
News
US Air Force awards SpaceX $20m contract to support its biggest spy satellites
Slipping beneath the watchful eye of many skilled defense journalists, the government contracting database FPDS.gov indicates that the US Air Force awarded SpaceX more than $20 million in November 2017 to conduct a design study of vertical integration capabilities (VIC). Describing what exactly this means first requires some background.
Vertical whaaaat?
The flood of acronyms and technical terminology that often follow activities of the Federal government should not detract from the significance of this contract award. First and foremost, what exactly is “vertical integration” and why is significant for SpaceX? Not to be confused with more abstract descriptions of corporate organization (vertical integration describes one such style), integration here describes the literal process of attaching satellite and spacecraft payloads to the rockets tasked with ferrying them to orbit.
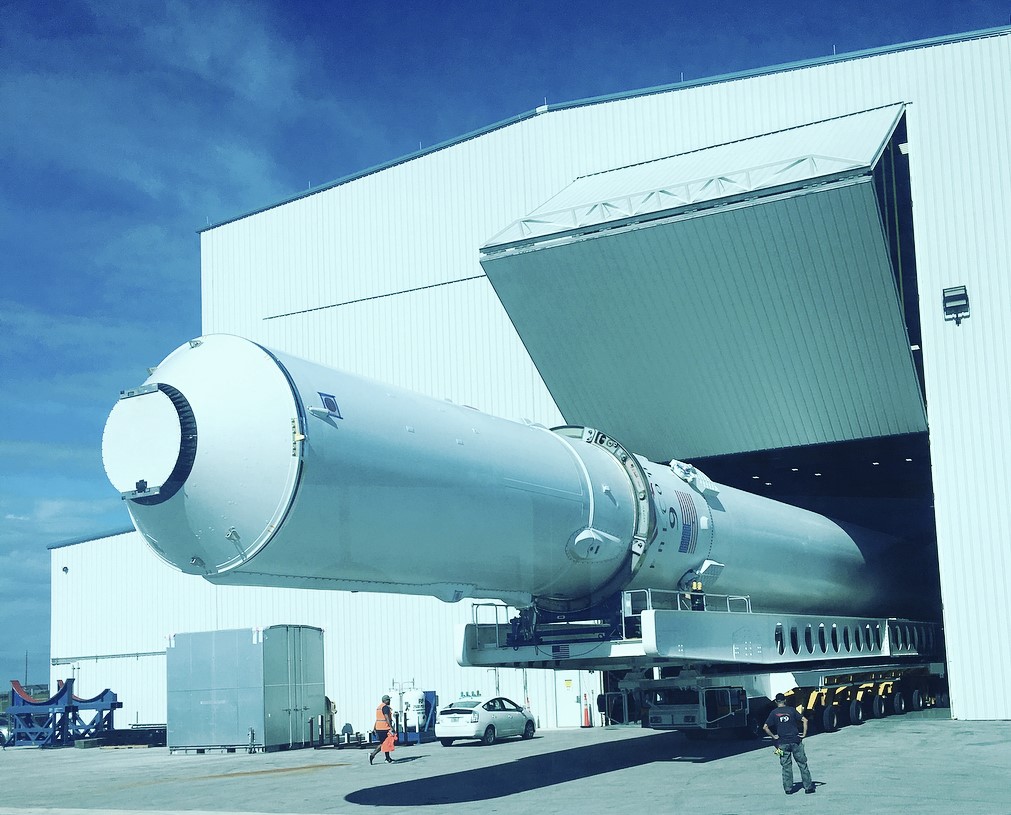
Likely as a result of its relative simplicity, SpaceX has used a system of horizontal integration for as long as they have been in the business of launching rockets, be it Falcon 1, Falcon 9, or Falcon Heavy. In order to integrate payloads to the rocket horizontally, SpaceX has a number of horizontal integration facilities (HIF) directly beside each of their three launch pads – two in Florida, one in California. After being transported from the company’s Hawthorne, CA rocket factory, Falcon 9 and Heavy boosters, second stages, payload fairings, and other miscellaneous components are all brought into a HIF, where they are craned off of their transporters (a semi-trailer in most cases) and placed on horizontal stands inside the building.
