

News
GM buys LIDAR company for self-driving car program to take Tesla head-on
General Motors issued a press release on Monday announcing that it will acquire Strobe, a California-based technology startup that makes affordable chip-scale LIDAR technology for self-driving cars. An 11-person team from Strobe will be joining GM’s Cruise Automation unit as part of the acquisition.
With more affordable and higher accuracy LIDAR sensors coming to market, automakers that are looking to transition to all-electric fleets are assessing the strategic value with investing into self-driving technology. GM’s purchase of Strobe can be seen as just that. Acquiring a small and nimble startup that has a core focus on developing the key sensor used in autonomous vehicles allows the Detroit-based auto giant to speed its path to market with a self-driving car.
Kyle Vogt, GM’s Cruise Automation Founder and CEO, said through a press release, “Strobe’s LIDAR technology will significantly improve the cost and capabilities of our vehicles so that we can more quickly accomplish our mission to deploy driverless vehicles at scale.”
While GM continues to charge forward with implementing LIDAR technology into its self-driving program, the company also complements its technology with radar sensors to create a fault-tolerant sensing suite. Tesla CEO Elon Musk has famously touted LIDAR as ‘unnecessary’ in the context of an autonomous car due to its high cost. Instead, Tesla has opted to use a combination of cameras, radars and ultrasonic sensors to form the foundation for its Autopilot system. But as pricing for LIDAR technology continues to drop, could we see a change of core design in future versions of Autopilot?
Good thing about radar is that, unlike lidar (which is visible wavelength), it can see through rain, snow, fog and dust
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) July 15, 2016
Vogt asserts that radar can operate under more challenging weather conditions, however it lacks the precision needed when making critical maneuvers at speed. “Strobe’s LIDAR sensors provide both accurate distance and velocity information, which can be checked against similar information from a RADAR sensor for redundancy. RADARs typically also provide distance and velocity information and operate under more challenging weather conditions, but they lack the angular resolution needed to make certain critical maneuvers at speed. When used together, cameras, LIDARs, and RADARs can complement each other to create a robust and fault-tolerant sensing suite that operates in a wide range of environmental and lighting conditions.” said Vogt in a blog post on Medium.
LIDAR on the other hand uses laser or concentrated light to map a high resolution 3D view of a the world, which arguably provides a higher precision view of a self-driving car’s surroundings. GM’s Director of autonomous vehicle integration has recently spoken up against Musk’s narrative that Tesla Autopilot will be fully autonomous and capable of piloting a car from California to New York on its own by the end of the year.
“The level of technology and knowing what it takes to do the mission, to say you can be a full level five with just cameras and radars is not physically possible,” said Miller about Tesla’s Autopilot suite. “Could you do it with what’s in a current Tesla Model S? I don’t think so.”
As the race to produce a fully autonomous car continues to heat up between Tesla, GM, Uber, and Google, and hardware prices decline, it’s only a matter of time before a tried and true combination of hardware will become the de-facto self-driving hardware suite. What will it be?
Elon Musk
Tesla reveals it is using AI to make factories more sustainable: here’s how
Tesla is using AI in its Gigafactory Nevada factory to improve HVAC efficiency.
