

News
Tesla’s software fixes, the NHTSA’s status quo, and an impending need for updated recall terminologies
It is no secret that Tesla is a popular topic, so much so that the coverage around the company is immense. Couple this with CEO Elon Musk’s rockstar persona and you get a company whose vehicles are looked at under a microscope constantly. It might feel unfair for some, but it’s just the way it is. Tesla — by simply being Tesla — is newsworthy.
Tesla’s newsworthiness is a double-edged sword. A look at the coverage for the company’s vehicle recalls from the NHTSA would prove this point. So notable is Tesla’s news coverage that a mainstream newsreader would likely get the impression that Teslas get recalls frequently. The opposite is true. As evidenced by Reuters in the graphic below, data from January 1, 2020, through February 17, 2022, shows that Tesla actually recalls its vehicles less frequently than some of the market’s leading automakers. Tesla is also the only carmaker performing a large share of its vehicle recalls through over-the-air software updates.
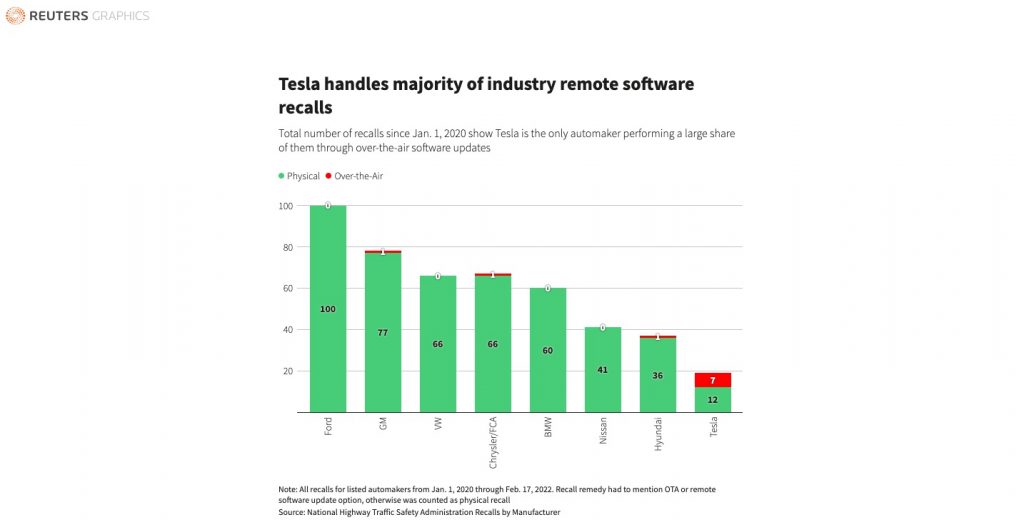
Tesla currently handles the majority of the industry’s remote software recalls, but it would soon not be the only one. New electric vehicle makers have used the idea of software updates as a means to promote their EVs’ capabilities. Rivian has performed OTA updates to its R1 vehicles, and those cars are only starting customer deliveries. Lucid is the same with its Air sedan, with the company rolling out features like Automatic Emergency Braking, Cross-Traffic Protection, Lane Departure Protection, Traffic Drive-Off Alert, and other features earlier this month through a software update. Ford has been rolling out updates called “Power-Ups” to the Mustang Mach-E as well.
Considering that software-based fixes are only bound to get more widespread over the coming years, one must then ask the question: Should software-based over-the-air fixes be dubbed and classified with the same terminologies as physical recalls, which typically involve the replacement of vehicle hardware?
A Vastly Different “Recall” Experience
Any car owner has likely experienced a recall for their vehicle at some point in their driving life. And more likely than not, one’s experience is probably not that pleasant. I certainly count myself among drivers who look at vehicle recalls with trepidation. My current vehicle, a Japanese-made van, was part of a minor fuel pump recall a couple of years ago, and even addressing that took a whole day out of my weekend. The dealer was overwhelmed with the number of cars it was fixing that day, and tempers among owners were flaring by the hour — all for a simple fuel pump replacement. I’ve been told that my experiences with vehicle recalls are not that unique.
In comparison, a software-based fix, such as the disabling of FSD Beta’s “rolling stops” feature, only required affected vehicles to be connected to the internet. There was no dealer visit, no forms to fill out, and no staff to argue with. The car was connected to the internet, a software fix was implemented, and the issue was resolved. One can argue that Tesla’s software fix to disable FSD Beta’s “rolling stops” feature was safety-related, and that’s true. But one could also argue that at least from a driver’s point of view, the experience related to software and hardware-based recalls is vastly different.
