

Space
Mars buildings could be built using components made from bacteria
Bacteria could be useful construction tools when it comes to building cities on Mars.
Elon Musk recently detailed his plans for establishing a city on Mars. But before we take up residence on the red planet, we’re going to need some help laying the groundwork. Here’s where bacteria come in.
A special group of microorganisms, called Shewanella oneidensis, would make excellent helpers, says Benjamin Lehner, a doctoral candidate at Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands.
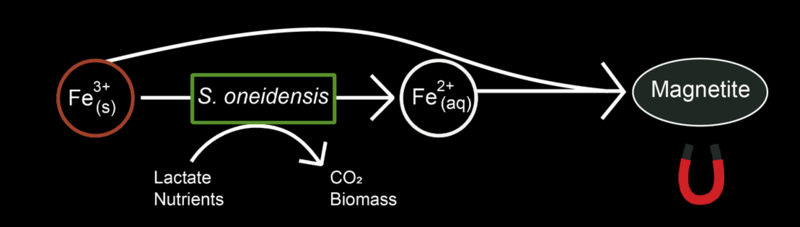
Shewanella belongs to a group of bacterium called exoelectrogens, which possess an unusual skill: They can produce electricity. But that’s not all. Lehner says the bacterium can also mine iron out of the Martian soil.
In 2018, NASA sent a batch of these helpful bacterium to the space station to see how well they thrive in space. Now Lehner wants to send them on to Mars, ahead of human explorers.
“In its natural form, we can’t use much of the iron in the Martian soil,” Lehner said in a statement. “But S. oneidensis has the ability to turn part of the soil into magnetite, a magnetic oxide of iron.”
That iron would then be used as building materials for future structures on Mars.
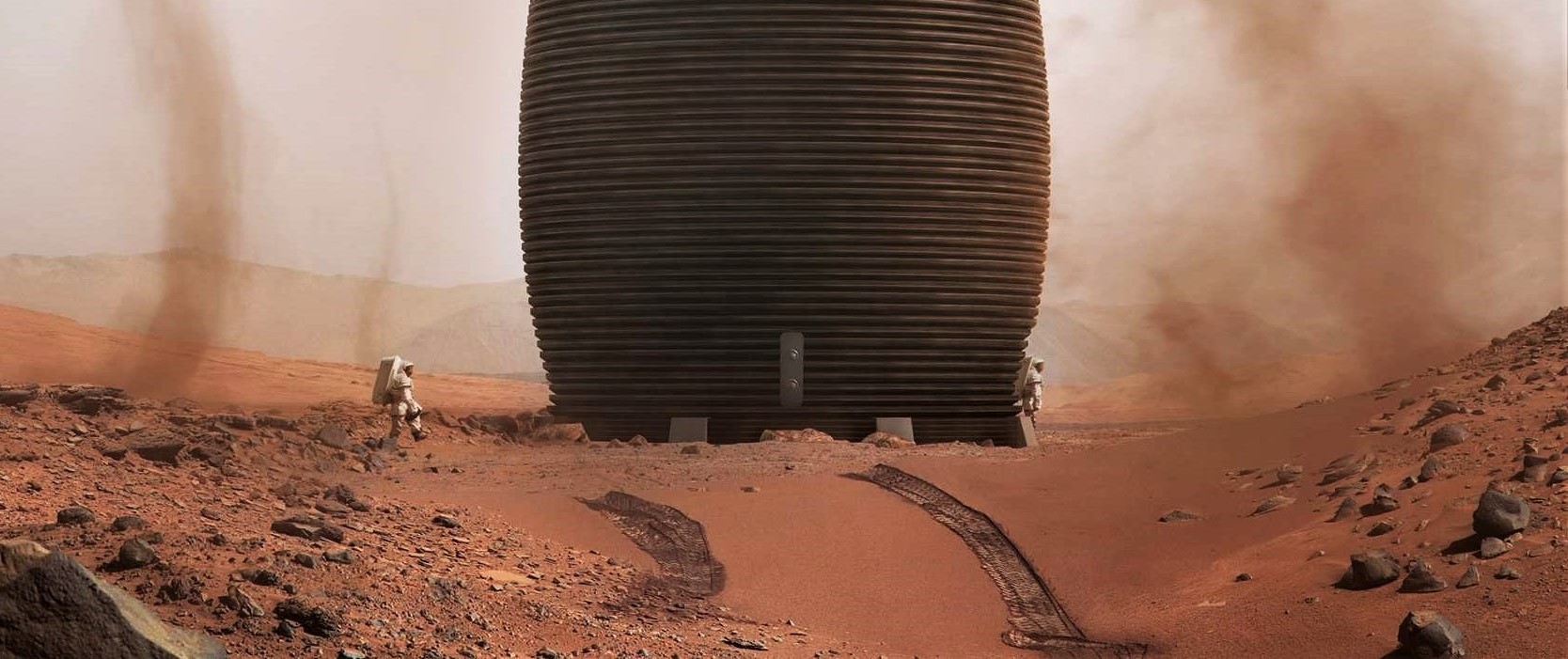