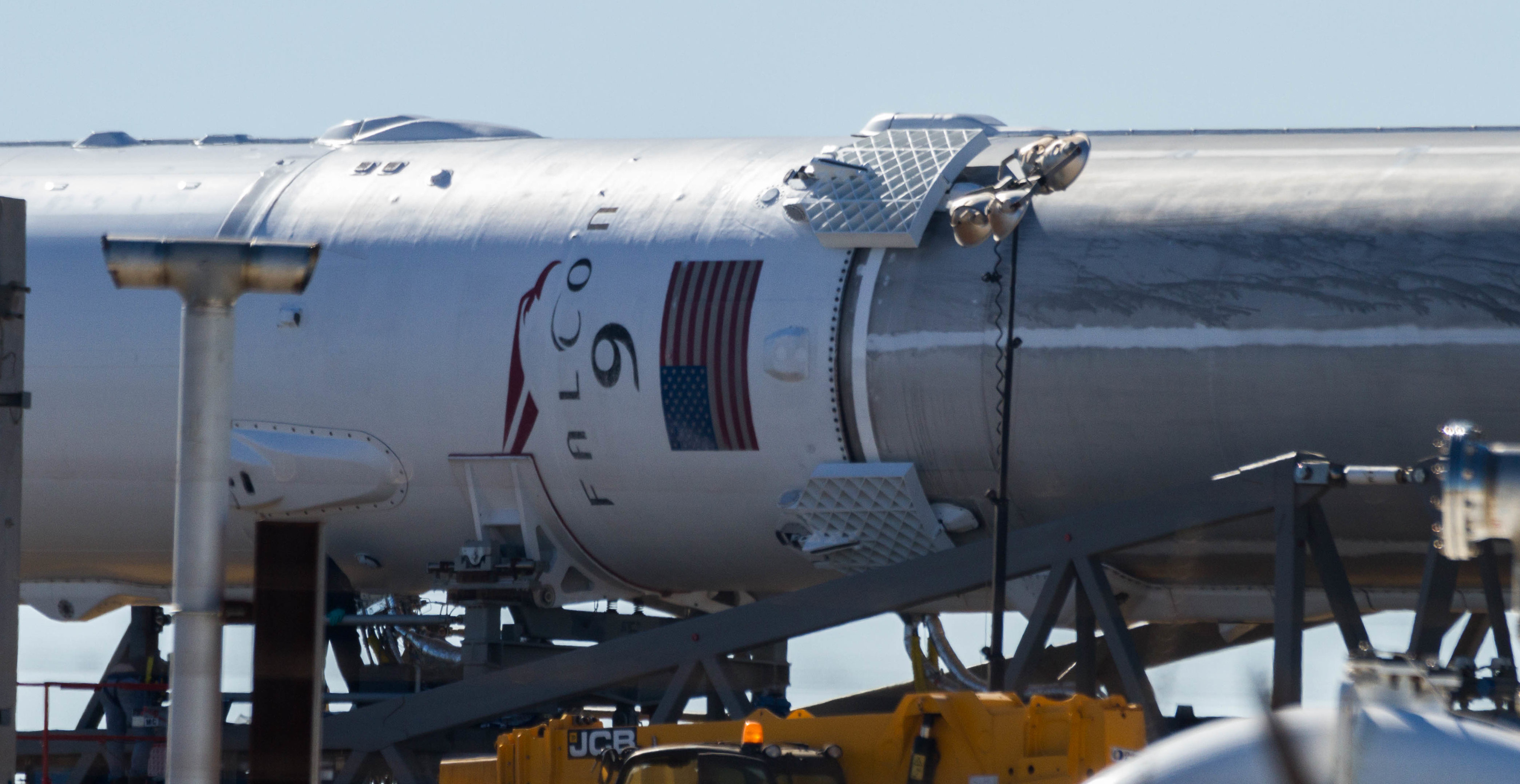
- The large, white crawler underneath Falcon 9 is one of several methods of transportation SpaceX uses. (Instagram /u/robhubar)
- Falcon Heavy is composed of a Falcon 9 upper stage and three Falcon 9-class boosters. (SpaceX)
- The fully-integrated Falcon Heavy rolls out to Pad 39A. For vertical integration, think of this… but vertical. (SpaceX)
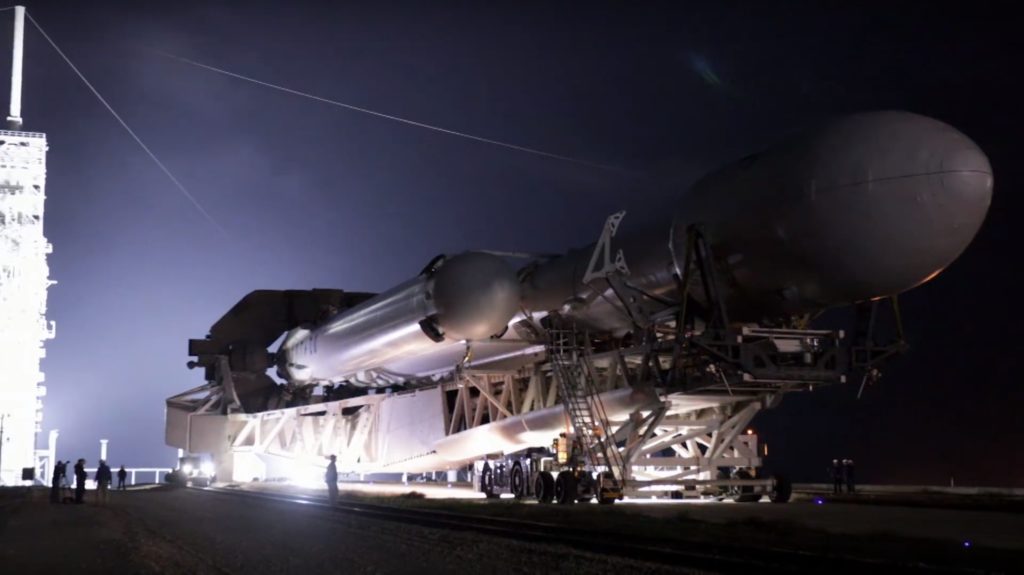
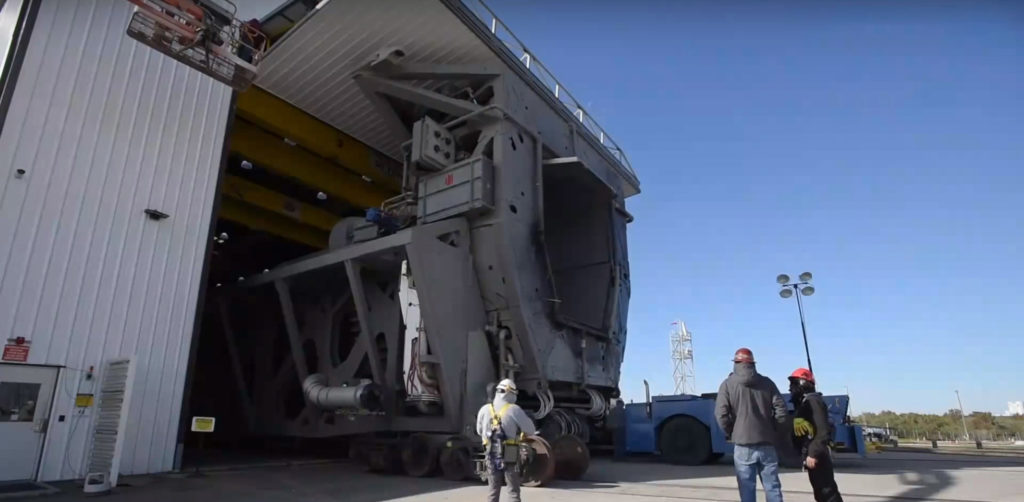
While in the HIF, all three main components are eventually attached together (integrated). The booster or first stage (S1) has its landing legs and grid fins installed soon after arrival at the launch site, followed by the mating of the first and second stages. Once these two primary components of the rocket are attached, the entire stack – as the mated vehicle is called – is once again lifted up by cranes inside the facility and placed atop what SpaceX calls the strongback (also known as the Transporter/Launcher/Erector, or TEL). A truly massive steel structure, the TEL is tasked with carrying the rocket to the launch pad, typically a short quarter mile trek from the integration facility. Once it reaches the pad, the TEL uses a powerful hydraulic lift system to rotate itself and its rocket payload from horizontal to vertical. It may look underwhelming, but it serves to remember that a complete Falcon 9/Heavy and its TEL are both considerably more than twice as tall as a basketball court is long.
