

News
Why The Boring Company’s $10 million dollars per mile price tag is a game changer
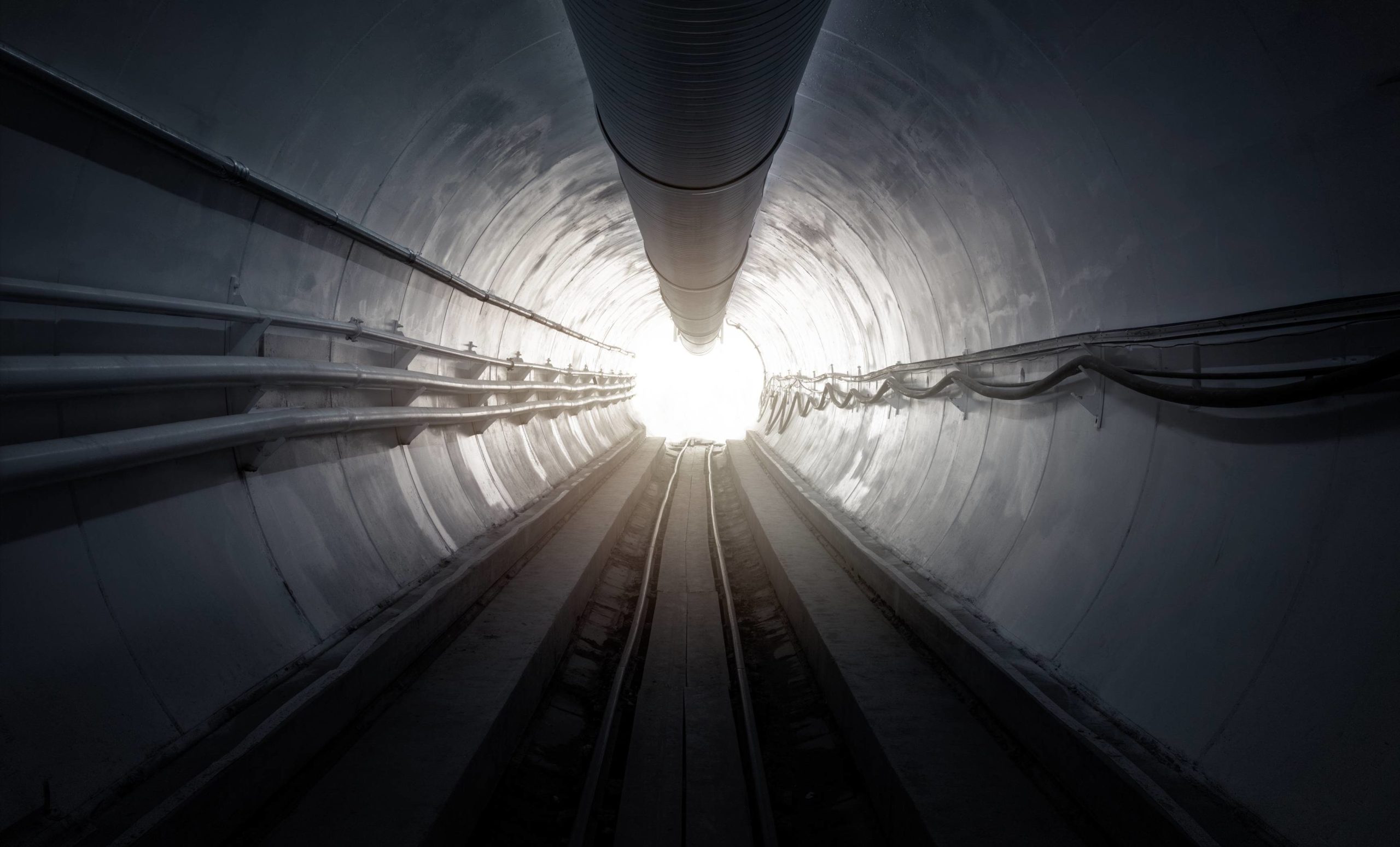
With The Boring Company, Elon Musk hopes to overcome the pitfalls that drive up the costs of underground rail transport construction using good old-fashioned innovation with a dash of Silicon Valley startup dust (dirt?). Currently, most U.S. local and state governments (i.e., tax payers) hand over an average of $200-$500 million dollars per mile to construct a subway system, with hundreds of millions more per mile a common occurrence and even a $1 billion dollars per mile price tag having happened a few times already. The reasons for such expense seems to be multi-faceted and stubborn: regulations, unions, and project management. So, when the Tesla CEO and Boring Company founder cited $10 million dollars as the final price of their mile-long demonstration tunnel, including internal infrastructure, lighting, comms/video, safety systems, ventilation, and tracks, he seemed to be threatening to completely upend yet another industry, this one having been at the core of transportation for nearly 200 years.
