
News
SpaceX readies its California landing pad for September rocket recovery debut
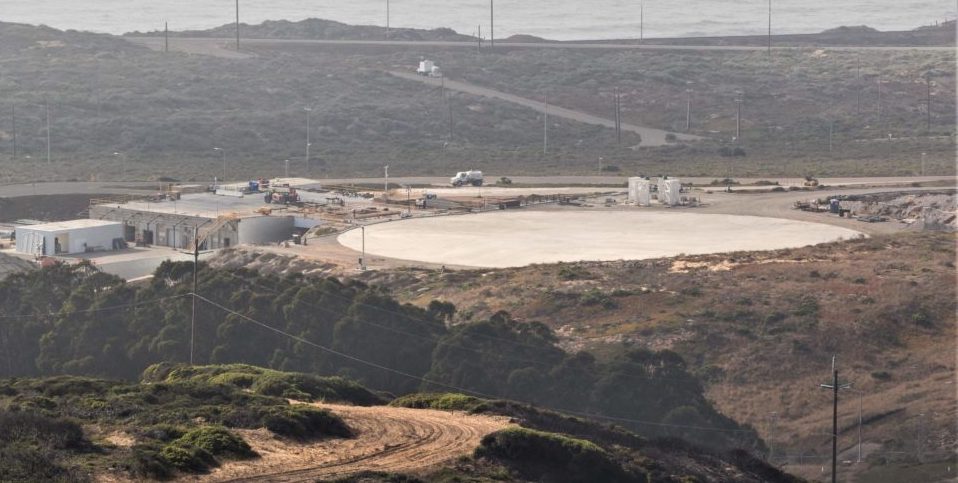
Just as SpaceX successfully debuted Falcon 9 Block 5 at their California launch pad and returned drone ship Just Read The Instructions (JRTI) to rocket recovery duty after a nine-month leave, the company’s next West Coast mission is already aligning for an early-September launch. The mission, SAOCOM-1A, will feature yet another inaugural event – the first use of a West Coast landing pad less than a mile from SpaceX’s Vandenberg launch pad.
For the last two and a half years, SpaceX’s Florida launch sites (Pad 40 and Pad 39A) have also been privy to a unique secondary facility known as Landing Zone-1, located a few miles away from both pads inside the boundaries of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). In fact, although a number of attempts were made to recover a Falcon 9 booster aboard drone ship Of Course I Still Love You (OCISLY) in 2015, the first successful Falcon 9 booster landing happened to occur at LZ-1, followed four months later by the first successful recovery by sea.
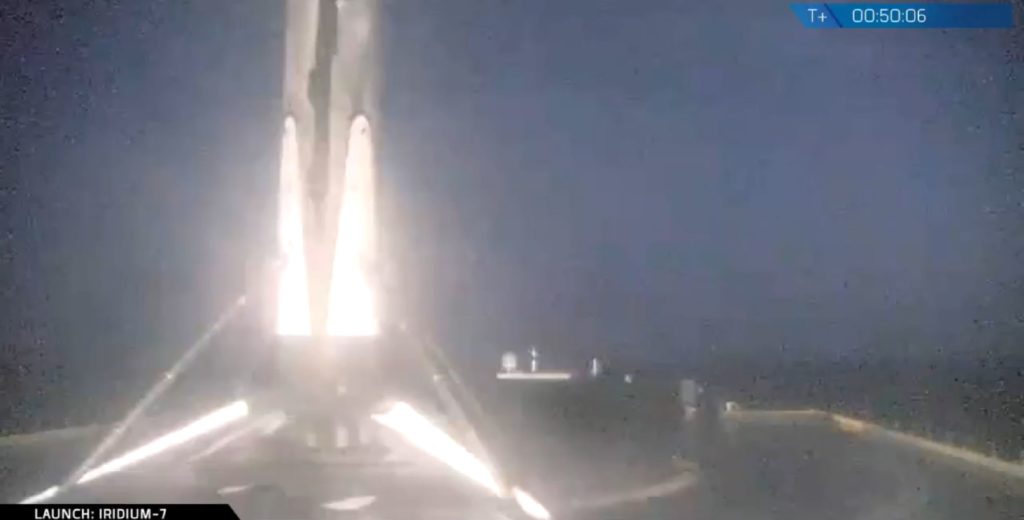
SLC-4E after a foggy launch of Iridium-7 at Vandenberg. #spacex #iridium7 pic.twitter.com/YQkXbpBooj
— Pauline Acalin (@w00ki33) July 25, 2018
Why land on land, why land at sea?
