

Space
NASA’s next Mars rover will pave the way for humans
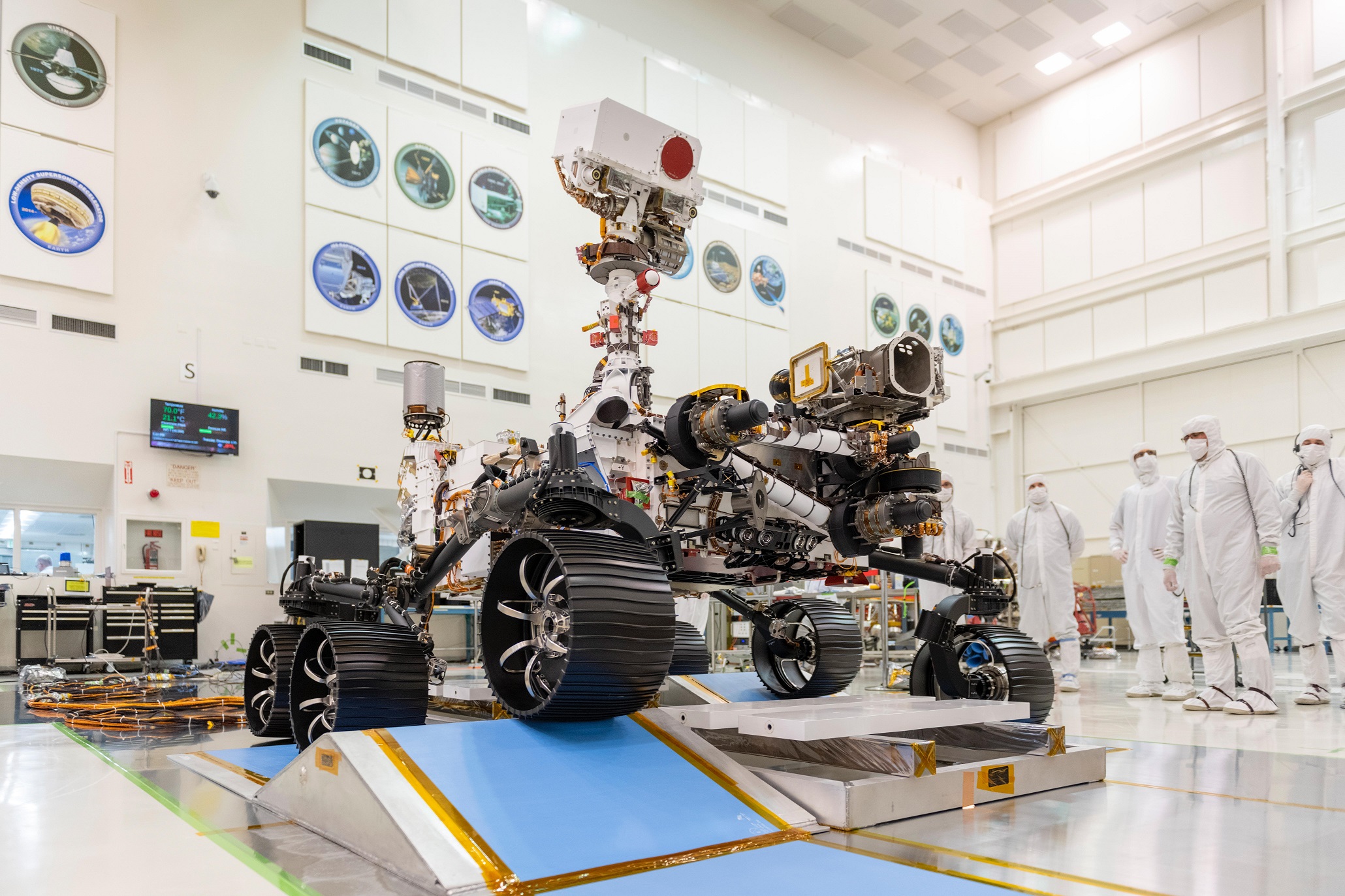
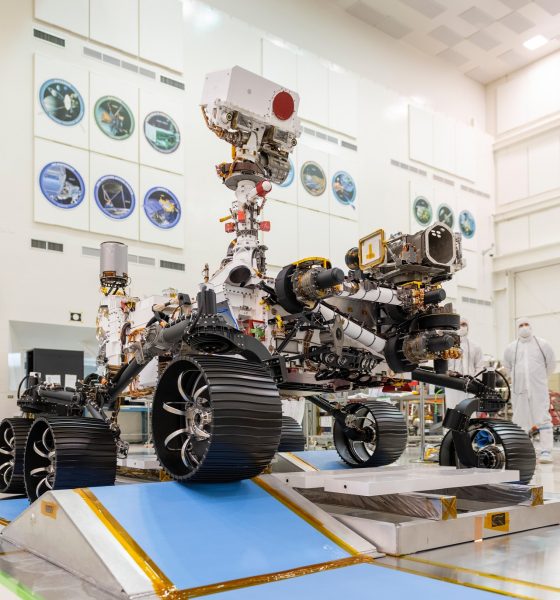
NASA’s Mars 2020 rover is scheduled to land on the red planet in February 2021, and when it does, it will touch down in Jezero Crater, the site of an ancient lake that existed 3.5 billion years ago. The next generation rover, which will get an official name soon, will build on the success of the robotic explorers who came before it by collecting the first samples of Mars for a future return to Earth.
