News
Tesla Full Self-Driving could soon be allowed in Germany, gov approves legislation aimed at autonomous driving

The national Parliament of the Federal Republic of Germany decided on Thursday to change an existing traffic law that had prohibited vehicles from being engaged in autonomous mode. Drawing on votes from both the Social Democratic Party (SPD) and the Christian Democratic Union (CSU), the Bundestag has agreed to allow fully autonomous driving vehicles to travel on Germany’s streets. The (translated) law reads, in part,
“During vehicle driving, the driver may turn away from traffic and vehicle control by means of highly automated or fully automated driving function… [but must] immediately [assume control] if he recognizes that the conditions for the intended use of the highly or fully automated driving functions no longer exist… even if he does not control the vehicle in the context of the intended use of this function.”
The law provides a balance between driver responsibility in the event of traffic incident and the ability of the the driver to release control of the vehicle to a control system, depending on situation and duration. The driver must retain the capacity to reassume control as well as to deactivate the control system. All vehicles with autonomous driving systems would have a “black box” data storage system, which would assist in determining fault in the event of an accident.
The new German law supersedes the 1968 “Vienna Convention on Road Traffic,” which specified that human drivers must have full control over their vehicle at any time. Of course, at that time of that law’s implementation, autonomous vehicles had not yet been introduced.
Tensions were high immediately preceding the vote, according to Germany’s golem.de newspaper, which described the level of autonomy to be permitted as “highly automated and fully automatic vehicles.” SPD deputy Kirsten Lühmann accusing the body of assigning drivers the roles of “experimental rabbits for new technology.” Stephan Kühn, the Green party deputy, also disagreed with the extent of the law. “It is not enough just to formulate in the justification of the legal text what the driver is allowed to do without worry while the computer is driving the car. This must be re-written into the law itself.”
The SPD defended the amendments as sound and timely.
German Federal Minister of Transport Alexander Dobrindt (CSU) had offered draft legislation for the new law in February, but it received violent criticism and underwent significant revision, particularly around data protection regulations. At the beginning of this week’s debate, he envisioned Germany as having “the most modern road traffic law in the world.” Dobrindt has rationalized the law as providing value added software innovation that could be homegrown in Germany and Europe. With the new systems, he said, will come increased traffic safety, fewer traffic jams, and reduced environmental pollution [emphasis added].
Germany is a forerunner for European autonomous driving, with some sections of public highways already designated as live testing zones. The Institute for the German Economy calculates that Germany has registered 58% of all global patents in autonomous driving since 2010.
The approved revision states that the owner of the car is still liable for actions taken while under autonomous mode, as prescribed by section 7 of the Road Traffic Act (Hazard Liability). Specific German autonomous driving regulations have not yet been established; those will come alongside international regulations and definitions and will likely change, too, as technological development in autonomous driving continues to progress. Like so many in the auto industry today, German engineers, scientists, and regulators are in a race to figure out the details of how autonomous cars will function so that they can be market ready by the early 2020’s.
Of course, Elon Musk, Tesla’s CEO, has stated that his company’s electric vehicles will have autonomous capability by the second half of 2017. The Society of Automotive Engineers has identified different levels of autonomy, ranging from 0 to Level 5, with Level 5 signifying that a vehicle can drive itself at all times under all conditions and need no input from a human. Level 4 autonomy refers to a vehicle that can be autonomous almost all the time, within determined parameters, as seems to be outlined by the Bundestag.
Interestingly, according to Musk’s statements, Teslas may soon be able to approach Level 4. That would make Tesla R&D far ahead of any German innovation currently underway.
With a bicameral parliament, Germany has two chambers: the Bundestag (lower house) and the Bundesrat (Federal Council or upper house). Both chambers can initiate legislation, and most bills must be approved by both chambers, as well as the executive branch, before becoming law. Now that the autonomous driving legislation has been approved by the Bundestag, it will go before the Federal Council. Coalition forces feel confident that this week’s modifications to Dobrindt’s original draft proposal are sufficient to pass through the Bundestrat.
