

News
SpaceX Falcon 9 Starlink launch eyes two reusability milestones as new satellite details emerge
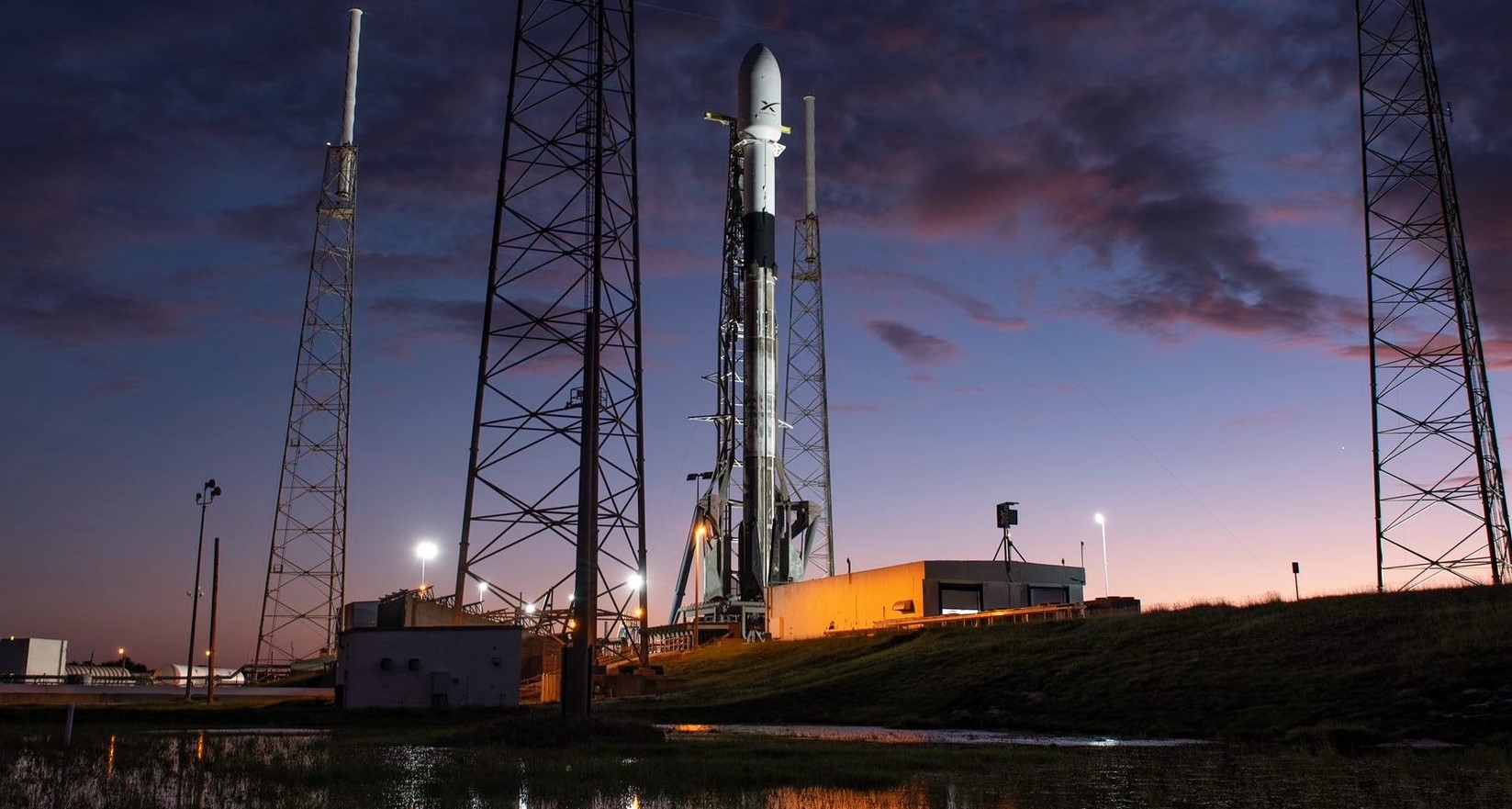
SpaceX is set for Falcon 9’s first orbital launch in more than three months. Known as Starlink-1, the mission will launch the company’s heaviest satellite payload ever and feature an impressive array of Falcon 9 booster and fairing reusability milestones.