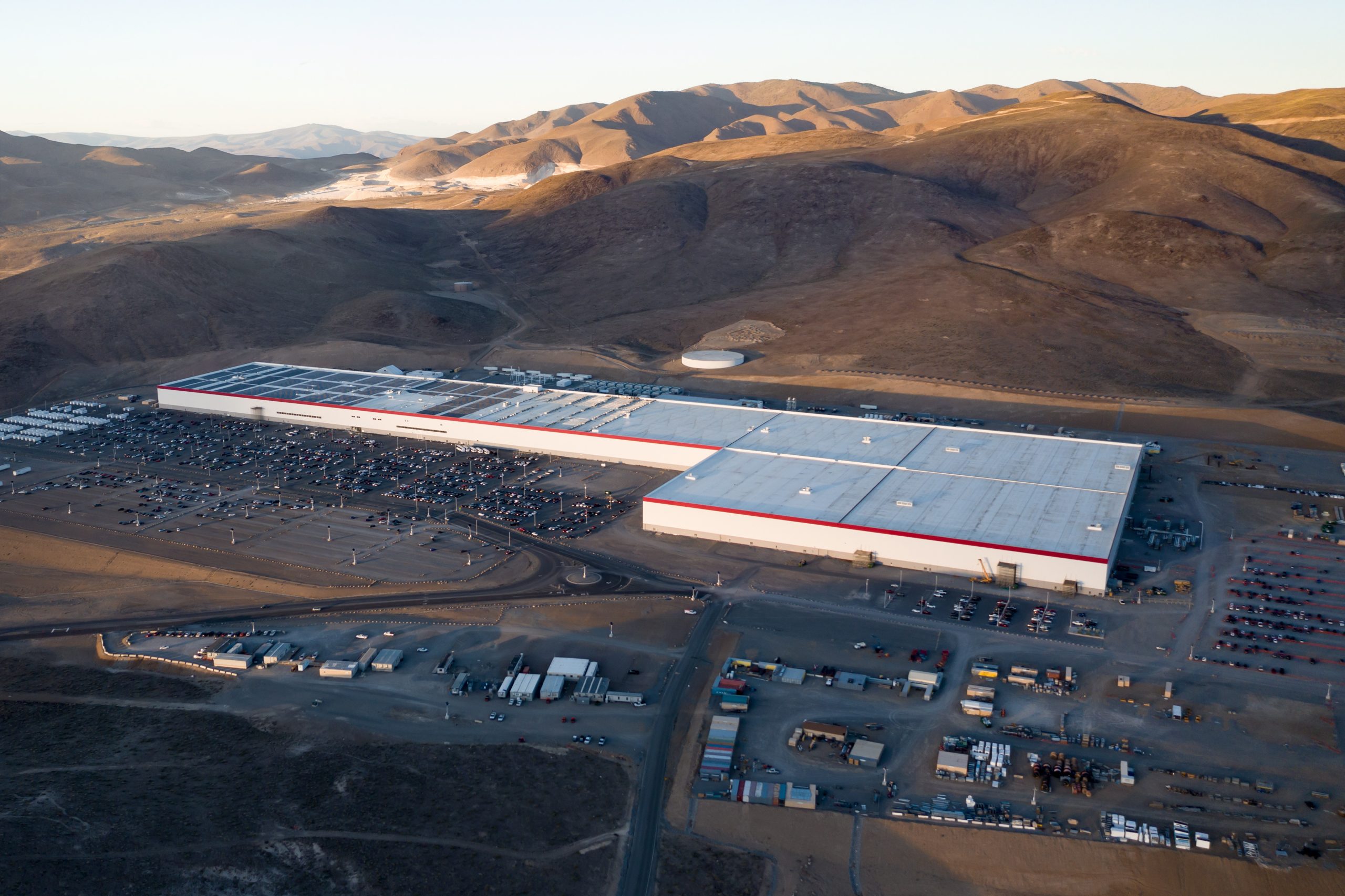

Tesla has revealed in its Extended Impact Report for 2024 that it is using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enable its factories to be more sustainable. One example it used was its achievement of managing “the majority of the HVAC infrastructure at Gigafactory Nevada is now AI-controlled” last year.
In a commitment to becoming more efficient and making its production as eco-friendly as possible, Tesla has been working for years to find solutions to reduce energy consumption in its factories.
For example, in 2023, Tesla implemented optimization controls in the plastics and paint shops located at Gigafactory Texas, which increased the efficiency of natural gas consumption. Tesla plans to phase out natural gas use across its factories eventually, but for now, it prioritizes work to reduce emissions from that energy source specifically.
It also uses Hygrometric Control Logic for Air Handling Units at Giafactory Berlin, resulting in 17,000 MWh in energy savings each year. At Gigafactory Nevada, Tesla saves 9.5 GWh of energy through the use of N-Methylpyrrolidone refineries when extracting critical raw material.
Perhaps the most interesting way Tesla is conserving energy is through the use of AI at Gigafactory Nevada, as it describes its use of AI to reduce energy demand:
“In 2023, AI Control for HVAC was expanded from Nevada and Texas to now include our Berlin-Brandenburg and Fremont factories. AI Control policy enables HVAC systems within each factory to work together to process sensor data, model factory dynamics, and apply control actions that safely minimize the energy required to support production. In 2024, this system achieved two milestones: the majority of HVAC infrastructure at Gigafactory Nevada is now AI-controlled, reducing fan and thermal energy demand; and the AI algorithm was extended to manage entire chiller plants, creating a closed-loop control system that optimizes both chilled water consumption and the energy required for its generation, all while maintaining factory conditions.”
