News
SpaceX’s Starlink satellite internet was tested by the US Air Force and the results are in
SpaceX President and Chief Operating Officer Gwynne Shotwell recently provided information about the company’s Starlink satellite internet constellation after a panel at the International Aeronautical Congress in Washington D.C. Shotwell spoke of a partnership with the U.S. military and just how far she believes Starlink is ahead of rival mega-constellation efforts.
While competitors are still developing very early prototypes and worrying about launch options, SpaceX has already launched 60 Starlink ‘v0.9’ satellite prototypes, 50 of which continue to successfully operate in low Earth orbit approximately half a year after launch. As part of a $29M contract awarded in late-2018, SpaceX is also working directly with the U.S. Air Force to test military applications of commercial space-based internet.
As previously reported by Teslarati, SpaceX was awarded a $29 million contract in December 2018 to collaborate with the U.S. Air Force Strategic Development Planning and Experimentation Office. Together, the organizations are testing potential military applications of Starlink satellite internet, as well as prospective constellations from other companies like Telesat.
From LEO to aircraft
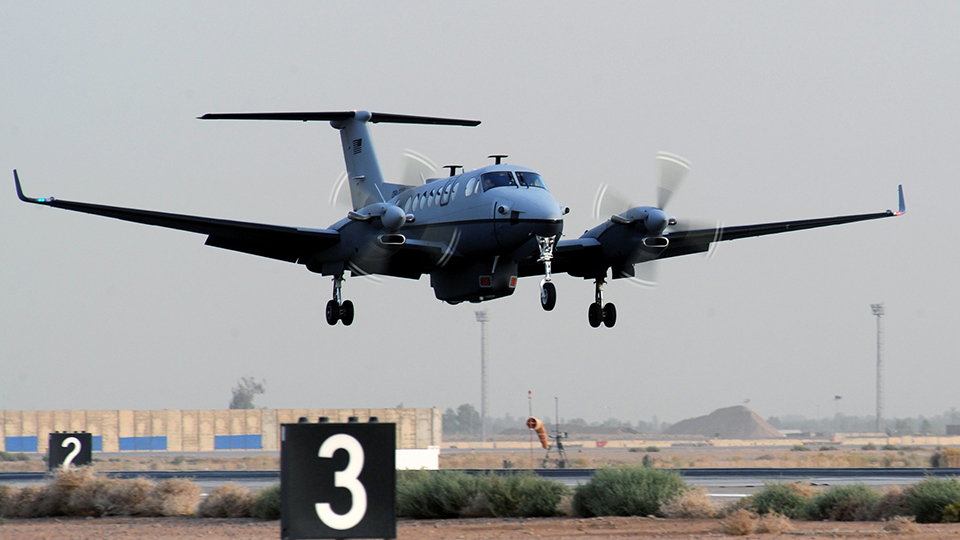

The technical viability and utility of beaming high speed, low-latency broadband internet directly into the cockpits of military aircraft is being tested under a program called Global Lightning. SpaceX has engaged the initiative and was awarded $29M to pursue development and testing, far more than any other contract recipient. In October 2019, SpaceX and the USAF began publicly discussing the latest results of that effort to test Starlink’s capabilities in the realm of in-flight connectivity. As reported by SpaceNews, SpaceX COO Gwynne Shotwell revealed that Starlink had successfully demonstrated a data link to the cockpit of a military aircraft with a bandwidth of 610 megabits per second (Mbps), equivalent to a gigabyte every ~13 seconds.
Following a previous speaking engagement on Oct. 15th at the Association of the U.S. Army’s annual conference, Shotwell and U.S. Army officials provided further insight regarding military applications of Starlink. Army officials spoke about the possibility of using Starlink satellite internet and other prospective constellations to support the military’s rapidly growing demand for high-speed communications.
During the panel with U.S. Army officials, Shotwell stated that “SpaceX is new to this forum and this service,” when addressing the possibilities that SpaceX could provide for the U.S. military. While working with the military is not a new concept to SpaceX, serving as a satellite communications provider would be unlike anything the company has yet attempted.
Up next, the USAF has plans to install Starlink terminals and test connectivity with an AC-130 gunship and a KC-135 tanker aircraft.
Falcon 9 to support frequent Starlink launches – customers and rocket reusability benefit
While Shotwell acknowledged the potential of a partnership with the US. military, she also noted that Starlink is first and foremost a commercial business meant to enhance the internet experience globally and nominally provide connectivity to anyone that wants it. She further noted that Starlink would remain an “additive to [SpaceX’s] business,” implying that it will not supersede SpaceX’s current launch service business.
