

News
Mars travelers can use ‘Star Trek’ Tricorder-like features using smartphone biotech: study
Plans to take humans to the Moon and Mars come with numerous challenges, and the health of space travelers is no exception. One of the ways any ill-effects can be prevented or mitigated is by detecting relevant changes in the body and the body’s surroundings, something that biosensor technology is specifically designed to address on Earth. However, the small size and weight requirements for tech used in the limited habitats of astronauts has impeded its development to date.
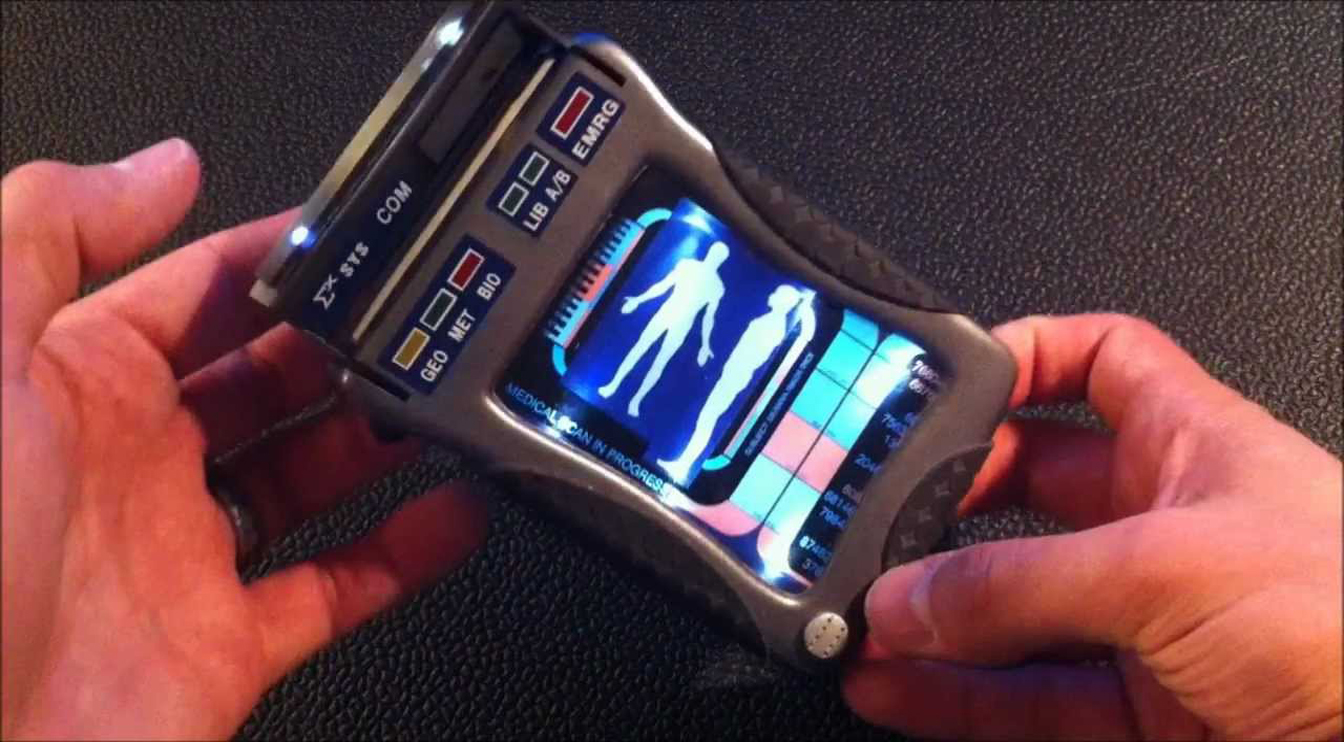
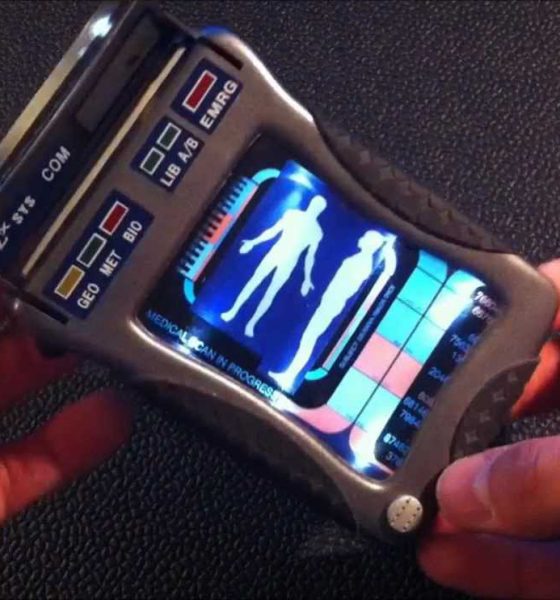
A recent study of existing smartphone-based biosensors by scientists from Queen’s University Belfast (QUB) in the UK identified several candidates under current use or development that could be also used in a space or Martian environment. When combined, the technology could provide functionality reminiscent of the “Tricorder” devices used for medical assessments in the Star Trek television and movie franchises, providing on-site information about the health of human space travelers and biological risks present in their habitats.
Biosensors focus on studying biomarkers, i.e., the body’s response to environmental conditions. For example, changes in blood composition, elevations of certain molecules in urine, heart rate increases or decreases, and so forth, are all considered biomarkers. Health and fitness apps tracking general health biomarkers have become common in the marketplace with brands like FitBit leading the charge for overall wellness sensing by tracking sleep patterns, heart rate, and activity levels using wearable biosensors. Astronauts and other future space travelers could likely use this kind of tech for basic health monitoring, but there are other challenges that need to be addressed in a compact way.