Tesla utilizes AI Control “primarily on systems that heat or cool critical factory production spaces and equipment.” AI Control communicates with the preexisting standard control logic of each system, and any issues can be resolved by quickly reverting back to standard control. There were none in 2024.
Tesla says that it is utilizing AI to drive impact at its factories, and it has proven to be a valuable tool in reducing energy consumption at one of its facilities.
Elon Musk
Tesla analysts believe Musk and Trump feud will pass
Tesla CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump’s feud shall pass, several bulls say.
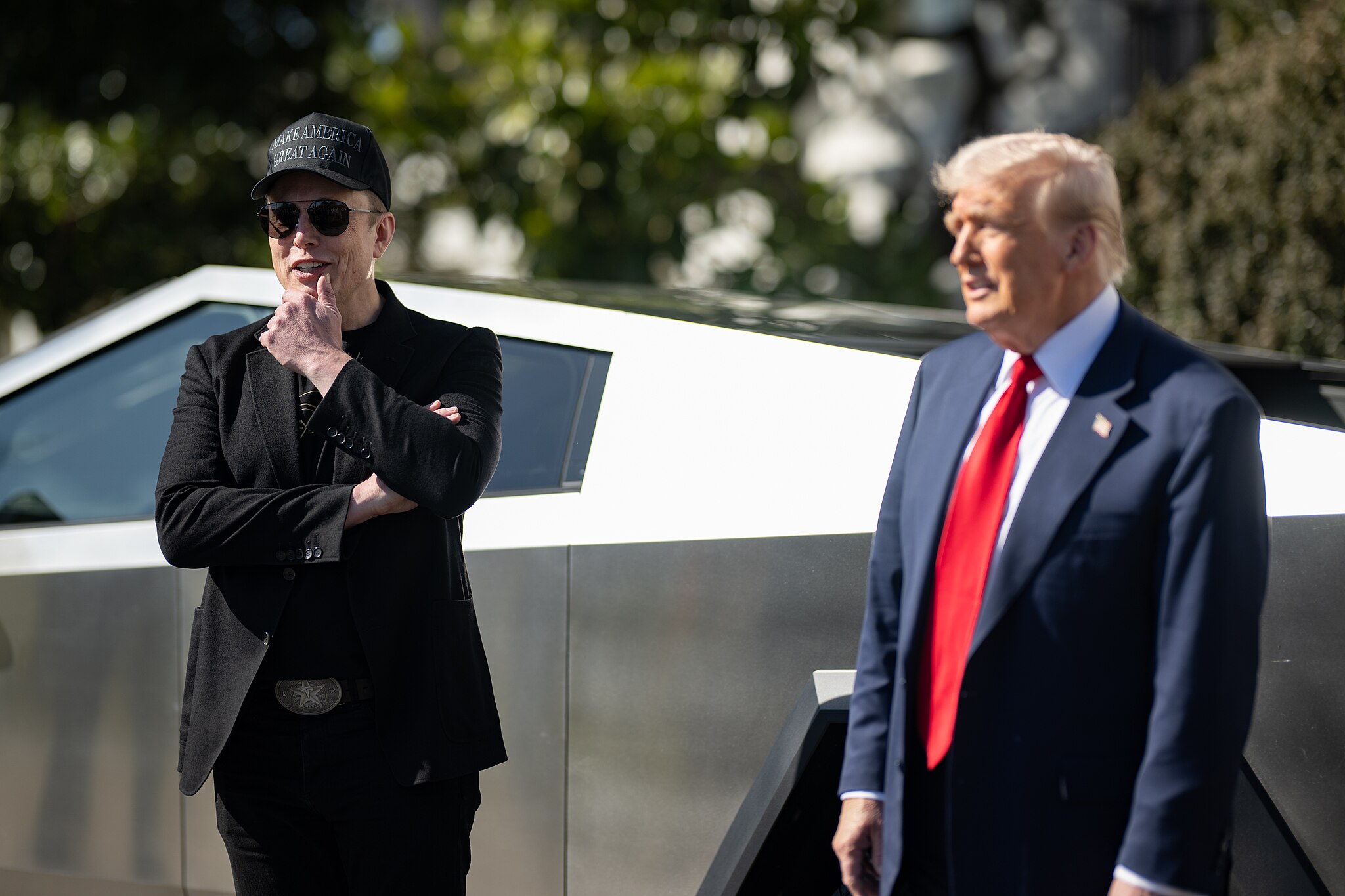

Tesla analysts are breaking down the current feud between CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump, as the two continue to disagree on the “Big Beautiful Bill” and its impact on the country’s national debt.