Bitkom CEO Bernhard Rohleder was excited about the law, saying, “The Bundestag has cleared the way for the Automnation Deutschland to be the world leader in autonomous driving.” He acknowledged that changes will occur around liability rules or the use of data. “But we must not make the mistake of trying to settle everything down to the end in a long-term debate, then other countries will create facts and we will have the opportunity to use this technology.”
The first production vehicles equipped with autonomous driving features will be introduced to Germany sometime in 2017. “We can also be innovative in the legal framework and do not need to hide from the Silicon Valley ,” said Ulrich Lange (CSU), a CSU member, argued during the final moments of debate.
Elon Musk
Tesla reveals it is using AI to make factories more sustainable: here’s how
Tesla is using AI in its Gigafactory Nevada factory to improve HVAC efficiency.
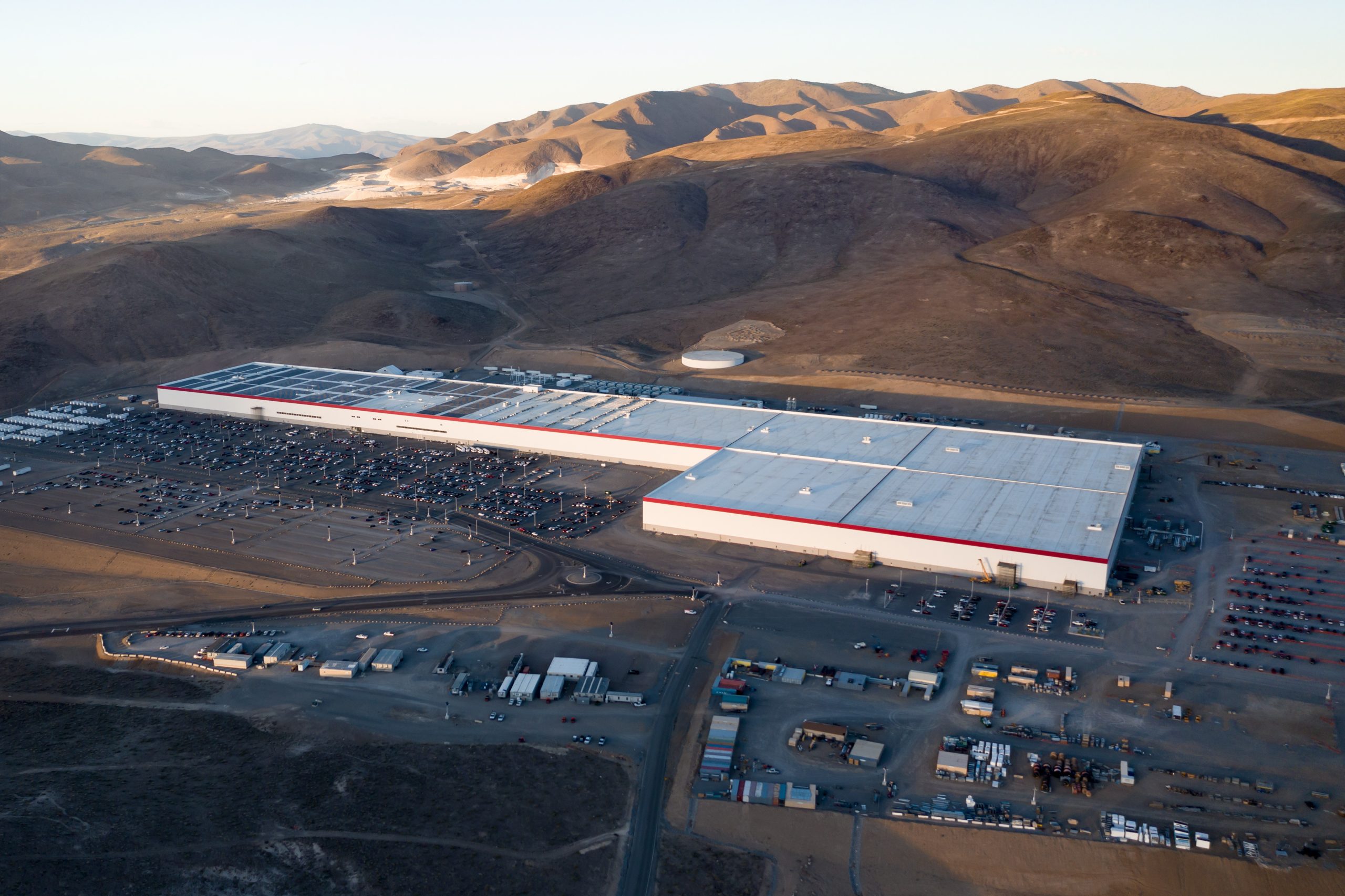

Tesla has revealed in its Extended Impact Report for 2024 that it is using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enable its factories to be more sustainable. One example it used was its achievement of managing “the majority of the HVAC infrastructure at Gigafactory Nevada is now AI-controlled” last year.
In a commitment to becoming more efficient and making its production as eco-friendly as possible, Tesla has been working for years to find solutions to reduce energy consumption in its factories.
For example, in 2023, Tesla implemented optimization controls in the plastics and paint shops located at Gigafactory Texas, which increased the efficiency of natural gas consumption. Tesla plans to phase out natural gas use across its factories eventually, but for now, it prioritizes work to reduce emissions from that energy source specifically.