So how would it work? Lehner says that three things should sent to Mars ahead of any human expeditions: a rover, a bioreactor and a 3D printer. The rover would fetch batches of Martian soil, called regolith, then feed it into the bioreactor.
The Martian soil is rich in iron and the S. oneidensis loves to munch on iron, so it would be waiting in the bioreactor, ready to chow down.
The bacteria would then produce magnetite as a byproduct from the regolith. The magnetite would then be extracted and separated from the rest of the soil with magnets. Finally, the 3D printer would turn this raw metal material into a host of valuable parts for humans.
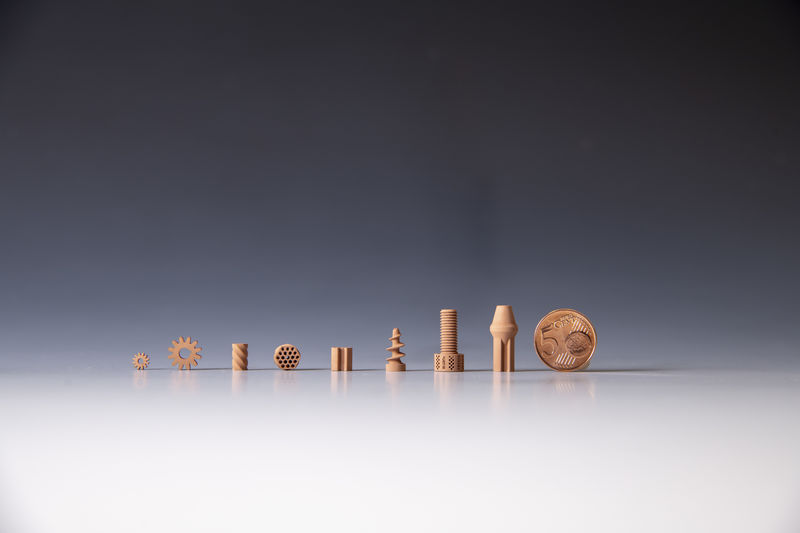

The printer could create any part necessary—screws, nuts, bolts—for building structures (including human habitats) on Mars.
So how much iron could these microbes realistically produce? Leher and his team estimate they could have a substantial amount in a few year’s time.
According to the researchers, a 370-gallon (1,400-liter) reactor could yield about 770-lbs. (350 kilograms) of the material each year. “After 3.3 years, it would produce more iron than can fit inside the capsule,” he explained. “By sending several of these unmanned modules to Mars, we can produce a good amount of iron in a few years’ time.”

Bacteria are advantageous because they’re self-replicating, can withstand the harsh radiation on Mars, and are cheap to transport. They only need one thing: food.
To that end, Lehner suggests sending microalgae along with the bacteria. These organisms live off of sunlight and CO2, two things that are plentiful on Mars. The microalgae will turn those ingredients into nutrients and oxygen, perfect for the bacteria.
But what if some rogue bacteria make their way out of the reactor? Would we then contaminate Mars with Earth microbes? What does this mean for the search for life?
“We want to prevent our bacteria from contaminating the planet, since that could hinder the search for life on Mars,” Lehner said. To mitigate any chances of contamination, Lehner’s team says that the bioreactor and any iron material produced needs to be safely contained.