Musk, who headed the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) under the Trump Administration, left his post in May. Soon thereafter, he and President Trump entered a very public and verbal disagreement, where things turned sour. They reconciled to an extent, and things seemed to be in the past.
However, the second disagreement between the two started on Monday, as Musk continued to push back on the “Big Beautiful Bill” that the Trump administration is attempting to sign into law. It would, by Musk’s estimation, increase spending and reverse the work DOGE did to trim the deficit.
Every member of Congress who campaigned on reducing government spending and then immediately voted for the biggest debt increase in history should hang their head in shame!
And they will lose their primary next year if it is the last thing I do on this Earth.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) June 30, 2025
President Trump has hinted that DOGE could be “the monster” that “eats Elon,” threatening to end the subsidies that SpaceX and Tesla receive. Musk has not been opposed to ending government subsidies for companies, including his own, as long as they are all abolished.
How Tesla could benefit from the ‘Big Beautiful Bill’ that axes EV subsidies
Despite this contentious back-and-forth between the two, analysts are sharing their opinions now, and a few of the more bullish Tesla observers are convinced that this feud will pass, Trump and Musk will resolve their differences as they have before, and things will return to normal.
ARK Invest’s Cathie Wood said this morning that the feud between Musk and Trump is another example of “this too shall pass:”
BREAKING: CATHIE WOOD SAYS — ELON AND TRUMP FEUD “WILL PASS” 👀 $TSLA
She remains bullish ! pic.twitter.com/w5rW2gfCkx
— TheSonOfWalkley (@TheSonOfWalkley) July 1, 2025
Additionally, Wedbush’s Dan Ives, in a note to investors this morning, said that the situation “will settle:”
“We believe this situation will settle and at the end of the day Musk needs Trump and Trump needs Musk given the AI Arms Race going on between the US and China. The jabs between Musk and Trump will continue as the Budget rolls through Congress but Tesla investors want Musk to focus on driving Tesla and stop this political angle…which has turned into a life of its own in a roller coaster ride since the November elections.”
Tesla shares are down about 5 percent at 3:10 p.m. on the East Coast.
Elon Musk
Tesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales
Tesla CEO Elon Musk is reportedly overseeing sales in North America and Europe, Bloomberg reports.

Tesla scrambled its executives around following the exit of CEO Elon Musk’s sidekick last week, Omead Afshar. Afshar was relieved of his duties as Head of Sales for both North America and Europe.
Bloomberg is reporting that Musk is now overseeing both regions for sales, according to sources familiar with the matter. Afshar left the company last week, likely due to slow sales in both markets, ending a seven-year term with the electric automaker.
Tesla’s Omead Afshar, known as Elon Musk’s right-hand man, leaves company: reports
Afshar was promoted to the role late last year as Musk was becoming more involved in the road to the White House with President Donald Trump.
Afshar, whose LinkedIn account stated he was working within the “Office of the CEO,” was known as Musk’s right-hand man for years.
Additionally, Tom Zhu, currently the Senior Vice President of Automotive at Tesla, will oversee sales in Asia, according to the report.
It is a scramble by Tesla to get the company’s proven executives over the pain points the automaker has found halfway through the year. Sales are looking to be close to the 1.8 million vehicles the company delivered in both of the past two years.
Tesla is pivoting to pay more attention to the struggling automotive sales that it has felt over the past six months. Although it is still performing well and is the best-selling EV maker by a long way, it is struggling to find growth despite redesigning its vehicles and launching new tech and improvements within them.
The company is also looking to focus more on its deployment of autonomous tech, especially as it recently launched its Robotaxi platform in Austin just over a week ago.
However, while this is the long-term catalyst for Tesla, sales still need some work, and it appears the company’s strategy is to put its biggest guns on its biggest problems.
-

 Elon Musk1 day ago
Elon Musk1 day agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Grok integration will be more realistic with this cool feature
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla China roars back with highest vehicle registrations this Q2 so far
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla dominates Cars.com’s Made in America Index with clean sweep
-
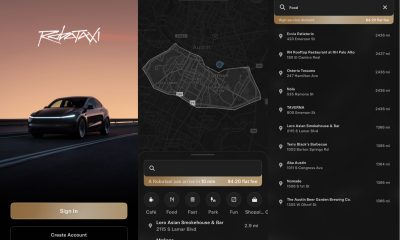
 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more