It also uses Hygrometric Control Logic for Air Handling Units at Giafactory Berlin, resulting in 17,000 MWh in energy savings each year. At Gigafactory Nevada, Tesla saves 9.5 GWh of energy through the use of N-Methylpyrrolidone refineries when extracting critical raw material.
Perhaps the most interesting way Tesla is conserving energy is through the use of AI at Gigafactory Nevada, as it describes its use of AI to reduce energy demand:
“In 2023, AI Control for HVAC was expanded from Nevada and Texas to now include our Berlin-Brandenburg and Fremont factories. AI Control policy enables HVAC systems within each factory to work together to process sensor data, model factory dynamics, and apply control actions that safely minimize the energy required to support production. In 2024, this system achieved two milestones: the majority of HVAC infrastructure at Gigafactory Nevada is now AI-controlled, reducing fan and thermal energy demand; and the AI algorithm was extended to manage entire chiller plants, creating a closed-loop control system that optimizes both chilled water consumption and the energy required for its generation, all while maintaining factory conditions.”
Tesla utilizes AI Control “primarily on systems that heat or cool critical factory production spaces and equipment.” AI Control communicates with the preexisting standard control logic of each system, and any issues can be resolved by quickly reverting back to standard control. There were none in 2024.
Tesla says that it is utilizing AI to drive impact at its factories, and it has proven to be a valuable tool in reducing energy consumption at one of its facilities.
Elon Musk
Tesla analysts believe Musk and Trump feud will pass
Tesla CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump’s feud shall pass, several bulls say.
