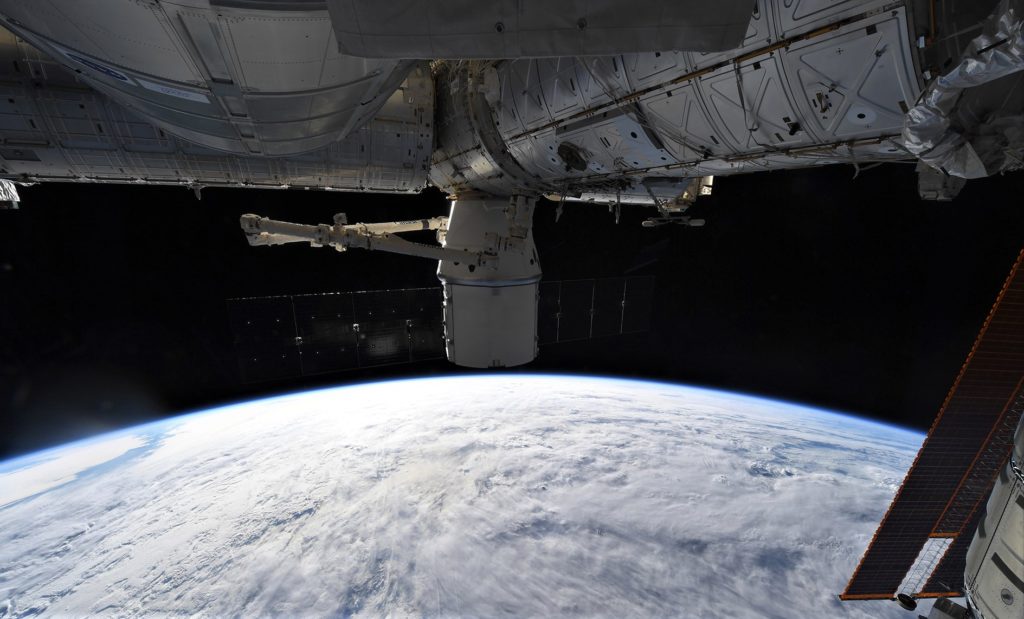
- The ISS orbits just a few hundred miles above the surface of the Earth and hosts an average of six crewmembers at any given moment. (NASA)
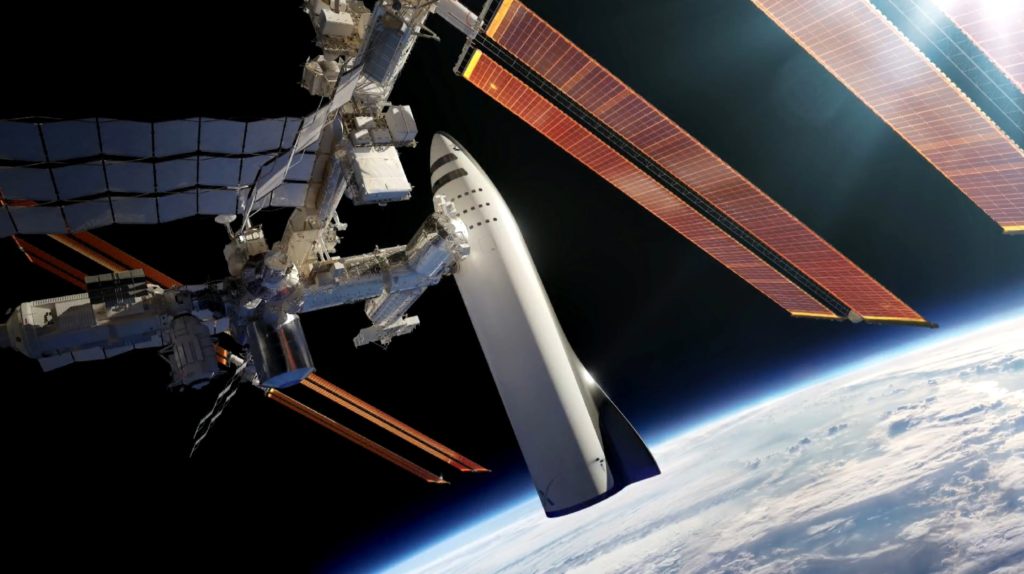
- The massive BFR spaceship docked to the International Space Station. (SpaceX)
Despite the inhospitable conditions, human presence aboard the ISS has been uninterrupted for nearly 20 years, even though the average stay per crewmember sits around six months. The ISS also has the luxury of a 90 minute day/night cycle, 100% unfiltered sunlight for peak solar panel efficiency, regular resupply missions from Earth, and an escape route in the event of a catastrophic failure. That escape method (Soyuz capsules docked to the station) has not once been used, aside from a handful of instances where crew boarded their escape vehicles as a cautionary measure during unusually risky space debris events, an absolute non-issue on Mars’ surface.