Intriguingly, this is utterly counter to forecasts SpaceX has provided investors over the last several years, in which Starlink – if successful – would almost certainly come to produce one or two magnitudes more income than launch services ever could. Shotwell – speaking to a variety of US military (and Air Force) officials – may have wanted to avoid sending the message that SpaceX’s launch services business – crucial to the US military – might soon be absolutely dwarfed by Starlink revenue.
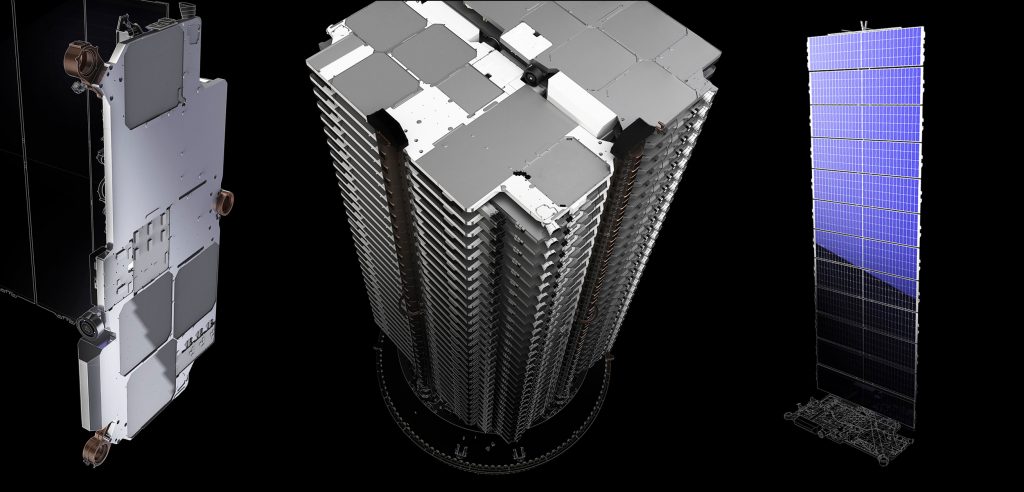

Previously hinted at by CEO Elon Musk, SpaceX hopes that revenue from Starlink will enable the company to independently fund the development and mass-production of its next-generation Starship launch vehicle, eventually enabling a permanent, large-scale human presence on Mars.
Currently, SpaceX’s Starlink plans involve several distinct phases, beginning with ~1500 satellites around 500km, another ~2900 around 1000 km, and an additional ~7500 in the 300-400 km range. Finally, SpaceX recently revealed even longer-term plans for Starlink that could involve launching up to 42,000 satellites, all in the name of expanding network coverage and bandwidth – pending, of course, consumer demand. To accomplish that feat, SpaceX will have to push rocket reusability to the absolute limits, beginning with Falcon 9 boosters and fairings and ultimately moving to Starship. According to Shotwell, “(SpaceX’s) intent is to use Starlink to push the capability of those boosters and see how many missions they can do.”
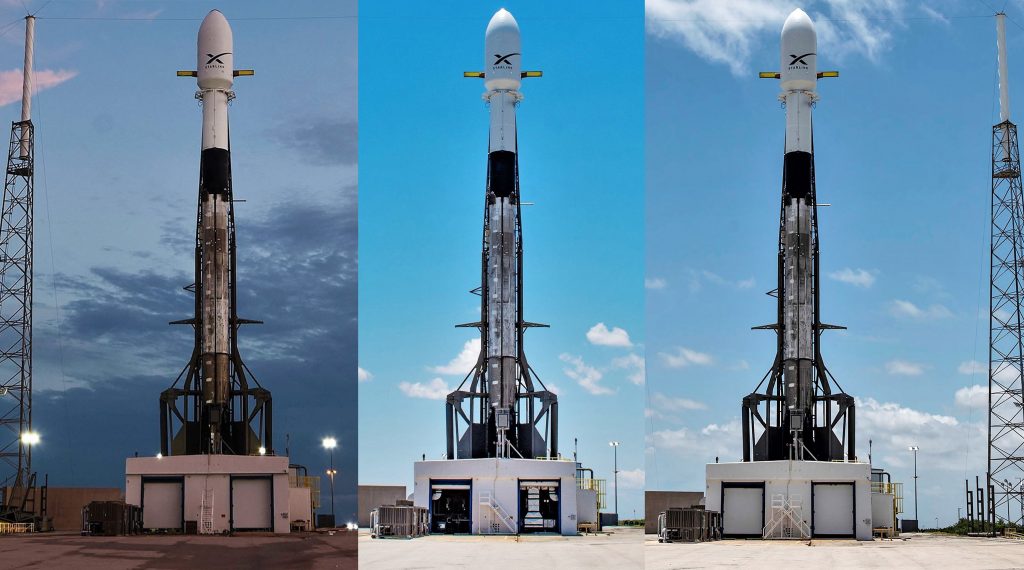

SpaceX’s next Starlink mission – also the company’s next mission and first launch in more than three months – will simultaneously attempt two new rocket reusability firsts, marking the first time that SpaceX has reused a Falcon payload fairing and the first time a single Falcon 9 booster has launched four times. Starlink-1 is scheduled to lift off no earlier than 9:55 am ET (14:55 UTC), November 11th.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

Elon Musk
Tesla Giga Berlin growth could stall if not “free from external influences”: Elon Musk
The comments were delivered in a pre-recorded video discussion.