Elon Musk
Starbase after dark: Musk’s latest photo captures a Spaceport on the brink of history
SpaceX’s Starbase city in Boca Chica, Texas is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
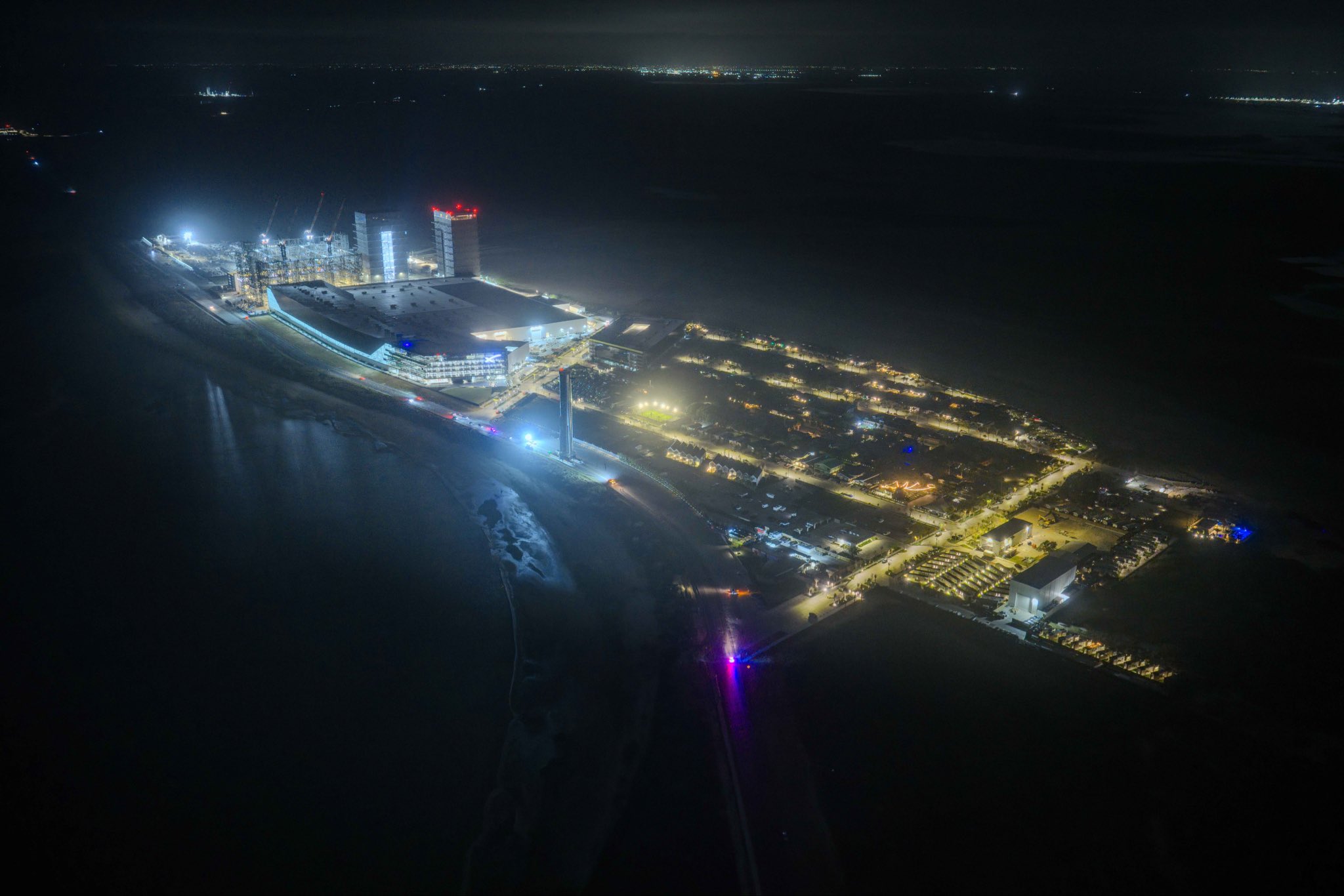

A striking nighttime photograph of SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas, shared recently by Elon Musk on X, offers a dramatic glimpse of an operation that is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
The most immediately visible change in the photo is the presence of two fully erected Starship launch towers dominating the coastal skyline. The second orbital launch pad, known as Pad B, now features its fully erected tower, OLIT-3, which stands approximately 474 feet tall and incorporates an integrated water-cooled flame trench designed to minimize damage and reduce turnaround time between launches. The dual-tower silhouette against the night sky signals a decisive shift from experimental testing facility to high-cadence launch operations.
Grok Image concept of Elon Musk’s latest Starbase photo via X
Back at Starbase, Pad 2 is approaching hardware completion, with upgraded chopstick arms, a new chilldown vent system, and all 20 hold-down arms now fitted with protective doors to shield them from the intense exhaust of up to 33 Raptor 3 engines, according to a deeper dive by NASASpaceFlight.
SpaceX has also received approval to nearly double the footprint of the Starbase launch site, with groundwork already underway to add LNG liquefaction plants, expanded propellant storage, and additional ground support infrastructure.
The photo also carries a milestone civic dimension. Starbase officially became a Texas city in May 2025 after a community vote, with SpaceX employees elected as mayor and commissioners of the newly incorporated municipality. That legal status streamlines launch approvals and gives SpaceX direct control over local infrastructure decisions.
The FAA has approved an increase in launches from Starbase in Texas from five to twenty-five per year, clearing the runway for the kind of flight frequency needed to fulfill Starship’s ultimate mission of ferrying cargo and crew to the Moon, servicing the Department of Defense, deploying next-generation Starlink satellites, and eventually establishing Elon Musk’s long sought after goal of a self-sustaining human presence on Mars.
Seen from above in the dark, Starbase looks less like a test site and more like a spaceport.
News
Starlink gets its latest airline adoptee for stable and reliable internet access
The company said it plans to “rapidly integrate Starlink into its fleet,” and that the first Starlink-equipped aircraft will enter service this Summer.

