News
Electric trucks from large to small vital to Tesla’s Master Plan
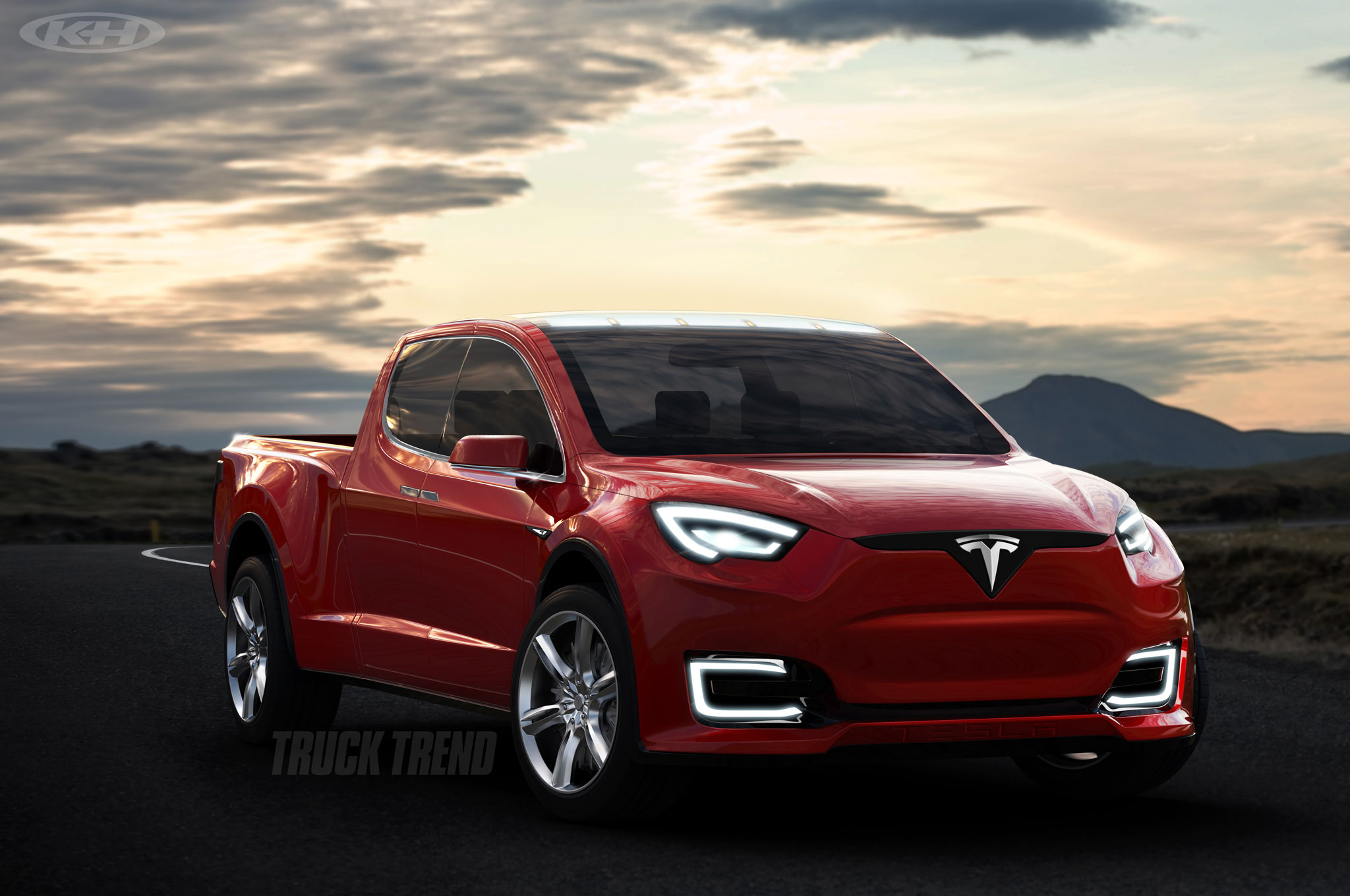

It all goes back to Elon Musk’s original secret Master Plan from 2006, when the billionaire entrepreneur issued his famous vision of the future: “[T]he overarching purpose of Tesla Motors (and the reason I am funding the company) is to help expedite the move from a mine-and-burn hydrocarbon economy towards a solar electric economy, which I believe to be the primary, but not exclusive, sustainable solution.”
