

News
Tesla’s success ushers in a new era of electric flight
Electric flight may not be as far away as we once thought. In the next decade, aircraft are set to see dramatic changes as companies both large and small work to bring fully electric and hybrid flight to market. Airlines, manufacturers, and startups all seem to be moving towards this goal (see below). The race is clearly on and it will change the way we think about flight.
Yet as it was for the introduction of electric vehicles, the first aircraft is short range and seat just a few passengers. Their applications today are limited but to think the industry will stay in this nascent stage would be a mistake. Successes in these small and short-range aircraft will translate forward into larger and longer-range aircraft. The companies that find success here will emerge as leaders in a new era of electric flight.

Companies working on electric flight
On the Market Today:
First, it’s important to appreciate that only recently have small electric powered aircraft gone from concepts to commercial use.
Pipistrel’s Alpha Electro is one of these all-electric aircraft. It’s meant primarily for pilot training and just received its airworthiness certification from the FAA in April 2018, becoming the first in the USA to do so. The Alpha Electro only seats two people and is good for an hour of flight plus reserves. That might not sound like much but it could be disruptive. Pipistrel says the aircraft cuts beginner pilot training costs by as much as 70% while producing zero emissions and low noise.
In China, the Ruixiang RX1E is a similar style trainer sold there commercially. They also have a new, longer-range model that was recently tested, the RX1E-A. With a two-hour flight time the new version doubles its previous capabilities. At this size of aircraft the technology is getting close to parity with comparable gasoline-powered aircraft, like the Cessna 162 which has a flight time of about three hours.
Full parity might be here sooner than you think. Coming small electric aircraft have better specs and more seating, with many nearly ready for certification (pictured below). Pipistrel has their Panthera (top right), which will hold four passengers and will come in options for combustion, hybrid, and all-electric powertrains. There’s also BYE Aerospace in Colorado, which has a four-seater in development and just completed the first test flight of the two-seater Sun Flyer 2 — it has a flight time of 3 hours. Ruixiang also announced they have a 4-seater aircraft in development. The other important consideration is that their initial costs appear to be comparable to combustion options as well.
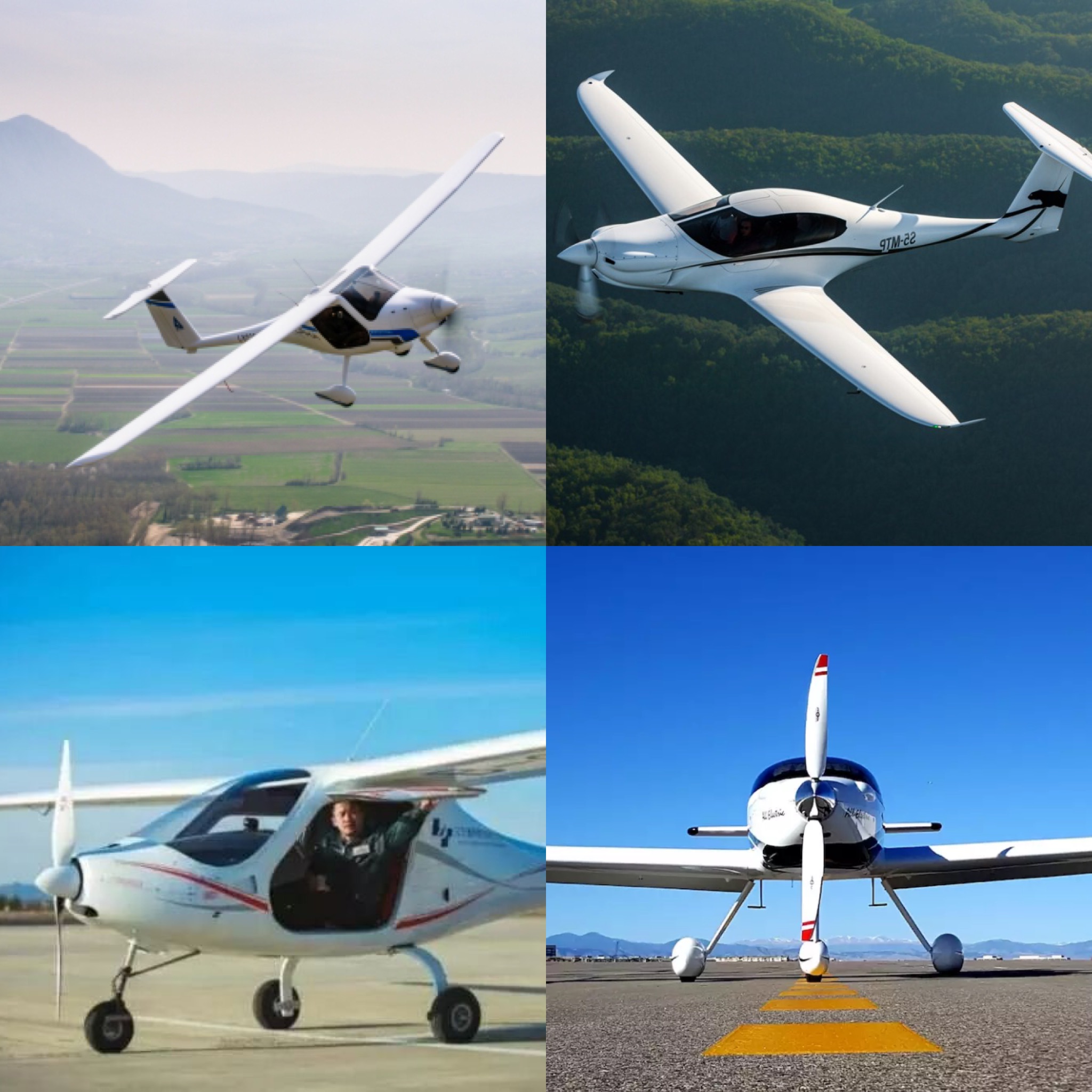