Falcon Heavy goes vertical pic.twitter.com/uG1k0WISv1
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 5, 2018
Once at the pad, the TEL serves as the rocket’s connection to the pad’s many different ground systems. Crucially, it is tasked with loading the rocket with at least four different fuels, fluids, and gases at a broad range of temperatures, as well as holding the rocket down with giant clamps at its base, providing connection points to transmit a flood of data back to SpaceX launch control. SpaceX’s relatively unique TEL technology is to some extent the foundation of the company’s horizontal integration capabilities – such a practice would be impossible without reliable systems and methods that allow the rocket to be easily transported about and connected to pad systems.
Still, after the Amos-6 mishap in September 2016, which saw a customer’s payload entirely destroyed by a launch vehicle anomaly ahead of a static fire test, SpaceX has since changed their procedures, and now conducts those static fire tests with just the first and second stages – the payload is no longer attached until after the test is completed. For such a significant decrease in risk, the tradeoff of an additional day or so of work is minimal to SpaceX and its customers. Once completed, the rocket is brought horizontal and rolled back into the HIF, where the rocket’s payload fairing is finally attached to the vehicle while technicians ensure that the rocket is in good health after a routine test-ignition of its first stage engines.
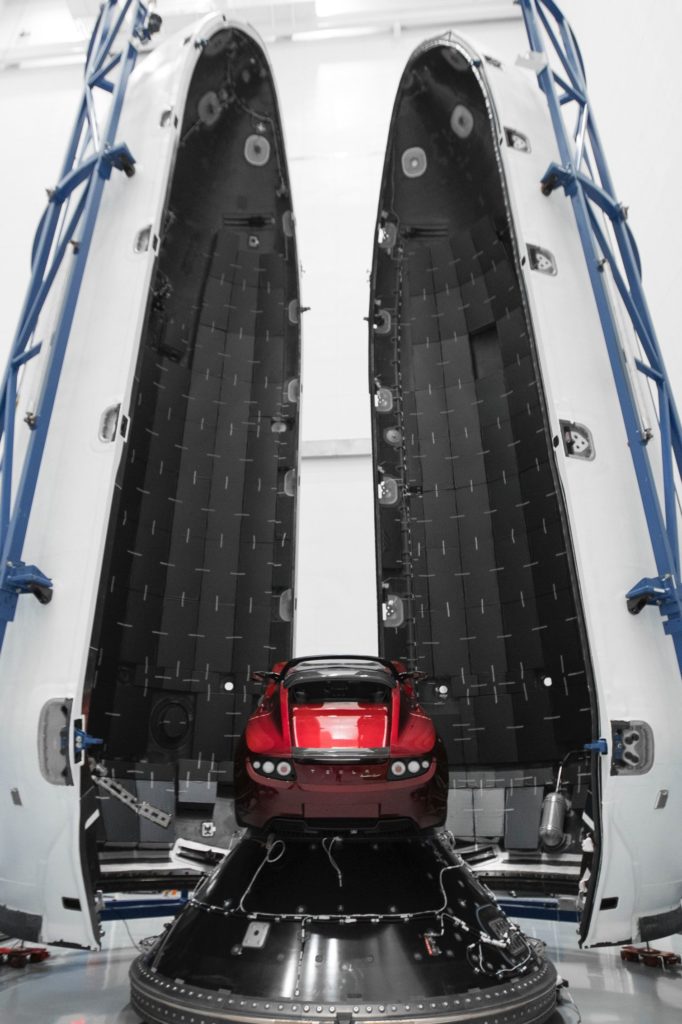
- Elon Musk’s Roadster seen before being encapsulated in Falcon Heavy’s massive payload fairing. Below the Tesla is the payload adapter, which connects it to the rocket. (SpaceX)
- Imagine this building-sized fairing traveling approximately TWO MILES PER SECOND. (USAF)
- Finally, the fairing is transported vertically to the HIF, where it can be flipped horizontal and attached to its rocket. (Reddit /u/St-Jed-of-Calumet)
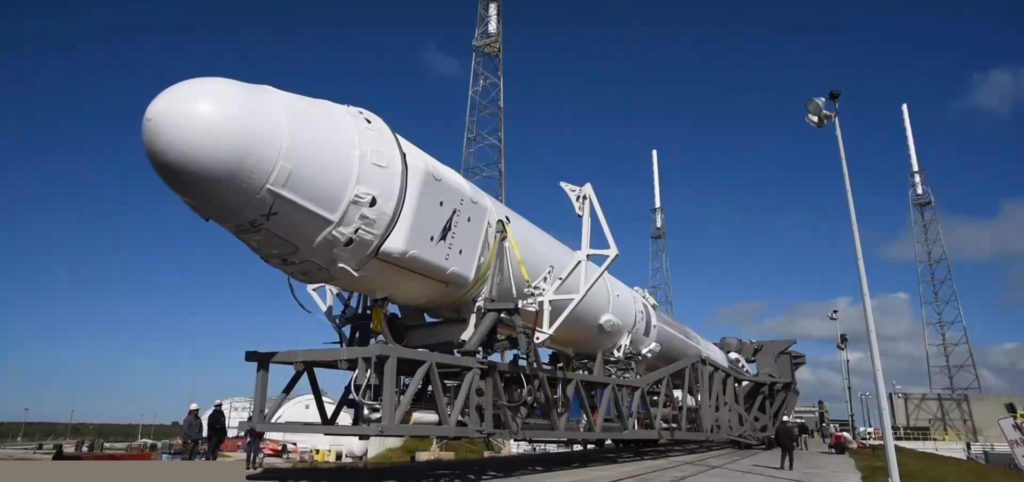
Before being connected to the rocket, the payload itself must also go through its own integration process. Recently demonstrated by a flurry of SpaceX images of Falcon Heavy and its Roadster payload, this involves attaching the payload to a payload adapter, tasked with both securing the payload and fairing to the launch vehicle. Thankfully, the fairing is far smaller than the rocket itself, and this means it can be vertically integrated with the payload and adapter. The final act of joining and bolting together the two fairing halves is known as encapsulation – at which point the payload is now snug inside the fairing and ready for launch. Finally, the integrated payload and fairing are lifted up by cranes, rotated horizontally, and connected to the top of the rocket’s second stage, marking the completion of the integration process.
A different way to integrate
