News
SpaceX a bastion of independent US, European spaceflight amid Russian threats
Russia has invaded Ukraine without provocation, triggering a series of diplomatic responses – sanctions in particular – that recently culminated in the aggressor deciding to cut ties with Europe on a number of cooperative spaceflight projects.
Dmitry Rogozin, director of Russia’s national ‘Roscosmos’ space agency, went as far as implying that the country might respond to the West’s aerospace sanctions by ending its support of the International Space Station (ISS), a move that could cause the football-field-sized structure to gradually deorbit and reenter Earth’s atmosphere. Were it not for the existence of two extraordinarily successful NASA programs and SpaceX in particular, Russia’s response – which, today, reads like a child’s tantrum – could easily have been a grave threat with far-reaching consequences.
In response to sanctions after its unprovoked invasion, Russia announced that it was withdrawing support from Europe’s French Guinea Soyuz launch operations, effectively killing Arianespace’s Soyuz offering and potentially delaying several upcoming European launches indefinitely.
As a quick side note, it’s worth noting that ULA’s lack of readily available rockets and the fact that Arianespace is likely at least a year or more away from regular Ariane 6 launches means that SpaceX may be the only Western launch provider in the world capable of filling in the gap that Arianespace’s Soyuz loss will leave. Aside from pursuing Chinese launch services, which is likely a diplomatic non-starter, the only alternative to rebooking former European Soyuz payloads on SpaceX rockets is to accept one or even several years of expensive delays.
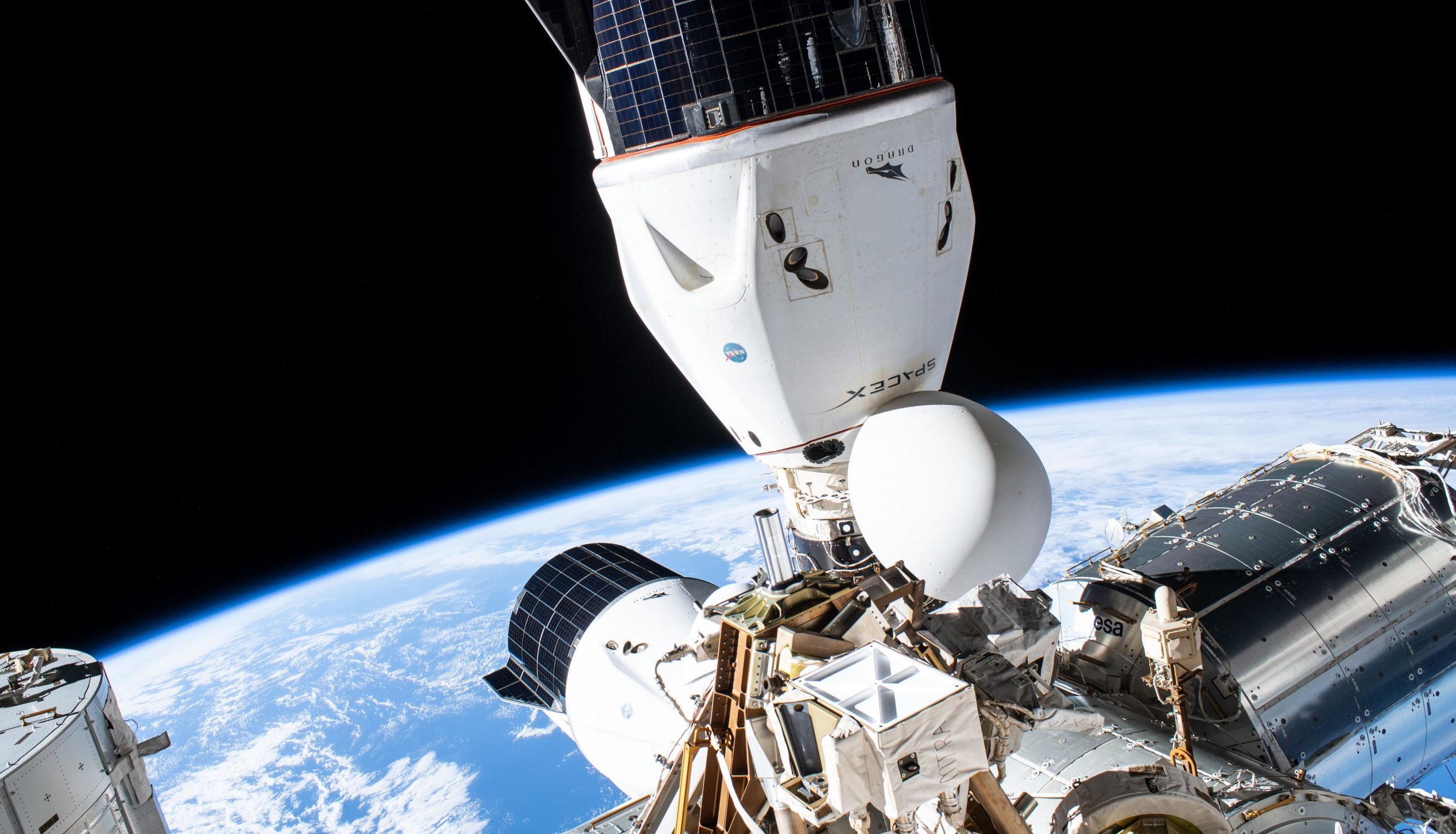
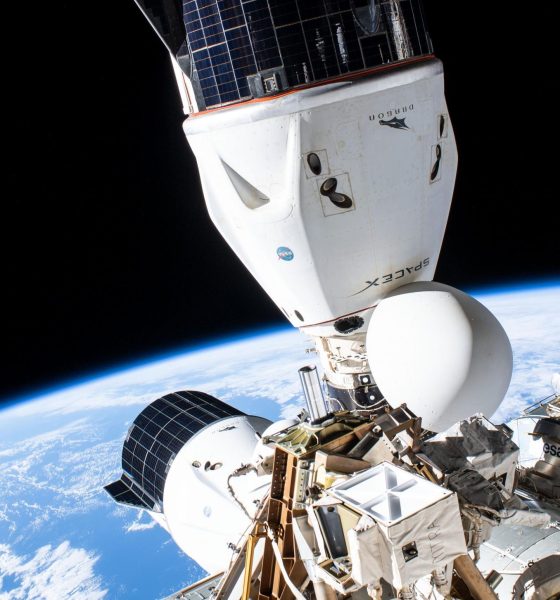
On the other half of the coin is the International Space Station. NASA signed its first major contract with SpaceX in 2008, awarding the company $1.6 billion (and up to $3.5 billion) to launch a dozen Cargo Dragon supply missions to the ISS. Aside from effectively pulling SpaceX back from the brink of dissolution, those funds also covered a large portion of the development of its Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft and simultaneously funded Orbital Science’s (later Orbital ATK and now Northrop Grumman) Cygnus cargo spacecraft and Antares rocket.
Despite suffering two failures in 2014 and 2015, NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program has been an extraordinary success. Together, Cygnus (17) and Dragon (24) have completed 41 deliveries in the last 12 years, carrying more than 110 tons (~240,000 lb) of cargo to the ISS.