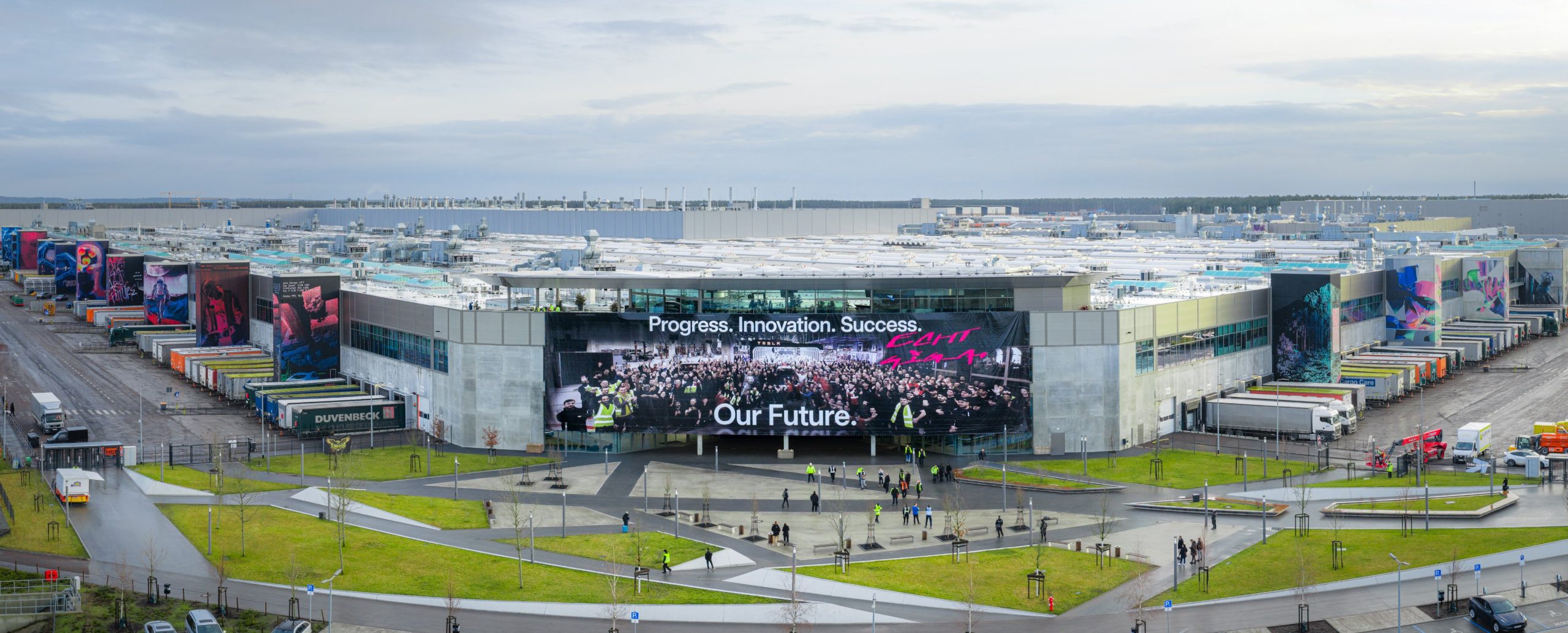

Tesla CEO Elon Musk has reportedly warned that future expansion of Gigafactory Berlin could be jeopardized if the site does not remain “free from external influences.”
Musk’s comments were delivered in a pre-recorded video discussion with employees and came at a sensitive moment for the facility, where union representation has been a recurring issue.
According to reports from Handelsblatt and Der Spiegel, citing participants at the event, Musk suggested that if Giga Berlin is no longer “free from external influences,” further expansion would become unlikely. He did not, however, hint that the plant would shut down.