Flatsat stack
Prior to Falcon 9 going vertical on the launch pad, SpaceX technicians had to construct and encapsulate a massive stack of 60 Starlink satellites, each weighing more than 260 kg (570 lb) apiece. This is the second time SpaceX has launched sixty of the advanced spacecraft, although the satellites that will launch on Starlink-1 feature a number of upgrades and refinements not present on the Starlink v0.9 satellites that launched in May 2019.
Without an identical angle from the Starlink v0.9 mission to compare against, it’s difficult to immediately point out visual differences between v0.9 and v1.0 spacecraft. Still, there are some clear general changes. Most notably, SpaceX appears to have dramatically reduced the area of shiny, metallic surfaces. Additionally, the small downward-facing dishes just left of center in the above image were not obviously present on Starlink v0.9 satellites or SpaceX’s official renders.
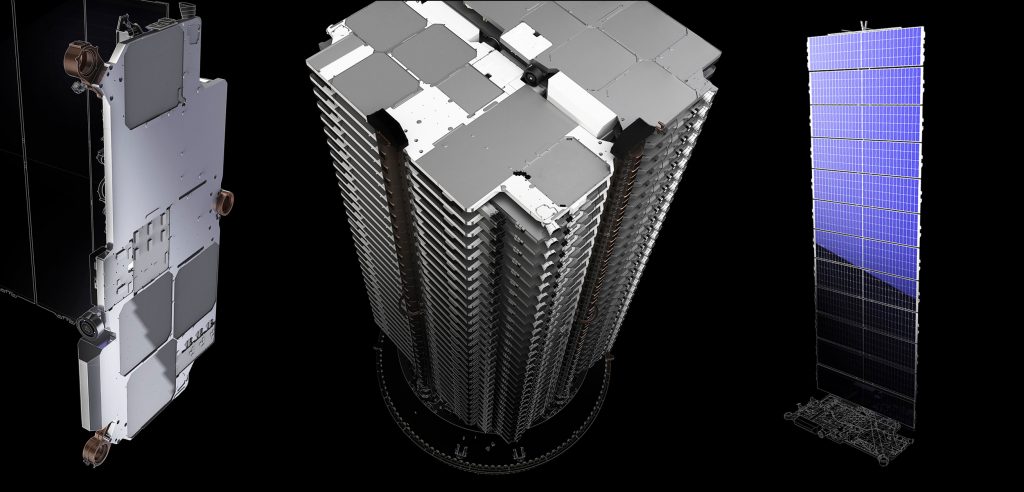
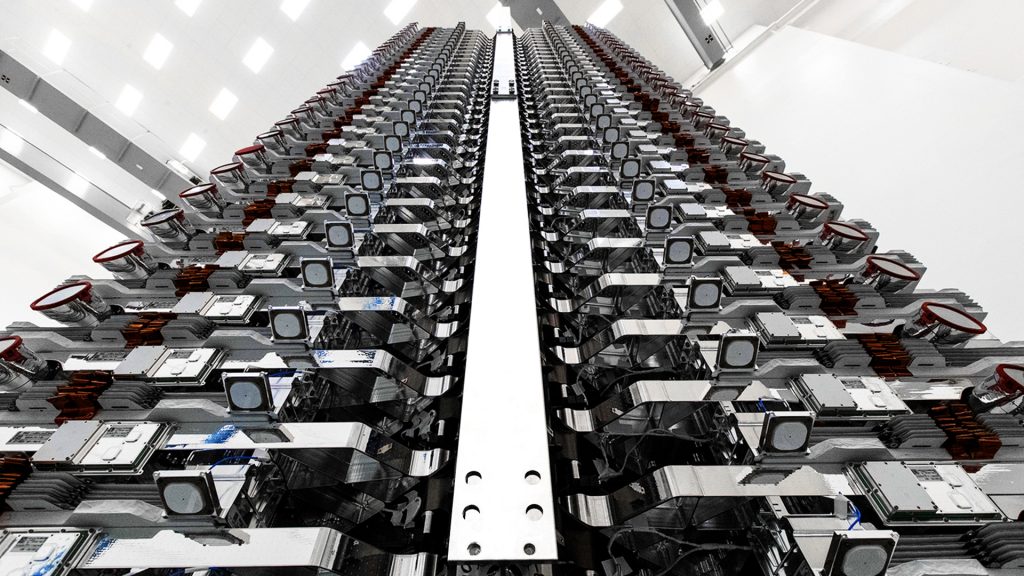


Those new dishes could be traditional dish antennas meant to serve as a more basic telemetry, tracking, and command (TTC) communications link for ground controllers. They could even be a prototype of Starlink’s planned inter-satellite laser data links. Regardless, it’s obvious that SpaceX is continuing its preferred cycle of rapid prototyping, flight-testing, and data-based refinement with Starlink.