The primary draw of an equivalent land-based pad is both simple and massive: while SpaceX’s autonomous drone ship vessels are complex, comparatively easy to damage, and extremely expensive to both operate and maintain, a concrete circle on land has relatively tiny fixed and variable costs, does not have to concern itself with volatile ocean conditions, and does not require a fleet of tugboats and service vessels to operate. Rough estimates place the cost of taking a drone ship, tugboat, and crew transport vessel hundreds of miles off the coast on missions that can last 7-14 days anywhere from $500,000 to $2 million or more, depending on how you tabulate costs. Either way, the drone ship fleet will always be more complex and more expensive than simple concrete pads on land.
One problem with land-based landing zones is that returning rockets to their launch sites is very fuel-intensive, requiring propellant margins at booster stage separation that dramatically reduce the payload that can be placed into low Earth orbit (LEO), let alone higher-energy missions to geostationary orbit. As such, without massive performance improvements, drone ships like JRTI and OCISLY will be irreplaceable for as long as Falcon 9 and Heavy are flying – SpaceX simply cannot recover rockets during the geostationary launches that comprise a huge portion of their manifest unless they have those vessels.
- Elon Musk walks among his recovered Falcon Heavy boosters at LZ-1 and 2. (Elon Musk)
- The drone ship Of Course I Still Love You spotted in Port Canaveral, FL last December. (Instagram /u/ johnabc123)
- West Coast drone ship Just Read The Instructions headed out to sea to catch a Block 5 booster on July 22. It succeeded. (Pauline Acalin)
This brings us to another conundrum. SpaceX’s Florida launch facilities support heavy commercial geostationary satellite launches as much as or more than any other type of payload in a given year of launches, meaning that the company’s now-doubled landing pad at LZ-1 is only used every once and awhile for Cargo Dragon launches and other miscellaneous and rare launches that leave enough margin in Falcon 9. SpaceX’s Vandenberg pad, on the other hand, is effectively bound to launching satellites into polar orbits (orbiting over Earth’s poles versus around the equator) – safety regulations prevent large rockets from launching over populated areas like the entire continental U.S., as an example for California launches.