Out of sheer coincidence, on February 19th, mere days before Russia’s act of war, Northrop Grumman launched the first Cygnus spacecraft designed to help ‘re-boost’ (raise the orbit of) the International Space Station. Since NASA’s premature 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle, that task has been exclusively conducted by a combination of Russian spacecraft and the station’s Russian Zvezda module. Without regular Russian re-boost support, the station would deorbit and be destroyed. In other words, if push came to shove, the ISS could very literally fail without direct Russian involvement. Rogozin’s threat, then, was that Russia might cease to support ISS re-boosting if sanctions went too far.
However, even while ignoring the fact that NASA itself actually paid for and owns the ISS Zvezda propulsion module and in light of the first Cygnus spacecraft upgraded with a re-boost capability berthing with the station the very same week of the invasion, Russia’s threat rang decidedly hollow. Further, if Cygnus weren’t available, it’s still difficult to imagine that SpaceX wouldn’t be able to quickly develop its own Dragon re-boost capability if asked to do so.
While re-boosting is crucial, the situation has also emphasized just how little leverage Russia now has over even more important aspects of the International Space Station. Were it not for the existence of SpaceX and NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP), the situation could be even direr for Europe and the US. Despite some pressure from lawmakers to only award the CCP contract to Boeing, NASA ultimately selected Boeing and SpaceX to develop independent crew capsules capable of carrying US astronauts to and from ISS in 2014. Following a near-flawless uncrewed Crew Dragon test flight in 2019 and an equally successful crewed demo mission in 2020, SpaceX completed its first operational Crew Dragon launch in November 2020.
Since then, SpaceX has launched another two operational ‘crew rotation’ missions, meaning that the company has now singlehandedly supported all US astronaut launch and recovery operations for 16 months. Due in part to extensive mismanagement, Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft was nearly destroyed twice during its first catastrophic uncrewed test flight in December 2019. The spacecraft is still months away from a second attempt at that test flight, likely at least 9-12 months away from a hypothetical crewed test flight, and potentially 18+ months away from even less certain operational NASA astronaut launches. Further, though ULA CEO Tory Bruno claims that the company doesn’t need any support from Russia, all Atlas Vs – the rocket responsible for launching Starliner – depend on Russian-built RD-180 engines.