Here lies the point at which the Air Force’s $20m contract with SpaceX comes into play. As a result of certain (highly classified) aspects of some of the largest military satellites, the Department of Defense (DoD) and National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) prefer or sometimes outright require that their payloads remain vertical while being attached to a given rocket. The United Launch Alliance (ULA), SpaceX’s only competition for military launches, almost exclusively utilizes vertical integration for all of their launches, signified by the immense buildings (often themselves capable of rolling on tracks) present at their launch pads. SpaceX has no such capability, at present, and this means that they are effectively prevented from competing for certain military launch contracts – contracts that are often the most demanding and thus lucrative.
It’s clear that the Air Force itself is the main impetus pushing SpaceX to develop vertical integration capabilities, a reasonable continuation of the military’s general desire for assured access to orbit in the event of a vehicle failure grounding flights for the indefinite future. For example, if ULA or SpaceX were to suffer a failure and be forced to ground their rockets for months while investigating the incident, the DoD could choose to transfer time-sensitive payload(s) to the unaffected company for the time being. With vertical integration, this rationale could extend to all military satellites, not simply those that support horizontal integration.
- A hop and a skip south of 39A is SpaceX’s LC-40 pad. (SpaceX)
- Like all SpaceX pads, horizontal integration is a central feature. (SpaceX)
- LC-40’s brand new TEL carries a flight-proven Falcon 9 and Dragon out to the pad. (SpaceX)
Fittingly, the ability to vertically integrate satellites is likely a necessity if SpaceX hopes to derive the greatest possible value from its recently and successfully introduced Falcon Heavy rocket, a highly capable vehicle that the government is likely very interested in. Although the specific Air Force contract blandly labels it a “Design Study,” (FPDS.gov account required) its hefty $21 million award may well be far more money than SpaceX needs to design a solution. In fact, knowing SpaceX’s famous ability to develop and operate technologies with exceptional cost efficiency, it would not be shocking to discover that the intrepid launch company has accepted the design study grant and instead jumped head-first into prototyping, if not the construction of an operational solution. More likely than not, SpaceX would choose to take advantage of the fixed tower (known as the Fixed Service Structure, FSS) currently present at Pad 39A, atop which a crane and work platforms could presumably be attached
Intriguingly, it is a real possibility that Fairing 2.0 – its first launch scheduled to occur as early as Feb. 21 – could have been upgraded in part to support present and future needs of the Department of Defense, among numerous other benefits. Fairing 2.0’s larger size may have even been precipitated by physical requirements for competing for and dealing with the largest spysats operating by the DoD and NRO, although CEO Elon Musk’s characterization of that change as a “slightly larger diameter” could suggest otherwise. On the other hand, Musk’s offhand mention of the possibility of significantly lengthening the payload fairing is likely aimed directly at government customers in both the civil and military spheres of space utilization. Time will tell, and it certainly will not hurt SpaceX or its customers if Fairing 2.0 is also considerably easier to recover and reuse.