Equatorial launches from East to West are much less efficient than their opposite, as Earth’s own rotation (West to East) provides rockets an appreciable performance boost. The point is that SpaceX’s Vandenberg launches are for fairly particular payloads, usually LEO communications satellites and imaging satellites that thrive in polar orbits, where one or a handful of satellites can observe almost anywhere on Earth over the course of a normal 24-hour. Those satellites also happen to be lightweight more often than not, meaning that many of the booster recoveries on drone ship JRTI could instead return to launch site (RTLS) for a dramatically simpler and cheaper recovery.
Enter Block 5
A West Coast LZ is even more intriguing and important with respect to the recent debut of Falcon 9 Block 5 at Vandenberg and the fact that all future launches. Even compared to SpaceX’s Florida LZ-1, the company’s Western pad is incredibly close to the launch pad. By landing less than a mile from SpaceX’s VAFB integration and refurbishment facilities (and launch pad), recovery and refurbishment operations should be more effortless than any before it.
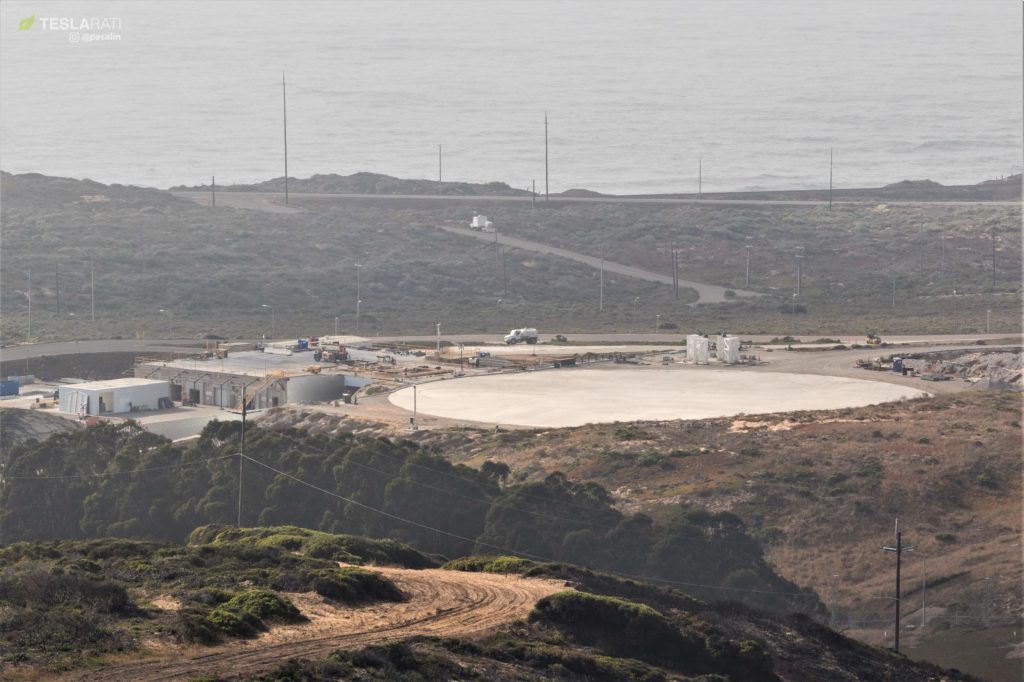
- SpaceX’s yet-unused Californian Landing Zone, seen ahead of Falcon 9 Block 5’s Iridium-7 debut. (Pauline Acalin)
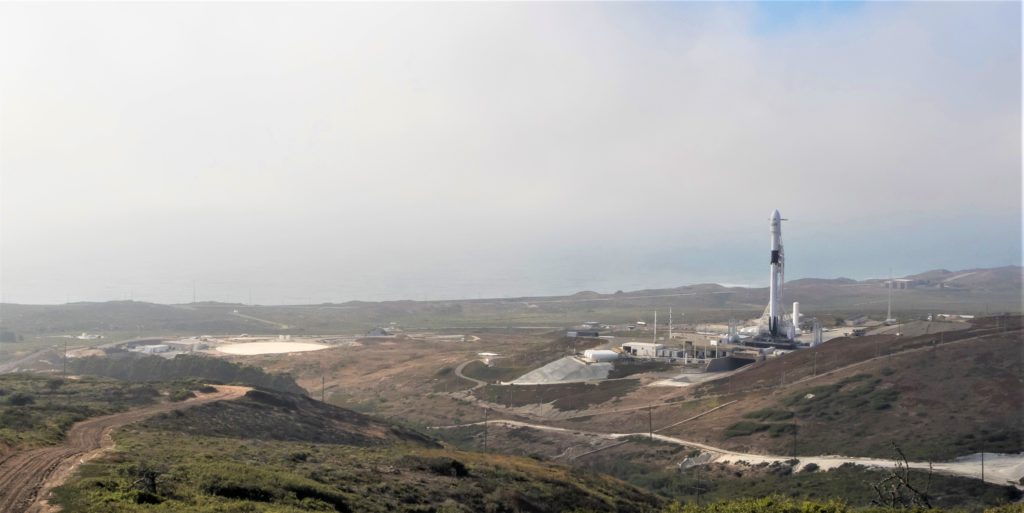
- SpaceX’s Vandenberg launch pad (right) and landing zone (left) ahead of the pad’s first Falcon 9 Block 5 launch, Iridium-7. (Pauline Acalin)
While the company’s VAFB launch pad is a bit older than its Eastern cousins and requires at least 3-5 weeks between launches for repairs and refurbishment, that relaxed schedule may be unbeatable for proving out the Block 5 upgrade’s true rapid reusability, as well as its ability to far more than two orbital missions per booster lifespan. SAOCOM-1A, one of two Argentinian Earth observations scheduled for launch with SpaceX, will begin that new era for SpaceX’s Vandenberg operations, including a landing pad debut permit officially granted by the FCC in the last few weeks. The Falcon 9 booster that launches that mission is bound to have a storied future ahead of itself.
For prompt updates, on-the-ground perspectives, and unique glimpses of SpaceX’s rocket recovery fleet (including fairing catcher Mr Steven) check out our brand new LaunchPad and LandingZone newsletters!
Elon Musk
Tesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
Jim Cramer is now speaking positively about Tesla, especially in terms of its Robotaxi performance and its perception as a company.

Tesla investors will be shocked by analyst Jim Cramer’s latest assessment of the company.
When it comes to Tesla analysts, many of them are consistent. The bulls usually stay the bulls, and the bears usually stay the bears. The notable analysts on each side are Dan Ives and Adam Jonas for the bulls, and Gordon Johnson for the bears.
Jim Cramer is one analyst who does not necessarily fit this mold. Cramer, who hosts CNBC’s Mad Money, has switched his opinion on Tesla stock (NASDAQ: TSLA) many times.
