

News
SpaceX’s Elon Musk hints at “notable” Starship changes, explains static fire anomaly
CEO Elon Musk has offered an explanation for SpaceX’s recent Starship static fire anomaly and says that an overview of the next-generation rocket development program will be delayed to account for some “notable” design changes.
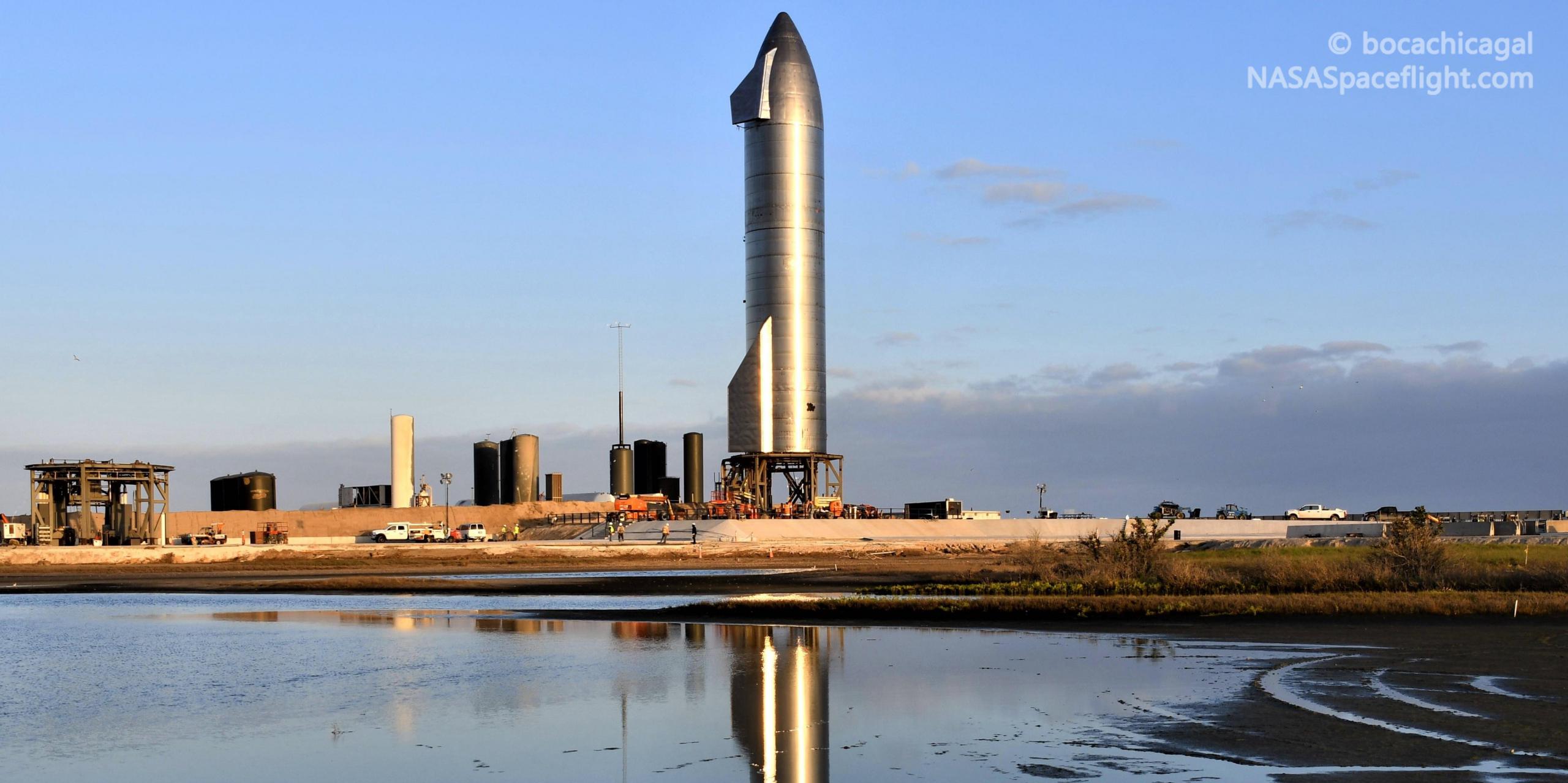
Over the last several months, Musk has promised to do one of his (thus far) usual annual Starship updates, either in the form of a presentation in South Texas, an article published on SpaceX’s website, or both. Originally expected in September or October, the CEO’s tentative schedules have come and gone several times. Simultaneously, however, SpaceX has been preparing Starship serial number 8 (SN8) for a range of crucial tests and Starship program firsts, recently culminating in a successful cryogenic proof test, multiple wet dress rehearsals (WDRs), nosecone installation, the first triple-Raptor static fire test, engine tests using smaller ‘header’ tanks, and more.
Unfortunately for SN8, the most recent Raptor engine header static fire – drawing propellant from two small internal tanks mainly used for landing burns – did not go according to plan, resulting in some kind of high-temperature fire and severing Starship’s hydraulic systems. For SpaceX test controllers, that meant a total loss of control of most vehicle valves and pressurization systems, essentially putting one of Starship SN8’s header tanks through an unplanned pressure and failsafe test. In the days since, what exactly caused that unfortunate failure has been the subject of a great deal of discussion – discussion that can finally be put to rest with new information from Musk himself.
In a surprise, SpaceX had apparently decided to add a failsafe to Starship SN8’s new nose section, installing what is known as a burst disk – effectively an automatic single-use valve. Once the upper (liquid oxygen) header tank reached dangerous pressures, the force of that pressure broke the seal, allowing the rocket to vent excess pressure and avoid what would have otherwise been a potentially catastrophic explosion.
The cause of that near-miss, according to Elon Musk, was as simple as debris kicked up during the Starship SN8 Raptor engine static fire directly prior. Producing up to 200 metric tons (~450,000 lbf) of thrust and an exhaust stream traveling some 3.3 kilometers per second (2 mi/s, Mach ~10), Musk says that Raptor tore apart a special ceramic coating covering the concrete directly beneath Starship SN8. Likely accelerated to extreme velocities in milliseconds, shards of that coating reportedly “severed [an] avionics cable, causing [a] bad [Raptor engine shutdown].”

