

Energy
Tesla may revisit vehicle-to-grid (V2G) bi-directional charging solution
Tesla could soon revisit the idea of using its electric cars as a battery power source, likely as part of the company’s Vehicle-To-Grid (V2G) bi-directional solutions.
Musk’s update came as a response to a Twitter request from Cody Walker, a Tesla enthusiast, who inquired if the electric car maker would eventually introduce a feature where one car can provide battery power to another vehicle. Responding to the inquiry, Musk noted that previous Tesla vehicles had the capability to use its battery for outputting power.
Very early on, we had the ability to use the car as a battery outputting power. Maybe worth revisiting that.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) July 4, 2018
The Vehicle-To-Grid concept involves the use of electric car batteries to provide electricity back to the grid. The V2G model uses excess capacity from an electric car’s battery capacity to provide power to the electric grid in response to peak load demands. Such a system could result in several benefits, including lower power bills for homes adopting V2G.
The idea of using electric cars as a battery power source has been suggested in the past, particularly during the time of the SolarCity acquisition. For one, Ben Hill, Tesla’s vice president for energy in Europe and Africa back in 2016, mentioned that vehicle-to-grid systems would be introduced and be functional “very, very soon.” Speaking to at the 2016 Intersolar Conference at Dubai World Trade Centre, Hill noted that V2G technology is quite promising, though it still needs some fine-tuning.
“There is a lot of pilots programs going around the world right now. The ability for battery systems, which are connected to the grid, whether there in a vehicle or not, that ability is coming very, very soon,” he said.
Even teardown specialists critical of Tesla’s vehicles like the Model 3, such as Detroit veteran Sandy Munro, for example, have lauded Tesla’s progress in its battery technology. With this in mind, and with Elon Musk’s recent mention of a $100/kW breakthrough for battery cells in the near future, the time could very well be ripe for the electric car maker to revisit V2G solutions. Tesla’s battery packs, if any, are large enough for the task, considering that an average US household consumes roughly 30 kWh of electricity per day, and Tesla’s smallest battery pack in its vehicles stores 75 kWh of energy.
Vehicle-To-Grid bi-directional charging solutions have been explored by other carmakers in the past. Back in 2013, Nissan introduced a 6 kW bi-directional “LEAF-To-Home” system in Japan, which uses the electric car’s batteries to help lower the electricity bills of homes. As a means to demonstrate the potential of the technology, Nissan introduced the “Vehicle-To-Building” concept, which involved connecting six LEAFs to a building’s power distribution board, saving on power costs during peak hours. The potential savings of Nissan’s system was only around $5,000 per year for the Vehicle-To-Building model, but it was nonetheless a demonstration of how the technology could work.
The introduction of V2G solutions for Tesla vehicles might be coming at the right time for the electric car and energy company. The necessary components for the system, after all, are pretty much in place after Tesla merged with SolarCity. The former, after all, produces battery packs, while the latter provides homes with solar solutions. The companies’ technologies already came together for the Tesla Powerwall and the Solar Roof tiles. Thus, an idea like V2G would be a logical step forward for the company.
There is a certain risk with V2G solutions, however. The technology, after all, could be abused by charging the electric cars at Superchargers (which are free) and using the stored energy for their homes. If Tesla could come up with a way to prevent this from happening, however, the company could very well have another killer system in its hands.
Energy
Tesla Lathrop Megafactory celebrates massive Megapack battery milestone
The Tesla Megapack is the backbone of Tesla Energy’s battery deployments.