He has been bullish, like he was when he said the stock was a “sleeping giant” two years ago, and he has been bearish, like he was when he said there was “nothing magnificent” about the company just a few months ago.
Now, he is back to being a bull.
Cramer’s comments were related to two key points: how NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang describes Tesla after working closely with the Company through their transactions, and how it is not a car company, as well as the recent launch of the Robotaxi fleet.
Jensen Huang’s Tesla Narrative
Cramer says that the narrative on quarterly and annual deliveries is overblown, and those who continue to worry about Tesla’s performance on that metric are misled.
“It’s not a car company,” he said.
He went on to say that people like Huang speak highly of Tesla, and that should be enough to deter any true skepticism:
“I believe what Musk says cause Musk is working with Jensen and Jensen’s telling me what’s happening on the other side is pretty amazing.”
Tesla self-driving development gets huge compliment from NVIDIA CEO
Robotaxi Launch
Many media outlets are being extremely negative regarding the early rollout of Tesla’s Robotaxi platform in Austin, Texas.
There have been a handful of small issues, but nothing significant. Cramer says that humans make mistakes in vehicles too, yet, when Tesla’s test phase of the Robotaxi does it, it’s front page news and needs to be magnified.
He said:
“Look, I mean, drivers make mistakes all the time. Why should we hold Tesla to a standard where there can be no mistakes?”
It’s refreshing to hear Cramer speak logically about the Robotaxi fleet, as Tesla has taken every measure to ensure there are no mishaps. There are safety monitors in the passenger seat, and the area of travel is limited, confined to a small number of people.
Tesla is still improving and hopes to remove teleoperators and safety monitors slowly, as CEO Elon Musk said more freedom could be granted within one or two months.
News
Tesla launches ultra-fast V4 Superchargers in China for the first time
Tesla has V4 Superchargers rolling out in China for the first time.
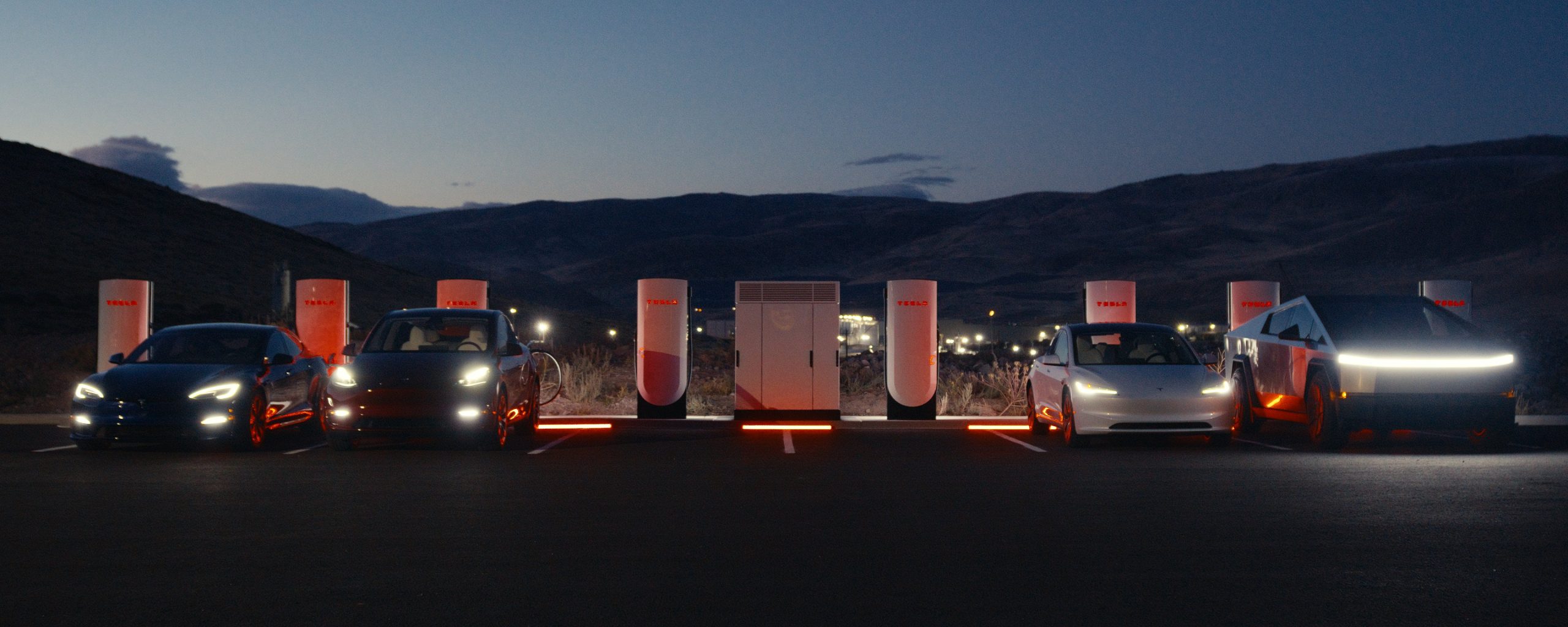

Tesla already has nearly 12,000 Supercharger piles across mainland China. However, the company just initiated the rollout of the ultra-fast V4 Superchargers in China for the first time, bringing its quick-charging piles to the country for the first time since their launch last year.