SpaceX is also focused on dramatically lowering the albedo (reflectivity) of Starlink satellites and working closely with the astronomy and astrophysics communities to minimize any disruption the spacecraft might cause for scientific observations of the night sky. For any part that will be ground-facing during routine operations, this likely involves replacing shiny surfaces with matte finishes and adding dark or non-reflective coatings/insulation where possible, among other potential tweaks.
The more milestones, the merrier
Beyond the many apparent satellite upgrades Starlink-1 is set to debut, the mission will also mark no less than three (or possibly even four) reusability milestones. Falcon 9 booster B1048 has been selected by SpaceX to support Starlink-1 and has already completed three successful orbital-class missions since it debuted in July 2018. Assuming all goes well, B1048 will thus become the first SpaceX booster to launch (and land) four times, an excellent – if increasingly unsurprising – step forward for Falcon 9’s Block 5 upgrade. Falcon 9 B1048 will attempt its fourth landing – this time on drone ship Of Course I Still Love You (OCISLY) – shortly after launch.
Designed to enable up to 10 reuses of each Falcon booster, the successful completion of Starlink-1 will place Block 5 just one reuse away from the halfway point to proving its 10-reuse design. While Block 5 has yet to materialize any tangible improvements in booster turnaround time, an imminent ramp in Starlink launch cadence will hopefully give SpaceX plenty of opportunities to start making progress on that front.
Starlink-1 is also set to mark the inaugural launch of a flight-proven Falcon 9 fairing, essentially putting a bow on the bulk of SpaceX’s challenging fairing recovery and reusability development. Unintuitively, Starlink-1’s fairing previously supported Falcon Heavy Block 5’s April 209 launch debut, meaning that both halves traveled both faster and higher than any halves that previously attempted recovery.
Simultaneously, both halves splashed down in the Atlantic Ocean with no attempt to catch them, meaning that SpaceX has apparently successfully refurbished the fairings despite the fact that their recovery was more or less the worst-case scenario.
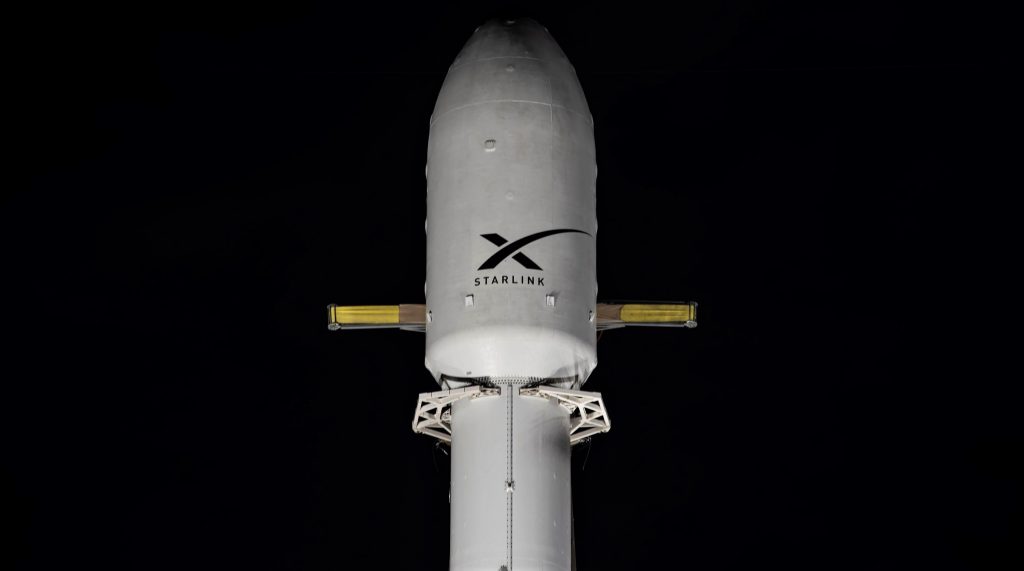

Last but not least, Starlink-1 will also mark the first time SpaceX’s just-finished fairing recovery ship GO Ms. Chief attempts to catch a Falcon 9 fairing, as well as the first time two fairing recovery ships – Ms. Tree & Ms. Chief – attempt to catch both halves of a Falcon fairing after launch. The twin recovery vessels departed Port Canaveral, Florida a few days ago and arrived at their recovery point ~750 km (460 mi) downrange on November 10th.