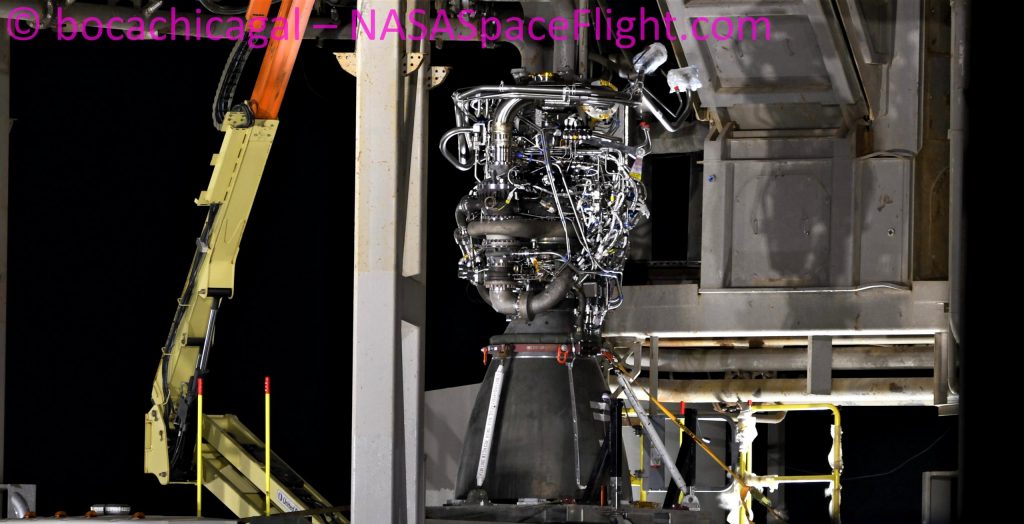
Prior to Musk’s comments, SpaceX technicians had already removed on of SN8’s three Raptors – SN32 – on November 14th and replaced it with Raptor SN42 on November 16th, effectively confirming that any damage suffered by Starship’s engine section was easily repairable. It’s unclear how exactly a single severed cable could result in a Raptor engine seemingly dripping molten metal but regardless of the cause, the fix appears to have been a quick one.
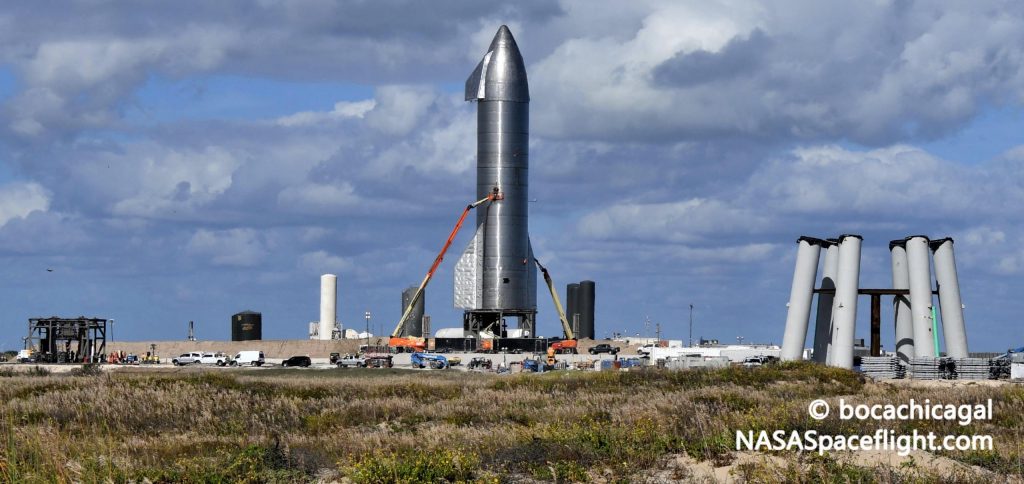

In response to the anomaly, Musk says that Starship avionics cables will ultimately be routed inside steel pipes to shield them from debris, while “water-cooled steel pipes” will be added to the launch pad to help limit the damage Raptors can cause. Perhaps as a partial result of SN8’s troubles at the launch pad, Musk says that his Starship blog post will have to wait, as SpaceX “[may be] making some notable changes” to the launch vehicle.
Prior to Starship SN8’s failed November 12th Raptor test, SpaceX was expected to attempt three consecutive static fires before clearing the rocket for an ambitious 15 km (9.5 mi) flight test. One of those static fires had already been completed on November 10th and it’s unclear if SpaceX’s SN8 test plan has remained unchanged or if the static fire counter has been effectively reset. Either way, barring more surprises, there’s still a definite possibility that Starship SN8 will be ready for its launch debut by the end of November and an even better chance that it will launch some time between now and 2021. Stay tuned for updates!
News
Tesla Robotaxi has already surpassed Waymo in this key metric
Tesla Robotaxi has already overtaken Waymo in Austin in one key metric, but there’s still more work to do.

Tesla Robotaxi has already surpassed Waymo in one extremely important key metric: size of service area.
Tesla just expanded its service area in Austin on Monday morning, pushing the boundaries of its Robotaxi fleet in an interesting fashion with new capabilities to the north. Yes, we know what it looks like:
🚨 Tesla’s new Robotaxi geofence is…
Finish the sentence 🥸 pic.twitter.com/3bjhMqsRm5
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 14, 2025
The expansion doubled Tesla Robotaxi’s potential travel locations, which now include the University of Texas at Austin, a school with over 53,000 students.
The doubling of the service area by Tesla has already made its travel area larger than Waymo’s, which launched driverless rides in October 2024. It became available to the public in March 2025.
According to Grok, the AI agent on X, Tesla Robotaxi’s current service area spans 42 square miles, which is five square miles larger than Waymo’s service area of 37 square miles.
Tesla Robotaxi (red) vs. Waymo geofence in Austin.
Much can be said about the shape… but the Robotaxi area is now ~3.9 mi² (10 km²) larger than Waymo’s!! pic.twitter.com/dVfh2ODxJC
— Robin (@xdNiBoR) July 14, 2025
The service area is one of the most important metrics in determining how much progress a self-driving ride-hailing service is making. Safety is the priority of any company operating a ride-hailing network, especially ones that are making it a point to use autonomy to deploy it.
However, these companies are essentially racing for a larger piece of the city or cities they are in. Waymo has expanded to several different regions around the United States, including Arizona and Los Angeles.
Tesla is attempting to do the same in the coming months as it has already filed paperwork in both California and Arizona to deploy its Robotaxi fleet in states across the U.S.
As the platform continues to show more prowess and accuracy in its operation, Tesla will begin to expand to new areas, eventually aiming for a global rollout of its self-driving service.
News
Tesla Megapacks arrive for massive battery replacing coal plant
Tesla Megapacks have started arriving on-site to the Stanwell Battery Project, just as Queensland prepares to wind down the Stanwell coal plant.