“I like trains, by the way. I really like trains a lot,” Musk assured his press audience at the company’s recent demonstration tunnel opening event. The Boring Company (TBC) began as a Twitter discussion wherein the tech mogul was venting about “soul-destroying” traffic in Los Angeles. A concept animation followed soon after (as well as hats and not-a-flamethrowers), imagining a transportation system where cars would be shuttled around at high speeds underground on electric skates. Ideas flowed, tunneling began, and the result of all those efforts went on display December 18, 2018, demo rides included. A rideable 1.14 mile tunnel had been constructed from Crenshaw Boulevard across from the Hawthorne, California headquarters of SpaceX, Musk’s private rocket company, to the 120th Street/Prairie Avenue crossroad of Hawthorne.
Around this time last year, Brian Rosenthal of the New York Times exposed several astonishing factors that added up to a $3.5 billion dollars per mile cost to construct a 3.5 mile tunnel to connect Grand Central Terminal to the Long Island Rail Road in New York City, aka the “East Side Access”. An infamous “first”, this price tag is 7 times more than the average of anywhere else in the world. A combination of trade union, construction company, and consulting firm practices, including significant staff redundancy, bred an environment ripe for cost pile-ups, and both incompetence and the lack of oversight within New York’s Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) added significantly to the issue. While the specific amount of money spent made the system’s cost unique in the world, the general underlying issues were not uncommon.
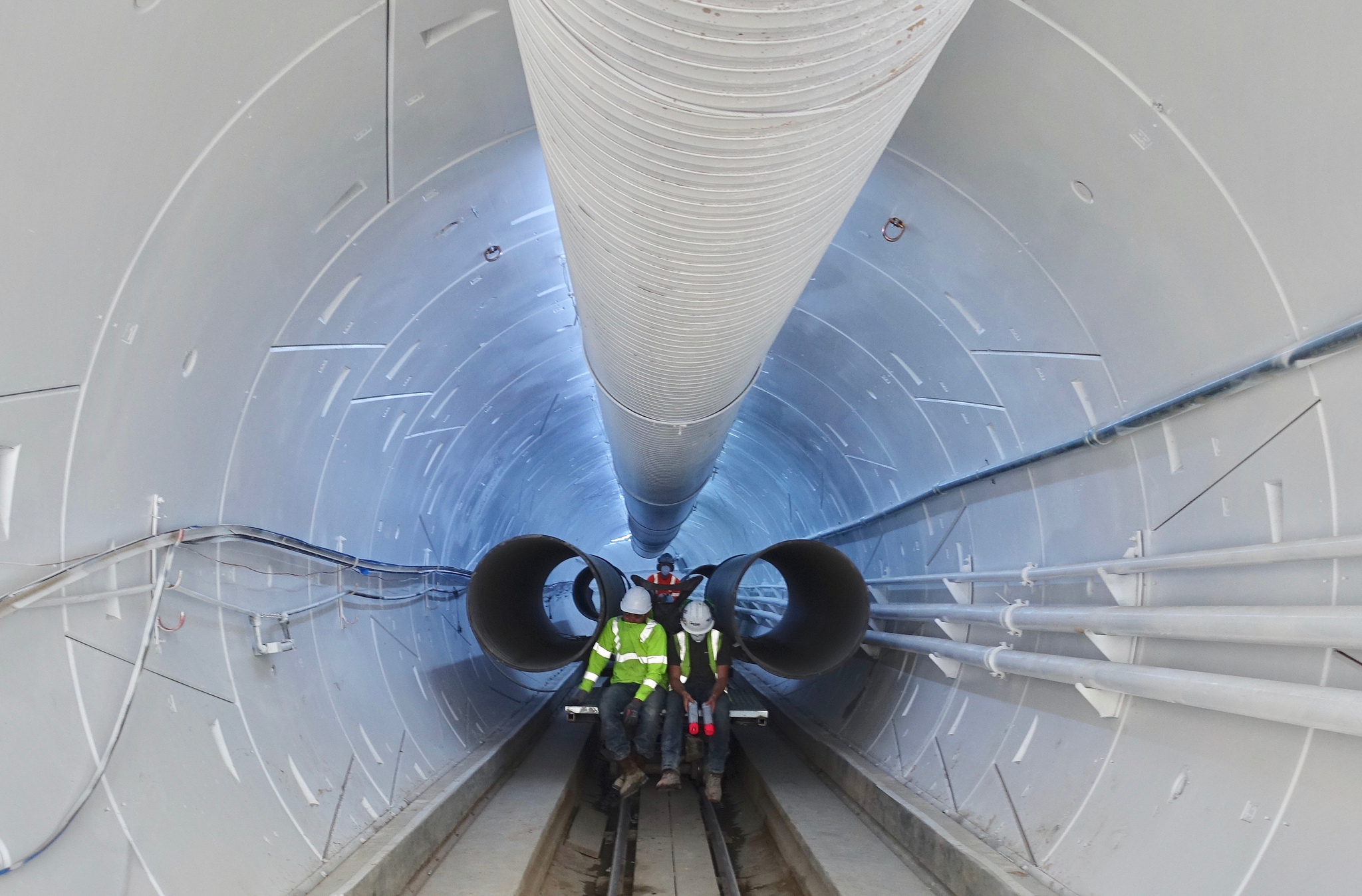

New York may be an exception to the already high-cost of rail construction rule, but there’s the rub: It’s already incredibly expensive. As documented in numerous articles by Alon Levy, an independent journalist whose 2011 blog post on the topic inspired the research that eventually led to the Times piece, $100-$500 million dollars per mile is a typical cost for building railed transporation