Pipistrel Alpha Electro (top left), Pipistrel Panthera (top right), Ruixiang RX1E-A (bottom left), BYE Aerospace Sunflyer 2 (bottom right)
Looking at these options, some will say that an electric aircraft is an isolated niche and for now, that’s mostly correct. These are small aircraft with limited applications. Yet when the Nissan Leaf and even the Tesla Roaster first came out many believed electric cars were a niche technology too. The range was too short, seating was too small, and costs were too high to realistically consider the technology going mainstream. Now we are in the midst of a market transformation, with automakers pouring billions into their EV programs and countries announcing they are phasing out combustion vehicles.
Market Transformation – Near-Term Preproduction:
The next major step for electric flight appears to be in small commuter aircraft. Aircraft that weigh less than 12,500 lbs, carry 5 to 20 passengers and travel up to 750 miles. In addition to regional commuter needs, they may also serve recreational and business purposes. If small aircraft are like the Tesla Roadster then these are like the Model S. They have more seats, longer range, and are made in higher volumes.
The use case of short range regional commuters is almost perfect for electrification. Much of their flight is spent just getting up to altitude, where cruising achieves the greatest efficiency. The time spent cruising however is relatively short and the result is that such regional flights are inherently less efficient than those over greater distances. On the plus side the high operating costs are a great opportunity for electrification. Consider that a turbine engine achieves an efficiency of around 55% at cruising, but on ascent that efficiency can drop by half (~25%). By comparison, an electric motor has efficiencies greater than 95%.
One of the companies working to electrify these regional aircraft is Wright Electric, based out of Los Angeles. They recently announced plans to bring to market a 9-seat electrified aircraft with a range of at least 340 miles. According to their website that would cover the distance of nearly 44% of all flights. The announcement is part of their new partnership with JetEx, a fixed-base operator based in Saudi Arabia with operations in over 30 countries. I recently spoke with Wright Electric’s CEO Jeff Engler about their coming aircraft and where he see’s the industry going. The first thing that surprised me is that their aircraft could be on the market very soon.
“We are certain that the first flight test will take place next year. It could be on the market in just over two years.” – Jeff Engler, CEO of Wright Electric
That means that sometime towards the end of 2020 or beginning of 2021 they could be in their air, operating with paying customers.