The projected human health needs during spaceflight have been detailed by NASA on its Human Research Program website, more specifically so in its web-based Human Research Roadmap (HRR) where the agency has its scientific data published for public review. Several hazards of human spaceflight are identified, such as environmental and mental health concerns, and the QUB scientists used that information to organize their study. Their research produced a 20-page document reviewing the specific inner workings of the relevant devices found in their searches, complete with tables summarizing each device’s methods and suitability for use in space missions. Here are some of the highlights.
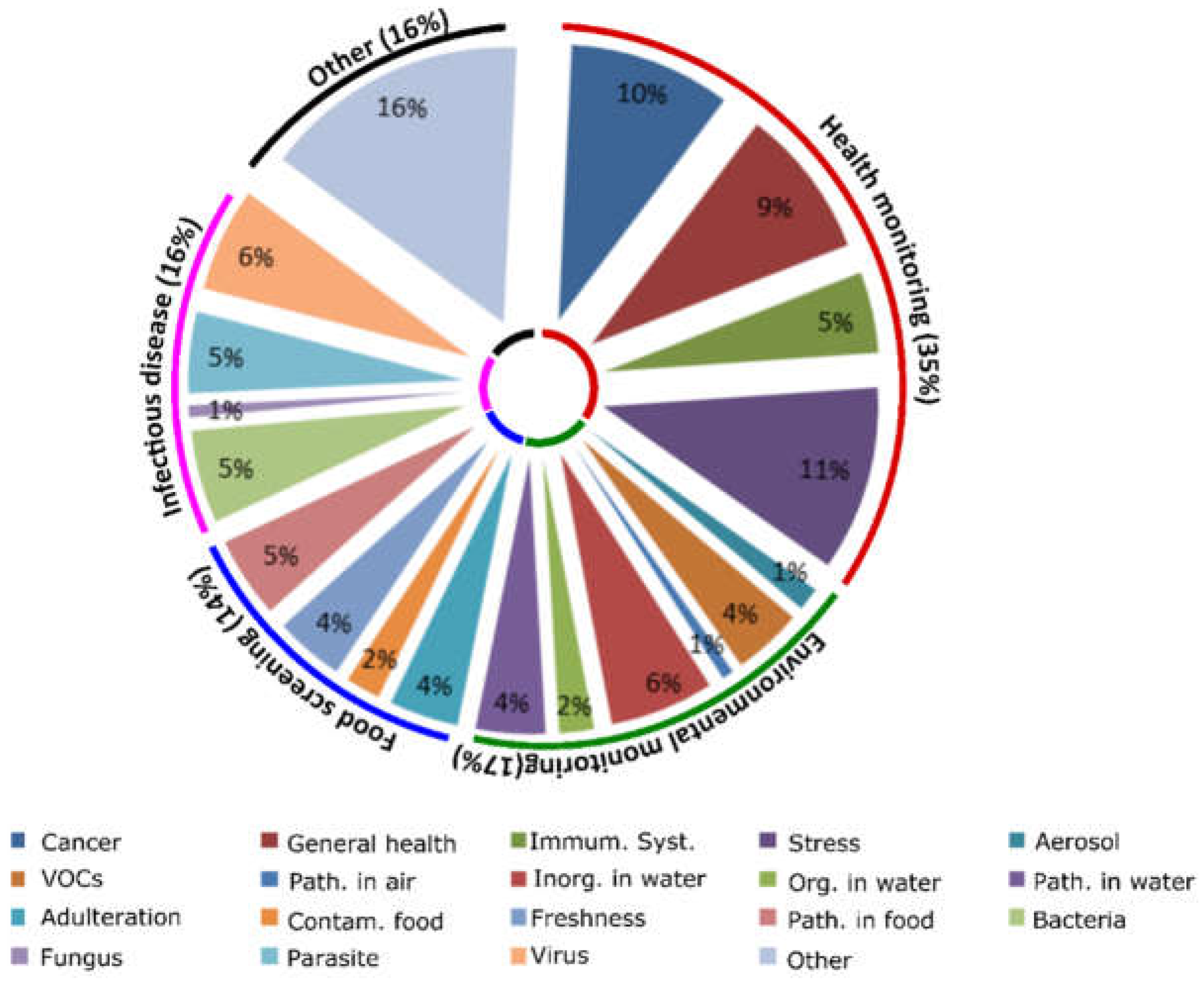
Risks in the Spacecraft Environment
During spaceflight, the environment is a closed system that has a two-fold effect: One, the immune system has been shown to decrease its functionality in long-duration missions, specifically by lowering white blood cell counts, and two, the weightless and non-competitive environment make it easier for microbes to transfer between humans and their growth rates increase. In one space shuttle era study, the number of microbial cells in the vehicle able to reproduce increased by 300% within 12 days of being in orbit. Also, certain herpes viruses, such as those responsible for chickenpox and mononucleosis, have been reactivated under microgravity, although the astronauts typically didn’t show symptoms despite the presence of active viral shedding (the virus had surfaced and was able to spread).
Frequent monitoring of the spacecraft environment and the crew’s biomarkers is the best way to mitigate these challenges, and NASA is addressing these issues to an extent with traditional instruments and equipment to collect data, although often times the data cannot be processed until the experiments are returned to Earth. An attempt has also been made to rapidly quantify microorganisms aboard the International Space Station (ISS) via a handheld device called the Lab-on-a-Chip Application Development-Portable Test System (LOCAD-PTS). However, this device cannot distinguish between microorganism species yet, meaning it can’t tell the difference between pathogens and harmless species. The QUB study found several existing smartphone-based technologies generally developed for use in remote medical care facilities that could achieve better identification results.

One of the devices described was a spectrometer (used to identify substances based on the light frequency emitted) which used the smartphone’s flashlight and camera to generate data that was at least as accurate as traditional instruments. Another was able to identify concentrations of an artificial growth hormone injected into cows called recominant bovine somatrotropin (rBST) in test samples, and other systems were able to accurately detect cyphilis and HIV as well as the zika, chikungunya, and dengue viruses. All of the devices used smartphone attachments, some of them with 3D-printed parts. Of course, the types of pathogens detected are not likely to be common in a closed space habitat, but the technology driving them could be modified to meet specific detection needs.