Put simply: if humans can live in orbit for long periods, they can also survive on Mars with at least the same level of difficulty.
Getting there is the hardest part
By taking natural resources available on Mars (namely water and carbon dioxide) and using them to repopulate the planet’s withered atmosphere, it has long been hoped that the Martian surface might be brought much closer to that of Earth, with a thicker atmosphere translating into familiar air pressure and a far warmer climate. In its current state, humans would always need to wear pressure suits and carry oxygen when traveling beyond their Martian habitats, as Mars’ 0.06 bar atmosphere would be approximately as forgiving as the naked vacuum of space and only moderately warmer.
https://twitter.com/_TheSeaning/status/1026194288886071296
Terraforming could potentially alleviate those significant points against the Red Planet, although updated research published this year (2018) appears to indicate otherwise. In reality, Jakosky and Edwards’ study simply emphasizes and adds on to what should already have been wildly apparent – making desolate planets Earthlike is almost invariably going to be an unfathomably difficult (but by no means impossible) challenge, and is most likely beyond the reach of present-day humanity.
- Effectively unreleased, an updated Mars colonization video shown in 2018 replaces 2016’s ITS with the newer BFR design. (SpaceX)
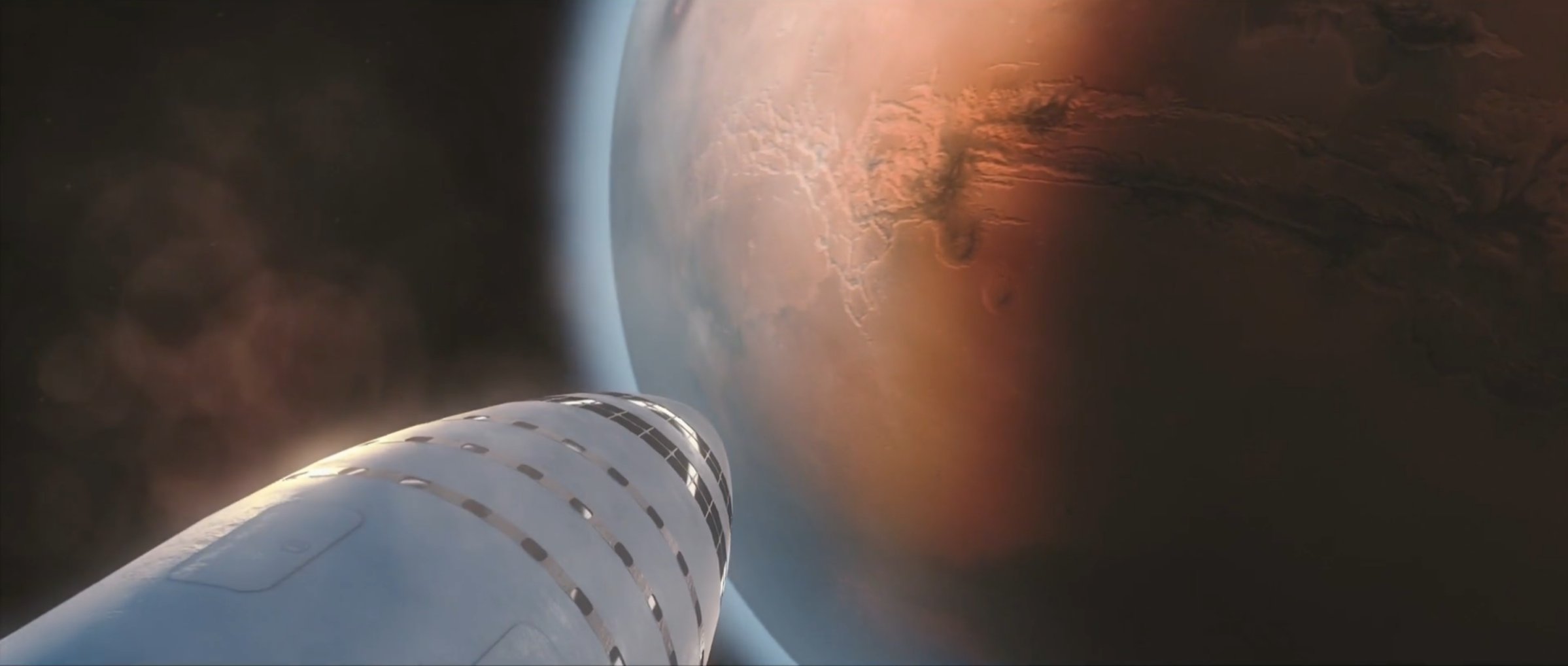