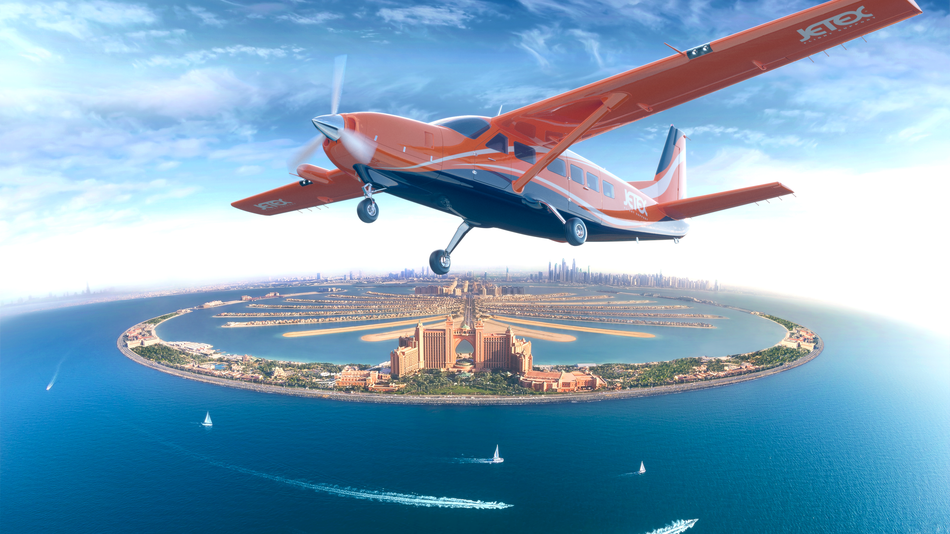

Wright Electric / JetEx
Their aircraft is intended for intercity travel and recreational activities Jeff said, but it’s not the end goal. In fact, their approach may be familiar to fans of electric cars.
“Our plan is similar to the Tesla approach, in the sense that they started with the Roadster and then scaled up to larger more mass market vehicles. Our first plane to market will be a premium aircraft meant to travel short distances with a small number of passengers… perfect for intercity flights and recreational activities like skydiving. This initial program is the springboard for development of larger longer-range aircraft”. – Jeff Engler, CEO of Wright Electric
In regards to the technology Jeff said they are developing the hybrid and all electric powertrains concurrently. He noted that battery advancements will dictate the transition to fully electric flight but in the interim, hybrid solutions will significantly reduce fuel costs, noise, and pollution. With restrained enthusiasm, he was cautiously optimistic about the coming advances in battery technology. Yet battery technology isn’t holding them up.
The beauty of hybrid options is that as batteries improve they can be seamlessly integrated into the design, allowing more of the flight to be electric. For their electric hybrid, Wright Electric likes to use the term “helper motor”. A helper motor can run hard during takeoff and ascent to help bring the aircraft up to altitude, thereby reducing the burden on the combustion engines, improving overall efficiency, and reducing fuel consumption. Once at altitude, the combustion engines can take over, where they operate most efficiently.
Even without being fully electric hybrid aircraft would have surprising benefits to fuel economy, pollution, and noise. Wright Electric has estimated the potential for reducing fuel use by nearly 2/3’s, while fellow electric aircraft startup Zunum Aero indicated 40% to 80% operating savings. Zunum Aero also noted a potential 70% reduction in community noise.
More Regional Commuter Aircraft are Coming Too:
Wright electric isn’t the only one working in this space. Other startups are also pushing the industry forward and they’ve partnered with established manufacturers and airlines to help make it happen. It’s similar to the approach Tesla took early on by partnering with established companies like Daimler and Toyota, and even in their recent developments of the Semi.
Zunum Aero is another one of the leaders in the electric aircraft space, based out of the west coast near Seattle. They are developing a 12-seat hybrid-electric, with a targeted range of over 700 miles. First test flights are targeted for 2019 and commercial operation is planned for 2022 (pictured below). Their partners include Boeing and JetBlue and just last week JetSuite announced they would order up to 100 of Zunum’s hybrid aircraft.