worldwide. “These are crazy numbers,” Musk exclaimed at the tunnel opening event after summarizing the multiple billions of dollars short tunneling projects cost to complete in L.A. and New York. If the building cost wasn’t enough sticker shock, it gets worse: The daily operating costs of rail systems in the U.S. exceed the amount earned.
Another metric that is used to estimate the true cost of rail construction is cost per rider. After the time and money is spent building a public rail system, it needs to be staffed and repaired, expenses which are difficult to match with revenue without a large number of riders. As cited by Alon Levy in an article Elon Musk tweeted recently, New York’s Second Avenue Subway will cost $25,000 per rider to complete 200,000 trips per day. In Los Angeles, the Purple Line will cost $45,000 per rider for 150,000 trips per day as will Boston’s Green Line Extension for 52,000 trips. Looking at rider fares, New York loses a bit less than $1 per ride taken and L.A. loses over $2 per ride.
So, how will The Boring Company “do” underground transportation system building better than the traditional, money-heavy methods? To put it simply: Be efficient.
Building a better mouse snail trap
They’ve designed their tunneling machines to bore faster and more efficiently. While the first generation machine is conventional and named Godot after the Samuel Backett play, Waiting for Godot due to the length of time it took to understand the machine’s functionality and assemble it, two other improved generations will be part of the Boring family.
The second generation machine, named “Line-Storm” after a Robert Frost love poem with the same phrase in its title that’s about overcoming hardships, is a conventional boring machine that has been highly modified. It uses a redesigned cutting head that takes in significantly more dirt and is 2 times faster than Godot.
The third generation machine, named “Prufrock”, will be a ground-up, fully designed TBC machine that’s 15 times better than the next best boring system, and that means 15 times faster than the next best machine out there, period.