Further adding to the mire, even Cygnus is not immune. The first stage of the Antares rocket that mainly launches it is both built in Ukraine and dependent upon Russian Energomash RD-181 engines. Northrop Grumman only has the hardware on hand for the next two Cygnus-Antares launches, at which point the company will have to either abandon its NASA contract or find an alternative launch provider. Once again, SpaceX is the only US provider obviously capable of filling that gap on such short notice and without incurring major delays of half a year or more.

In fewer words, without SpaceX, NASA would still be exclusively dependent upon Russian Soyuz rockets and spacecraft to get its astronauts to and from the space station it spent tens of billions of dollars to help build. Even in a best-case SpaceX-free scenario, NASA might instead be dependent upon a rocket with Russian engines to launch its own astronauts. Needless to say, the presence of US astronauts on Russian launches and ULA’s use of Russian engines were already extremely sensitive issues after Russia ‘merely’ invaded Ukraine’s Crimea region in 2014.
It’s hard not to imagine that US and European responses to Russia’s aggression would have been weakened if NASA and ESA astronauts were still entirely dependent upon Russia to access the International Space Station. Further, in the same scenario, given its withdrawal from French Guinea, it’s also not implausible to imagine that Russia might have severely hampered or even fully withdrawn its support of Western access to the ISS.
Put simply, Crew Dragon – now a bastion of independent European and US human spaceflight in an age of extraordinary Russian recklessness – has arguably never been more important and SpaceX’s success never more of a triumph than they are today.

Elon Musk
Tesla Full Self-Driving set to get an awesome new feature, Elon Musk says
Tesla Full Self-Driving is set to get an awesome new feature in the near future, CEO Elon Musk confirmed on X.
Full Self-Driving is the company’s semi-autonomous driving program, which is among the best available to the general public. It still relies on the driver to ultimately remain in control and pay attention, but it truly does make traveling less stressful and easier.
However, Tesla still continuously refines the software through Over-the-Air updates, which are meant to resolve shortcomings in the performance of the FSD suite. Generally, Tesla does a great job of this, but some updates are definitely regressions, at least with some of the features.
Tesla Cybertruck owner credits FSD for saving life after freeway medical emergency
Tesla and Musk are always trying to improve the suite’s performance by fixing features that are presently available, but they also try to add new things that would be beneficial to owners. One of those things, which is coming soon, is giving the driver the ability to prompt FSD with voice demands.
For example, asking the car to park close to the front door of your destination, or further away in an empty portion of the parking lot, would be an extremely beneficial feature. Adjusting navigation is possible through Grok integration, but it is not always effective.
Musk confirmed that voice prompts for FSD would be possible:
Coming
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 21, 2026
Tesla Full Self-Driving is a really great thing, but it definitely has its shortcomings. Navigation is among the biggest complaints that owners have, and it is easily my biggest frustration with using it. Some of the routes it chooses to take are truly mind-boggling.
Another thing it has had issues with is being situated in the correct lane at confusing intersections or even managing to properly navigate through local traffic signs. For example, in Pennsylvania, there are a lot of stop signs with “Except Right Turn” signs directly under.
This gives those turning right at a stop sign the opportunity to travel through it. FSD has had issues with this on several occasions.
Parking preferences would be highly beneficial and something that could be resolved with this voice prompt program. Grocery stores are full of carts not taken back by customers, and many people choose to park far away. Advising FSD of this preference would be a great advantage to owners.
Cybertruck
Elon Musk clarifies Tesla Cybertruck ’10 day’ comment, fans respond
Some are arguing that the decision to confirm a price hike in ten days is sort of counterproductive, especially considering it is based on demand. Giving consumers a timeline of just ten days to make a big purchase like a pickup truck for $60,000, and basically stating the price will go up, will only push people to make a reservation.

Elon Musk has clarified what he meant by his comment on X yesterday that seemed to indicate that Tesla would either do away with the new All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck or adjust the price.
The response was cryptic as nobody truly knew what Musk’s plans were for the newest Tesla Cybertruck trim level. We now have that answer, and fans of the company are responding in a polarizing fashion.
On Thursday night, Tesla launched the Cybertruck All-Wheel-Drive, priced competitively at $59,990. It was a vast improvement from the Rear-Wheel-Drive configuration Tesla launched last year at a similar price point, which was eventually cancelled just a few months later due to low demand.