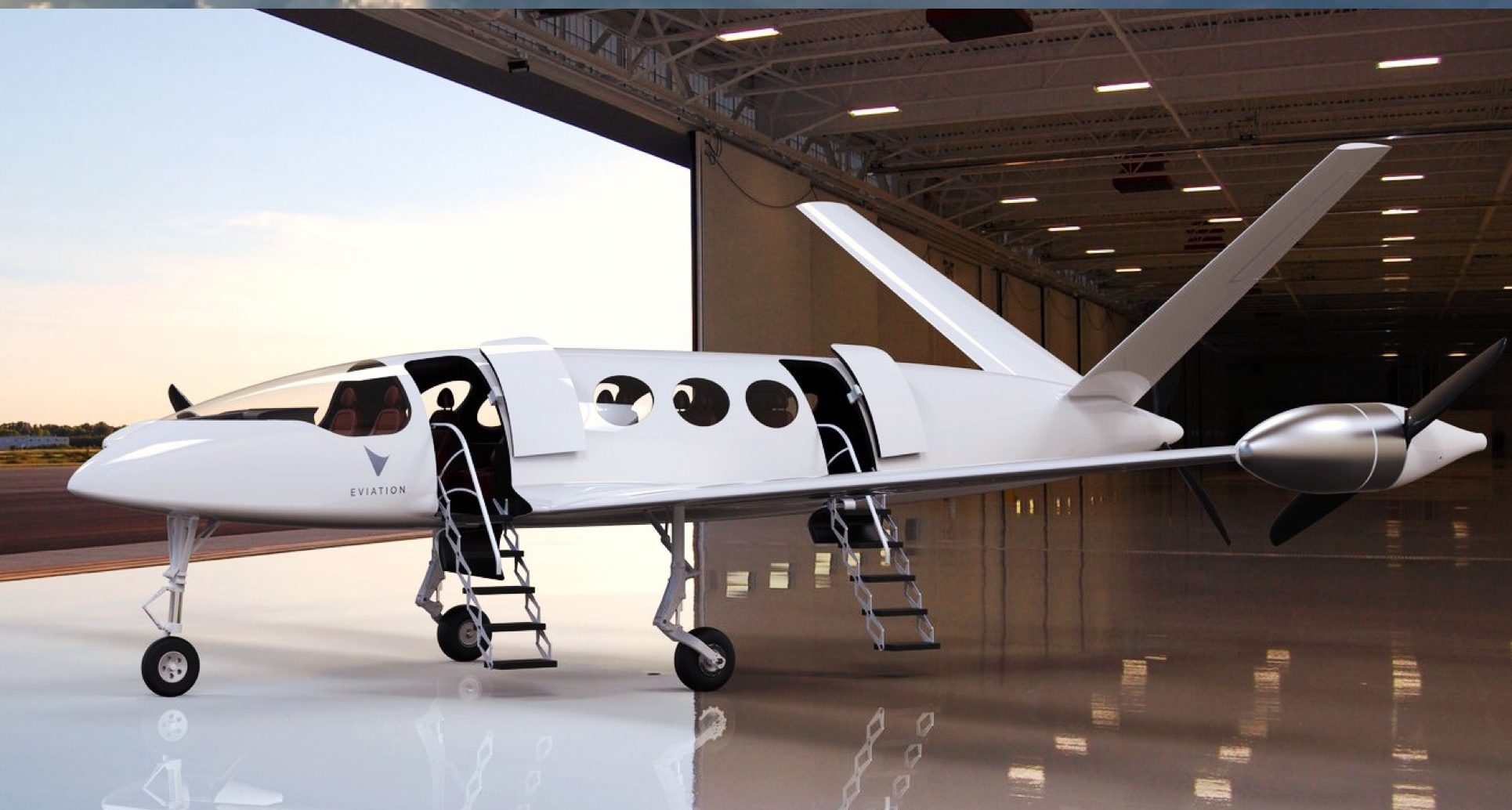
Eviation Aircraft is an Israel based company and has great ambitions for their first aircraft named “Alice”. It will be a 9-seat 650 mile aircraft and most importantly “all-electric”. They are targeting brining it to market by 2021. Is all-electric flight on that scale possible by 2021? They’ve said the aircraft will use a 950 kWh battery and just recently signed Kokam as their battery supplier, so they seem to be serious. I hope they make it happen. Alice is gorgeous.