The Status Quo
Despite the different experiences involved when software and hardware-based vehicle recalls are addressed, it appears that the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) will, at least for now, keep the status quo. Teslarati reached out to the NHTSA to inquire if it was considering the adoption of updated terminologies for cars whose fixes are completed through OTA software updates, but the agency suggested that this would likely not be the case, at least for now. According to the NHTSA, vehicle manufacturers must initiate a recall for any repair that remedies a safety risk, regardless of whether the issue is fixed by software update or by hardware replacement.
“The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is committed to ensuring the highest safety standards on the nation’s roadways. NHTSA is empowered with robust tools and authorities to protect the public, to investigate potential safety issues, and to compel recalls when it finds evidence of noncompliance or an unreasonable risk to safety. Manufacturers are required to initiate a recall for any repair, including a software update, that remedies an unreasonable risk to safety. NHTSA recalls can include any required repair, which includes a software update, to remedy a potential safety risk. Manufacturers are also required to submit any communications to owners, dealers, and others about any software updates that address a defect, whether it is safety-related or not,” the NHTSA stated.
Product recall specialist and associate professor at the Indiana University Kelley School of Business Professor George Ball told Teslarati that while the NHTSA’s use of similar terminologies for software and hardware-based recalls is “definitely an example of regulators and industry moving at a different pace on technology,” the agency’s hesitation in adopting new terminologies for OTA fixes is understandable. Professor Ball further explained that using terms such as “soft recall” to refer to software-based vehicle fixes might imply a reduced level of risk, and this is something that the NHTSA would likely be unwilling to do.
“I believe NHTSA would resist ‘soft recall’ terminology because it implies a reduced level of customer hazard and allows the firm to be under less scrutiny by the press and public for quality corrections. While some updates are minor, some of the Tesla software upgrades are actually quite serious, and if not done, can allow a harmful defect to persist,” the recall specialist said.
But while the NHTSA’s stance on recall terminologies is completely understandable, one cannot deny the fact that the issues covered by vehicle recalls have a very wide range of risks. Take Tesla’s recall for 817,143 vehicles, which was announced earlier this month, for example. The recall was initiated since a software error may prevent a warning chime from activating even if drivers do not have their seat belts on. From a layman’s perspective, this recall seems grave as it affects over 800,000 Teslas on the road today. However, the issue was simply addressed through firmware release 2021.43.101.1 and later, which included a remedy for the seat belt chime error.
Compare this with General Motors’ recall last year of 400,000 pickup trucks in the US. Granted, it only affected about half as many vehicles as Tesla’s seat belt chime recall, but its hardware-based nature suggested that the risk presented by the issue was great. The recall covered certain 2015 and 2016 Chevrolet and GMC Sierra 1500, 2500, and 3500 trucks, and it involved a faulty airbag inflator that may rupture without warning. To fix the issue, owners of the affected trucks were required to head to a dealer so that they could get their airbag modules replaced. Since parts were in short supply last year, however, owners were notified with a letter to inform them when their trucks’ replacement parts were available.
What Can Be Done
While the NHTSA will likely continue to maintain the status quo with its recall terminologies for the foreseeable future, Professor Ball told Teslarati that the agency can actually implement some adjustments now that can make distinguishing safety fixes and issues clearer. This would likely be extremely important in the near future as more connected cars are rolled out and software updates become the norm.
“If I were to provide advice to the NHTSA, I would recommend that they get out ahead of this issue before every car maker starts updating cars like Tesla. One way to do it is to require the automaker to send all auto updates to NHTSA when pushed out, and to classify updates as ‘minor’ or ‘major.’ Any major update that impacts customer safety would be classified as a recall. Automakers won’t like this, but it will help keep the safety fixes transparent for all, especially consumers. By sending all updates to NHSTA, the agency could assign qualified people to audit the classifications assigned by the manufacturer, to ensure they are making good decisions there.
“I think any language that de-emphasizes the importance of a safety recall is not likely to be supported by NHTSA, and it doesn’t likely help customer safety. A clear distinction needs to be made between minor updates and major updates that influence safety. Those major updates should be classified as a recall, and NHTSA needs to get their arms around these updates and keep on top of them soon, or they will fall way behind the industry,” the recall specialist said.