Tesla launches new Cybertruck trim with more features than ever for a low price
However, Musk said early on Friday, “just for 10 days,” the truck would either be available or priced at $59,990. We can now confirm Tesla will adjust the price based on more recent comments from the CEO.
Musk said the price will fluctuate, but it “depends on how much demand we see at this price level.”
Depends on how much demand we see at this price level
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 20, 2026
Some are defending the decision, stating that it is simply logical to see how the Cybertruck sells at this price and adjust accordingly.
Case 1: You don’t like it -> don’t buy it
Case 2 (me): You like it, it’s fits your situation and needs -> you buy it.
Case 3: Complain endlessly for no reason, you weren’t going to get one anyway, but you want people to know you’re mad, for some reason.
Silly netizens.— Ryan Scanlan 👥 (@Xenius) February 21, 2026
Others, not so much.
Alright I’m obviously not the one successful enough to be calling the shots at Tesla and worth almost a trillion dollars
But people were excited about the awesome Cybertruck news and then it got taken away, that’s why people are annoyed. The wording felt more like a threat.… pic.twitter.com/NWVNklcXoJ— Dirty Tesla (@DirtyTesLa) February 21, 2026
No but fr wtf you doing dude???????
— Greggertruck (@greggertruck) February 20, 2026
It’s how it was communicated.
If it had been stated clearly on the website for everyone to see, everyone would be fine.
— KiTT_2020 (@kitt_2020) February 20, 2026
Some are arguing that the decision to confirm a price hike in ten days is sort of counterproductive, especially considering it is based on demand. Giving consumers a timeline of just ten days to make a big purchase like a pickup truck for $60,000, and basically stating the price will go up, will only push people to make a reservation.
Demand will look strong because people want to lock in this price. The price will inevitably go up, and demand for the trim will likely fall a bit because of the increased cost.
Many are arguing Musk should have kept this detail internal, but transparency is a good policy to have. It is a polarizing move to confirm a price increase in just a week-and-a-half, but the community is obviously split on how to feel.
Cybertruck
Tesla Cybertruck’s newest trim will undergo massive change in ten days, Musk says
It appears as if the new All-Wheel-Drive trim of Cybertruck won’t be around for too long, however. Elon Musk revealed this morning that it will be around “only for the next 10 days.”

Tesla’s new Cybertruck trim has already gotten the axe from CEO Elon Musk, who said the All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the all-electric pickup will only be available “for the next ten days.”
Musk could mean the price, which is $59,990, or the availability of the trim altogether.
Last night, Tesla launched the All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck, a pickup that comes in at less than $60,000 and features a competitive range and features that are not far off from the offerings of the premium trim.
Tesla launches new Cybertruck trim with more features than ever for a low price
It was a nice surprise from Tesla, considering that last year, it offered a Rear-Wheel-Drive trim of the Cybertruck that only lasted a few months. It had extremely underwhelming demand because it was only $10,000 cheaper than the next trim level up, and it was missing a significant number of premium features.
Simply put, it was not worth the money. Tesla killed the RWD Cybertruck just a few months after offering it.
With the news that Tesla was offering this All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck, many fans and consumers were encouraged. The Cybertruck has been an underwhelming seller, and this seemed to be a lot of truck for the price when looking at its features:
- Dual Motor AWD w/ est. 325 mi of range
- Powered tonneau cover
- Bed outlets (2x 120V + 1x 240V) & Powershare capability
- Coil springs w/ adaptive damping
- Heated first-row seats w/ textile material that is easy to clean
- Steer-by-wire & Four Wheel Steering
- 6’ x 4’ composite bed
- Towing capacity of up to 7,500 lbs
- Powered frunk
It appears as if this trim of Cybertruck won’t be around for too long, however. Musk revealed this morning that it will be around “only for the next 10 days.”
Only for the next 10 days https://t.co/82JnvZQGh2
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 20, 2026
Musk could mean the price of the truck and not necessarily the ability to order it. However, most are taking it as a cancellation.
If it is, in fact, a short-term availability decision, it is baffling, especially as Tesla fans and analysts claim that metrics like quarterly deliveries are no longer important. This seems like a way to boost sales short-term, and if so many people are encouraged about this offering, why would it be kept around for such a short period of time?
Some are even considering the potential that Tesla axes the Cybertruck program as a whole. Although Musk said during the recent Q4 Earnings Call that Cybertruck would still be produced, the end of the Model S and Model X programs indicates Tesla might be prepared to do away with any low-volume vehicles that do not contribute to the company’s future visions of autonomy.
The decision to axe the car just ten days after making it available seems like a true head-scratcher.