The first of over 300 Tesla Megapacks have arrived to the site of a massive battery energy storage system (BESS) being built in Australia, dubbed the Stanwell Battery Project after a coal plant it’s set to replace.
In a press release last week, the Stanwell Battery Project announced that the first Tesla Megapack 2XL units had arrived to the site, which is located outside of Rockhampton in Queensland, Australia. The project will eventually feature 324 Megapack units, set to arrive in the coming months, in order to support the 300MW/1,200MWh battery project.
“The Stanwell Battery is part of the diversification of our portfolio, to include cleaner and more flexible energy solutions,” said Angie Zahra, Stanwell Central Generation General Manager. “It is just one part of the 800 MW of battery energy storage capacity we have in our pipeline.
“Capable of discharging 300 MW of energy for up to four hours (1,200 MWh), our mega battery will be one of the largest in Queensland.”

Credit: Stanwell
Did you know Tesla’s Lathrop facility churns out a Megapack every 68 minutes? That’s enough energy to power 3,600 homes for an hour per unit! ⚡️ pic.twitter.com/bG6fpHkB9O
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) June 11, 2025
READ MORE ON TESLA MEGAPACKS: Tesla Lathrop Megafactory celebrates massive Megapack battery milestone
The state is working with government-owned company Yurika to facilitate construction, and the process is expected to create roughly 80 jobs. The project is expected to come fully online in May 2027, with initial commissioning of the Megapacks aiming for November 2025.
The Stanwell Battery is set to replace the nearby Stanwell coal generation plant, which the government is planning to wind down starting in 2026 as part of efforts to reach an 80 percent renewable energy generation ratio by 2035. Meanwhile, the government is also set to begin winding down the Tarong and Callide coal plants, while several other Megapack projects are being built or coming online. o ya
Tesla currently has two Megapack production facilities, located in Lathrop, California, in the U.S. and another that came online earlier this year in Shanghai, China. The Shanghai Megafactory shipped its first units to Australia in March, while both factories are expected to be capable of producing 10,000 Megapack units per year upon reaching volume production.
News
The Tesla Diner is basically finished—here’s what it looks like
The company first broke ground on the Diner, Drive-in, and Supercharger location in September 2023. Now, it has served one of its first internal customers.
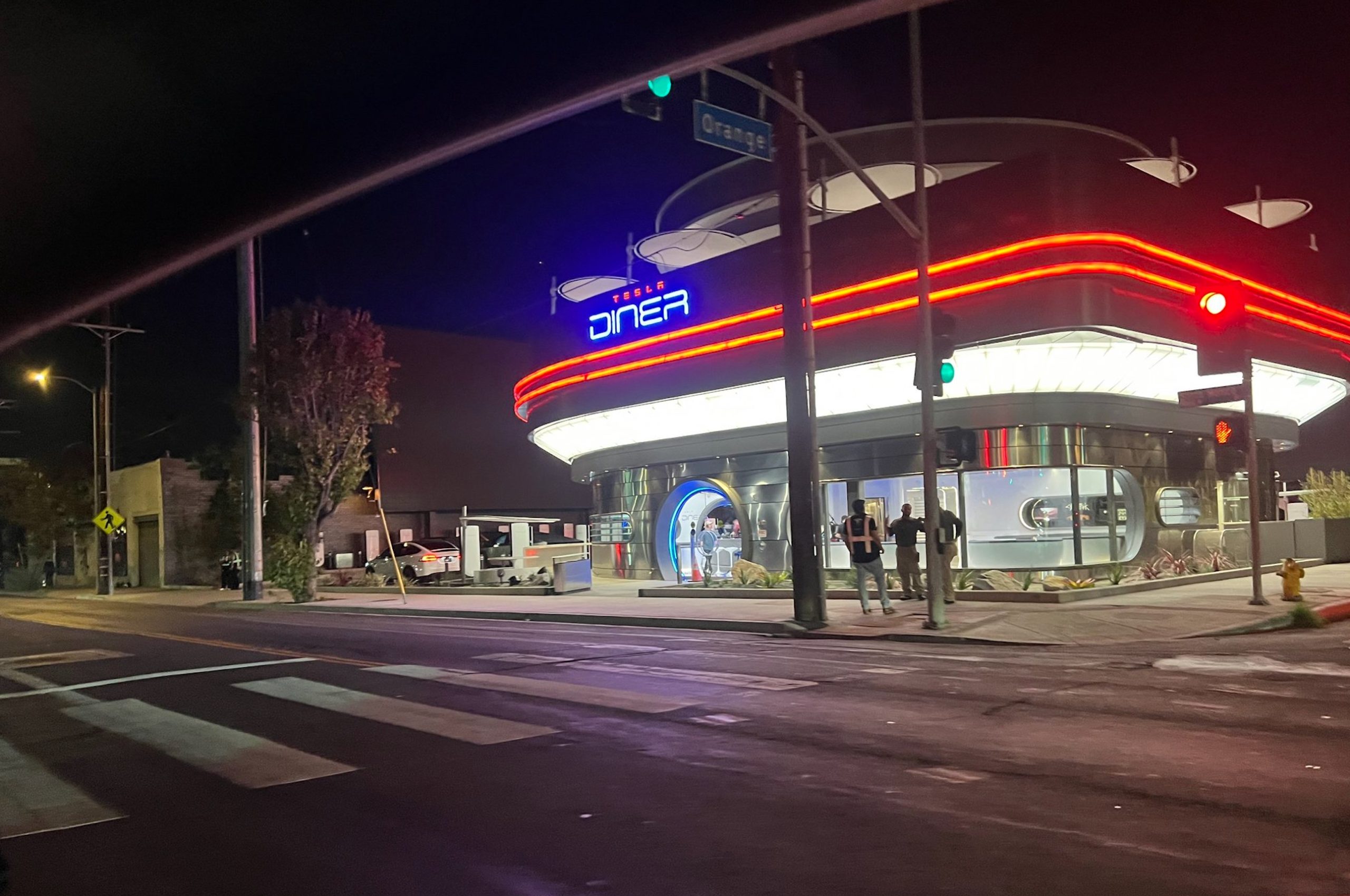