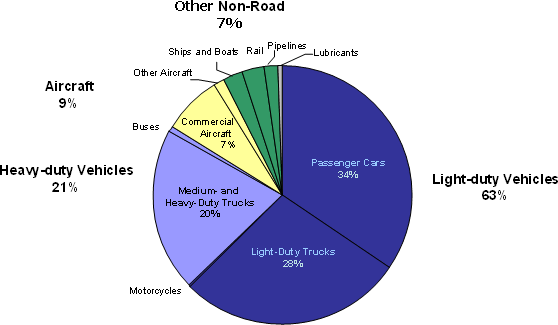
Musk made an executive decision right from the beginning to target customers whose opinions influence others by building premium electric cars that would make people sit up and take notice. Until Tesla came along, electric cars were little more than glorified golf carts. But if Tesla is going to make significant progress toward its ultimate goal, it is going to have to make electric trucks as well as passenger cars. Trucks are responsible for about 50% of all emissions created by the transportation sector according to the EPA. It’s no wonder Musk’s follow up plan calls for a zero emissions Tesla targeted at the mid to heavy duty truck segment.
The Tesla Plan
“In addition to consumer vehicles, there are two other types of electric vehicle needed: heavy-duty trucks and high passenger-density urban transport. Both are in the early stages of development at Tesla and should be ready for unveiling next year,” outlines Musk in his Master Plan Part Deux.
Aaron Turpen previously gave us an excellent analysis of what characteristics a Tesla pickup would need to have in order to be successful. He set out in detail what Tesla would need to do to build such a truck.
- V8-like performance including roughly 400 hp and 380 lb-ft
- Extended and four-door cab offerings
- Cargo bed size of 5.5 feet with option for 7 feet
- Towing capacity of about 10,000 pounds
- Payload capacity of 1/2 ton to 3,000 pounds
- 4×4 capability
- Driving range, under load, of at least 150 miles
- Conventional styling and appeal
How is Tesla going to make batteries with the energy and power needed to move such heavy vehicles? The Powerwall may offer clues. Just one year after it was introduced, Tesla brought its second generation version to market with roughly double the capacity of the original. Tesla doesn’t reveal very much about its ongoing battery research programs, other than to say that improvements of between 5 and 7 percent a year are anticipated as it ramps up production at the Gigafactory.
One assumption is that batteries for trucks will be significantly different from those used on its passenger cars, with more focus on energy and less focus on power. While a Tesla pickup that breaks the 3 second 0-60 barrier would be very cool, that sort of acceleration would have little relevance to how a truck gets used in daily driving.
When it comes to trucks that haul freight, it’s possible that the company has some sort of battery swapping plan in mind at truck stops along major transportation routes. Another approach would be to simply swap tractors at designated service areas much the way Formula E drivers swap cars during a race. Tesla could own the trucks and lease them to freight companies. The idea is as old as the Pony Express.
What About The Competition?
While Tesla is busy planning its truck strategy, other companies are chasing the same low emissions dream. Most of them rely on some form of range extender engine to build a truck that has low emissions but is cost competitive. The most promising of those ventures may be from Workhorse, which claims it will have a full size plug-in hybrid pickup truck with dual motors on the market by 2018. It uses the two cylinder range extender engine from the BMW i3 REx to provide electricity to the battery when needed. A rendering of the truck by Australia’s Motoring shows a truck that is purposeful rather than svelte in its design.
Delivery and cargo vans are another target market. Four large cities — Mexico City, Paris, Madrid, and Athens — announced their intention to ban all diesel powered vehicles from their streets by 2025. Many of the medium duty trucks used to deliver food and consumer goods to city dwellers are powered by diesel engines, especially in Europe.