Finally, thanks to the fact that Falcon 9’s fairing is flight-proven, Starlink-1 will additionally feature the first attempted recovery (catch or splashdown) of a flight-proven Falcon fairing. SpaceX could scarcely fit in another milestone if it wanted to go out of its way to do so.
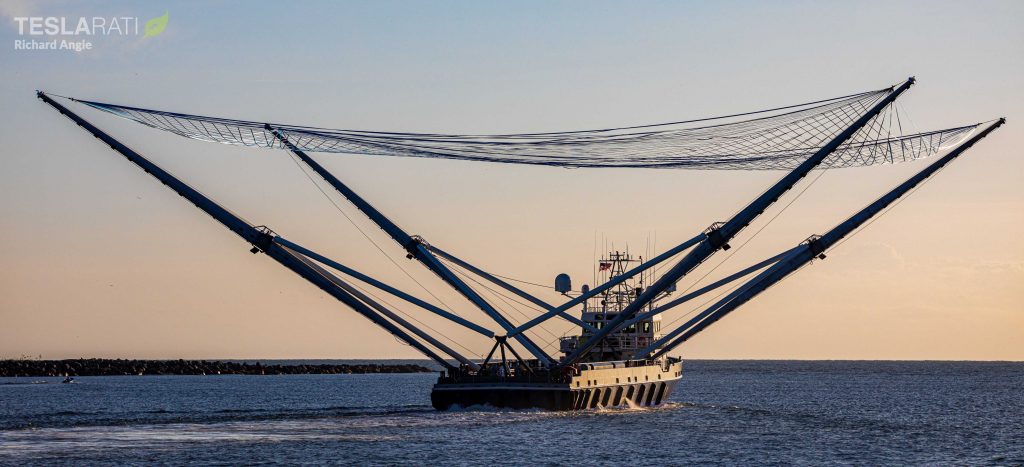
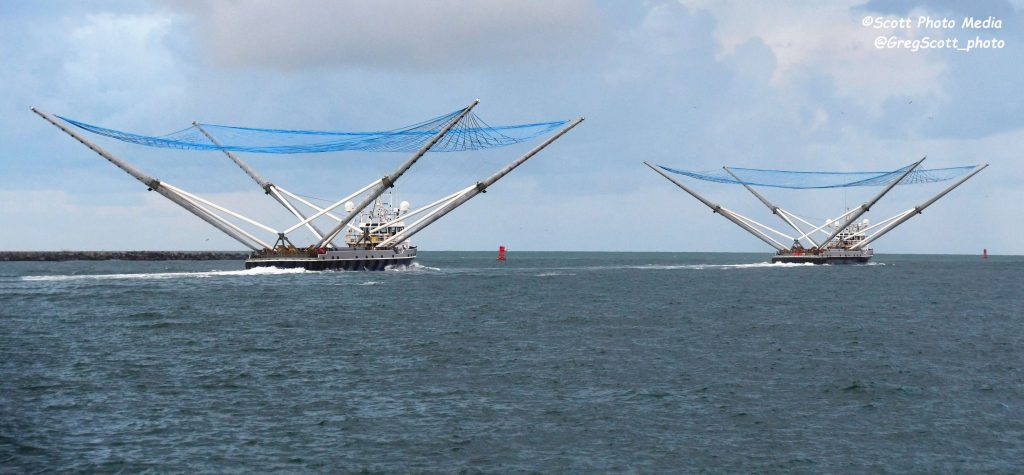


Falcon 9 is scheduled to lift off no earlier than 9:56 am ET (14:56 UTC), November 11th. Weather is 80% GO and SpaceX has a backup launch window around the same time on November 12th with a 70%-favorable weather forecast.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.
News
Tesla cleared in Canada EV rebate investigation
Tesla has been cleared in an investigation into the company’s staggering number of EV rebate claims in Canada in January.
Canadian officials have cleared Tesla following an investigation into a large number of claims submitted to the country’s electric vehicle (EV) rebates earlier this year.
Transport Canada has ruled that there was no evidence of fraud after Tesla submitted 8,653 EV rebate claims for the country’s Incentives for Zero-Emission Vehicles (iZEV) program, as detailed in a report on Friday from The Globe and Mail. Despite the huge number of claims, Canadian authorities have found that the figure represented vehicles that had been delivered prior to the submission deadline for the program.