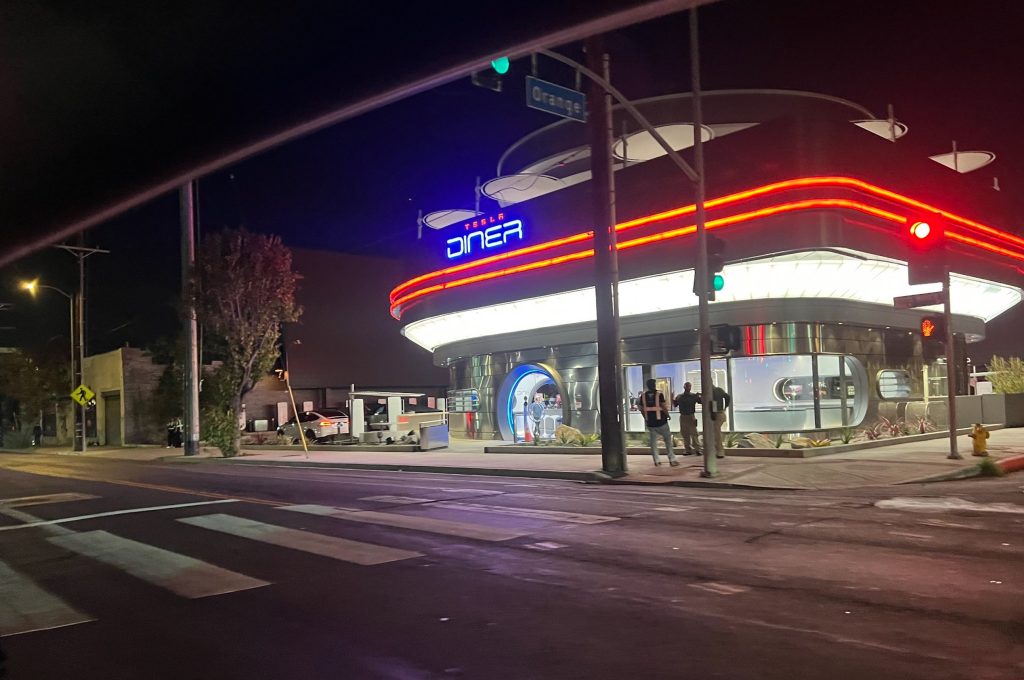
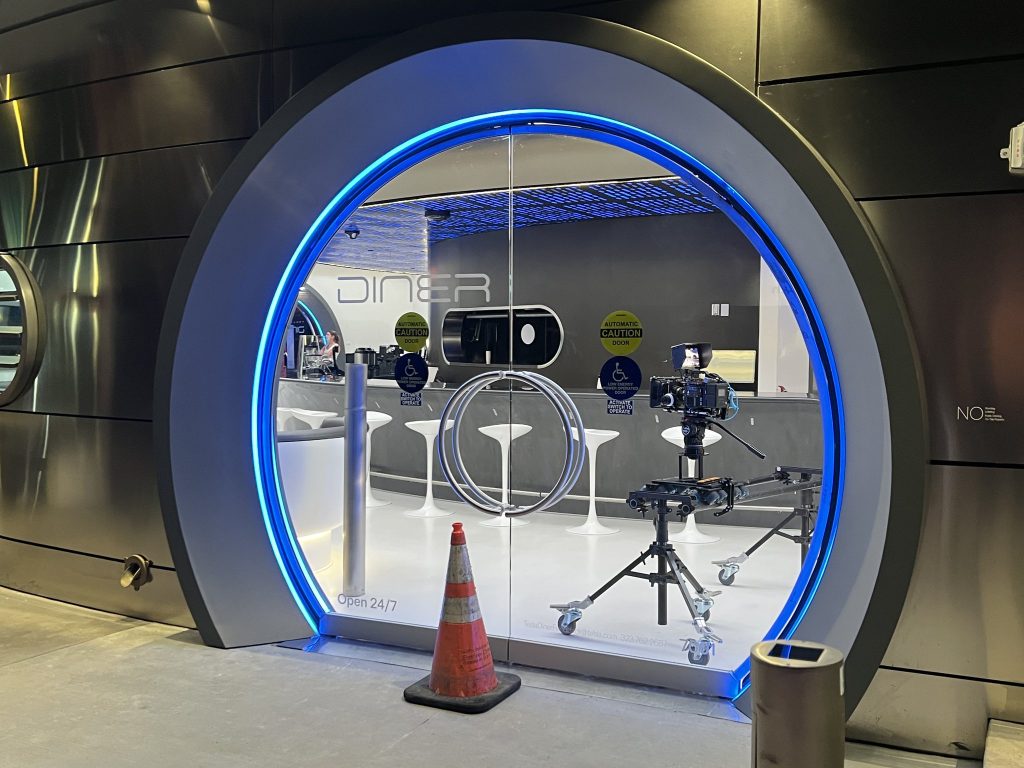
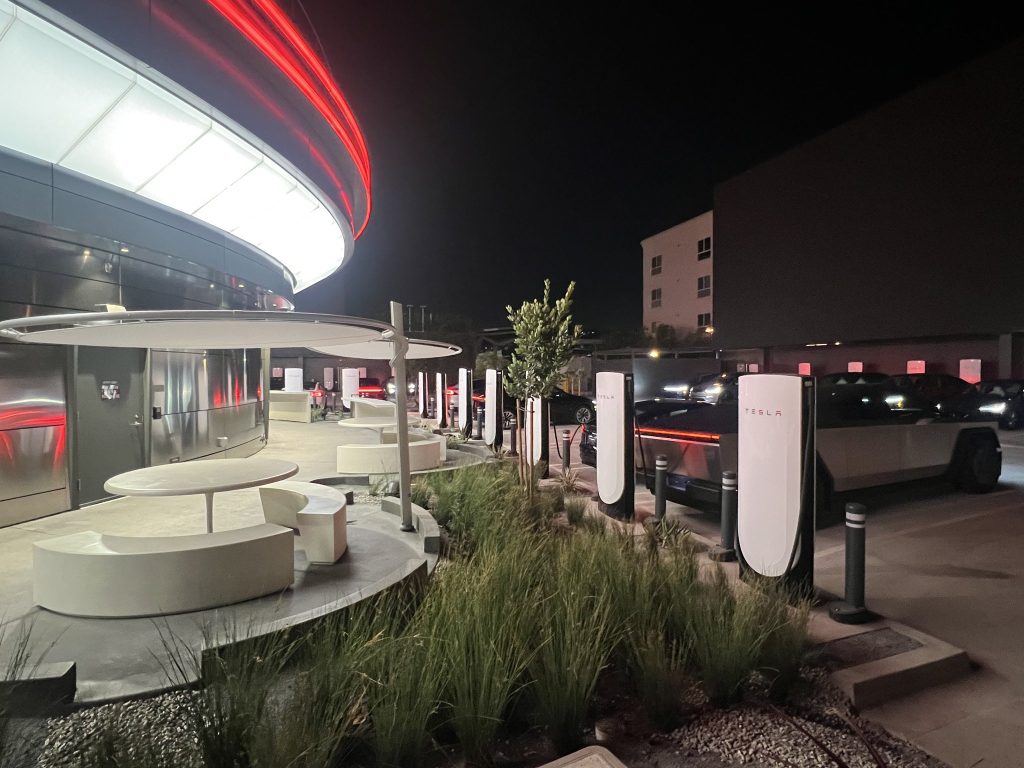
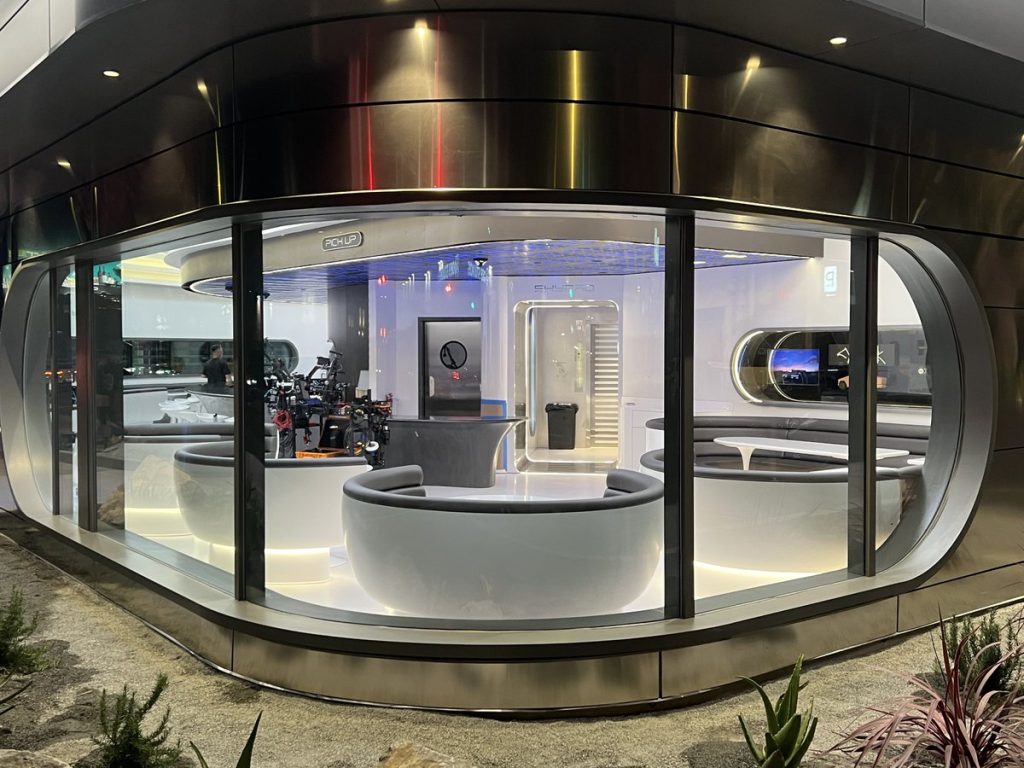
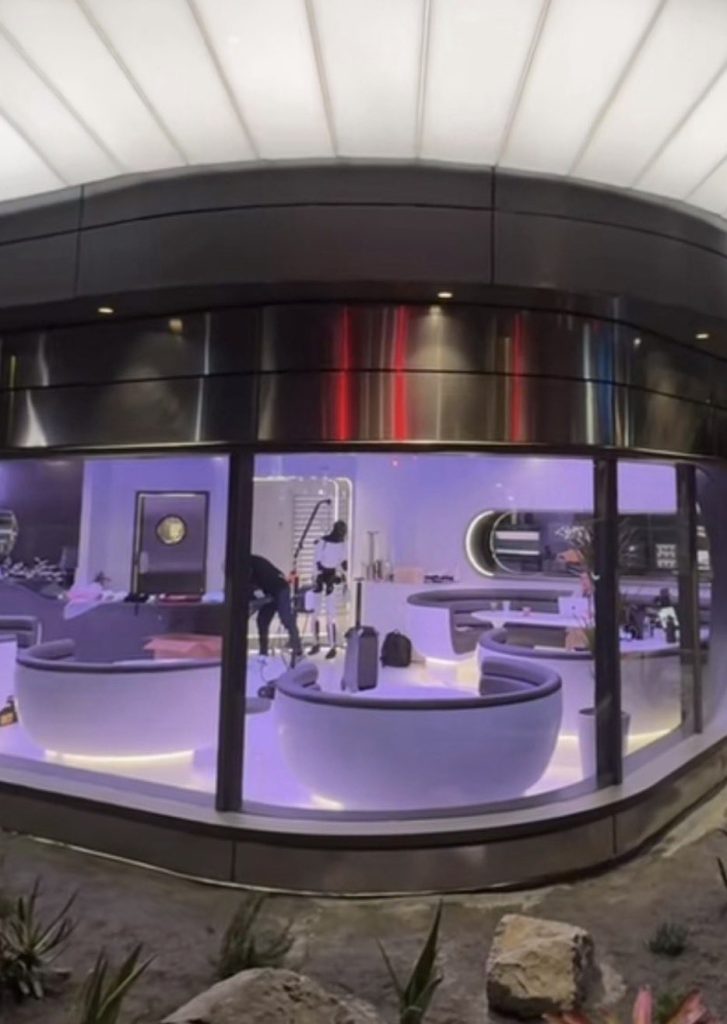
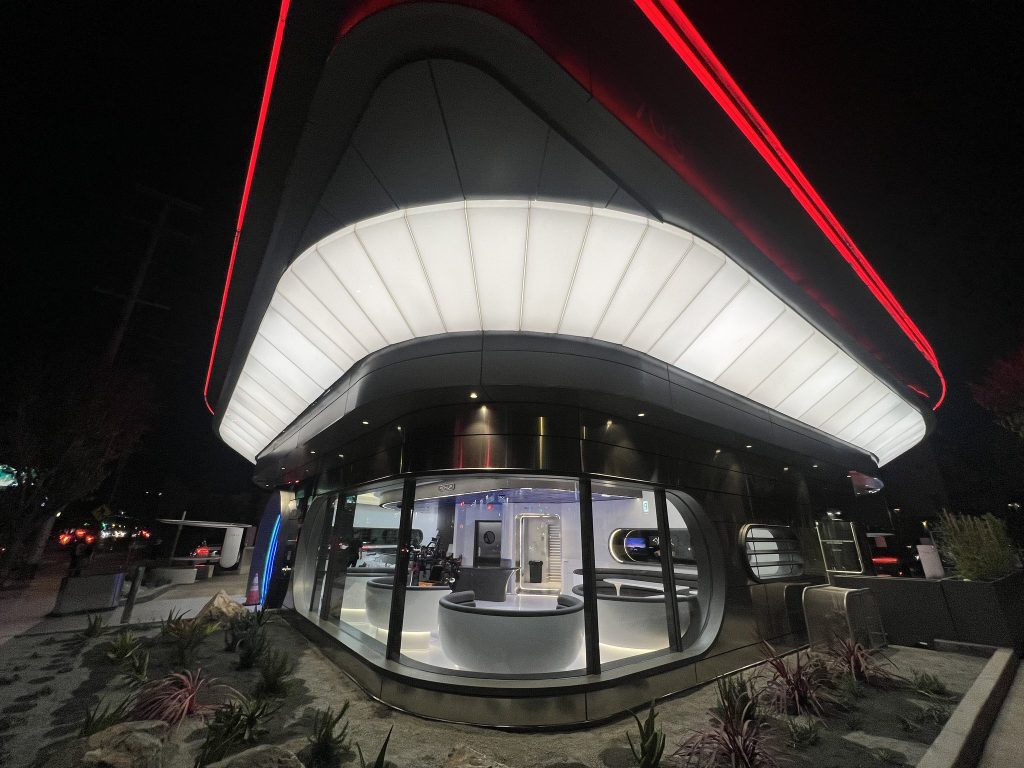
Tesla has finally completed the construction of its highly anticipated Diner, Drive-in, and Supercharger in Los Angeles, and recent photos of the interior’s “retro-futuristic” style are making their way around the internet.
X user Brad Goldberg shared photos from the Tesla Diner site last Tuesday, depicting some of the Supercharger stalls, indoor and outdoor seating areas, multiple neon lights, and even an Optimus robot. Goldberg also noted that there had been a “flurry of activity on site” while he was snapping the photos last week, suggesting that the restaurant location could be getting close to opening.
The Tesla Diner also served one of its first internal customers in the past few days, as Elon Musk posted on X on early Monday morning that he had just finished up eating a meal at the site:
I just had dinner at the retro-futuristic Tesla diner and Supercharger.
Team did great work making it one of the coolest spots in LA!
The photos also show that the site is pretty much done, with some of them even showing vehicles charging at the charging stalls.
You can see some of the latest photos of the Tesla Diner below.