Under consideration. We’ve already stretched the upper stage once. Easiest part of the rocket to change. Fairing 2, flying soon, also has a slightly larger diameter. Could make fairing much longer if need be & will if BFR takes longer than expected.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) February 12, 2018
Ultimately, it should come as no surprise that SpaceX would attempt to leverage this contract and the DoD’s interest in ways that might also facilitate the development of the company’s futuristic BFR rocket, intended to eventually take humans to the Moon, Mars, and beyond. As shown by both 2016 and 2017 iterations of the vehicle, it appears that SpaceX intends to use vertical integration to attach the spaceship (BFS) to the booster (BFR). While it’s unlikely that this Air Force contract will result in the creation of a vertical integration system that could immediately be applied to or replicated for BFS testing, the experience SpaceX would gain in the process of building something similar for the Air Force would be invaluable and essentially kill two birds with one stone.

While now outdated, SpaceX’s 2016 Mars rocket featured a giant crane used for vertical integration. BFR appears to use the same approach. (SpaceX)
Follow along live as I and launch photographers Tom Cross and Pauline Acalin cover these exciting proceedings live and in person.
Teslarati – Instagram – Twitter
Tom Cross – Twitter
Pauline Acalin – Twitter
Eric Ralph – Twitter
Elon Musk
Tesla begins expanding Robotaxi access: here’s how you can ride
You can ride in a Tesla Robotaxi by heading to its website and filling out the interest form. The company is hand-picking some of those who have done this to gain access to the fleet.

Tesla has begun expanding Robotaxi access beyond the initial small group it offered rides to in late June, as it launched the driverless platform in Austin, Texas.
The small group of people enjoying the Robotaxi ride-hailing service is now growing, as several Austin-area residents are receiving invitations to test out the platform for themselves.
The first rides took place on June 22, and despite a very small number of very manageable and expected hiccups, Tesla Robotaxi was widely successful with its launch.
Tesla Robotaxi riders tout ‘smooth’ experience in first reviews of driverless service launch
However, Tesla is expanding the availability of the ride-hailing service to those living in Austin and its surrounding areas, hoping to gather more data and provide access to those who will utilize it on a daily basis.
Many of the people Tesla initially invited, including us, are not local to the Austin area.
There are a handful of people who are, but Tesla was evidently looking for more stable data collection, as many of those early invitees headed back to where they live.
The first handful of invitations in the second round of the Robotaxi platform’s Early Access Program are heading out to Austin locals:
I just got a @robotaxi invite! Super excited to go try the service out! pic.twitter.com/n9mN35KKFU
— Ethan McKanna (@ethanmckanna) July 1, 2025
Tesla likely saw an influx of data during the first week, as many traveled far and wide to say they were among the first to test the Robotaxi platform.
Now that the first week and a half of testing is over, Tesla is expanding invites to others. Many of those who have been chosen to gain access to the Robotaxi app and the ride-hailing service state that they simply filled out the interest form on the Robotaxi page of Tesla’s website.
That’s the easiest way you will also gain access, so be sure to fill out that form if you have any interest in riding in Robotaxi.
Tesla will continue to utilize data accumulated from these rides to enable more progress, and eventually, it will lead to even more people being able to hail rides from the driverless platform.
With more success, Tesla will start to phase out some of the Safety Monitors and Supervisors it is using to ensure things run smoothly. CEO Elon Musk said Tesla could start increasing the number of Robotaxis to monitors within the next couple of months.
Elon Musk
Tesla analyst issues stern warning to investors: forget Trump-Musk feud

A Tesla analyst today said that investors should not lose sight of what is truly important in the grand scheme of being a shareholder, and that any near-term drama between CEO Elon Musk and U.S. President Donald Trump should not outshine the progress made by the company.
Gene Munster of Deepwater Management said that Tesla’s progress in autonomy is a much larger influence and a significantly bigger part of the company’s story than any disagreement between political policies.
Munster appeared on CNBC‘s “Closing Bell” yesterday to reiterate this point:
“One thing that is critical for Tesla investors to remember is that what’s going on with the business, with autonomy, the progress that they’re making, albeit early, is much bigger than any feud that is going to happen week-to-week between the President and Elon. So, I understand the reaction, but ultimately, I think that cooler heads will prevail. If they don’t, autonomy is still coming, one way or the other.”