Deutsche Post, known globally as DHL, is one of the largest parcel delivery companies in the world. It is working hard to reduce its carbon footprint but could not find an all electric van suitable for its needs. So it built its own. “We designed it as a tool. So the fit and finish does not need to be as good as in a passenger car,” Win Neidlinger, director of business development at Deutsche Post tells Fortune. “It did not cost billions to develop and produce. You will not believe how cheap it is to make.” The company now plans to become a manufacturer and start selling the vans, which it calls StreetScooters, to customers in 2017.
UPS is also in the delivery business and is a world leader in testing alternative fuels and alternative powertrains in its trucks. It has invested more than $750 million in alternative fuel and advanced technology vehicles since 2009. UPS now has 7,700 low emission vehicles in its “rolling laboratory” test fleet and is evaluating vehicles that run on natural gas, renewable natural gas, and propane according to Electric Cars Report.
It also is using electric powertrains in some of its vehicles. A version of the Workhorse plug-in hybrid range extender system is being tested in several of its delivery vans. It is also thinking small when it comes to what is known in the industry as the “last mile” conundrum. How do companies like UPS create nimble, zero emissions vehicles that can access congested urban areas? One solution being tried in Hamburg, Germany and Portland, Oregon is a hybrid electric tricycle called the eBike. It has a battery and electric motor and can move using pedal power, electric power, or a combination of both.

Photo credit: UPS
Some of the biggest polluters are garbage and trash hauling trucks. Because the stop and start hundreds of times a day, their diesel engines are constant spewing toxic pollutants into the atmosphere. While their total numbers are small, they discharge a disproportionate amount of emissions to the atmosphere. Taming the emissions from beasts would be an important step forward.
Ian Wright, a Tesla co-founder and former board member, thinks he has a solution. His company, Wrightspeed, builds heavy trucks powered solely by electricity but with a twist. Wright and his engineering staff have invented a small natural gas powered turbine that acts as a range extender engine. He claims his turbine operates so cleanly, it does not require a catalytic converter to meet California’s strict tailpipe emissions laws.
Salt Lake City start-up Nikola Motors recently revealed its idea for a 1000 HP low emissions electric truck called the Nikola One. Sleek and futuristic, it relies on battery power to turn its six electric motors but also has an onboard hydrogen fuel cell that is says will give the tractor a range of 800 to 1000 miles. The company says it has over a billion dollars worth of reservations in hand. While it did present a full size prototype at the reveal, many are taking a wait and see attitude toward Nikola Motors, which has no factory at the present time but claims it will begin production in 2018.
Summary
Trucks will play an important role in reducing global emissions from the transportation sector. A recent report from Navigant Research predicts annual sales of electric trucks — including hybrids and plug-in hybrids — will increase by a factor of ten over the next decade. From 31,000 worldwide today, Navigant says more than 332,000 electric trucks will be sold annually by 2026. That’s a big market for manufacturers to target.
Tesla has refused to consider any sort of range extender device for its cars, but solving the problems of building low emissions trucks for delivering freight and cargo across long distances may make such things a necessity. The need is great and the time is short. If hybrid trucks are what are needed, even as a stop gap measure while battery technology catches up with energy and cost constraints, that would be important for a world struggling to limit carbon emissions.

News
Tesla adds awesome new driving feature to Model Y
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.

Tesla is adding an awesome new driving feature to Model Y vehicles, effective on Juniper-updated models considered model year 2026 or newer.
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.
Tesla writes in the release notes for the feature:
“Your Tesla now provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.”
🚨 Tesla has added a new “Comfort Braking” update with 2026.8
“Your Tesla provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.” https://t.co/afqCpBSVeA pic.twitter.com/C6MRmzfzls
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
Interestingly, we’re not too sure what catalyzed Tesla to try to improve braking smoothness, because it hasn’t seemed overly abrupt or rough from my perspective. Although the brake pedal in my Model Y is rarely used due to Regenerative Braking, it seems Tesla wanted to try to make the ride comfort even smoother for owners.
There is always room for improvement, though, and it seems that there is a way to make braking smoother for passengers while the vehicle is coming to a stop.
This is far from the first time Tesla has attempted to improve its ride comfort through Over-the-Air updates, as it has rolled out updates to improve regenerative braking performance, handling while using Full Self-Driving, improvements to Steer-by-Wire to Cybertruck, and even recent releases that have combatted Active Road Noise.