According to Transport Minister Chrystia Freeland, the claims “were determined to legitimately represent cars sold before January 12,” which was the final day for OEMs to submit these claims before the government suspended the program.
Upon initial reporting of the Tesla claims submitted in January, it was estimated that they were valued at around $43 million. In March, Freeland and Transport Canada opened the investigation into Tesla, noting that they would be freezing the rebate payments until the claims were found to be valid.
READ MORE ON ELECTRIC VEHICLES: EVs getting cleaner more quickly than expected in Europe: study
Huw Williams, Canadian Automobile Dealers Association Public Affairs Director, accepted the results of the investigation, while also questioning how Tesla knew to submit the claims that weekend, just before the program ran out.
“I think there’s a larger question as to how Tesla knew to run those through on that weekend,” Williams said. “It doesn’t appear to me that we have an investigation into any communication between Transport Canada and Tesla, between officials who may have shared information inappropriately.”
Tesla sales have been down in Canada for the first half of this year, amidst turmoil between the country and the Trump administration’s tariffs. Although Elon Musk has since stepped back from his role with the administration, a number of companies and officials in Canada were calling for a boycott of Tesla’s vehicles earlier this year, due in part to his association with Trump.
News
Tesla Semis to get 18 new Megachargers at this PepsiCo plant
PepsiCo is set to add more Tesla Semi Megachargers, this time at a facility in North Carolina.
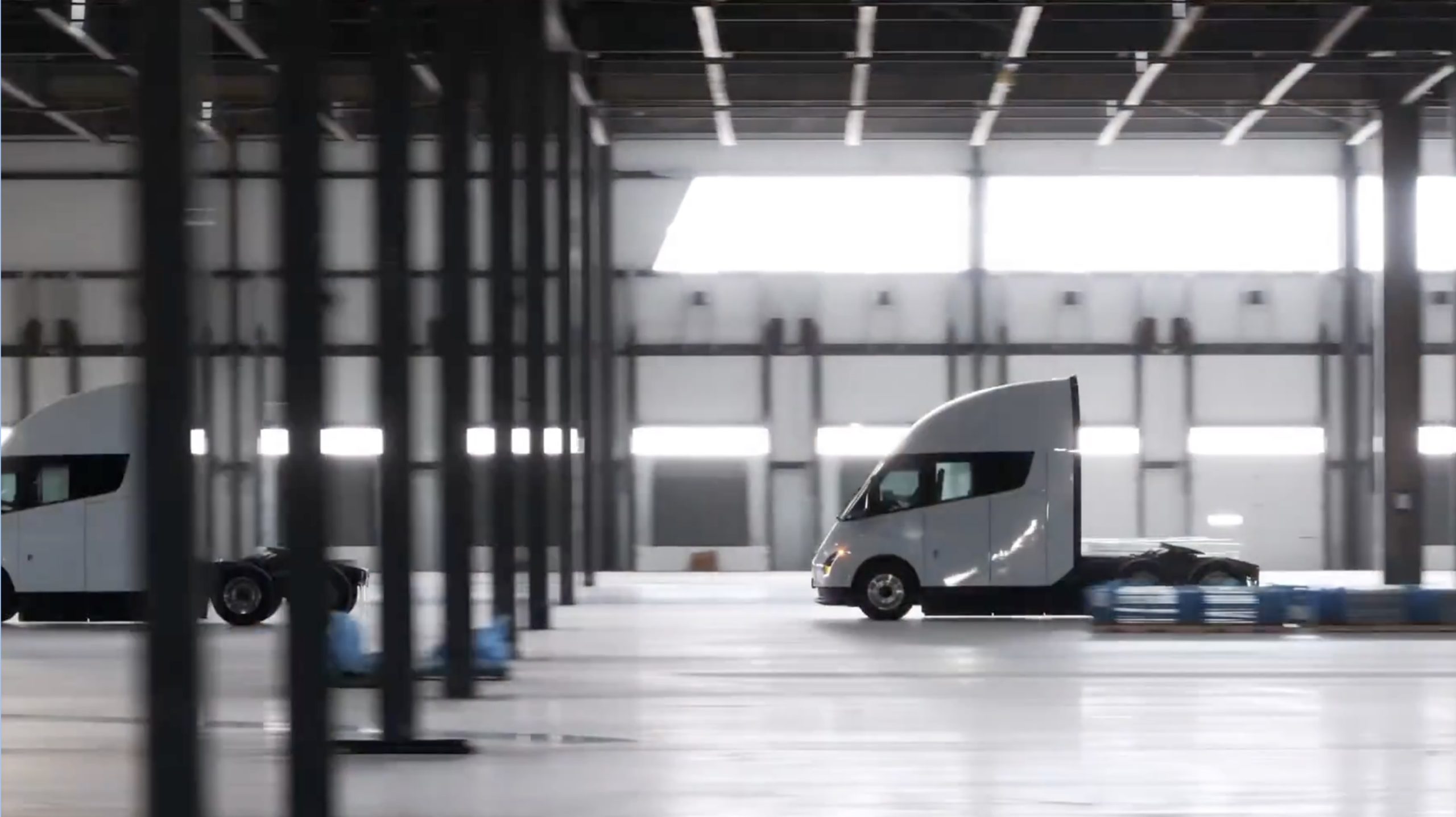

Tesla partner PepsiCo is set to build new Semi charging stations at one of its manufacturing sites, as revealed in new permitting plans shared this week.