Recalls can affect the perception of a company to the public. Software fixes should be one of the factors that are considered an edge for automakers like Tesla, not the other way around. Gary Black, Managing Partner of The Future Fund LLC, explained this from the point of view of a Tesla investor. “Since every NHTSA recall so far has been quickly solvable via Tesla OTA updates, ‘recalls’ are noise to most investors. Tesla’s huge software edge highlights one of the key advantages of owning Tesla over every other EV manufacturer,” the Wall Street veteran told Teslarati.
OTA updates, including those related to vehicle safety, are coming. With automakers like Ford joining the group of carmakers embracing OTA updates, software-based fixes are inevitable. Ultimately, I am inclined to agree with the recall specialist. By refusing to adapt to the advent of software-based vehicle fixes, the NHTSA may risk being left behind by the automotive industry. And that’s a scenario that I believe no automaker — or government agency for that matter — would prefer.
Don’t hesitate to contact us with news tips. Just send a message to simon@teslarati.com to give us a heads up.

News
Tesla VP explains latest updates in trade secret theft case
Tesla reportedly caught Matthews copying the tech into machines that were sold to competitors, claiming they lied about doing so for three years, and continued to ship it. That is when Tesla chose to sue Matthews in July 2024 in Federal court, demanding over $1 billion in damages due to trade secret theft.

Tesla Vice President Bonne Eggleston explained the latest updates in a trade secret theft case the company has against a former manufacturing equipment supplier, Matthews International.
Back in 2024, Tesla had filed a lawsuit against Matthews International, alleging that the firm stole trade secrets about battery manufacturing and shared those details with some of Tesla’s competitors.
Early last year, a U.S. District Court Judge denied Tesla’s request to block Matthews International from selling its dry battery electrode (DBE) technology across the world. The judge, Edward Davila, said that the patent for the tech was due to Matthews’ “extensive research and development.”
The two companies’ relationship began back in 2019, as Tesla hired Matthews to help build the equipment for its 4680 battery cell. Tesla shared confidential software, designs, and know-how under strict secrecy rules.
Fast forward a few years, and Tesla reportedly caught Matthews copying the tech into machines that were sold to competitors, claiming they lied about doing so for three years, and continued to ship it. That is when Tesla chose to sue Matthews in July 2024 in Federal court, demanding over $1 billion in damages due to trade secret theft.
Now, the latest twist, as this month, a Judge issued a permanent injunction—a court order banning Matthews from using certain stolen Tesla parts or designs in their machines. Matthews is also officially “liable” for damages. The exact amount would still to be calculated later.
Bonne Eggleston, a VP for Tesla, said on X today that Matthews is a supplier who “exploited customer IP through theft or deception,” and has no place in Tesla’s ecosystem:
Buyer beware: Matthews International stole Tesla’s DBE technology and is now subject to an injunction and liable for damages.
During our work with Matthews, we caught them red-handed copying our technology—including proprietary software and sensitive mechanical designs—into… https://t.co/Toc8ilakeM
— Bonne Eggleston (@BonneEggleston) March 10, 2026
Tesla calls this a big win and warns other companies: “Buyer beware—don’t buy from thieves.”
Matthews hit back with a press release claiming victory. They say an arbitrator ruled they can keep selling their own DBE equipment to anyone and rejected Tesla’s request for a total sales ban. They call Tesla’s claims “nonsense” and insist their 20-year-old tech is independent. Both sides are spinning the same narrow ruling: Matthews can sell their version, but they’re blocked from using Tesla’s specific secrets.
What are Tesla’s Current Legal Options
The case isn’t over—it’s moving to the damages phase. Tesla can:
- Push forward in court or arbitration to calculate and collect huge financial penalties (potentially $1 billion+ if willful theft is proven).
- Enforce the permanent injunction with contempt charges, fines, or even jail time if Matthews violates it.
- Challenge Matthews’ new patents that allegedly copy Tesla’s work, asking courts to invalidate them or add Tesla as co-inventor.
- Seek extra damages, lawyer fees, and possibly punitive awards under the federal Defend Trade Secrets Act and California law.
Tesla could also refer evidence to federal prosecutors for possible criminal trade-secret charges (rare but serious). Settlement is always possible, but Tesla’s fiery public response suggests they want full accountability.
This isn’t just corporate drama. It shows why trade secrets matter even when Tesla open-sources some patents, confidential know-how shared in trust must stay protected. For the EV industry, it’s a reminder: steal from your biggest customer, and you risk losing everything.