The Stress of Spaceflight
A group of people crammed together in a small space for long periods of time will be impacted by the situation despite any amount of careful selection or training due to the isolation and confinement. Declines in mood, cognition, morale, or interpersonal interaction can impact team functioning or transition into a sleep disorder. On Earth, these stress responses may seem common, or perhaps an expected part of being human, but missions in deep space and on Mars will be demanding and need fully alert, well-communicating teams to succeed. NASA already uses devices to monitor these risks while also addressing the stress factor by managing habitat lighting, crew movement and sleep amounts, and recommending astronauts keep journals to vent as needed. However, an all-encompassing tool may be needed for longer-duration space travels.
As recognized by the QUB study, several “mindfulness” and self-help apps already exist in the market and could be utilized to address the stress factor in future astronauts when combined with general health monitors. For example, the popular FitBit app and similar products collect data on sleep patterns, activity levels, and heart rates which could potentially be linked to other mental health apps that could recommend self-help programs using algorithms. The more recent “BeWell” app monitors physical activity, sleep patterns, and social interactions to analyze stress levels and recommend self-help treatments. Other apps use voice patterns and general phone communication data to assess stress levels such as “StressSense” and “MoodSense”.
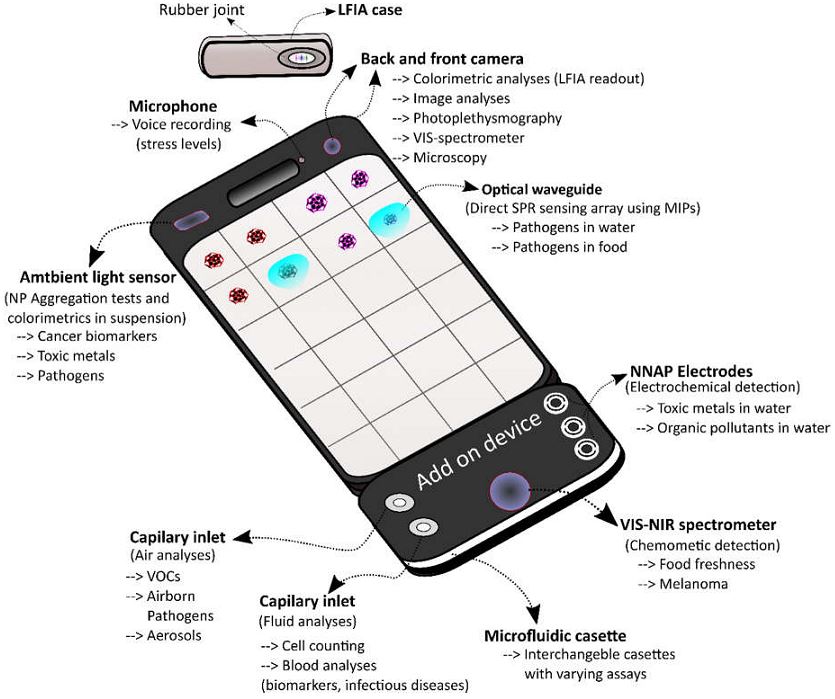
Advances in smartphone technology such as high resolution cameras, microphones, fast processing speed, wireless connectivity, and the ability to attach external devices provide tools that can be used for an expanding number of “portable lab” type functionalities. Unfortunately, though, despite the possibilities that these biosensors could mean for human spaceflight needs, there are notable limitations that would need to be overcome in some of the devices. In particular, any device utilizing antibodies or enzymes in its testing would risk the stability of its instruments thanks to radiation from galactic cosmic rays and solar particle events. Biosensor electronics might also be damaged by these things as well. Development of new types of shielding may be necessary to ensure their functionality outside of Earth and Earth orbit or, alternatively, synthetic biology could also be a source of testing elements genetically engineered to withstand the space and Martian environments.