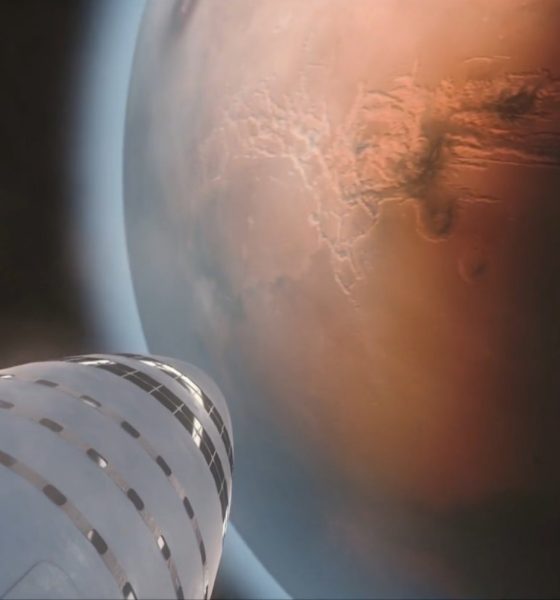
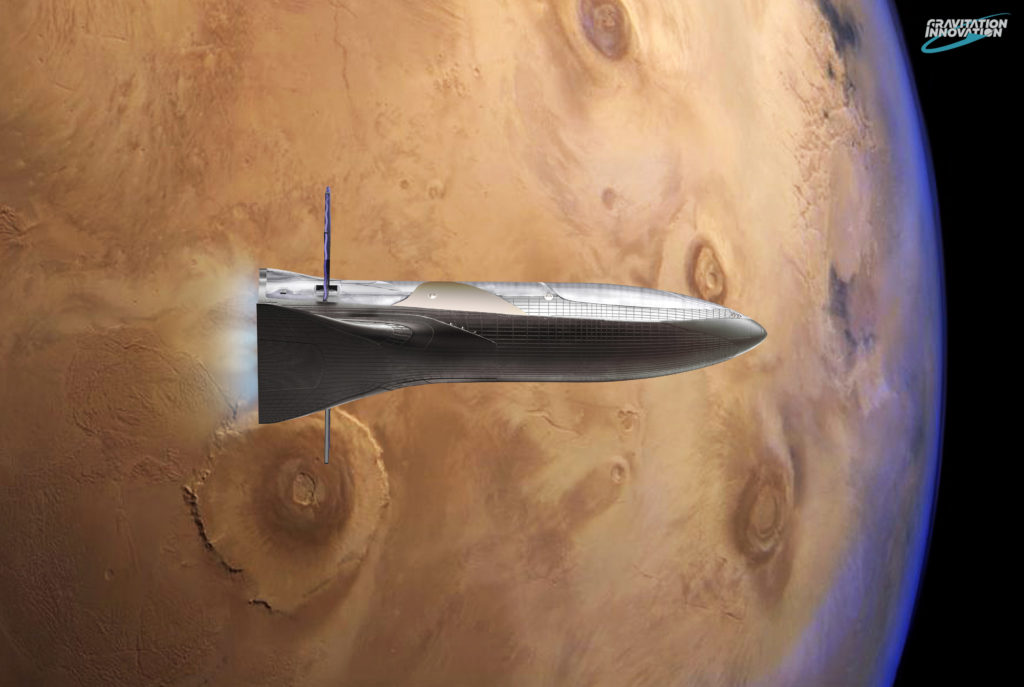
- Artist David Romax’s jaw-dropping rendition of a BFR burning to Mars orbit. The craft’s various curves and hull complexities will likely rely on cutting-edge composite joining tech to function. (Gravitation Innovation)
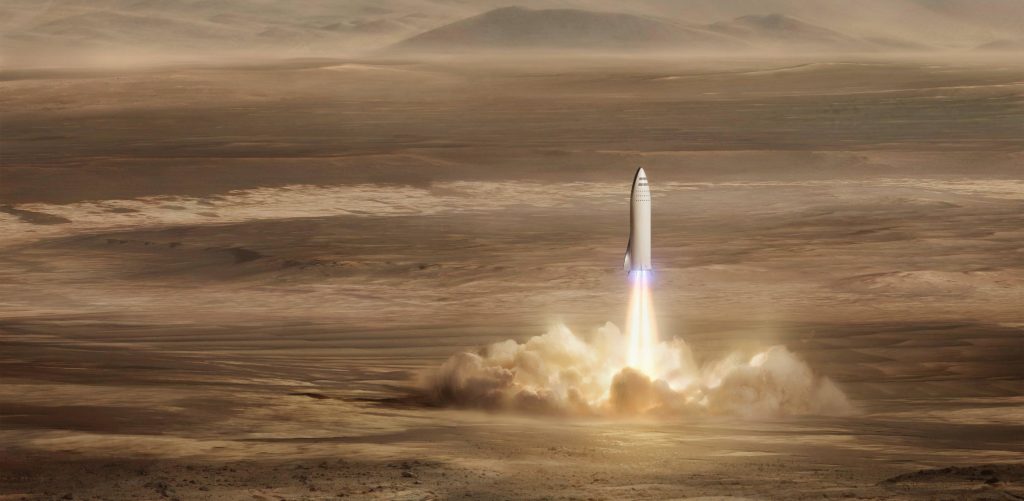
- A Crew BFS (Big F____ Spaceship) pictured landing on Mars. (SpaceX)
It also happens to be the case that terraforming as a concept is utterly irrelevant without the means to get to and – more importantly – transport respectable amounts of cargo to the bodies one hopes to one day transform. SpaceX’s BFR transportation system is one such acknowledgment of that problem – the issue with Mars colonization or really any basic human presence at all is not surviving after arrival, but instead actually getting there in the first place and doing so without taking decades or bankrupting entire nations.
Extremely affordable transport to, from, and between orbits happen to be the most unequivocal requirement for both a permanent human presence on other planets and have any hope at all of terraforming them, but it just so happens that the latter is 100% irrelevant and impossible without the former. Let’s seriously worry and argue about terraforming Mars once we can do so from the surface of the Red Planet and focus first on getting there.
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet (including fairing catcher Mr Steven) check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!

Elon Musk
Will Tesla join the fold? Predicting a triple merger with SpaceX and xAI

With the news of a merger between SpaceX and xAI being confirmed earlier this week by CEO Elon Musk directly, the first moves of an umbrella company that combines all of the serial tech entrepreneur’s companies have been established.
The move aims to combine SpaceX’s prowess in launches with xAI’s expanding vision in artificial intelligence, as Musk has detailed the need for space-based data centers that will require massive amounts of energy to operate.
It has always been in the plans to bring Musk’s companies together under one umbrella.
“My companies are, surprisingly in some ways, trending toward convergence,” Musk said in November. With SpaceX and xAI moving together, many are questioning when Tesla will be next. Analysts believe it is a no-brainer.
SpaceX officially acquires xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise
Dan Ives of Wedbush wrote in a note earlier this week that there is a “growing chance” Tesla could be merged in some form with the new conglomeration over the next 12 to 18 months.
“In our view, there is a growing chance that Tesla will eventually be merged in some form into SpaceX/xAI over time. The viewis this growing AI ecosystem will focus on Space and Earth together… and Musk will look to combine forces,” Ives said.
Let’s take a look at the potential.