The first batch of V4 Superchargers is now officially up and running in China, the company announced in a post on Chinese social media outlet Weibo today.
The company said in the post:
“The first batch of Tesla V4 Superchargers are online. Covering more service areas, high-speed charging is more convenient, and six-layer powerful protection such as rain and waterproof makes charging very safe. Simultaneously open to non-Tesla vehicles, and other brands of vehicles can also be charged. There are more than 70,000 Tesla Superchargers worldwide. The charging network layout covers 100% of the provincial capitals and municipalities in mainland China. More V4 Superchargers will be put into use across the country. Optimize the charging experience and improve energy replenishment efficiency. Tesla will accompany you to the mountains, rivers, lakes, and seas with pure electricity!”
The first V4 Superchargers Tesla installed in China are available in four cities across the country: Shanghai, Zhejiang, Gansu, and Chongqing.

Credit: Tesla China
Tesla has over 70,000 Superchargers worldwide. It is the most expansive and robust EV charging network in the world. It’s the main reason why so many companies have chosen to adopt Tesla’s charging connector in North America and Europe.
In China, some EVs can use Tesla Superchargers as well.
The V4 Supercharger is capable of charging vehicles at speeds of up to 325kW for vehicles in North America. This equates to over 1,000 miles per hour of charging.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk hints at when Tesla could reduce Safety Monitors from Robotaxi
Tesla could be reducing Safety Monitors from Robotaxi within ‘a month or two,’ CEO Elon Musk says.
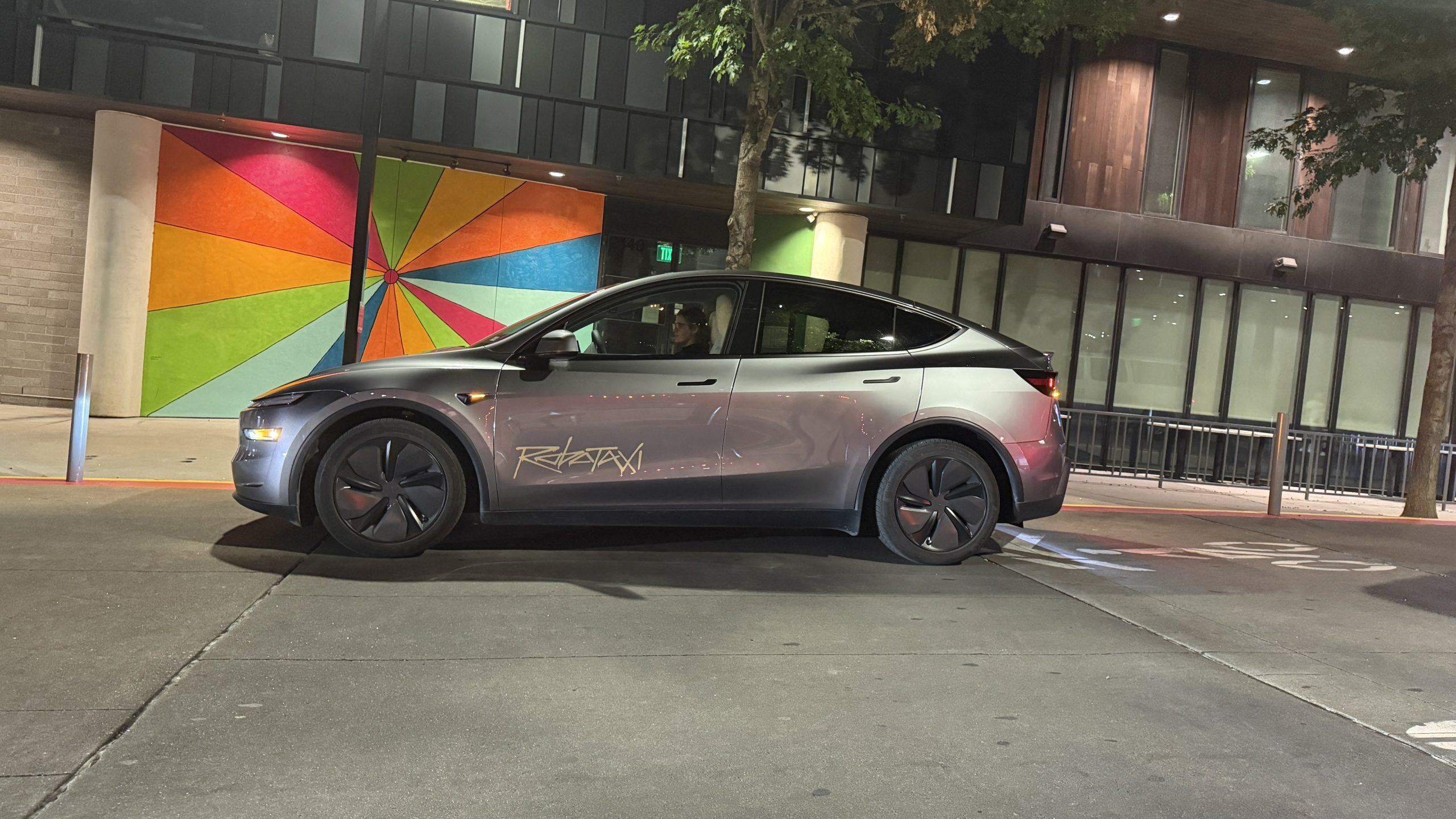

Elon Musk hinted at when Tesla could begin reducing Safety Monitors from its Robotaxis. Safety Monitors are Tesla employees who sit in the front passenger seat during the driverless rides, and are there to ensure safety for occupants during the earliest rides.
Tesla launched its Robotaxi fleet in Austin last Sunday, and after eight days, videos and reviews from those who have ridden in the driverless vehicles have shown that the suite is safe, accurate, and well coordinated. However, there have been a few hiccups, but nothing that has put anyone’s safety in danger.
A vast majority — close to all of the rides — at least according to those who have ridden in the Robotaxi, have been performed without any real need for human intervention. We reported on what was the first intervention last week, as a Safety Monitor had to step in and stop the vehicle in a strange interaction with a UPS truck.