Improved construction practices and project management
During construction, TBC reinforced tunnel segments as they were dug, those reinforcements being created on-site out of materials comprising 70% of the dirt dug and the remaining 30% primarily cement. This recycled material, as-you-go system enabled quick construction with cost efficiency, the demo tunnel taking 2 years almost to the day from Musk’s initial Tweet that inspired the undertaking.
Function-focused engineering
TBC’s tunnels are smaller than the typical underground rail system because they’re designed for specific types of vehicles that are smaller than traditional transports (autonomous electrics) and don’t require extra space for maintenance. This in itself reduces costs by 3-4 times.
Although The Boring Company has the advantage of being the new kid on the block whose founder has a unique background in shaking up traditional systems, there may still be a few hangups that will never quite go away. Anything involving the general public, especially public transit, will have serious bureaucracy involved. To achieve the company’s mile-long demo track feat, it had to face the extreme regulatory environment of Los Angeles. California overall has earthquakes, is a methane zone, and has oil and gas fields, all which add to a long list of rules to be followed for any construction projects to commence. “The amount of paperwork we had to go through to do this was enormous,” Musk said at TBC’s recent event.
Additionally, a lawsuit filed last year by the Brentwood Residents Coalition and the Sunset Coalition objecting to the company’s Sepulveda tunnel eventually led to their abandonment of that leg of the demonstration project. The coalitions primarily alleged that TBC was skirting environmental review requirements by “chopping large projects into smaller pieces that taken individually appear to have no significant environmental impacts”, citing a conceptual map the company released showing its planned Los Angeles tunnel system. Musk hasn’t let these hurdles damage his confidence, however. While speaking with press at TBC’s opening event, he added his own spin to the Broadway mantra (and Frank Sinatra hit, “New York, New York”) about “making it” there : “If you can build a tunnel in L.A., you can build it anywhere.”
As CEO of an innovative electric car company and a commercial rocket company set on sending humans to Mars, Musk is known as an industry disruptor. Even if the cost of boring tunnels for public transportation projects rises somewhat above the $10 million per mile price demonstrated with the LA/Hawthorne tunnel, it will be still be well under the typical costs in the boring industry. It’s obvious already that a potential disruption is underway. “We have people hounding us to invest nonstop…it’s kinda ridiculous how much interest we’ve had in investing in Boring Company,” Musk stated at the tunnel unveiling. Steve Davis, president of the company, added that they receive “greater than 5 and less than 20 requests per week from different municipalities and stakeholders.”
Also in the works for the tunneling newcomers: A transport line connecting downtown Chicago to Chicago O’Hare International Airport. The company won a contract to build a transport system for the city’s fliers in June 2017, and ground breaking is planned for sometime in the next few months. The Boring Company’s calendar still includes plans for an “urban loop system” as well, an underground network of pod-type buses for pedestrians and cyclists connecting numerous points throughout city centers.

News
Tesla adds awesome new driving feature to Model Y
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.

Tesla is adding an awesome new driving feature to Model Y vehicles, effective on Juniper-updated models considered model year 2026 or newer.
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.
Tesla writes in the release notes for the feature:
“Your Tesla now provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.”
🚨 Tesla has added a new “Comfort Braking” update with 2026.8
“Your Tesla provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.” https://t.co/afqCpBSVeA pic.twitter.com/C6MRmzfzls
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
Interestingly, we’re not too sure what catalyzed Tesla to try to improve braking smoothness, because it hasn’t seemed overly abrupt or rough from my perspective. Although the brake pedal in my Model Y is rarely used due to Regenerative Braking, it seems Tesla wanted to try to make the ride comfort even smoother for owners.
There is always room for improvement, though, and it seems that there is a way to make braking smoother for passengers while the vehicle is coming to a stop.
This is far from the first time Tesla has attempted to improve its ride comfort through Over-the-Air updates, as it has rolled out updates to improve regenerative braking performance, handling while using Full Self-Driving, improvements to Steer-by-Wire to Cybertruck, and even recent releases that have combatted Active Road Noise.
Tesla holds a unique ability to change the functionality of its vehicles through software updates, which have come in handy for many things, including remedying certain recalls and shipping new features to the Full Self-Driving suite.