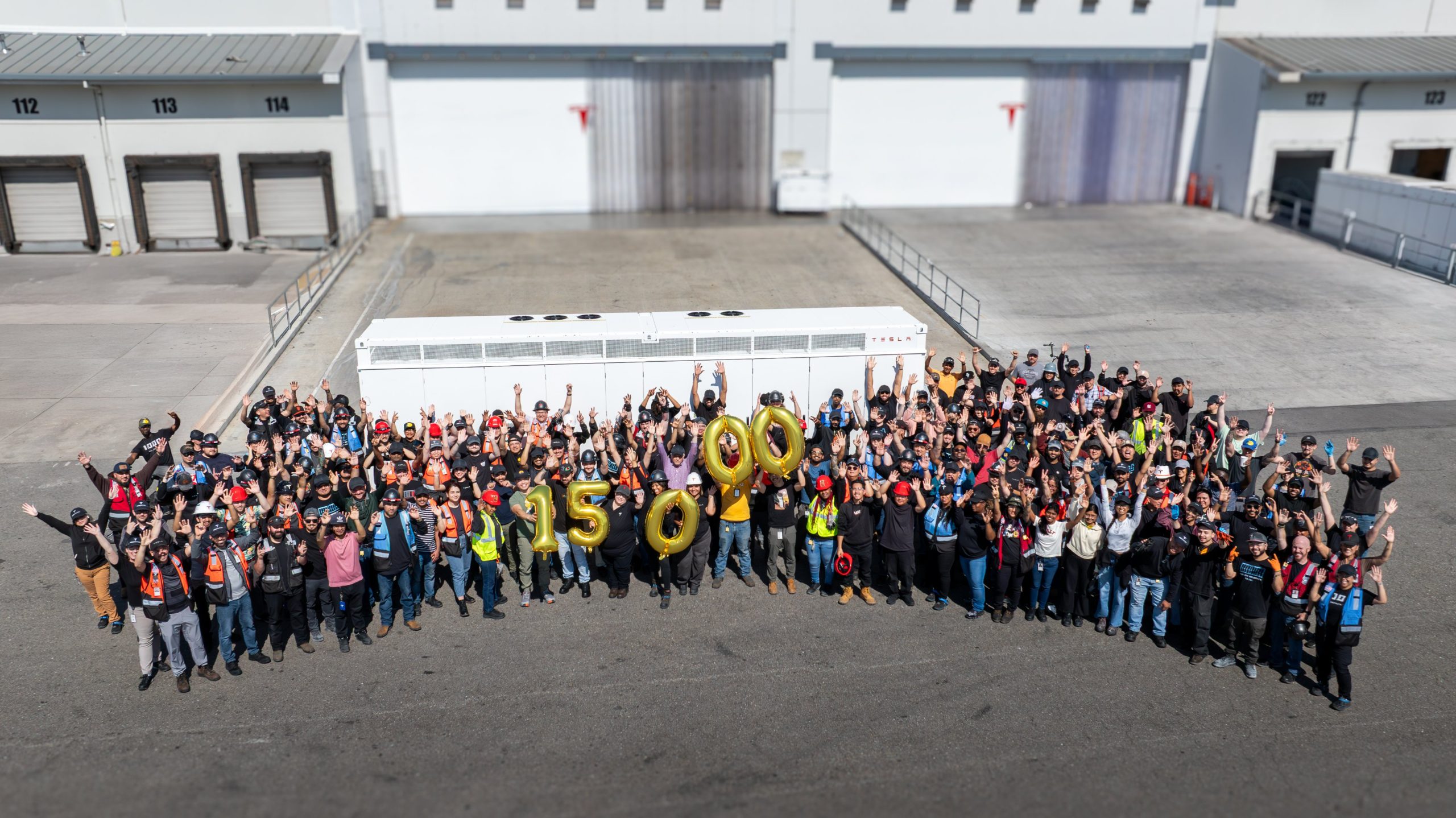

The Tesla Lathrop Megafactory recently achieved a new milestone. As per the official Tesla Megapack account on X, the Lathrop Megafactory has produced its 15,000th Megapack 2 XL battery.
15,000 Megapack Batteries
Tesla celebrated the milestone with a photo of the Lathrop Megafactory team posing with a freshly produced Megapack battery. To commemorate the event, the team held balloons that spelled out “15,000” as they posed for the photo.
The Tesla Megapack is the backbone of Tesla Energy’s battery deployments. Designed for grid-scale applications, each Megapack offers 3.9 MWh of energy and 1.9 MW of power. The battery is extremely scalable, making it perfect for massive energy storage projects.
More Megafactories
The Lathrop Megafactory is Tesla’s first dedicated facility for its flagship battery storage system. It currently stands as the largest utility-scale battery factory in North America. The facility is capable of producing 10,000 Megapack batteries every year, equal to 40 GWh of clean energy storage.
Thanks to the success of the Megapack, Tesla has expanded its energy business by building and launching the Shanghai Megafactory, which is also expected to produce 40 GWh of energy storage per year. The ramp of the Shanghai Megafactory is quite impressive, with Tesla noting in its Q1 2025 Update Letter that the Shanghai Megafactory managed to produce over 100 Megapack batteries in the first quarter alone.
Tesla Energy’s Potential
During the first quarter earnings call, CEO Elon Musk stated that the Megapack is extremely valuable to the energy industry.