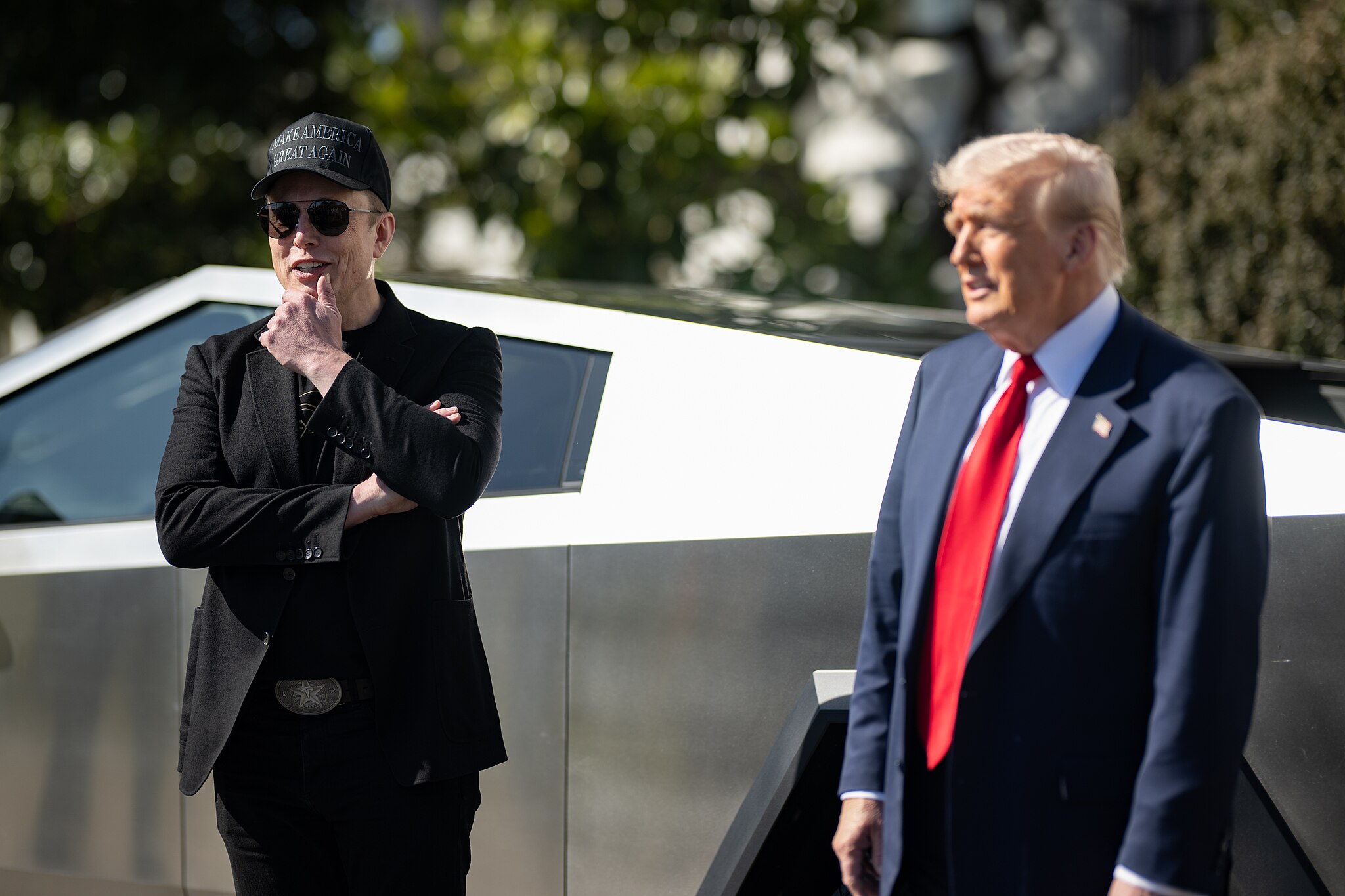

Tesla analysts are breaking down the current feud between CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump, as the two continue to disagree on the “Big Beautiful Bill” and its impact on the country’s national debt.
Musk, who headed the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) under the Trump Administration, left his post in May. Soon thereafter, he and President Trump entered a very public and verbal disagreement, where things turned sour. They reconciled to an extent, and things seemed to be in the past.
However, the second disagreement between the two started on Monday, as Musk continued to push back on the “Big Beautiful Bill” that the Trump administration is attempting to sign into law. It would, by Musk’s estimation, increase spending and reverse the work DOGE did to trim the deficit.
Every member of Congress who campaigned on reducing government spending and then immediately voted for the biggest debt increase in history should hang their head in shame!