The interest in smartphone-based solutions for space travelers has been garnering more attention over the years as tech-centric societies have moved in the “app” direction overall. NASA itself has hosted a “Space Apps Challenge” for the last 8 years, drawing thousands of participants to submit programs that interpret and visualize data for greater understanding of designated space and science topics. Some of the challenges could be directly relevant to the biosensor field. For example, in the 2018 event, contestants are asked to develop a sensor to be used by humans on Mars to observe and measure variables in their environments; in 2017, contestants created visualizations of potential radiation exposure during polar or near-polar flight.
While the QUB study implied that the combination of existing biosensor technology could be equivalent to a Tricorder, the direct development of such a device has been the subject of its own specific challenge. In 2012, the Qualcomm Tricorder XPRIZE competition was launched, asking competitors to develop a user-friendly device that could accurately diagnose 13 health conditions and capture 5 real-time health vital signs. The winner of the prize awarded in 2017 was Pennsylvania-based family team called Final Frontier Medical Devices, now Basil Leaf Technologies, for their DxtER device. According to their website, the sensors inside DxtER can be used independently, one of which is in a Phase 1 Clinical Trial. The second place winner of the competition used a smartphone app to connect its health testing modules and generate a diagnosis from the data acquired from the user.
The march continues to develop the technology humans will need to safely explore regions beyond Earth orbit. Space is hard, but it was hard before we went there the first time, and it was hard before we put humans on the moon. There may be plenty of challenges to overcome, but as the Queen’s University Belfast study demonstrates, we may already be solving them. It’s just a matter of realizing it and expanding on it.

Cybertruck
Tesla confirms date when new Cybertruck trim will go up in price
Tesla has officially revealed that this price will only be available until February 28, as the company has placed a banner atop the Design Configurator on its website reflecting this.

Tesla has confirmed the date when its newest Cybertruck trim level will increase in price, after CEO Elon Musk noted that the All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the all-electric pickup would only be priced at its near-bargain level for ten days.
Last week, Tesla launched the All-Wheel-Drive configuration of the Cybertruck. Priced at $59,990, the Cybertruck featured many excellent features and has seemingly brought some demand to the pickup, which has been underwhelming in terms of sales figures over the past couple of years.
Tesla launches new Cybertruck trim with more features than ever for a low price
When Tesla launched it, many fans and current owners mulled the possibility of ordering it. However, Musk came out and said just hours after launching the pickup that Tesla would only keep it at the $59,990 price level for ten days.
What it would be priced at subsequently was totally dependent on how much demand Tesla felt for the new trim level, which is labeled as a “Dual Motor All-Wheel-Drive” configuration.
Tesla has officially revealed that this price will only be available until February 28, as the company has placed a banner atop the Design Configurator on its website reflecting this:
NEWS: Tesla has officially announced that the price of the new Cybertruck Dual-Motor AWD will be increasing after February 28th. pic.twitter.com/vZpA521ZwC
— Sawyer Merritt (@SawyerMerritt) February 24, 2026
Many fans and owners have criticized Tesla’s decision to unveil a trim this way, and then price it at something, only to change that price a few days later based on how well it sells.
Awful way to treat customers – particularly when they already sent out a marketing email announcing the $59,990 truck…with zero mention of it being a limited-time offer.
— Ryan McCaffrey (@DMC_Ryan) February 24, 2026
It seems the most ideal increase in price would be somewhere between $5,000 and $10,000, but it truly depends on how many orders Tesla sees for this new trim level. The next step up in configuration is the Premium All-Wheel-Drive, which is priced at $79,990.
The difference between the Dual Motor AWD Cybertruck and the Premium AWD configuration comes down to towing, interior quality, and general features. The base package is only capable of towing up to 7,500 pounds, while the Premium can handle 11,000 pounds. Additionally, the seats in the Premium build are Vegan Leather, while the base trim gets the textile seats.
It also has only 7 speakers compared to the 15 that the Premium trim has. Additionally, the base model does not have an adjustable ride height, although it does have a coil spring with an adaptive damping suspension package.