Tesla holds a unique ability to change the functionality of its vehicles through software updates, which have come in handy for many things, including remedying certain recalls and shipping new features to the Full Self-Driving suite.
Tesla seems to have the most seamless OTA processes, as many automakers have the ability to ship improvements through a simple software update.
We’re really excited to test the update, so when we get an opportunity to try out Comfort Braking when it makes it to our Model Y.
News
Tesla finally brings a Robotaxi update that Android users will love
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android.

Tesla is finally bringing an update of its Robotaxi platform that Android users will love — mostly because it seems like they will finally be able to use the ride-hailing platform that the company has had active since last June.
Based on a decompile of software version 26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app, Tesla looks to be ready to roll out access to Android users.
According to the breakdown, performed by Tesla App Updates, the company is preparing to roll out an Android version of the app as it is developing several features for that operating system.
🚨 It looks like Tesla is preparing to launch the Robotaxi app for Android users at last!
A decompile of v26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app shows some progress on the Android side for Robotaxi 🤖 🚗 https://t.co/mThmoYuVLy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android:
“Strings like notification_channel_robotaxid_trip_name and android_native_alicorn_eta_text show exactly how Tesla plans to replicate the iOS Live Activities experience. Instead of standard push alerts, Android users are getting a persistent, dynamically updating notification channel.”
This is a big step forward for several reasons. From a face-value perspective, Tesla is finally ready to offer Robotaxi to Android users.
The company has routinely prioritized Apple releases because there is a higher concentration of iPhone users in its ownership base. Additionally, the development process for Apple is simply less laborious.
Tesla is working to increase Android capabilities in its vehicles
Secondly, the Robotaxi rollout has been a typical example of “slowly then all at once.”
Tesla initially released Robotaxi access to a handful of media members and influencers. Eventually, it was expanded to more users, so that anyone using an iOS device could download the app and hail a semi-autonomous ride in Austin or the Bay Area.
Opening up the user base to Android users may show that Tesla is preparing to allow even more users to utilize its Robotaxi platform, and although it seems to be a few months away from only offering fully autonomous rides to anyone with app access, the expansion of the user base to an entirely different user base definitely seems like its a step in the right direction.
News
Lucid unveils Lunar Robotaxi in bid to challenge Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
Lucid’s Lunar robotaxi is gunning for Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering.jpg)
Lucid Group pulled back the curtain on its purpose-built autonomous robotaxi platform dubbed the Lunar Concept. Announced at its New York investor day event, Lunar is arguably the company’s most ambitious concept yet, and a direct line of sight toward the autonomous ride haling market that Tesla looks to control.
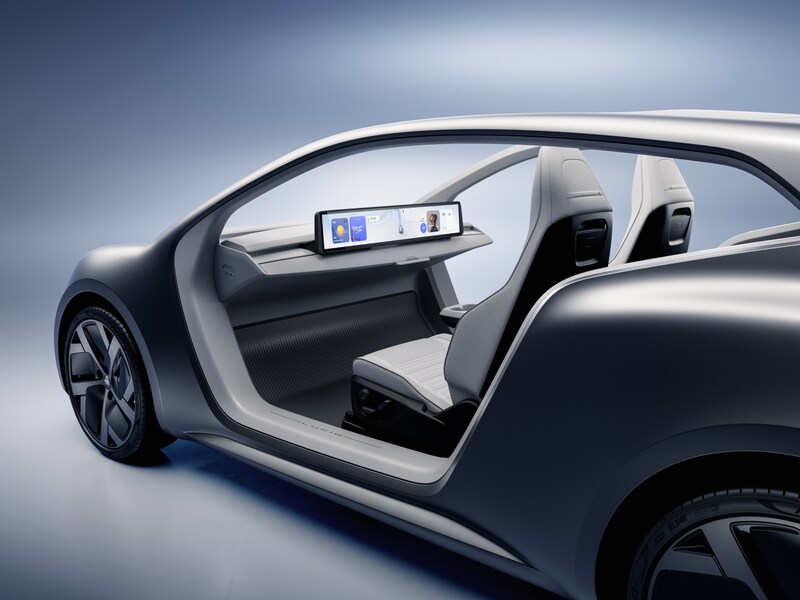

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
A comparison to Tesla’s Cybercab is unavoidable. The concept of a Tesla robotaxi was first introduced by Elon Musk back in April 2019 during an event dubbed “Autonomy Day,” where he envisioned a network of self-driving Tesla vehicles transporting passengers while not in use by their owners. That vision took another major step in October 2024 when, Musk unveiled the Cybercab at the Tesla “We, Robot” event held at Warner Bros. Studios in Burbank, California, where 20 concept Cybercabs autonomously drove around the studio lot giving rides to attendees.