Watch the first true Tesla Robotaxi intervention by safety monitor
The Tesla and UPS delivery truck were going for the same street parking space, and the Tesla began to turn into it. The UPS driver parallel parked into the spot, which was much smaller than his truck. It seemed to be more of an instance of human error instead of the Robotaxi making the wrong move. This is something that the driverless cars will have to deal with because humans are aggressive and sometimes make moves they should not.
The Safety Monitors have not been too active in the vehicles. After all, we’ve only seen that single instance of an intervention. There was also an issue with the sun, when the Tesla braked abnormally due to the glare, but this was an instance where the car handled the scenario and proceeded normally.
With the Robotaxi fleet operating impressively, some are wondering when Tesla will begin scaling back both the Safety Monitors and Teleoperators that it is using to ensure safety with these early rides.
CEO Elon Musk answered the inquiry by stating, “As soon as we feel it is safe to do so. Probably within a month or two.”
As soon as we feel it is safe to do so.
Probably within a month or two. We continue to improve the Tesla AI with each mile driven.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) June 30, 2025
Musk’s response seems to confirm that there will be fewer Teleoperators and Safety Monitors in the coming months, but there will still be some within the fleet to ensure safety. Eventually, that number will get to zero.
Reaching a point where Tesla’s Robotaxi is driverless will be another significant milestone for the company and its path to fully autonomous ride-sharing.
Eventually, Tesla will roll out these capabilities to consumer-owned vehicles, offering them a path to generate revenue as their car operates autonomously and completes rides.
For now, Tesla is focusing on perfecting the area of Austin where it is currently offering driverless rides for just $4.20 to a small group of people.
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla confirms massive hardware change for autonomy improvement
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla China roars back with highest vehicle registrations this Q2 so far
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla features used to flunk 16-year-old’s driver license test
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla dominates Cars.com’s Made in America Index with clean sweep
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Grok integration will be more realistic with this cool feature




