Tesla seems to have the most seamless OTA processes, as many automakers have the ability to ship improvements through a simple software update.
We’re really excited to test the update, so when we get an opportunity to try out Comfort Braking when it makes it to our Model Y.
News
Tesla finally brings a Robotaxi update that Android users will love
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android.

Tesla is finally bringing an update of its Robotaxi platform that Android users will love — mostly because it seems like they will finally be able to use the ride-hailing platform that the company has had active since last June.
Based on a decompile of software version 26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app, Tesla looks to be ready to roll out access to Android users.
According to the breakdown, performed by Tesla App Updates, the company is preparing to roll out an Android version of the app as it is developing several features for that operating system.
🚨 It looks like Tesla is preparing to launch the Robotaxi app for Android users at last!
A decompile of v26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app shows some progress on the Android side for Robotaxi 🤖 🚗 https://t.co/mThmoYuVLy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android:
“Strings like notification_channel_robotaxid_trip_name and android_native_alicorn_eta_text show exactly how Tesla plans to replicate the iOS Live Activities experience. Instead of standard push alerts, Android users are getting a persistent, dynamically updating notification channel.”
This is a big step forward for several reasons. From a face-value perspective, Tesla is finally ready to offer Robotaxi to Android users.
The company has routinely prioritized Apple releases because there is a higher concentration of iPhone users in its ownership base. Additionally, the development process for Apple is simply less laborious.
Tesla is working to increase Android capabilities in its vehicles
Secondly, the Robotaxi rollout has been a typical example of “slowly then all at once.”
Tesla initially released Robotaxi access to a handful of media members and influencers. Eventually, it was expanded to more users, so that anyone using an iOS device could download the app and hail a semi-autonomous ride in Austin or the Bay Area.
Opening up the user base to Android users may show that Tesla is preparing to allow even more users to utilize its Robotaxi platform, and although it seems to be a few months away from only offering fully autonomous rides to anyone with app access, the expansion of the user base to an entirely different user base definitely seems like its a step in the right direction.
News
Lucid unveils Lunar Robotaxi in bid to challenge Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
Lucid’s Lunar robotaxi is gunning for Tesla’s Cybercab in the autonomous ride hailing race
![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering.jpg)
Lucid Group pulled back the curtain on its purpose-built autonomous robotaxi platform dubbed the Lunar Concept. Announced at its New York investor day event, Lunar is arguably the company’s most ambitious concept yet, and a direct line of sight toward the autonomous ride haling market that Tesla looks to control.
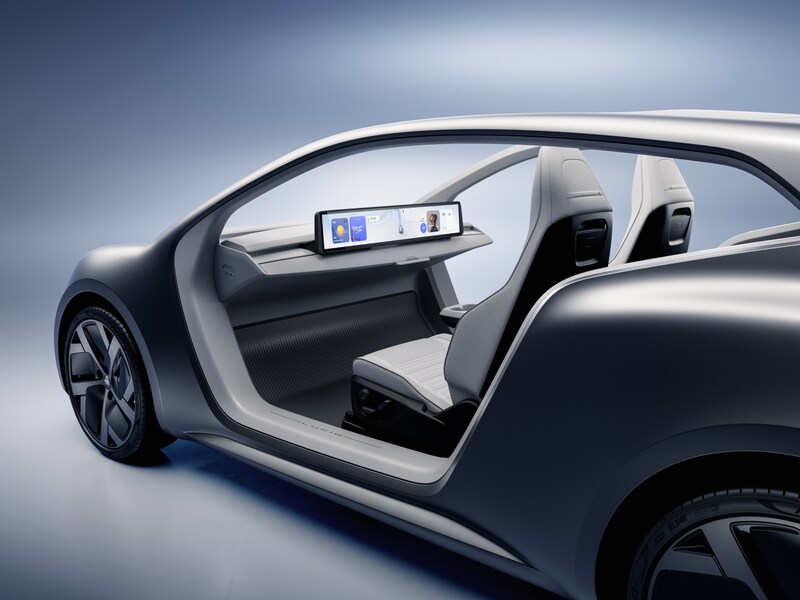

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
A comparison to Tesla’s Cybercab is unavoidable. The concept of a Tesla robotaxi was first introduced by Elon Musk back in April 2019 during an event dubbed “Autonomy Day,” where he envisioned a network of self-driving Tesla vehicles transporting passengers while not in use by their owners. That vision took another major step in October 2024 when, Musk unveiled the Cybercab at the Tesla “We, Robot” event held at Warner Bros. Studios in Burbank, California, where 20 concept Cybercabs autonomously drove around the studio lot giving rides to attendees.