Fast forward to today, and Tesla’s ambitions are finally materializing, but not without friction. As we recently reported, the Cybercab is being spotted with increasing frequency on public roads and across the grounds of Gigafactory Texas, suggesting that the company’s road testing and validation program is ramping meaningfully ahead of mass production. Tesla already operates a small scale robotaxi service in Austin using supervised Model Ys, but the Cybercab is designed from the ground up for high-volume, low-cost production, with Musk stating an eventual goal of producing one vehicle every 10 seconds.
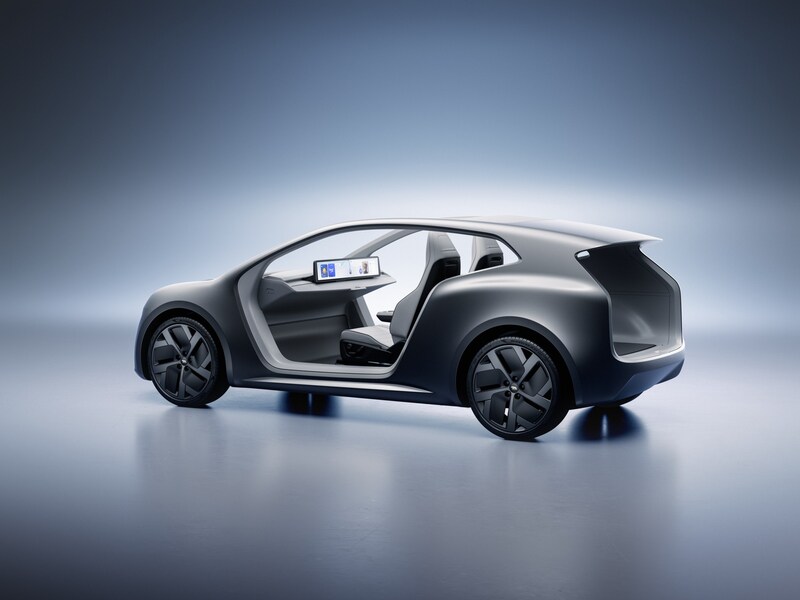

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
Into this landscape steps Lucid’s Lunar. Built on the company’s all-new Midsize EV platform, which will also underpin consumer SUVs starting below $50,000. The Lunar mirrors the Cybercab’s core philosophy of having two seats, no driver controls, and a focus on fleet economics. The platform introduces Lucid’s redesigned Atlas electric drive unit, engineered to be smaller, lighter, and cheaper to manufacture at scale.
Unlike Tesla’s strategy of building its own ride hailing network from scratch, Lucid is partnering with Uber. The companies are said to be in advanced discussions to deploy Midsize platform vehicles at large scale, with Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi publicly backing Lucid’s engineering credentials and autonomous-ready architecture.
In the investor day event, Lucid also outlined a recurring software revenue model, with an in-vehicle AI assistant and monthly autonomous driving subscriptions priced between $69 and $199. This can be seen as a nod to the software revenue stream that Tesla has long championed with its Full Self-Driving subscription.
Tesla’s Cybercab is targeting a price point below $30k and with operating costs as low as 20 cents per mile. But with regulatory hurdles still ahead, the window for competition is open. Lucid’s Lunar may not have a launch date yet, but it arrives at a pivotal moment, and when the robotaxi race is no longer viewed as hypothetical. Rather, every serious EV player needs to come to bat on the same plate that Tesla has had countless practice swings on over the last seven years.




![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)