While Musk did not name IG Metall directly, his remarks were widely interpreted as referencing the union, which is currently the largest faction on the works council but does not hold a majority, as noted in an electrive report.
The video conversation was conducted between Musk in Austin and Grünheide plant manager André Thierig, then played back to the workforce in Germany. Works council elections are scheduled for early March, heightening the tension between management and organized labor.
The CEO has previously voiced concerns that stronger union influence could limit Tesla’s operational flexibility and long-term strategy in Germany.
Despite the warning on expansion, Musk praised the Giga Berlin site during the same address, describing it as one of the most advanced factories worldwide and highlighting its cleanliness and team culture.
The discussion also reportedly touched on battery cell production. According to attendees cited in German media, Musk indicated that Tesla has begun ramping cell production at the site. That would mark a notable shift from earlier expectations that large-scale cell manufacturing in Brandenburg would not begin until 2027.
Elon Musk
Tesla Full Self-Driving’s newest behavior is the perfect answer to aggressive cars
According to a recent video, it now appears the suite will automatically pull over if there is a tailgater on your bumper, the most ideal solution for when a driver is riding your bumper.

Tesla Full Self-Driving appears to have a new behavior that is the perfect answer to aggressive drivers.
According to a recent video, it now appears the suite will automatically pull over if there is a tailgater on your bumper, the most ideal solution for when a driver is riding your bumper.
With FSD’s constantly-changing Speed Profiles, it seems as if this solution could help eliminate the need to tinker with driving modes from the person in the driver’s seat. This tends to be one of my biggest complaints from FSD at times.
A video posted on X shows a Tesla on Full Self-Driving pulling over to the shoulder on windy, wet roads after another car seemed to be following it quite aggressively. The car looks to have automatically sensed that the vehicle behind it was in a bit of a hurry, so FSD determined that pulling over and letting it by was the best idea:
Tesla appears to be implementing some sort of feature that will now pull over if someone is tailgating you to let the car by
Really cool feature, definitely get a lot of this from those who think they drive race cars
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 26, 2026
We can see from the clip that there was no human intervention to pull over to the side, as the driver’s hands are stationary and never interfere with the turn signal stalk.
This can be used to override some of the decisions FSD makes, and is a great way to get things back on track if the semi-autonomous functionality tries to do something that is either unneeded or not included in the routing on the in-car Nav.
FSD tends to move over for faster traffic on the interstate when there are multiple lanes. On two-lane highways, it will pass slower cars using the left lane. When faster traffic is behind a Tesla on FSD, the vehicle will move back over to the right lane, the correct behavior in a scenario like this.
Perhaps one of my biggest complaints at times with Full Self-Driving, especially from version to version, is how much tinkering Tesla does with Speed Profiles. One minute, they’re suitable for driving on local roads, the next, they’re either too fast or too slow.
When they are too slow, most of us just shift up into a faster setting, but at times, even that’s not enough, see below:
What has happened to Mad Max?
At one point it was going 32 in a 35. Traffic ahead had pulled away considerably https://t.co/bjKvaMVTNX pic.twitter.com/aaZSWmLu5v
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 24, 2026
There are times when it feels like it would be suitable for the car to just pull over and let the vehicle that is traveling behind pass. This, at least up until this point, it appears, was something that required human intervention.
Now, it looks like Tesla is trying to get FSD to a point where it just knows that it should probably get out of the way.
Elon Musk
Tesla Megapack powers $1.1B AI data center project in Brazil
By integrating Tesla’s Megapack systems, the facility will function not only as a major power consumer but also as a grid-supporting asset.