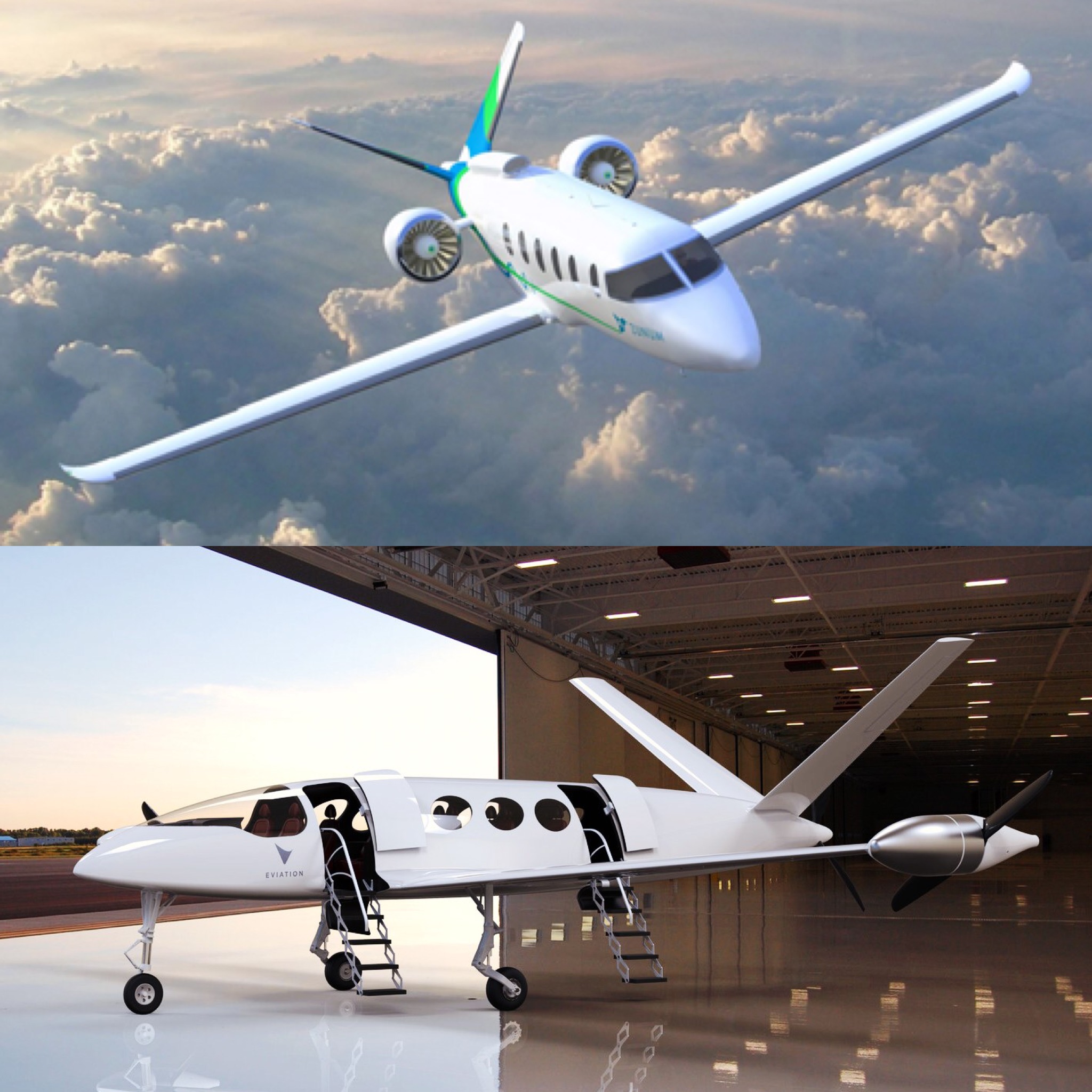

Zunum Aero (top), Eviation Aircraft (bottom)
Other Exciting Developments Coming Soon:
In the heavyweight division Airbus, Siemens, and Rolls-Royce have their own partnership, working together on their E-Fan X after the successful small electric E-Fan program. The E-Fan X will be a hybrid demonstrator aircraft based on the 100-seat BAe146. The first test flight is planned for 2020 and they are looking to bring a similarly sized hybrid aircraft to market sometime around 2030. Originally they were going to bring a small electric trainer based on the E-Fan to market in 2017 or 2018 but said the pace of development has set their ambitions upwards. There’s also Airbus’s subsidiary A3 which is working on a small all-electric vertical takeoff and landing aircraft.