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X

Credit: TeslaKing420 | X

Credit: TeslaKing420 | X

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)
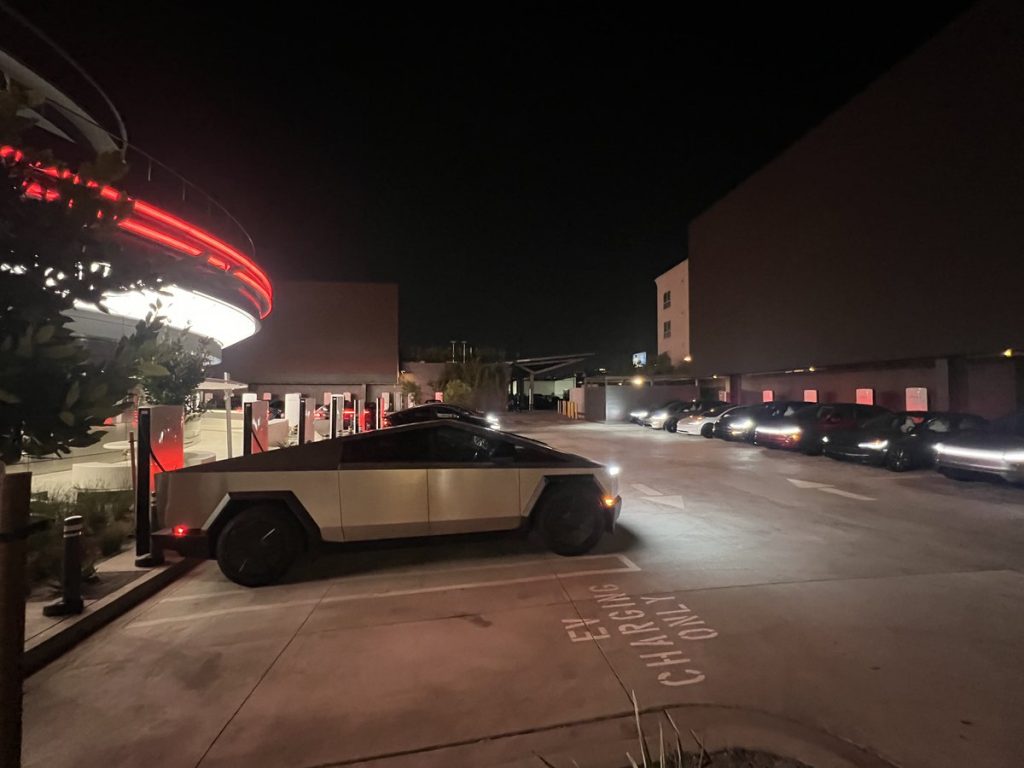