But the new rover will also lay the groundwork for future human exploration by testing new technologies.
The Mars 2020 rover, which looks nearly identical to the Curiosity rover that landed in 2012, will begin its mission exploring Jezero Crater. The six-wheeled rover is equipped with a suite of instruments designed to help it look for signs of life called biosignatures.
Artist rendition depicting the early Martian environment (right) versus the Mars we see today (left). Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center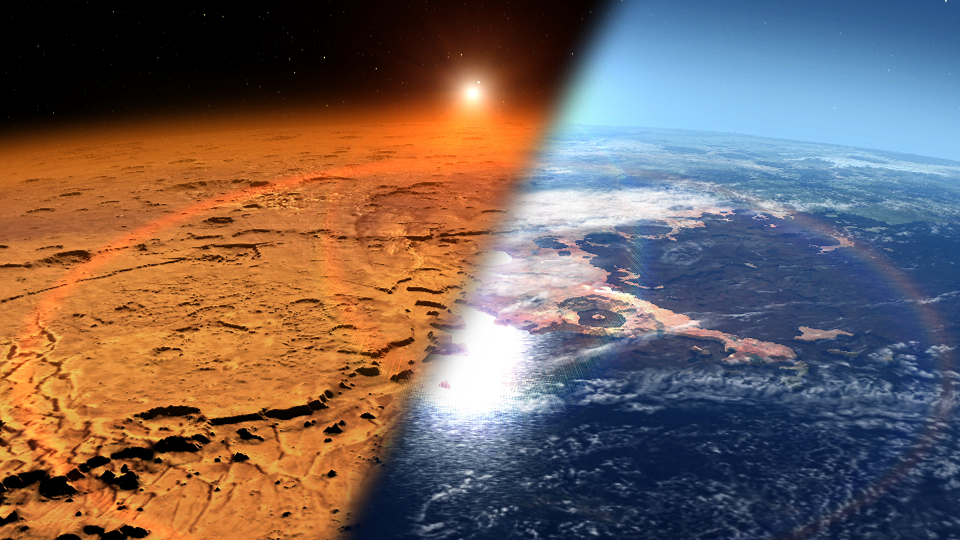
NASA believes that Mars was habitable sometime in its past. The inhospitable desert-like planet we see today was not always the case. Mars’ once ample atmosphere eroded over time, stripped away by solar particles, resulting in the thin atmosphere we see today.
But so far, we haven’t been able to detect any real signs of ancient life yet. The rover’s team thinks that its specialized suite of instruments will change that.
The twin Mars Exploration Rovers (Spirit and Opportunity) were tasked with finding evidence of water, and they were successful right out of the gate. The Mars Science Laboratory (aka Curiosity) was designed to understand habitability and if the conditions were right for life. Now, the Mars 2020 rover will take that one step further and search for actual signs of life.

Artist rendition depicting the early Martian environment (right) versus the Mars we see today (left). Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
The 2020 rover will do so by drilling into its surroundings and extracting samples that will be returned to Earth at a later time. Returning the samples is a challenge that NASA is already starting to tackle. The agency estimates that the earliest it can send a mission to fetch the rover’s samples would be some time around 2026 or 2027.
In the meantime, 2020 will be busy sciencing the heck out of Mars to search for microbial life as well as testing out technologies that future human missions will rely on.