“The Megapack enables utility companies to output far more total energy than would otherwise be the case… This is a massive unlock on total energy output of any given grid over the course of a year. And utility companies are beginning to realize this and are buying in our Megapacks at scale,” Musk said.
Energy
Tesla Megapacks powers the xAI Colossus supercomputer
Tesla Megapacks step in to stabilize xAI’s Colossus supercomputer, replacing natural gas turbines. Musk’s ventures keep intertwining.
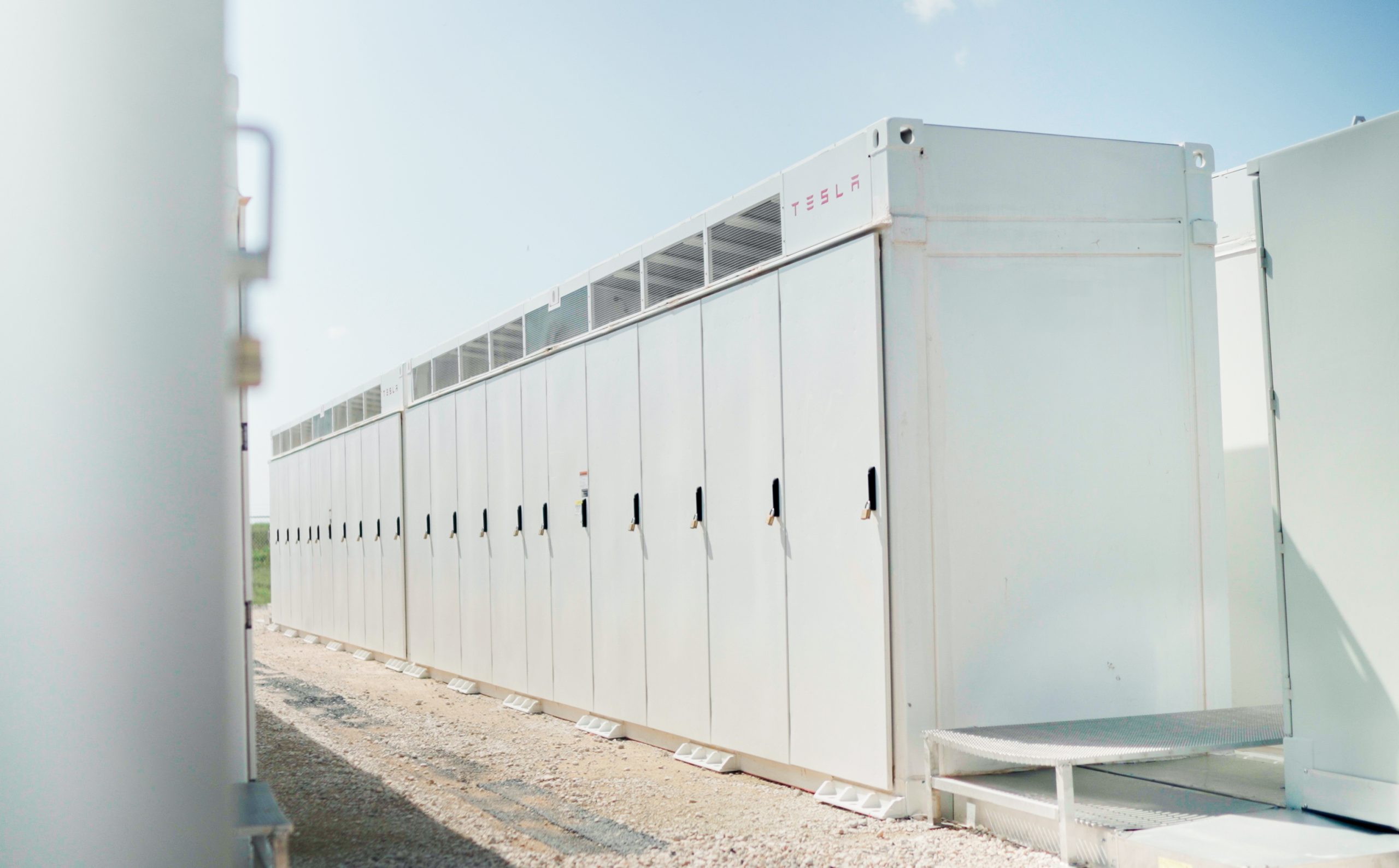

Tesla Megapack batteries will power the xAI Colossus supercomputer in Memphis to ensure power stability. The collaboration between Tesla and xAI highlights the synergy among Elon Musk’s ventures.