BREAKING: GENE MUNSTER SAYS — $TSLA AUTONOMY IS “MUCH BIGGER” THAN ANY FEUD 👀
He says robotaxis are coming regardless ! pic.twitter.com/ytpPcwUTFy
— TheSonOfWalkley (@TheSonOfWalkley) July 2, 2025
This is a point that other analysts like Dan Ives of Wedbush and Cathie Wood of ARK Invest also made yesterday.
On two occasions over the past month, Musk and President Trump have gotten involved in a very public disagreement over the “Big Beautiful Bill,” which officially passed through the Senate yesterday and is making its way to the House of Representatives.
Musk is upset with the spending in the bill, while President Trump continues to reiterate that the Tesla CEO is only frustrated with the removal of an “EV mandate,” which does not exist federally, nor is it something Musk has expressed any frustration with.
In fact, Musk has pushed back against keeping federal subsidies for EVs, as long as gas and oil subsidies are also removed.
Nevertheless, Ives and Wood both said yesterday that they believe the political hardship between Musk and President Trump will pass because both realize the world is a better place with them on the same team.
Munster’s perspective is that, even though Musk’s feud with President Trump could apply near-term pressure to the stock, the company’s progress in autonomy is an indication that, in the long term, Tesla is set up to succeed.
Tesla launched its Robotaxi platform in Austin on June 22 and is expanding access to more members of the public. Austin residents are now reporting that they have been invited to join the program.
Elon Musk
Tesla surges following better-than-expected delivery report
Tesla saw some positive momentum during trading hours as it reported its deliveries for Q2.

Tesla (NASDAQ: TSLA) surged over four percent on Wednesday morning after the company reported better-than-expected deliveries. It was nearly right on consensus estimations, as Wall Street predicted the company would deliver 385,000 cars in Q2.
Tesla reported that it delivered 384,122 vehicles in Q2. Many, including those inside the Tesla community, were anticipating deliveries in the 340,000 to 360,000 range, while Wall Street seemed to get it just right.
Tesla delivers 384,000 vehicles in Q2 2025, deploys 9.6 GWh in energy storage
Despite Tesla meeting consensus estimations, there were real concerns about what the company would report for Q2.
There were reportedly brief pauses in production at Gigafactory Texas during the quarter and the ramp of the new Model Y configuration across the globe were expected to provide headwinds for the EV maker during the quarter.
At noon on the East Coast, Tesla shares were up about 4.5 percent.
It is expected that Tesla will likely equal the number of deliveries it completed in both of the past two years.
It has hovered at the 1.8 million mark since 2023, and it seems it is right on pace to match that once again. Early last year, Tesla said that annual growth would be “notably lower” than expected due to its development of a new vehicle platform, which will enable more affordable models to be offered to the public.
These cars are expected to be unveiled at some point this year, as Tesla said they were “on track” to be produced in the first half of the year. Tesla has yet to unveil these vehicle designs to the public.
Dan Ives of Wedbush said in a note to investors this morning that the company’s rebound in China in June reflects good things to come, especially given the Model Y and its ramp across the world.
He also said that Musk’s commitment to the company and return from politics played a major role in the company’s performance in Q2:
“If Musk continues to lead and remain in the driver’s seat, we believe Tesla is on a path to an accelerated growth path over the coming years with deliveries expected to ramp in the back-half of 2025 following the Model Y refresh cycle.”
Ives maintained his $500 price target and the ‘Outperform’ rating he held on the stock:
“Tesla’s future is in many ways the brightest it’s ever been in our view given autonomous, FSD, robotics, and many other technology innovations now on the horizon with 90% of the valuation being driven by autonomous and robotics over the coming years but Musk needs to focus on driving Tesla and not putting his political views first. We maintain our OUTPERFORM and $500 PT.”
Moving forward, investors will look to see some gradual growth over the next few quarters. At worst, Tesla should look to match 2023 and 2024 full-year delivery figures, which could be beaten if the automaker can offer those affordable models by the end of the year.
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-
 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla Robotaxis are becoming a common sight on Austin’s public roads
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoSpaceX President meets India Minister after Starlink approval
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Grok 3 partners with Oracle Cloud for corporate AI innovation


