E-Fan X
Vertical takeoff and landing aircraft are extremely interesting. They could be the biggest disrupters of all (covered in more detail in a follow up article, part 2). They too seem to be much closer than people think. For flying short distances they don’t actually need massive advancements in battery technology. Norway’s Avinor, their national aircraft operator, seems to indicate the mid 2020’s for practical operation.
Companies like Uber, Lilium, Kittyhawk, A3, and many more are developing electric aircraft capable of vertical takeoff and landing. They look more like flying cars than airplanes and that seems to be the point. These “air-taxis” are meant for hyper-local travel. Something you would hop onto downtown and take to get to across the city or to another nearby city. Lilium is a relatively new startup, founded in 2015, but has already made significant advancements in the space. They’ve already had their first full-scale test flight which is viewable below. Watching it lift off is almost magical. They brought on former Ferrari designer Frank Stephenson to head their design program and raised $90M to proceed with further development.
Lilium VTOL
Final Thoughts and Intro to Part 2
For fully electric flight a lot depends on batteries, but the technology is already finding applications in short-range, small aircraft. Increasing larger hybrid aircraft are also set to see their application in the real world in just a few years and will yield substantial benefits of their own. These moves should not be discounted. They are a prelude of what’s to come.
At this point, you may be wondering exactly what are the benefits of electric flight. That’s the focus of the second part of this article, coming out soon. They are substantial and will drive the industry forward with haste.

Elon Musk
What is Digital Optimus? The new Tesla and xAI project explained
At its core, Digital Optimus operates through a dual-process architecture inspired by human cognition.
Tesla and xAI announced their groundbreaking joint project, Digital Optimus, also nicknamed “Macrohard” in a humorous jab at Microsoft, earlier this week.
This software-based AI agent is designed to automate complex office workflows by observing and replicating human interactions with computers. As the first major outcome of Tesla’s $2 billion investment in xAI, it represents a powerful fusion of hardware efficiency and advanced reasoning.
At its core, Digital Optimus operates through a dual-process architecture inspired by human cognition.
Macrohard or Digital Optimus is a joint xAI-Tesla project, coming as part of Tesla’s investment agreement with xAI.
Grok is the master conductor/navigator with deep understanding of the world to direct digital Optimus, which is processing and actioning the past 5 secs of…
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 11, 2026
Tesla’s specialized AI acts as “System 1”—the fast, instinctive executor—processing the past five seconds of real-time computer screen video along with keyboard and mouse actions to perform immediate tasks.
xAI’s Grok model serves as “System 2,” the strategic “master conductor” or navigator, providing high-level reasoning, world understanding, and directional oversight, much like an advanced turn-by-turn navigation system.
When combined, the two can create a powerful AI-based assistant that can complete everything from accounting work to HR tasks.
Will Tesla join the fold? Predicting a triple merger with SpaceX and xAI
The system runs primarily on Tesla’s low-cost AI4 inference chip, minimizing expensive Nvidia resources from xAI for competitive, real-time performance.
Elon Musk described it as “the only real-time smart AI system” capable, in principle, of emulating the functions of entire companies, handling everything from accounting and HR to repetitive digital operations.
Timelines point to swift deployment. Announced just days ago, Musk expects Digital Optimus to be ready for user experience within about six months, targeting rollout around September 2026.
It will integrate into all AI4-equipped Tesla vehicles, enabling parked cars to handle office work during downtime. Millions of dedicated units are also planned for deployment at Supercharger stations, tapping into roughly 7 gigawatts of available power.
Oh and it works in all AI4-equipped cars, so your car can do office work for you when not driving.
We’re also deploying millions of dedicated Digital Optimus units in the field at Superchargers where we have ~7 gigawatts of available power.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 12, 2026
Digital Optimus directly supports Tesla’s broader autonomy strategy. It leverages the same end-to-end neural networks, computer vision, and real-time decision-making tech that power Full Self-Driving (FSD) software and the physical Optimus humanoid robot.
By repurposing idle vehicle compute and extending AI4 hardware beyond driving, the project scales Tesla’s autonomy ecosystem from roads to digital workspaces.