On Friday, Tesla charging station scout MarcoRP shared plans on X for 18 Semi Megacharging stalls at PepsiCo’s facility in Charlotte, North Carolina, coming as the latest update plans for the company’s increasingly electrified fleet. The stalls are set to be built side by side, along with three Tesla Megapack grid-scale battery systems.
The plans also note the faster charging speeds for the chargers, which can charge the Class 8 Semi at speeds of up to 1MW. Tesla says that the speed can charge the Semi back to roughly 70 percent in around 30 minutes.
You can see the site plans for the PepsiCo North Carolina Megacharger below.
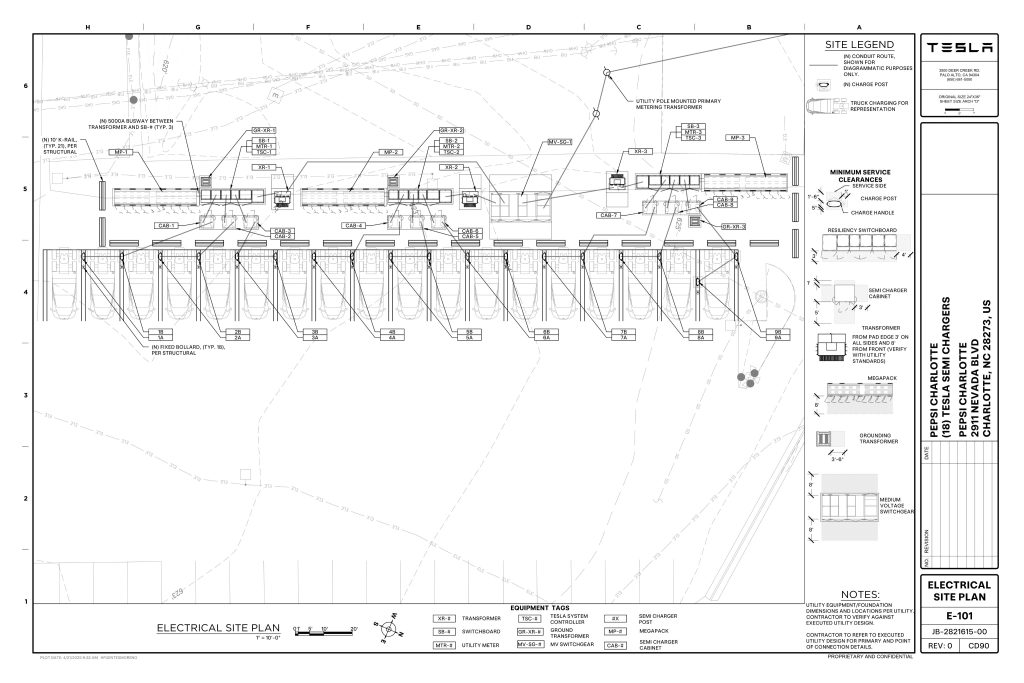
Credit: PepsiCo (via MarcoRPi1 on X)
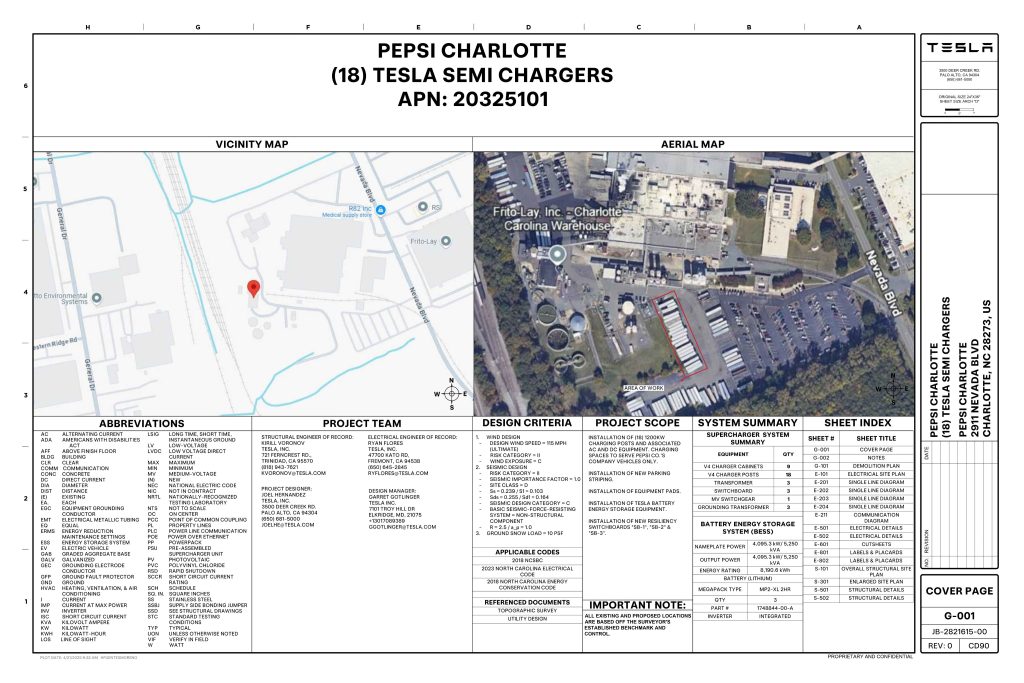
Credit: PepsiCo (via MarcoRPi1 on X)
READ MORE ON THE TESLA SEMI: Tesla to build Semi Megacharger station in Southern California
PepsiCo’s Tesla Semi fleet, other Megachargers, and initial tests and deliveries
PepsiCo was the first external customer to take delivery of Tesla’s Semis back in 2023, starting with just an initial order of 15. Since then, the company has continued to expand the fleet, recently taking delivery of an additional 50 units in California. The PepsiCo fleet was up to around 86 units as of last year, according to statements from Semi Senior Manager Dan Priestley.
Additionally, the company has similar Megachargers at its facilities in Modesto, Sacramento, and Fresno, California, and Tesla also submitted plans for approval to build 12 new Megacharging stalls in Los Angeles County.
Over the past couple of years, Tesla has also been delivering the electric Class 8 units to a number of other companies for pilot programs, and Priestley shared some results from PepsiCo’s initial Semi tests last year. Notably, the executive spoke with a handful of PepsiCo workers who said they really liked the Semi and wouldn’t plan on going back to diesel trucks.
The company is also nearing completion of a higher-volume Semi plant at its Gigafactory in Nevada, which is expected to eventually have an annual production capacity of 50,000 Semi units.
Tesla executive teases plan to further electrify supply chain
News
Tesla sales soar in Norway with new Model Y leading the charge
Tesla recorded a 54% year-over-year jump in new vehicle registrations in June.