News
Tesla Cybercab includes this small but significant feature
The Cybercab is Tesla’s big plan to introduce fully autonomous ride-sharing in a seamless fashion. In fact, the Full Self-Driving suite was geared toward alleviating the need to manually drive vehicles.

Tesla Cybercab manufacturing is strikingly close, as the company is still aiming for an April start date. But small and significant features are still being identified for the first time as production units appear all over the country for testing and for regulatory events, like one yesterday in Washington, D.C.
The Cybercab is Tesla’s big plan to introduce fully autonomous ride-sharing in a seamless fashion. In fact, the Full Self-Driving suite was geared toward alleviating the need to manually drive vehicles.
This was for everyone, including the disabled, who are widely reliant on ride-sharing platforms, family members, and medical shuttles for transportation of any kind. Cybercab aims to change that, and Tesla evidently put a focus on those riders while developing the vehicle, evident in a small but significant feature revealed during its appearance in the Nation’s Capital.
Tesla Cybercab display highlights interior wizardry in the small two-seater
Tesla has implemented Braille within the Cybercab to make it easier for blind passengers to utilize the vehicle. On both the ‘Stop/Hazard Lights’ button and the Door Releases, Tesla has placed Braille so that blind passengers can navigate their way through the vehicle:
The hazard lights button will be used as an emergency stop. Smart pic.twitter.com/vkYBioqmKm
— Whole Mars Catalog (@wholemars) March 10, 2026
We have braille on the interior door releases as well
— Eric (@EricETesla) March 11, 2026
This is a great addition to the Cybercab, especially as Full Self-Driving has been partially pointed at as a solution for those with disabilities that would keep them from driving themselves from place to place.
It truly is a great addition and just another way that Tesla is showing they are making this massive product inclusive for everyone out there, including those who have not been able to drive due to not having vision.
The Cybercab is set to enter mass production sometime in April, and it will be responsible for launching Tesla’s massive plans for an autonomous ride-sharing program.
Elon Musk
Tesla and xAI team up on massive new project
It is the latest move by a Musk company to automate, streamline, and reduce the manual, monotonous, and tedious work currently performed by humans through AI and robotics development. Digital Optimus will be capable of processing and actioning the past five seconds of a real-time computer screen video and keyboard and mouse actions.
Elon Musk teased a massive new project, to be developed jointly by Tesla and xAI, called “Digital Optimus” or “Macrohard,” the first development under Tesla’s investment agreement with xAI.
Musk announced on X that Digital Optimus will “be capable of emulating the function of entire companies.”
Macrohard or Digital Optimus is a joint xAI-Tesla project, coming as part of Tesla’s investment agreement with xAI.
Grok is the master conductor/navigator with deep understanding of the world to direct digital Optimus, which is processing and actioning the past 5 secs of…
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 11, 2026
It is the latest move by a Musk company to automate, streamline, and reduce the manual, monotonous, and tedious work currently performed by humans through AI and robotics development. Digital Optimus will be capable of processing and actioning the past five seconds of a real-time computer screen video and keyboard and mouse actions.
Essentially, it will be an AI version of a desk worker in many capacities, including accounting, HR tasks, and others.
Musk said:
“Grok is the master conductor/navigator with deep understanding of the world to direct digital Optimus, which is processing and actioning the past 5 secs of real-time computer screen video and keyboard/mouse actions. Grok is like a much more advanced and sophisticated version of turn-by-turn navigation software. You can think of it as Digital Optimus AI being System 1 (instinctive part of the mind) and Grok being System 2. (thinking part of the mind).”
Its key applications would be used for enterprise automation, simulating entire companies, high-volume repetitive tasks, and potentially, future hybrid use with the Optimus robot, which would handle physical tasks, while Digital Optimus would handle the clerical work.
The creation of a digital AI suite like Digital Optimus would help companies save time and money, as well as become more efficient in their operations through massive scalability. However, there will undoubtedly be concerns from people who are skeptical of a fully-integrated AI workhorse like this one.
From an energy consumption perspective and just a general concern for the human workforce, these types of AI projects are polarizing in nature.
However, Digital Optimus would be a great digital counterpart to Tesla’s physical Optimus robot, as it would be a hyper-efficient addition to any company that is looking for more production for less cost.
Musk maintains that there is no other company on Earth that will be able to do this.