Cybertruck
Tesla set to activate long-awaited Cybertruck feature
Tesla will officially activate the Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) feature on Cybertruck soon, as the company has officially added the feature to its list of features by trim on its website.

Tesla is set to activate a long-awaited Cybertruck feature, and no matter when you bought your all-electric pickup, it has the hardware capable of achieving what it is designed to do.
Tesla simply has to flip the switch, and it plans to do so in the near future.
Tesla will officially activate the Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) feature on Cybertruck soon, according to Not a Tesla App, as the company has officially added the feature to its list of features by trim on its website.
Tesla rolls out Active Road Noise Reduction for new Model S and Model X
The ANC feature suddenly appeared on the spec sheet for the Premium All-Wheel-Drive and Cyberbeast trims, which are the two configurations that have been delivered since November 2023.
However, those trims have both had the ANC disabled, and although they are found in the Model S and Model X, and are active in those vehicles, Tesla is planning to activate them.
In Tesla’s Service Toolbox, it wrote:
“ANC software is not enabled on Cybertruck even though the hardware is installed.”
Tesla has utilized an ANC system in the Model S and Model X since 2021. The system uses microphones embedded in the front seat headrests to detect low-frequency road noise entering the cabin. It then generates anti-noise through phase-inverted sound waves to cancel out or reduce that noise, creating quieter zones, particularly around the vehicle’s front occupants.
The Model S and Model X utilize six microphones to achieve this noise cancellation, while the Cybertruck has just four.
Tesla Cybertruck Dual Motor AWD estimated delivery slips to early fall 2026
As previously mentioned, this will be activated through a software update, as the hardware is already available within Cybertruck and can simply be activated at Tesla’s leisure.
The delays in activating the system are likely due to Tesla Cybertruck’s unique design, which is unlike anything before. In the Model S and Model X, Tesla did not have to do too much, but the Cybertruck has heavier all-terrain tires and potentially issues from the aluminum castings that make up the vehicle’s chassis, which are probably presenting some challenges.
Unfortunately, this feature will not be available on the new Dual Motor All-Wheel-Drive configuration, which was released last week.
News
Tesla Model S and X customization options begin to thin as their closure nears
Tesla’s Online Design Studio for both vehicles now shows the first color option to be listed as “Sold Out,” as Lunar Silver is officially no longer available for the Model S or Model X. This color is exclusive to these cars and not available on the Model S or Model X.

Tesla Model S and Model X customization options are beginning to thin for the first time as the closure of the two “sentimental” vehicles nears.
We are officially seeing the first options disappear as Tesla begins to work toward ending production of the two cars and the options that are available to those vehicles specifically.
Tesla’s Online Design Studio for both vehicles now shows the first color option to be listed as “Sold Out,” as Lunar Silver is officially no longer available for the Model S or Model X. This color is exclusive to these cars and not available on the Model S or Model X.
🚨 Tesla Model S and Model X availability is thinning, as Tesla has officially shown that the Lunar Silver color option on both vehicles is officially sold out
To be fair, Frost Blue is still available so no need to freak out pic.twitter.com/YnwsDbsFOv
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) February 25, 2026
Tesla is making way for the Optimus humanoid robot project at the Fremont Factory, where the Model S and Model X are produced. The two cars are low-volume models and do not contribute more than a few percent to Tesla’s yearly delivery figures.
With CEO Elon Musk confirming that the Model S and Model X would officially be phased out at the end of the quarter, some of the options are being thinned out.
This is an expected move considering Tesla’s plans for the two vehicles, as it will make for an easier process of transitioning that portion of the Fremont plant to cater to Optimus manufacturing. Additionally, this is likely one of the least popular colors, and Tesla is choosing to only keep around what it is seeing routine demand for.
During the Q4 Earnings Call in January, Musk confirmed the end of the Model S and Model X:
“It is time to bring the Model S and Model X programs to an end with an honorable discharge. It is time to bring the S/X programs to an end. It’s part of our overall shift to an autonomous future.”
Fremont will now build one million Optimus units per year as production is ramped.