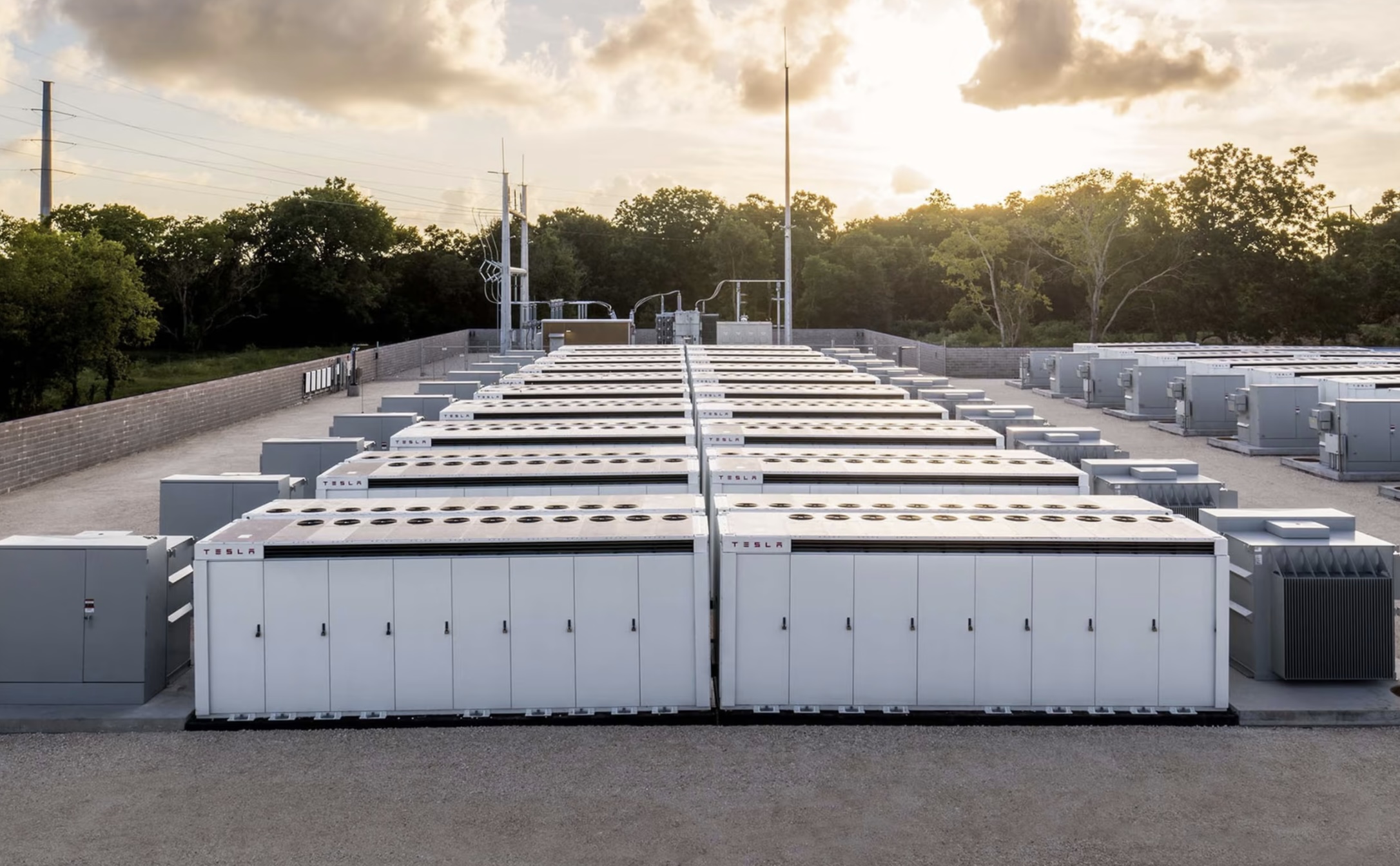

Tesla’s Megapack battery systems will be deployed as part of a 400MW AI data center campus in Uberlândia, Brazil. The initiative is described as one of Latin America’s largest AI infrastructure projects.
The project is being led by RT-One, which confirmed that the facility will integrate Tesla Megapack battery energy storage systems (BESS) as part of a broader industrial alliance that includes Hitachi Energy, Siemens, ABB, HIMOINSA, and Schneider Electric. The project is backed by more than R$6 billion (approximately $1.1 billion) in private capital.
According to RT-One, the data center is designed to operate on 100% renewable energy while also reinforcing regional grid stability.
“Brazil generates abundant energy, particularly from renewable sources such as solar and wind. However, high renewable penetration can create grid stability challenges,” RT-One President Fernando Palamone noted in a post on LinkedIn. “Managing this imbalance is one of the country’s growing infrastructure priorities.”
By integrating Tesla’s Megapack systems, the facility will function not only as a major power consumer but also as a grid-supporting asset.
“The facility will be capable of absorbing excess electricity when supply is high and providing stabilization services when the grid requires additional support. This approach enhances resilience, improves reliability, and contributes to a more efficient use of renewable generation,” Palamone added.
The model mirrors approaches used in energy-intensive regions such as California and Texas, where large battery systems help manage fluctuations tied to renewable energy generation.
The RT-One President recently visited Tesla’s Megafactory in Lathrop, California, where Megapacks are produced, as part of establishing the partnership. He thanked the Tesla team, including Marcel Dall Pai, Nicholas Reale, and Sean Jones, for supporting the collaboration in his LinkedIn post.