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)
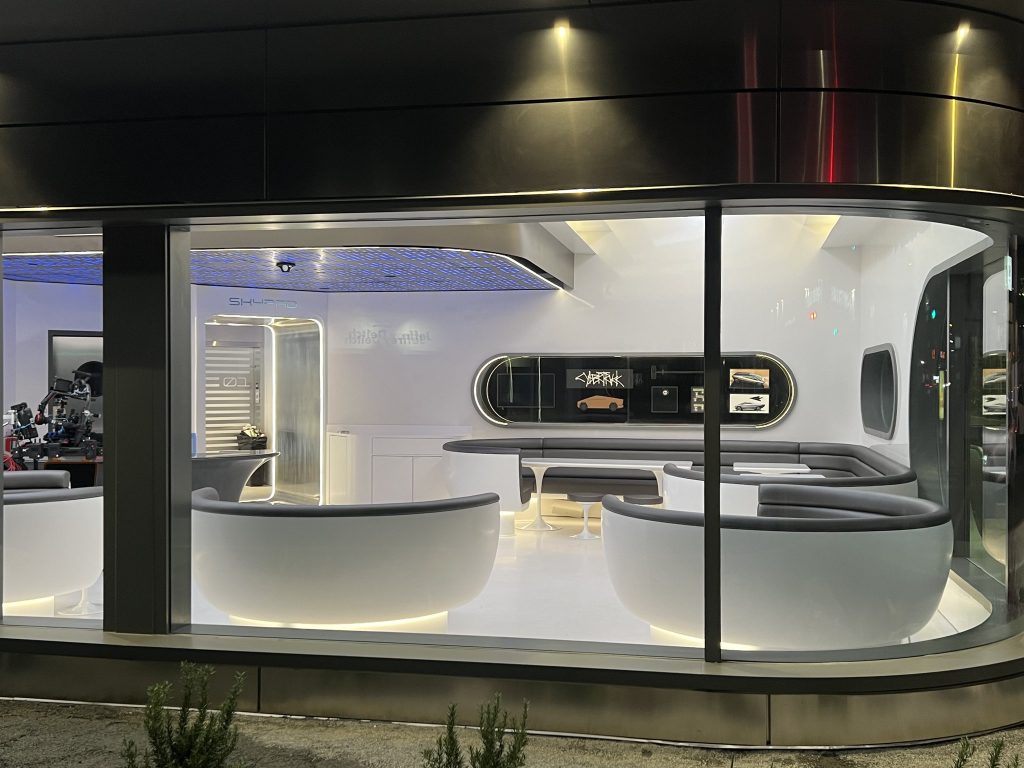

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)
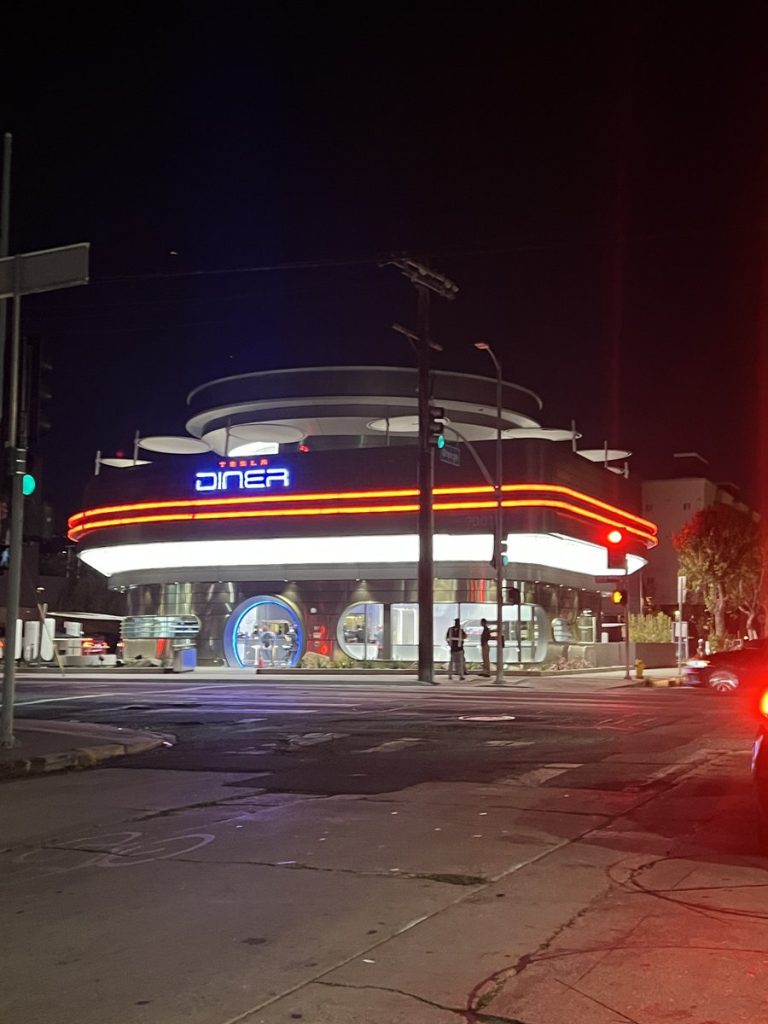