The artificial intelligence startup has integrated Tesla Megapacks to manage outages and demand surges, bolstering the facility’s reliability. The Greater Memphis Chamber announced that Colossus, recently connected to a new 150-megawatt electric substation, is completing its first construction phase. This transition addresses criticism from environmental justice groups over the initial use of natural gas turbines.
“The temporary natural gas turbines that were being used to power the Phase I GPUs prior to grid connection are now being demobilized and will be removed from the site over the next two months.
“About half of the operating turbines will remain operating to power Phase II GPUs of xAI until a second substation (#22) already in construction is completed and connected to the electric grid, which is planned for the Fall of 2025, at which time the remaining turbines will be relegated to a backup power role,” the Chamber stated.
xAI’s rapid development of Colossus reflects its ambition to advance AI capabilities, but the project has faced scrutiny for environmental impacts. The shift to Megapacks and grid power aims to mitigate these concerns while ensuring operational continuity.
The Megapack deployment underscores the collaboration among Musk’s companies, including Tesla, SpaceX, Neuralink, and The Boring Company. Tesla appears to be the common link between all of Musk’s companies. For example, The Boring Company built a tunnel in Giga, Texas. In addition, Musk has hinted at a potential collaboration between the Tesla Optimus Bot and Neuralink. And from January 2024 to February 2025, xAI invested $230 million in Megapacks, per a Tesla filing.
Tesla Energy reported a 156% year-over-year increase in Q1 2025, deploying 10.4 GWh of storage products, including Megapacks and Powerwalls. Tesla’s plans for a new Megapack factory in Waller County, Texas, which is expected to create 1,500 jobs in the area, further signal its commitment to scaling energy solutions.
As xAI leverages Tesla’s Megapacks to power Colossus, the integration showcases Musk’s interconnected business ecosystem. The supercomputer’s enhanced stability positions xAI to drive AI innovation, while Tesla’s energy solutions gain prominence, setting the stage for broader technological and economic impacts.
Energy
Tesla Energy celebrates one decade of sustainability
Tesla Energy has gone far since its early days, and it is now becoming a progressively bigger part of the company.

Tesla Energy recently celebrated its 10th anniversary with a dedicated video showcasing several of its milestones over the past decade.
Tesla Energy has gone far since its early days, and it is now becoming a progressively bigger part of the company.
Tesla Energy Early Days
When Elon Musk launched Tesla Energy in 2015, he noted that the business is a fundamental transformation of how the world works. To start, Tesla Energy offered the Powerwall, a 7 kWh/10 kWh home battery system, and the Powerpack, a grid-capable 100 kWh battery block that is designed for scalability. A few days after the products’ launch, Musk noted that Tesla had received 38,000 reservations for the Powerwall and 2,500 reservations for the Powerpack.
Tesla Energy’s beginnings would herald its quiet growth, with the company later announcing products like the Solar Roof tile, which is yet to be ramped, and the successor to the Powerwall, the 13.5 kWh Powerwall 2. In recent years, Tesla Energy also launched its Powerwall 3 home battery and the massive Megapack, a 3.9 MWh monster of a battery unit that has become the backbone for energy storage systems across the globe.
Key Milestones
As noted by Tesla Energy in its recent video, it has now established facilities that allow the company to manufacture 20,000 units of the Megapack every year, which should help grow the 23 GWh worth of Megapacks that have already been deployed globally.
The Powerwall remains a desirable home battery as well, with more than 850,000 units installed worldwide. These translate to 12 GWh of residential entry storage delivered to date. Just like the Megapack, Tesla is also ramping its production of the Powerwall, allowing the division to grow even more.
Tesla Energy’s Role
While Tesla Energy does not catch as much headlines as the company’s electric vehicle businesses, its contributions to the company’s bottom line have been growing. In the first quarter of 2025 alone, Tesla Energy deployed 10.4 GWh of energy storage products. Powerwall deployments also crossed 1 GWh in one quarter for the first time. As per Tesla in its Q1 2025 Update Letter, the gross margin for the Energy division has improved sequentially as well.
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla confirms massive hardware change for autonomy improvement
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla features used to flunk 16-year-old’s driver license test
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla China roars back with highest vehicle registrations this Q2 so far
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla dominates Cars.com’s Made in America Index with clean sweep
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Grok integration will be more realistic with this cool feature


