SpaceX’s Starlink, the satellite internet program launched by Elon Musk’s company, has gotten its latest airline adoptee, offering stable and reliable internet to passengers.
Southwest Airlines announced on Wednesday that it would enable Starlink on its aircraft, a new strategy that will expand to more than 300 planes by the end of the year.
The company said it plans to “rapidly integrate Starlink into its fleet,” and that the first Starlink-equipped aircraft will enter service this Summer.
Tony Roach, Executive Vice President, Chief Customer and Brand Officer for the airline, said:
“Free WiFi has been a huge hit with our Rapid Rewards Members, and we know our Customers expect seamless connectivity across all their devices when they travel. Starlink delivers that at-home experience in the air, giving Customers the ability to stream their favorite shows from any platform, watch live sports, download music, play games, work, and connect with loved ones from takeoff to landing.”
Southwest also said that this is just one of the latest upgrades it is making to provide a more well-rounded experience to its aircraft. In addition to Starlink, it is updating cabin designs, offering more legroom, and installing in-seat power to all passengers.
Southwest became one of several airlines to cross over to Starlink, as reviews for the internet provider have raved about reliability and speed. Over the past year, Hawaiian Airlines, United Airlines, Alaska Airlines, airBaltic, Air France, JSX, Emirates, British Airways, and others have all decided to install Starlink on their planes.
This has been a major move away from unpredictable and commonly unreliable WiFi offerings on planes. Starlink has been more reliable and has provided more stable connections for those using their travel time for leisure or business.
Jason Fritch, VP of Starlink Enterprise Sales at SpaceX, said:
“We’re thrilled to deliver a connectivity experience to Southwest Airlines and its Customers that really is similar, if not better, than what you can experience in your own home. Starlink is the future of connected travel, making every journey faster, smoother, and infinitely more enjoyable.”
Starlink recently crossed a massive milestone of over 10 million subscribers.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk confirms SpaceX is not developing a phone

Despite many recent rumors and various reports, Elon Musk confirmed today that SpaceX is not developing a phone based on Starlink, not once, but twice.
Today’s report from Reuters cited people familiar with the matter and stated internal discussions have seen SpaceX executives mulling the idea of building a mobile device that would connect directly to the Starlink satellite constellation.
Musk did state in late January that SpaceX developing a phone was “not out of the question at some point.” However, He also said it would have to be a major difference from current phones, and would be optimized “purely for running max performance/watt neural nets.”
Not out of the question at some point. It would be a very different device than current phones. Optimized purely for running max performance/watt neural nets.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 30, 2026
While Musk said it was not out of the question “at some point,” that does not mean it is currently a project SpaceX is working on. The CEO reaffirmed this point twice on X this afternoon.
Musk said, “Reuters lies relentlessly,” in one post. In the next, he explicitly stated, “We are not developing a phone.”
Reuters lies relentlessly
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 5, 2026
We are not developing a phone
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 5, 2026
Musk has basically always maintained that SpaceX has too many things going on, denying that a phone would be in the realm of upcoming projects. There are too many things in the works for Musk’s space exploration company, most notably the recent merger with xAI.
SpaceX officially acquires xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise
A Starlink phone would be an excellent idea, especially considering that SpaceX operates 9,500 satellites, serving over 9 million users worldwide. 650 of those satellites are dedicated to the company’s direct-to-device initiative, which provides cellular coverage on a global scale.
Nevertheless, there is the potential that the Starlink phone eventually become a project SpaceX works on. However, it is not currently in the scope of what the company needs to develop, so things are more focused on that as of right now.