Here’s how four of those instruments will work.
Terrain Relative Navigation
Landing on Mars is tricky. To date, only about half of the missions attempted have successfully touched down on the red planet. The 2020 rover will be equipped with a specialized feature to help it avoid any potential hazards in the landing zone.
Past missions, like Curiosity, needed a landing spot that was free of debris (like rocks, boulders, etc). But 2020 will be able to navigate around them. That’s because the rover is equipped with a unique lander vision system. This system take pictures during the parachute descent stage. It then compares those images to an onboard map.
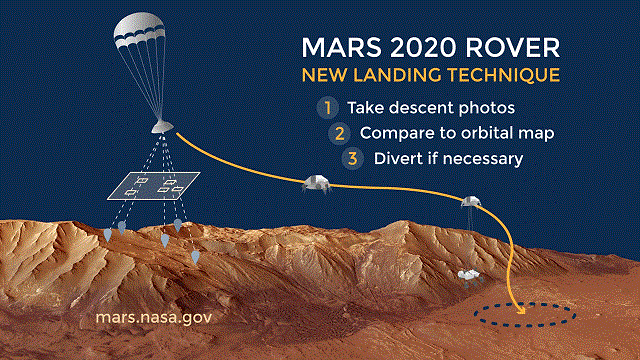
A view of how the terrain-relative navigation works. Credit: NASA/JPL_Caltech
The computer matches the map (which is created from orbital imagery), to create a guide that can identify landmarks such as craters and mountains.
The system then ranks landing sites based on safety, and can even identify a hazard. The Mars 2020 mission will be the first to test out this new system. If all goes well, it will be used on future missions, including human missions to Mars and even the moon.
MOXIE
Astronauts traveling to Mars will need oxygen to breathe and to use as rocket fuel. However, hauling it with the other cargo is expensive and not a viable solution. The Mars 2020 rover is equipped with an instrument on called the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE for short).
MOXIE will convert carbon dioxide (a gas that’s abundant on Mars) into the oxygen, which astronauts can use as needed. 2020 is equipped with a small, prototype version of the equipment needed for future human missions.
The team will study how the experiment performs and use that data to scale up the technology to use on subsequent missions. But how will it work?
MOXIE can only run for a few hours at a time, and only about once a month. (That’s because the system uses a full day’s worth of rover power each time it runs.) Humans use about 20 grams per hour of oxygen and MOXIE can only produce about half of that.
In order to support a crew of 4-6 astronauts and be able to generate propellant, future iterations of MOXIE will need to produce about 200 times that amount of oxygen.
MEDA
The Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer, aka MEDA, is a suite of sensors designed to study the Martian weather, as well as dust and radiation and how they change over the Martian seasons.
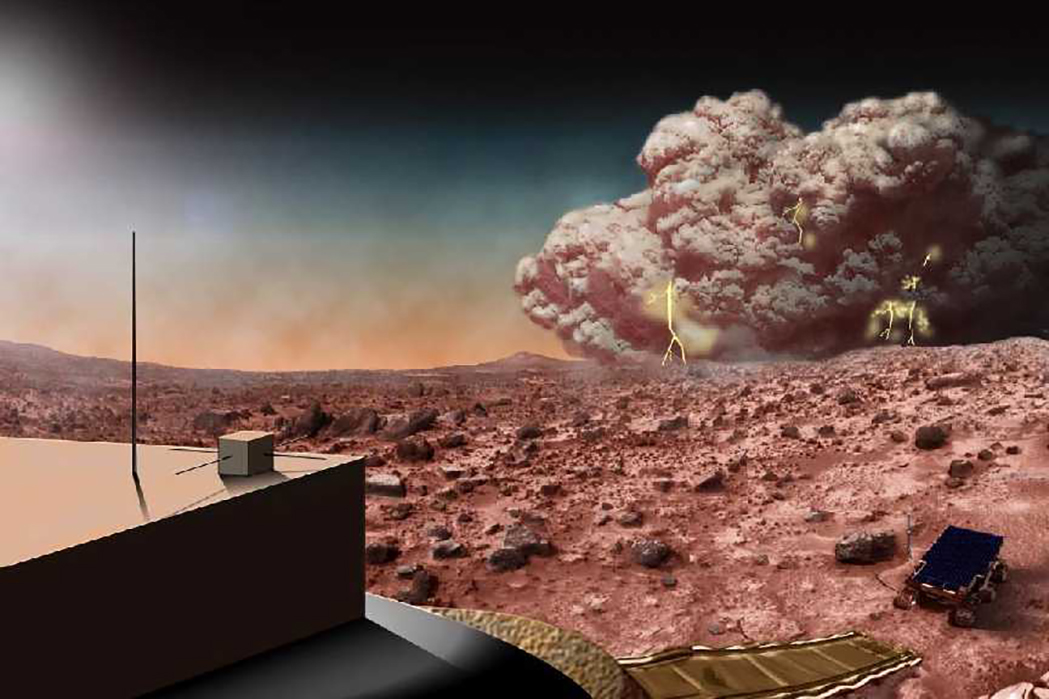

NASA is trying to better understand dust storms and other Martian weather phenomenon. Credit: NASA
Day and nighttime temperatures on Mars can fluctuate by as much as 80 or 90 degrees. MEDA will help scientists track those changes as well as measure radiation from the surface, to understand how much the sun heats the air. This solar heating causes changes in the Martian wind and can help scientists better understand the Martian water cycle.