The Case for Synergies – Building the Ultimate AI Ecosystem
A triple merger would create a unified “Musk Trinity,” blending Tesla’s physical AI with Robotaxi, Optimus, and Full Self-Driving, SpaceX’s orbital infrastructure through Starlink and potential space-based computer, and xAI’s advanced models, including Grok.
This could accelerate real-world AI applications, more specifically, ones like using satellite networks for global autonomy, or even powering massive training through solar-optimized orbital data centers.
The FCC welcomes and now seeks comment on the SpaceX application for Orbital Data Centers.
The proposed system would serve as a first step towards becoming a Kardashev II-level civilization and serve other purposes, according to the applicant. pic.twitter.com/TDnUPuz9w7
— Brendan Carr (@BrendanCarrFCC) February 4, 2026
This would position the entity, which could ultimately be labeled “X,” as a leader in multiplanetary AI-native tech.
It would impact every level of Musk’s AI-based vision for the future, from passenger use to complex AI training models.
Financial and Structural Incentives — and Risks
xAI’s high cash burn rate is now backed by SpaceX’s massive valuation boost, and Tesla joining the merger would help the company gain access to private funding channels, avoiding dilution in a public-heavy structure.
The deal makes sense from a capital standpoint, as it is an advantage for each company in its own specific way, addressing specific needs.
Because xAI is spending money at an accelerating rate due to its massive compute needs, SpaceX provides a bit of a “lifeline” by redirecting its growing cash flows toward AI ambitions without the need for constant external fundraising.
Additionally, Tesla’s recent $2 billion investment in xAI also ties in, as its own heavy CapEx for Dojo supercomputers, Robotaxis, and Optimus could potentially be streamlined.
Musk’s stake in Tesla and SpaceX, after the xAI merger, is also uneven. His ownership in Tesla equates to about 13 percent, only increasing as he achieves each tranche of his most recent compensation package. Meanwhile, he owns about 43 percent of the private SpaceX.
A triple merger between the three companies could boost his ownership in the combined entity to around 26 percent. This would give Musk what he wants: stronger voting power and alignment across his ventures.
It could also be a potential facilitator in private-to-public transitions, as a reverse merger structure to take SpaceX public indirectly via Tesla could be used. This avoids any IPO scrutiny while accessing the public markets’ liquidity.
Timeline and Triggers for a Public Announcement
As previously mentioned, Ives believes a 12-18 month timeline is realistic, fueled by Musk’s repeated hints at convergence between his three companies. Additionally, the recent xAI investment by Tesla only points toward the increased potential for a conglomeration.
Of course, there is speculation that the merger could happen in the shorter term, before June 30 of this year, which is a legitimate possibility. While this possibility exists but remains at low probability, especially when driven by rapid AI/space momentum, longer horizons, like 2027 or later, allow for key milestones like Tesla’s Robotaxi rollout and Cybercab ramp-up, Optimus scaling, or regulatory clarity under a favorable administration.

Credit: Grok Imagine
The sequencing matters: SpaceX-xAI merger as “step one” toward a unified stack, with a potential SpaceX IPO setting a valuation benchmark before any Tesla tie-up.
Full triple convergence could follow if synergies prove out.
Prediction markets are also a reasonable thing to look at, just to get an idea of where people are putting their money. Polymarket, for example, sits at between a 12 and 24 percent chance that a Tesla-SpaceX merger is officially announced before June 30, 2026.
Looking Ahead
The SpaceX-xAI merger is not your typical corporate shuffle. Instead, it’s the clearest signal yet that Musk is architecting a unified “Muskonomy” where AI, space infrastructure, and real-world robotics converge to solve humanity’s biggest challenges.
Yet the path is fraught with execution risks that could turn this visionary upside into a major value trap. Valuation mismatches remain at the forefront of this skepticism: Tesla’s public multiples are unlike any company ever, with many believing they are “stretched.” On the other hand, SpaceX-xAI’s private “marked-to-muth” pricing hinges on unproven synergies and lofty projects, especially orbital data centers and all of the things Musk and Co. will have to figure out along the way.
Ultimately, the entire thing relies on a high-conviction bet on Musk’s ability to execute at scale. The bullish case is transformative: a vertically integrated AI-space-robotics giant accelerates humanity toward abundance and multi-planetary civilization faster than any siloed company could.