As a virtual counterpart to physical Optimus, it divides labor: software agents manage screen-based tasks while humanoid robots tackle physical ones, accelerating Tesla’s vision of general-purpose AI for productivity, Robotaxi fleets, and beyond.
In essence, Digital Optimus bridges Tesla’s vehicle and robotics autonomy with enterprise-scale AI, promising massive efficiency gains. No other company currently matches its real-time capabilities on such accessible hardware.
It really could be one of the most crucial developments Tesla and xAI begin to integrate, as it could revolutionize how people work and travel.
News
Tesla adds awesome new driving feature to Model Y
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.

Tesla is adding an awesome new driving feature to Model Y vehicles, effective on Juniper-updated models considered model year 2026 or newer.
Tesla is rolling out a new “Comfort Braking” feature with Software Update 2026.8. The feature is exclusive to the new Model Y, and is currently unavailable for any other vehicle in the Tesla lineup.
Tesla writes in the release notes for the feature:
“Your Tesla now provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.”
🚨 Tesla has added a new “Comfort Braking” update with 2026.8
“Your Tesla provides a smoother feel as you come to a complete stop during routine braking.” https://t.co/afqCpBSVeA pic.twitter.com/C6MRmzfzls
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
Interestingly, we’re not too sure what catalyzed Tesla to try to improve braking smoothness, because it hasn’t seemed overly abrupt or rough from my perspective. Although the brake pedal in my Model Y is rarely used due to Regenerative Braking, it seems Tesla wanted to try to make the ride comfort even smoother for owners.
There is always room for improvement, though, and it seems that there is a way to make braking smoother for passengers while the vehicle is coming to a stop.
This is far from the first time Tesla has attempted to improve its ride comfort through Over-the-Air updates, as it has rolled out updates to improve regenerative braking performance, handling while using Full Self-Driving, improvements to Steer-by-Wire to Cybertruck, and even recent releases that have combatted Active Road Noise.
Tesla holds a unique ability to change the functionality of its vehicles through software updates, which have come in handy for many things, including remedying certain recalls and shipping new features to the Full Self-Driving suite.
Tesla seems to have the most seamless OTA processes, as many automakers have the ability to ship improvements through a simple software update.
We’re really excited to test the update, so when we get an opportunity to try out Comfort Braking when it makes it to our Model Y.
News
Tesla finally brings a Robotaxi update that Android users will love
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android.

Tesla is finally bringing an update of its Robotaxi platform that Android users will love — mostly because it seems like they will finally be able to use the ride-hailing platform that the company has had active since last June.
Based on a decompile of software version 26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app, Tesla looks to be ready to roll out access to Android users.
According to the breakdown, performed by Tesla App Updates, the company is preparing to roll out an Android version of the app as it is developing several features for that operating system.
🚨 It looks like Tesla is preparing to launch the Robotaxi app for Android users at last!
A decompile of v26.2.0 of the Robotaxi app shows some progress on the Android side for Robotaxi 🤖 🚗 https://t.co/mThmoYuVLy
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) March 13, 2026
The breakdown of the software version shows that Tesla is actively developing an Android-compatible version of the Robotaxi app, and the company is developing Live Activities for Android:
“Strings like notification_channel_robotaxid_trip_name and android_native_alicorn_eta_text show exactly how Tesla plans to replicate the iOS Live Activities experience. Instead of standard push alerts, Android users are getting a persistent, dynamically updating notification channel.”
This is a big step forward for several reasons. From a face-value perspective, Tesla is finally ready to offer Robotaxi to Android users.
The company has routinely prioritized Apple releases because there is a higher concentration of iPhone users in its ownership base. Additionally, the development process for Apple is simply less laborious.
Tesla is working to increase Android capabilities in its vehicles
Secondly, the Robotaxi rollout has been a typical example of “slowly then all at once.”
Tesla initially released Robotaxi access to a handful of media members and influencers. Eventually, it was expanded to more users, so that anyone using an iOS device could download the app and hail a semi-autonomous ride in Austin or the Bay Area.
Opening up the user base to Android users may show that Tesla is preparing to allow even more users to utilize its Robotaxi platform, and although it seems to be a few months away from only offering fully autonomous rides to anyone with app access, the expansion of the user base to an entirely different user base definitely seems like its a step in the right direction.