Fast forward to today, and Tesla’s ambitions are finally materializing, but not without friction. As we recently reported, the Cybercab is being spotted with increasing frequency on public roads and across the grounds of Gigafactory Texas, suggesting that the company’s road testing and validation program is ramping meaningfully ahead of mass production. Tesla already operates a small scale robotaxi service in Austin using supervised Model Ys, but the Cybercab is designed from the ground up for high-volume, low-cost production, with Musk stating an eventual goal of producing one vehicle every 10 seconds.
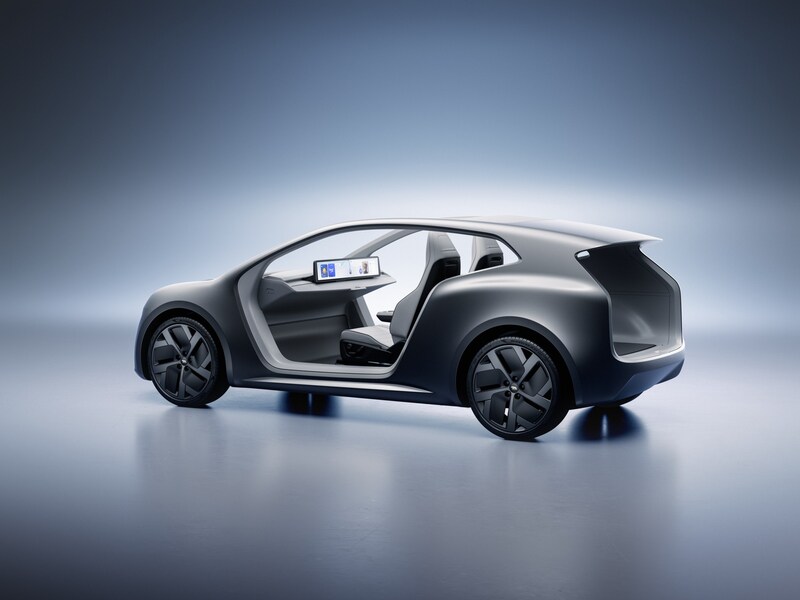

At Lucid Investor Day 2026, the company introduced Lunar, a purpose-built robotaxi concept based on the Midsize platform.
Into this landscape steps Lucid’s Lunar. Built on the company’s all-new Midsize EV platform, which will also underpin consumer SUVs starting below $50,000. The Lunar mirrors the Cybercab’s core philosophy of having two seats, no driver controls, and a focus on fleet economics. The platform introduces Lucid’s redesigned Atlas electric drive unit, engineered to be smaller, lighter, and cheaper to manufacture at scale.
Unlike Tesla’s strategy of building its own ride hailing network from scratch, Lucid is partnering with Uber. The companies are said to be in advanced discussions to deploy Midsize platform vehicles at large scale, with Uber CEO Dara Khosrowshahi publicly backing Lucid’s engineering credentials and autonomous-ready architecture.
In the investor day event, Lucid also outlined a recurring software revenue model, with an in-vehicle AI assistant and monthly autonomous driving subscriptions priced between $69 and $199. This can be seen as a nod to the software revenue stream that Tesla has long championed with its Full Self-Driving subscription.
Tesla’s Cybercab is targeting a price point below $30k and with operating costs as low as 20 cents per mile. But with regulatory hurdles still ahead, the window for competition is open. Lucid’s Lunar may not have a launch date yet, but it arrives at a pivotal moment, and when the robotaxi race is no longer viewed as hypothetical. Rather, every serious EV player needs to come to bat on the same plate that Tesla has had countless practice swings on over the last seven years.


![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)