News
IM Motors co-CEO apologizes to Tesla China over FUD comments
Liu said later investigations showed the accident was not caused by a brake failure on the Tesla’s part, contrary to his initial comments.

Liu Tao, co-CEO of IM Motors, has publicly apologized to Tesla China for comments he made in 2022 suggesting a Tesla vehicle was defective following a fatal traffic accident in Chaozhou, China.
Liu said later investigations showed the accident was not caused by a brake failure on the Tesla’s part, contrary to his initial comments.
IM Motors co-CEO issues apology
Liu Tao posted a statement addressing remarks he made following a serious traffic accident in Chaozhou, Guangdong province, in November 2022, as noted in a Sina News report. Liu stated that based on limited public information at the time, he published a Weibo post suggesting a safety issue with the Tesla involved in the crash. The executive clarified that his initial comments were incorrect.
“On November 17, 2022, based on limited publicly available information, I posted a Weibo post regarding a major traffic accident that occurred in Chaozhou, suggesting that the Tesla product involved in the accident posed a safety hazard. Four hours later, I deleted the post. In May 2023, according to the traffic police’s accident liability determination and relevant forensic opinions, the Chaozhou accident was not caused by Tesla brake failure.
“The aforementioned findings and opinions regarding the investigation conclusions of the Chaozhou accident corrected the erroneous statements I made in my previous Weibo post, and I hereby clarify and correct them. I apologize for the negative impact my inappropriate remarks made before the facts were ascertained, which caused Tesla,” Liu said.


Investigation and court findings
The Chaozhou accident occurred in Raoping County in November 2022 and resulted in two deaths and three injuries. Video footage circulated online at the time showed a Tesla vehicle accelerating at high speed and colliding with multiple motorcycles and bicycles. Reports indicated the vehicle reached a speed of 198 kilometers per hour.
The incident drew widespread attention as the parties involved provided conflicting accounts and investigation details were released gradually. Media reports in early 2023 said investigation results had been completed, though the vehicle owner requested a re-investigation, delaying the issuance of a final liability determination.
The case resurfaced later in 2023 following a defamation lawsuit filed by Tesla China against a media outlet. According to a court judgment cited by Shanghai Securities News, forensic analysis determined that the fatal accident was unrelated to any malfunction on the Tesla’s braking or steering systems. The court also ruled that the media outlet must publish an apology, address the negative impact on Tesla China’s reputation, and pay a penalty of 30,000 yuan.
Elon Musk
SpaceX is exploring a “Starlink Phone” for direct-to-device internet services: report
The update was reportedly shared to Reuters by people familiar with the matter.

SpaceX is reportedly exploring new products tied to Starlink, including a potential Starlink-branded phone.
The update was reportedly shared to Reuters by people familiar with the matter.
A possible Starlink Phone
As per Reuters’ sources, SpaceX has reportedly discussed building a mobile device designed to connect directly to the Starlink satellite constellation. Details about the potential device and its possible release are still unclear, however.
SpaceX has dabbled with mobile solutions in the past. The company has partnered with T-Mobile to provide Starlink connectivity to existing smartphones. And last year, SpaceX initiated a $19.6 billion purchase of satellite spectrum from EchoStar.
Elon Musk did acknowledge the idea of a potential mobile device recently on X, writing that a Starlink phone is “not out of the question at some point.” Unlike conventional smartphones, however, Musk described a device that is “optimized purely for running max performance/watt neural nets.”
Starlink and SpaceX’s revenue
Starlink has become SpaceX’s dominant commercial business. Reuters’ sources claimed that the private space company generated roughly $15–$16 billion in revenue last year, with about $8 billion in profit. Starlink is estimated to have accounted for 50% to 80% of SpaceX’s total revenue last year.
SpaceX now operates more than 9,500 Starlink satellites and serves over 9 million users worldwide. About 650 satellites are already dedicated to SpaceX’s direct-to-device initiative, which aims to eventually provide full cellular coverage globally.
Future expansion of Starlink’s mobile capabilities depends heavily on Starship, which is designed to launch larger batches of upgraded Starlink satellites. Musk has stated that each Starship launch carrying Starlink satellites could increase network capacity by “more than 20 times.”