And they will lose their primary next year if it is the last thing I do on this Earth.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) June 30, 2025
President Trump has hinted that DOGE could be “the monster” that “eats Elon,” threatening to end the subsidies that SpaceX and Tesla receive. Musk has not been opposed to ending government subsidies for companies, including his own, as long as they are all abolished.
How Tesla could benefit from the ‘Big Beautiful Bill’ that axes EV subsidies
Despite this contentious back-and-forth between the two, analysts are sharing their opinions now, and a few of the more bullish Tesla observers are convinced that this feud will pass, Trump and Musk will resolve their differences as they have before, and things will return to normal.
ARK Invest’s Cathie Wood said this morning that the feud between Musk and Trump is another example of “this too shall pass:”
BREAKING: CATHIE WOOD SAYS — ELON AND TRUMP FEUD “WILL PASS” 👀 $TSLA
She remains bullish ! pic.twitter.com/w5rW2gfCkx
— TheSonOfWalkley (@TheSonOfWalkley) July 1, 2025
Additionally, Wedbush’s Dan Ives, in a note to investors this morning, said that the situation “will settle:”
“We believe this situation will settle and at the end of the day Musk needs Trump and Trump needs Musk given the AI Arms Race going on between the US and China. The jabs between Musk and Trump will continue as the Budget rolls through Congress but Tesla investors want Musk to focus on driving Tesla and stop this political angle…which has turned into a life of its own in a roller coaster ride since the November elections.”
Tesla shares are down about 5 percent at 3:10 p.m. on the East Coast.
Elon Musk
Tesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales
Tesla CEO Elon Musk is reportedly overseeing sales in North America and Europe, Bloomberg reports.

Tesla scrambled its executives around following the exit of CEO Elon Musk’s sidekick last week, Omead Afshar. Afshar was relieved of his duties as Head of Sales for both North America and Europe.
Bloomberg is reporting that Musk is now overseeing both regions for sales, according to sources familiar with the matter. Afshar left the company last week, likely due to slow sales in both markets, ending a seven-year term with the electric automaker.
Tesla’s Omead Afshar, known as Elon Musk’s right-hand man, leaves company: reports
Afshar was promoted to the role late last year as Musk was becoming more involved in the road to the White House with President Donald Trump.
Afshar, whose LinkedIn account stated he was working within the “Office of the CEO,” was known as Musk’s right-hand man for years.
Additionally, Tom Zhu, currently the Senior Vice President of Automotive at Tesla, will oversee sales in Asia, according to the report.
It is a scramble by Tesla to get the company’s proven executives over the pain points the automaker has found halfway through the year. Sales are looking to be close to the 1.8 million vehicles the company delivered in both of the past two years.
Tesla is pivoting to pay more attention to the struggling automotive sales that it has felt over the past six months. Although it is still performing well and is the best-selling EV maker by a long way, it is struggling to find growth despite redesigning its vehicles and launching new tech and improvements within them.
The company is also looking to focus more on its deployment of autonomous tech, especially as it recently launched its Robotaxi platform in Austin just over a week ago.
However, while this is the long-term catalyst for Tesla, sales still need some work, and it appears the company’s strategy is to put its biggest guns on its biggest problems.
-

 Elon Musk1 day ago
Elon Musk1 day agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Grok integration will be more realistic with this cool feature
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla China roars back with highest vehicle registrations this Q2 so far
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla dominates Cars.com’s Made in America Index with clean sweep
-
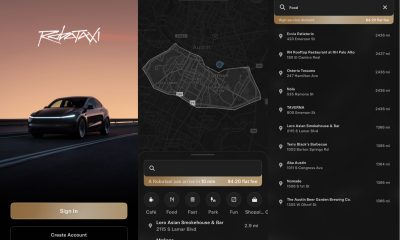
 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more




