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)
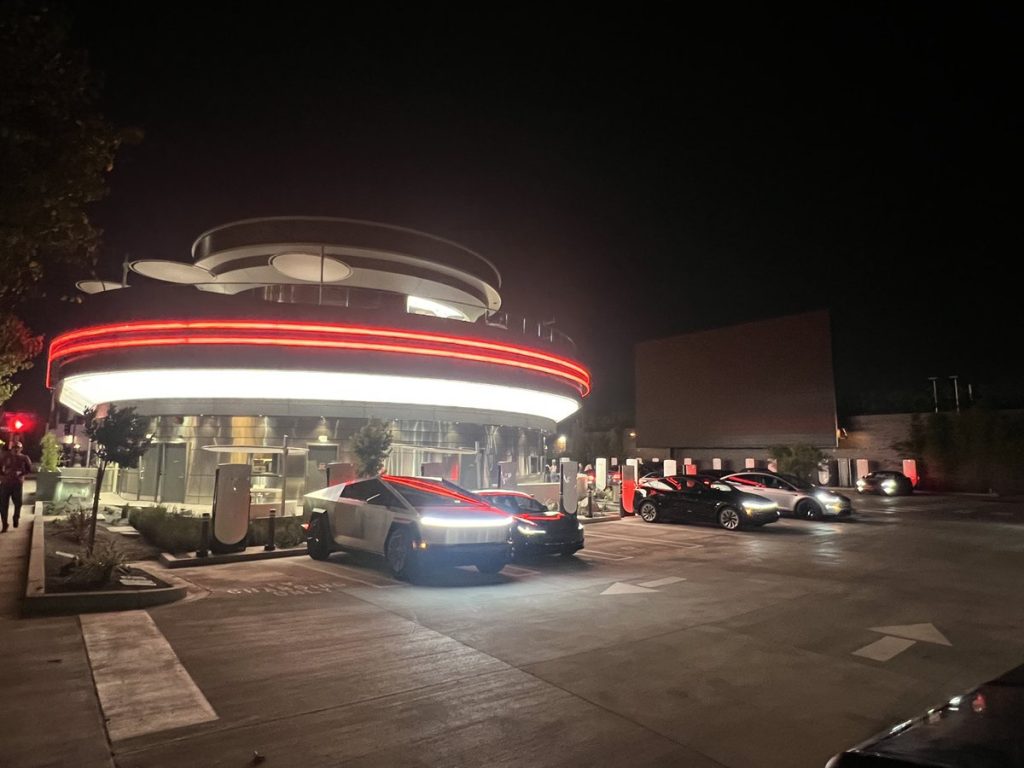

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)
READ MORE ON TESLA’S LA DINER: Tesla readies Drive-In Diner Supercharger for launch with app inclusion
When will the Tesla Diner open to external customers?
While it’s still not open to external customers yet, the news again suggests that the company could be close to an official opening date. Tesla first broke ground on the Diner in September 2023, after receiving a wave of building permit approvals throughout that year. Teslarati also covered much of the construction progress throughout last year, including when crews installed the first and second drive-in screens.
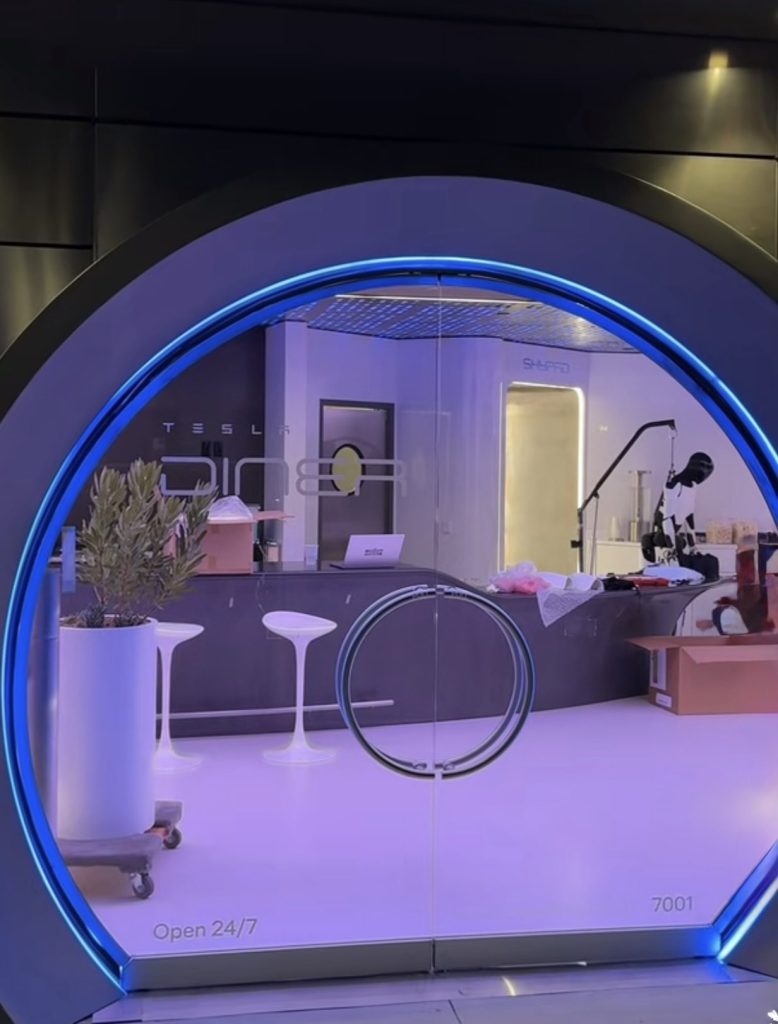
Located at 7001 West Santa Monica Boulevard, the idea was first discussed in 2018 by Musk and a few others on Twitter, featuring 1950s rock and roll, waiters on roller skates, and drive-in movie theater screens playing clips from some of history’s best movies. Notably, the photos of the front doors also show that the site will be open 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, whenever it does end up opening.
Tesla’s progress on Supercharger with diner, drive-in seen in aerial footage
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoTesla debuts hands-free Grok AI with update 2025.26: What you need to know
-

 Elon Musk4 days ago
Elon Musk4 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk6 days ago
Elon Musk6 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoTesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales















