

Lifestyle
Tesla’s fight for price parity is also taking shape in the sustainable food industry
Tesla’s mission for sustainability and goal to reach price parity with its petrol-powered competition in the transportation industry is also starting to take shape in the food industry. The world of meat alternatives is currently competing with animal products to achieve the same goal: price parity to promote environmental sustainability in food, an item crucial for everyday survival.
Since the release of Tesla CEO Elon Musk’s Master Plan, the goal has always been to offer affordable and environmentally sustainable options to drivers everywhere. To do this, Tesla’s ultimate goal is to drive the cost down of batteries to $100 per kWh and close the gap between the cost of electric vehicles and gas vehicles.
Similarly, meat alternatives are fighting for the same price parity in their own way. The goal of meat alternative companies like Beyond Meats and Impossible Foods is to offer options to traditional beef products at equal prices so the average consumer will consider buying sustainable and more environmentally-friendly foods that satisfy their cravings. After CNBC reported Impossible Foods’ prices were slashed by 15% earlier this week because manufacturing efficiencies and large scale production, price parity is closer than ever.
The argument against electric cars and sustainably-produced foods has always been price. As electric vehicles, Tesla’s, in particular, started expensive, they have slowly dropped in price while increasing performance and efficiency. Batteries that power the cars have become a mass-produced item, thus forcing the price of cells to drop dramatically. Eventually, this will lead to batteries being produced at the $100 kWh target, inducing price parity.
This story is no different than meat alternatives. When Beyond Meats and Impossible Foods were formed in 2009 and 2011 respectively, the goal was to create products that would give people “meat” without the adverse environmental or health effects that come from eating real beef. The battle with the new “meat” products was that they were expensive to produce; thus, many people did not see the advantage of buying them.
However, the environmental movement has grown considerably because of the increased awareness of climate change. People are now willing to cut some meat out of their diets to fight industrial farming and are replacing it with meat alternatives. As many people across the world have embraced these new meat alternatives, large scale businesses like Burger King have adapted the products because of increased demand.
Burger King added the Impossible Whopper to its menu in 2019. After prices for BK’s plant-based Whopper were noticeably higher than the company’s regular flagship sandwich, it was labeled a “premium” product. As demand for the Impossible meats rose, the cost of the went down. Now the Impossible Whopper is available on BK’s 2 for $6 menu.
The increase in demand for meat alternatives has led to lower prices. Just like electric vehicle batteries, mass production has contributed to a decrease in price, and eventually, this will lead to price parity with real meat. Beyond Meat CEO Ethan Brown predicts his company will reach price parity with natural beef products in 2024, one year after analysts believe EVs will reach parity with gas vehicles.
In the grand scheme of things, the goal between battery vehicles and meat substitutes is the same: increase environmental sustainability by offering products that are equivalent to the things people have been using for their whole lives. Turn people away from things that harm the environment and make sustainable alternatives just as affordable as their competitors, eliminating the argument that battery cars or meatless options are “too expensive” and “unaffordable.”
Elon Musk
X account with 184 followers inadvertently saves US space program amid Musk-Trump row
Needless to say, the X user has far more than 184 followers today after his level-headed feat.

An X user with 184 followers has become the unlikely hero of the United States’ space program by effectively de-escalating a row between SpaceX CEO Elon Musk and President Donald Trump on social media.
Needless to say, the X user has far more than 184 followers today after his level-headed feat.
A Near Fall
During Elon Musk and Donald Trump’s fallout last week, the U.S. President stated in a post on Truth Social that a good way for the United States government to save money would be to terminate subsidies and contracts from the CEO’s companies. Musk responded to Trump’s post by stating that SpaceX will start decommissioning its Dragon spacecraft immediately.
Musk’s comment was received with shock among the space community, partly because the U.S. space program is currently reliant on SpaceX to send supplies and astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS). Without Dragon, the United States will likely have to utilize Russia’s Soyuz for the same services—at a significantly higher price.
X User to the Rescue
It was evident among X users that Musk’s comments about Dragon being decommissioned were posted while emotions were high. It was then no surprise that an X account with 184 followers, @Fab25june, commented on Musk’s post, urging the CEO to rethink his decision. “This is a shame this back and forth. You are both better than this. Cool off and take a step back for a couple days,” the X user wrote in a reply.
Much to the social media platform’s surprise, Musk responded to the user. Even more surprising, the CEO stated that SpaceX would not be decommissioning Dragon after all. “Good advice. Ok, we won’t decommission Dragon,” Musk wrote in a post on X.
Not Planned, But Welcomed
The X user’s comment and Musk’s response were received extremely well by social media users, many of whom noted that @Fab25june’s X comment effectively saved the U.S. space program. In a follow-up comment, the X user, who has over 9,100 followers as of writing, stated that he did not really plan on being a mediator between Musk and Trump.
“Elon Musk replied to me. Somehow, I became the accidental peace broker between two billionaires. I didn’t plan this. I was just being me. Two great minds can do wonders. Sometimes, all it takes is a breather. Grateful for every like, DM, and new follow. Life’s weird. The internet’s weirder. Let’s ride. (Manifesting peace… and maybe a Model Y.)” the X user wrote.
Lifestyle
Tesla Cybertruck takes a bump from epic failing Dodge Charger
The Cybertruck seemed unharmed by the charging Charger.
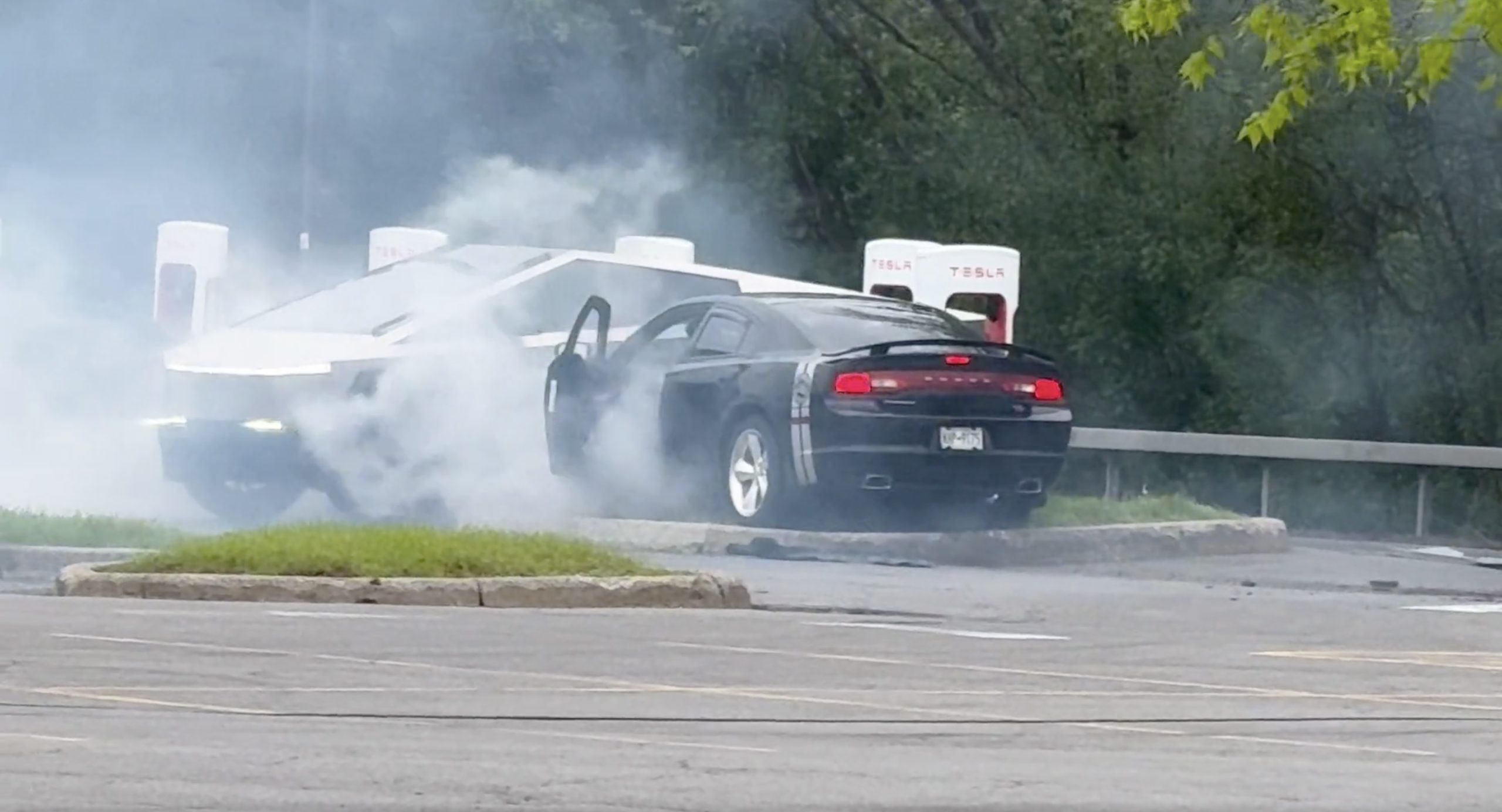

There comes a time in a driver’s life when one is faced with one’s limitations. For the driver of a Dodge Charger, this time came when he lost control and crashed into a Tesla Cybertruck–an absolute epic fail.
A video of the rather unfortunate incident was shared on the r/TeslaLounge subreddit.
Charging Charger Fails
As could be seen in the video, which was posted on the subreddit by Model Y owner u/Hammer_of_something, a group of teens in a Dodge Charger decided to do some burnouts at a Tesla Supercharger. Unfortunately, the driver of the Charger failed in his burnout or donut attempt, resulting in the mopar sedan going over a curb and bumping a charging Cybertruck.
Ironically, the Dodge Charger seemed to have been parked at a Supercharger stall before its driver decided to perform the failed stunt. This suggests that the vehicle was likely ICE-ing a charging stall before it had its epic fail moment. Amusingly enough, the subreddit member noted that the Cybertruck did not seem like it took any damage at all despite its bump. The Charger, however, seemed like it ran into some trouble after crashing into the truck.
Alleged Aftermath
As per the the r/TeslaLounge subreddit member, the Cybertruck owner came rushing out to his vehicle after the Dodge Charger crashed into it. The Model Y owner then sent over the full video of the incident, which clearly showed the Charger attempting a burnout, failing, and bumping into the Cybertruck. The Cybertruck owner likely appreciated the video, in part because it showed the driver of the Dodge Charger absolutely freaking out after the incident.
The Cybertruck is not an impregnable vehicle, but it can take bumps pretty well thanks to its thick stainless steel body. Based on this video, it appears that the Cybertruck can even take bumps from a charging Charger, all while chilling and charging at a Supercharger. As for the teens in the Dodge, they likely had to provide a long explanation to authorities after the incident, since the cops were called to the location.
Lifestyle
Anti-Elon Musk group crushes Tesla Model 3 with Sherman tank–with unexpected results
Ironically enough, the group’s video ended up highlighting something very positive for Tesla.
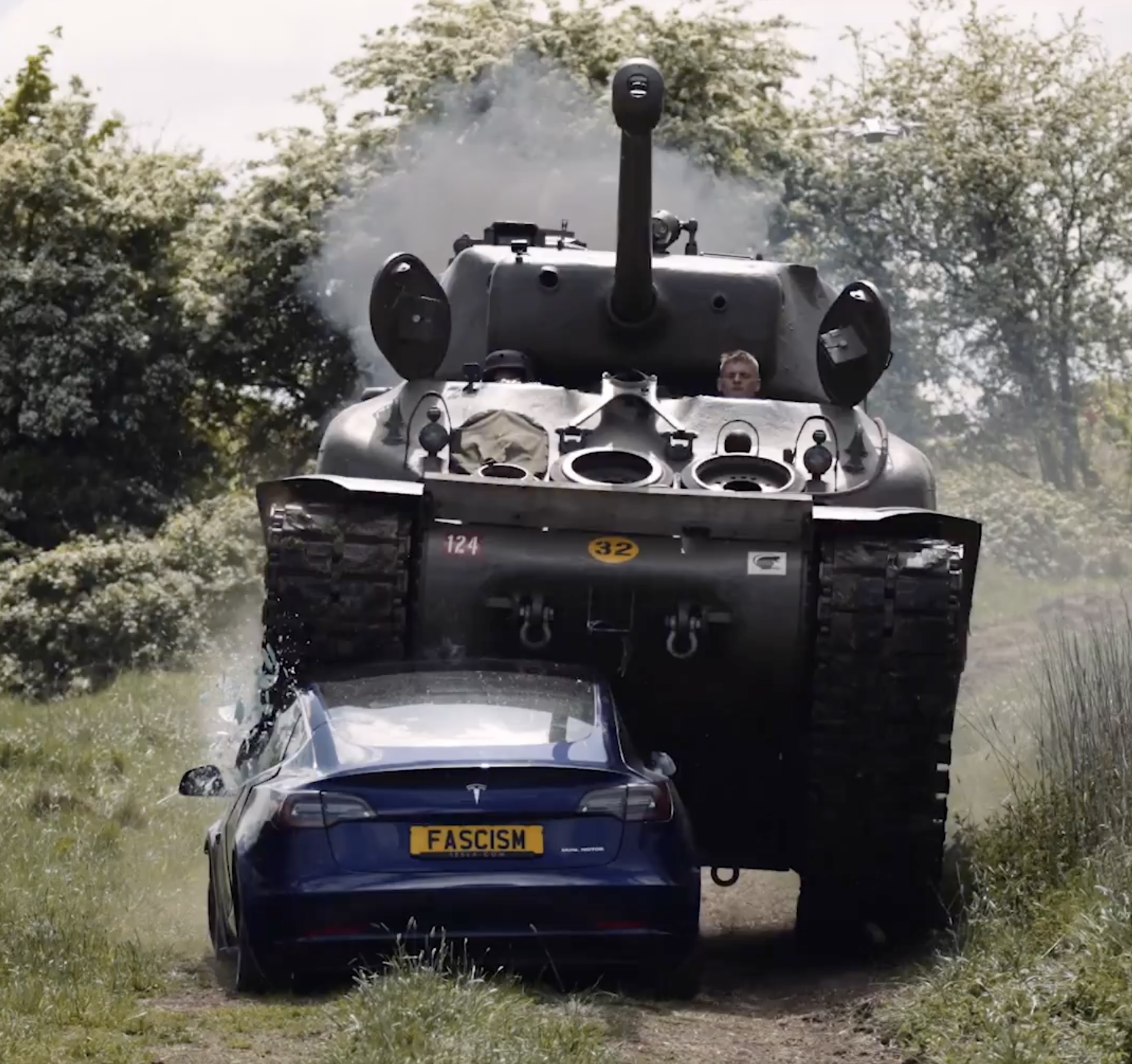

Anti-Elon Musk protesters and critics tend to show their disdain for the CEO in various ways, but a recent video from political action group Led By Donkeys definitely takes the cake when it comes to creativity.
Ironially enough, the group’s video also ended up highlighting something very positive for Tesla.
Tank vs. Tesla
In its video, Led By Donkeys featured Ken Turner, a 98-year-old veteran who served in the British army during World War II. The veteran stated that Elon Musk, the richest man in the world, is “using his immense power to support the far-right in Europe, and his money comes from Tesla cars.”
He also noted that he had a message for the Tesla CEO: “We’ve crushed fascism before and we’ll crush it again.” To emphasize his point, the veteran proceeded to drive a Sherman tank over a blue Tesla Model 3 sedan, which, of course, had a plate that read “Fascism.”
The heavy tank crushed the Model 3’s glass roof and windows, much to the delight of Led By Donkeys’ commenters on its official YouTube channel. But at the end of it all, the aftermath of the anti-Elon Musk demonstration ended up showcasing something positive for the electric vehicle maker.
Tesla Model 3 Tanks the Tank?
As could be seen from the wreckage of the Tesla Model 3 after its Sherman encounter, only the glass roof and windows of the all-electric sedan were crushed. Looking at the wreckage of the Model 3, it seemed like its doors could still be opened, and everything on its lower section looked intact.
Considering that a standard M4 Sherman weighs about 66,800 to 84,000 pounds, the Model 3 actually weathered the tank’s assault really well. Granted, the vehicle’s suspension height before the political action group’s demonstration suggests that the Model 3’s high voltage battery had been removed beforehand. But even if it hadn’t been taken off, it seemed like the vehicle’s battery would have survived the heavy ordeal without much incident.
This was highlighted in comments from users on social media platform X, many of whom noted that a person in the Model 3 could very well have survived the ordeal with the Sherman. And that, ultimately, just speaks to the safety of Tesla’s vehicles. There is a reason why Teslas consistently rank among the safest cars on the road, after all.
-

 Elon Musk1 day ago
Elon Musk1 day agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla’s Grok integration will be more realistic with this cool feature
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk slams Bloomberg’s shocking xAI cash burn claims
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla China roars back with highest vehicle registrations this Q2 so far
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTexas lawmakers urge Tesla to delay Austin robotaxi launch to September
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla dominates Cars.com’s Made in America Index with clean sweep
-
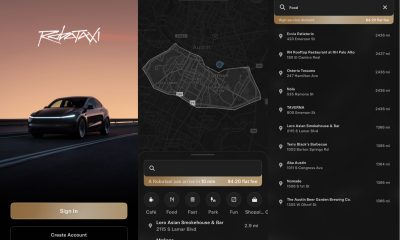
 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more