Understanding the current weather patterns and environment could also lead to a better understanding of Mars’s history and shed light on how it transitioned from a warm, habitable planet into the dusty, cold desert we see today.
RIMFAX
The Mars 2020 rover will be equipped with a ground-penetrating radar instrument: Radar Imager for Mars’ Subsurface Experiment, or RIMFAX.
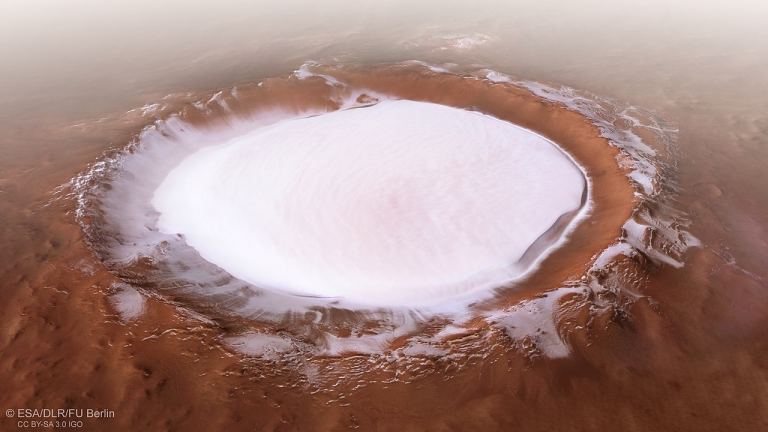

The Korolev crater on Mars as seen by Mars Express. Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin
Scientists hope that RIMAX will help them study the history of Jezero Crater by peering below the surface. With the instrument’s help, scientists will be able to look at subsurface rock and ice. To date, only orbital observations have been made of the Martian polar ice, but this will increase our understanding of the planet’s inner geology.
The Mars 2020 rover is scheduled to launch in July of 2020, and will land on the Martian surface six months later. If all goes according to plan, we may finally be able to answer the question of whether or not Mars once hosted life.