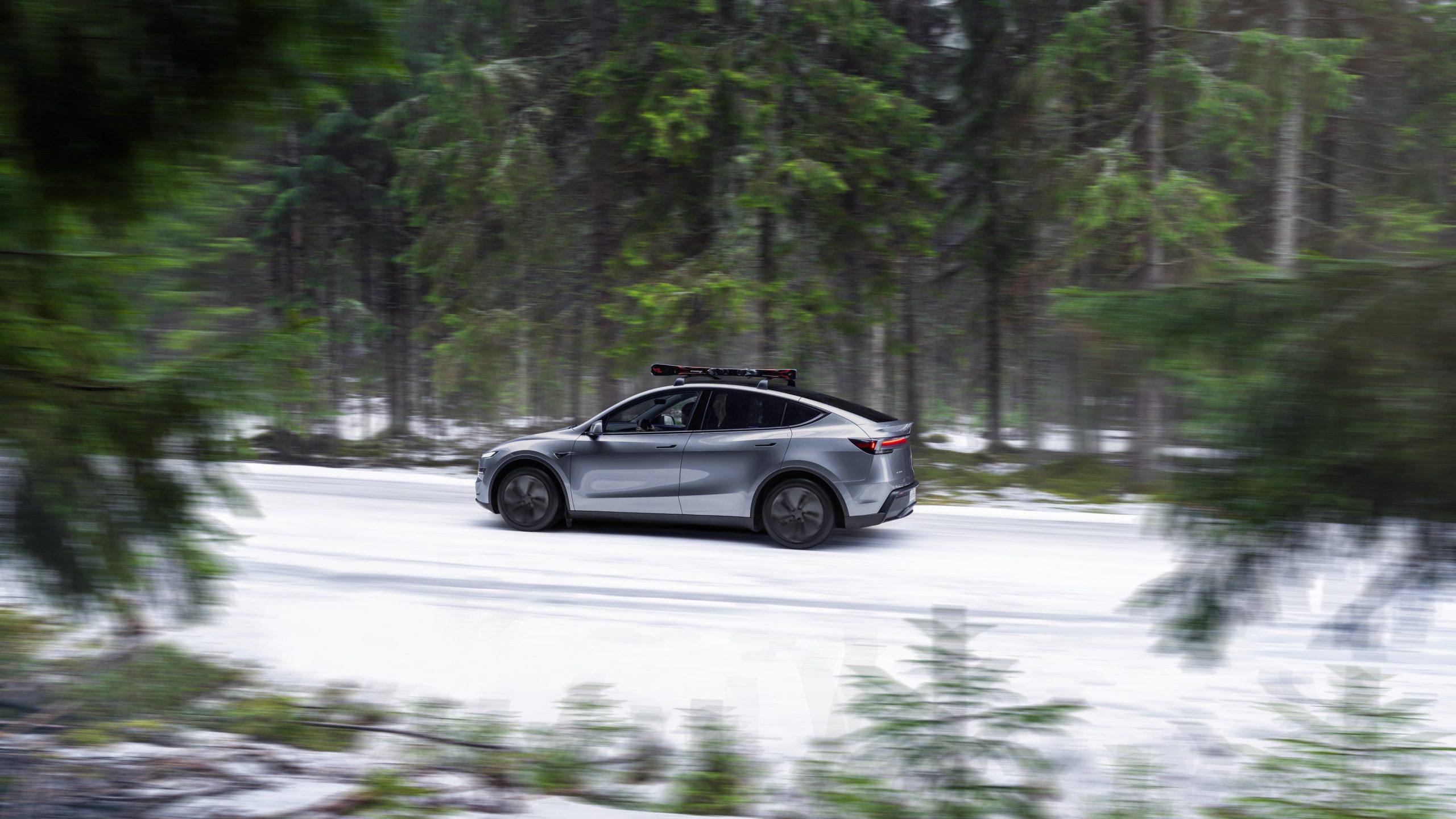

Tesla is seeing strong momentum in Norway, with sales of the new Model Y helping the company maintain dominance in one of the world’s most electric vehicle-friendly markets.
Model Y upgrades and consumer preferences
According to the Norwegian Road Federation (OFV), Tesla recorded a 54% year-over-year jump in new vehicle registrations in June. The Model Y led the charge, posting a 115% increase compared to the same period last year. Tesla Norway’s growth was even more notable in May, with sales surging a whopping 213%, as noted in a CNBC report.
Christina Bu, secretary general of the Norwegian EV Association (NEVA), stated that Tesla’s strong market performance was partly due to the updated Model Y, which is really just a good car, period.
“I think it just has to do with the fact that they deliver a car which has quite a lot of value for money and is what Norwegians need. What Norwegians need, a large luggage space, all wheel drive, and a tow hitch, high ground clearance as well. In addition, quite good digital solutions which people have gotten used to, and also a charging network,” she said.
Tesla in Europe
Tesla’s success in Norway is supported by long-standing government incentives for EV adoption, including exemptions from VAT, road toll discounts, and access to bus lanes. Public and home charging infrastructure is also widely available, making the EV ownership experience in the country very convenient.
Tesla’s performance in Europe is still a mixed bag, with markets like Germany and France still seeing declines in recent months. In areas such as Norway, Spain, and Portugal, however, Tesla’s new car registrations are rising. Spain’s sales rose 61% and Portugal’s sales rose 7% last month. This suggests that regional demand may be stabilizing or rebounding in pockets of Europe.
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk4 days ago
Elon Musk4 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”
-

 Investor's Corner2 weeks ago
Investor's Corner2 weeks agoTesla gets $475 price target from Benchmark amid initial Robotaxi rollout

