Elon Musk
Starbase after dark: Musk’s latest photo captures a Spaceport on the brink of history
SpaceX’s Starbase city in Boca Chica, Texas is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
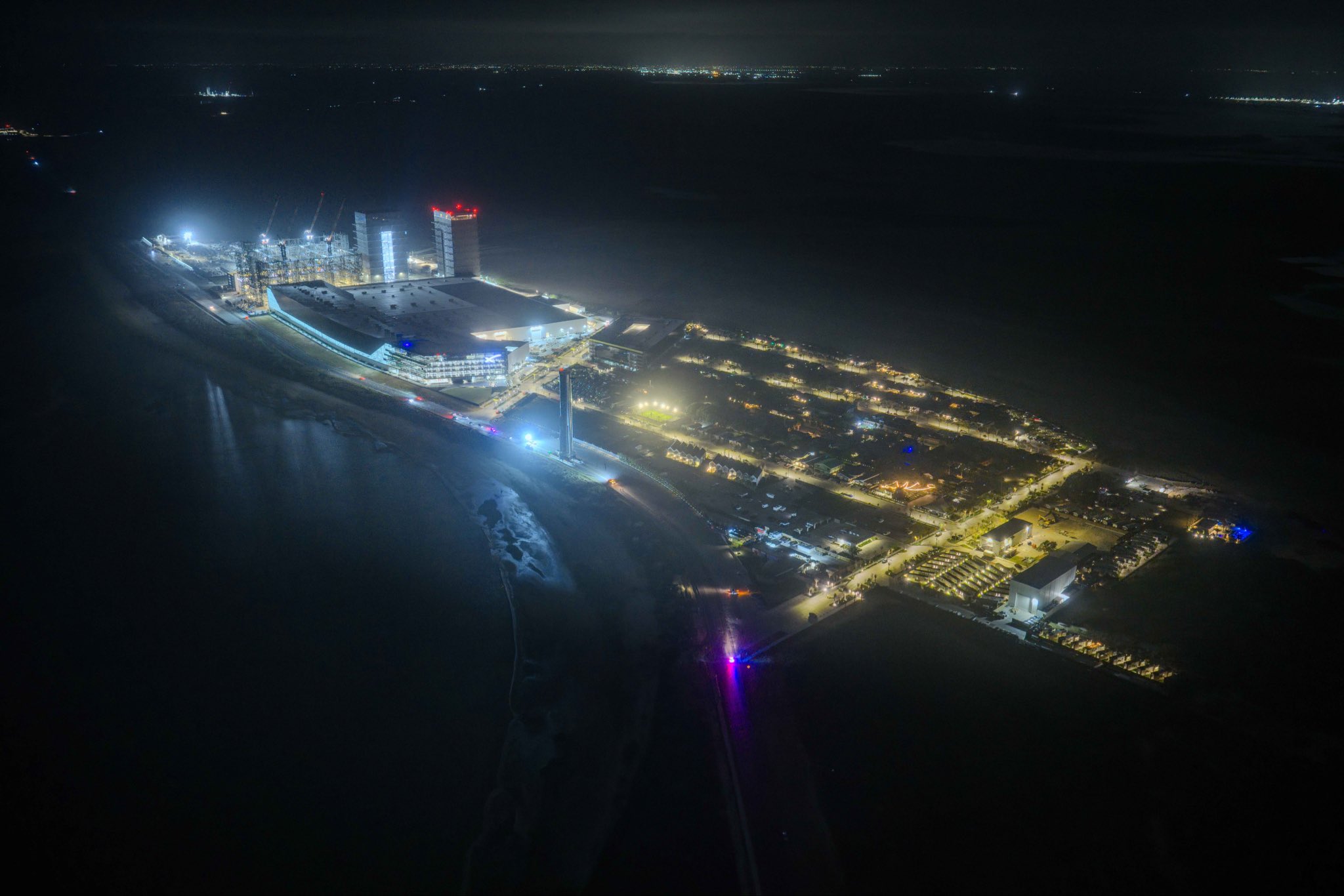

A striking nighttime photograph of SpaceX’s Starbase facility in Boca Chica, Texas, shared recently by Elon Musk on X, offers a dramatic glimpse of an operation that is rapidly transforming the southern tip of the Lone Star State into one of the most ambitious launch complexes in history.
The most immediately visible change in the photo is the presence of two fully erected Starship launch towers dominating the coastal skyline. The second orbital launch pad, known as Pad B, now features its fully erected tower, OLIT-3, which stands approximately 474 feet tall and incorporates an integrated water-cooled flame trench designed to minimize damage and reduce turnaround time between launches. The dual-tower silhouette against the night sky signals a decisive shift from experimental testing facility to high-cadence launch operations.
Grok Image concept of Elon Musk’s latest Starbase photo via X
Back at Starbase, Pad 2 is approaching hardware completion, with upgraded chopstick arms, a new chilldown vent system, and all 20 hold-down arms now fitted with protective doors to shield them from the intense exhaust of up to 33 Raptor 3 engines, according to a deeper dive by NASASpaceFlight.
SpaceX has also received approval to nearly double the footprint of the Starbase launch site, with groundwork already underway to add LNG liquefaction plants, expanded propellant storage, and additional ground support infrastructure.
The photo also carries a milestone civic dimension. Starbase officially became a Texas city in May 2025 after a community vote, with SpaceX employees elected as mayor and commissioners of the newly incorporated municipality. That legal status streamlines launch approvals and gives SpaceX direct control over local infrastructure decisions.
The FAA has approved an increase in launches from Starbase in Texas from five to twenty-five per year, clearing the runway for the kind of flight frequency needed to fulfill Starship’s ultimate mission of ferrying cargo and crew to the Moon, servicing the Department of Defense, deploying next-generation Starlink satellites, and eventually establishing Elon Musk’s long sought after goal of a self-sustaining human presence on Mars.
Seen from above in the dark, Starbase looks less like a test site and more like a spaceport.
News
Starlink gets its latest airline adoptee for stable and reliable internet access
The company said it plans to “rapidly integrate Starlink into its fleet,” and that the first Starlink-equipped aircraft will enter service this Summer.

SpaceX’s Starlink, the satellite internet program launched by Elon Musk’s company, has gotten its latest airline adoptee, offering stable and reliable internet to passengers.
Southwest Airlines announced on Wednesday that it would enable Starlink on its aircraft, a new strategy that will expand to more than 300 planes by the end of the year.
The company said it plans to “rapidly integrate Starlink into its fleet,” and that the first Starlink-equipped aircraft will enter service this Summer.
Tony Roach, Executive Vice President, Chief Customer and Brand Officer for the airline, said:
“Free WiFi has been a huge hit with our Rapid Rewards Members, and we know our Customers expect seamless connectivity across all their devices when they travel. Starlink delivers that at-home experience in the air, giving Customers the ability to stream their favorite shows from any platform, watch live sports, download music, play games, work, and connect with loved ones from takeoff to landing.”
Southwest also said that this is just one of the latest upgrades it is making to provide a more well-rounded experience to its aircraft. In addition to Starlink, it is updating cabin designs, offering more legroom, and installing in-seat power to all passengers.
Southwest became one of several airlines to cross over to Starlink, as reviews for the internet provider have raved about reliability and speed. Over the past year, Hawaiian Airlines, United Airlines, Alaska Airlines, airBaltic, Air France, JSX, Emirates, British Airways, and others have all decided to install Starlink on their planes.
This has been a major move away from unpredictable and commonly unreliable WiFi offerings on planes. Starlink has been more reliable and has provided more stable connections for those using their travel time for leisure or business.
Jason Fritch, VP of Starlink Enterprise Sales at SpaceX, said:
“We’re thrilled to deliver a connectivity experience to Southwest Airlines and its Customers that really is similar, if not better, than what you can experience in your own home. Starlink is the future of connected travel, making every journey faster, smoother, and infinitely more enjoyable.”
Starlink recently crossed a massive milestone of over 10 million subscribers.
Elon Musk
Elon Musk confirms SpaceX is not developing a phone

Despite many recent rumors and various reports, Elon Musk confirmed today that SpaceX is not developing a phone based on Starlink, not once, but twice.
Today’s report from Reuters cited people familiar with the matter and stated internal discussions have seen SpaceX executives mulling the idea of building a mobile device that would connect directly to the Starlink satellite constellation.
Musk did state in late January that SpaceX developing a phone was “not out of the question at some point.” However, He also said it would have to be a major difference from current phones, and would be optimized “purely for running max performance/watt neural nets.”
Not out of the question at some point. It would be a very different device than current phones. Optimized purely for running max performance/watt neural nets.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 30, 2026
While Musk said it was not out of the question “at some point,” that does not mean it is currently a project SpaceX is working on. The CEO reaffirmed this point twice on X this afternoon.
Musk said, “Reuters lies relentlessly,” in one post. In the next, he explicitly stated, “We are not developing a phone.”
Reuters lies relentlessly
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 5, 2026
We are not developing a phone
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 5, 2026
Musk has basically always maintained that SpaceX has too many things going on, denying that a phone would be in the realm of upcoming projects. There are too many things in the works for Musk’s space exploration company, most notably the recent merger with xAI.
SpaceX officially acquires xAI, merging rockets with AI expertise
A Starlink phone would be an excellent idea, especially considering that SpaceX operates 9,500 satellites, serving over 9 million users worldwide. 650 of those satellites are dedicated to the company’s direct-to-device initiative, which provides cellular coverage on a global scale.
Nevertheless, there is the potential that the Starlink phone eventually become a project SpaceX works on. However, it is not currently in the scope of what the company needs to develop, so things are more focused on that as of right now.


![Lucid Lunar robotaxi concept [Credit: Rendering by TESLARATI]](https://www.teslarati.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/lucid-lunar-robotaxi-concept-teslarati-rendering-80x80.jpg)





