

News
NASA aces most challenging Mars rover landing to date
After a nearly 300 million mile (480 million kilometer), seven-month-long journey, the world watched as NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance mission successfully completed the most challenging and precise landing the agency has ever attempted on Thursday (Feb. 18). Perseverance is NASA’s fifth rover and overall ninth mission to successfully land on the Red Planet.
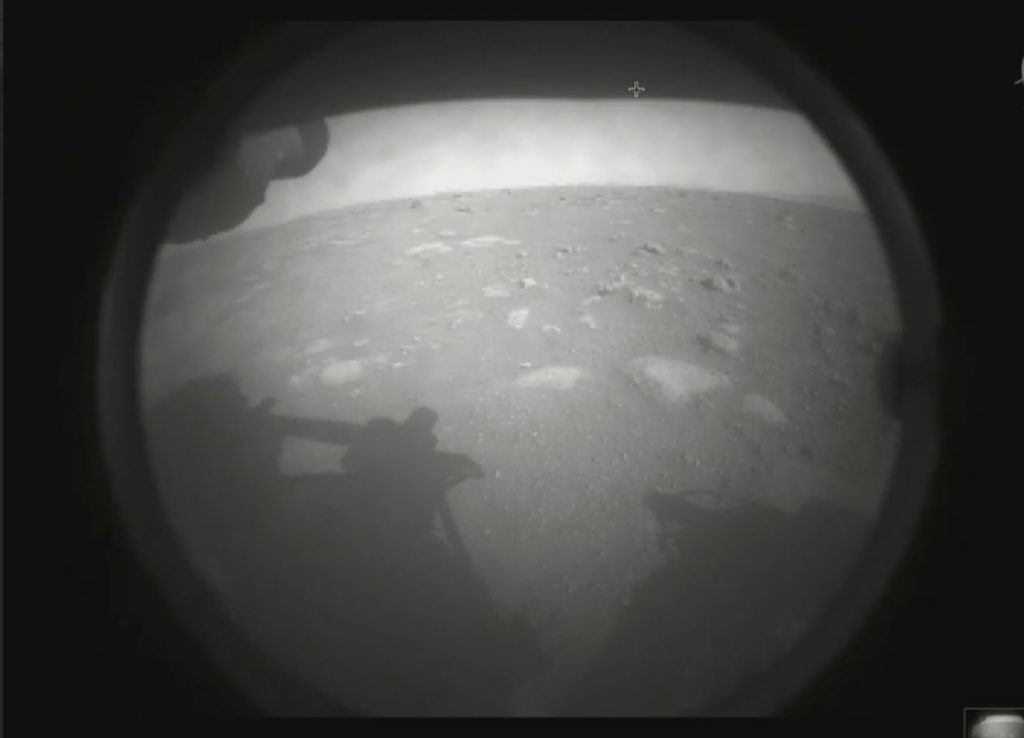

On Thursday afternoon, the alien invader punched through the relatively thin Martian atmosphere streaking across the sky at a blazing 12,100 mph (19,500 kph). Then it shed a few layers, deployed the largest-ever supersonic parachute, and slowed down just enough to use a rocket-propelled crane to drop an autonomous, nuclear-powered, robotic astrobiologist called Perseverance on the surface of Mars.
Flawlessly completing the entry, descent, and landing sequence of its mission to land in Mars’ hostile Jezero Crater, NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance mission officially marked the completion of its interplanetary travel phase and began its mission to collect evidence of ancient, microbial Martian life.
Getting to Mars
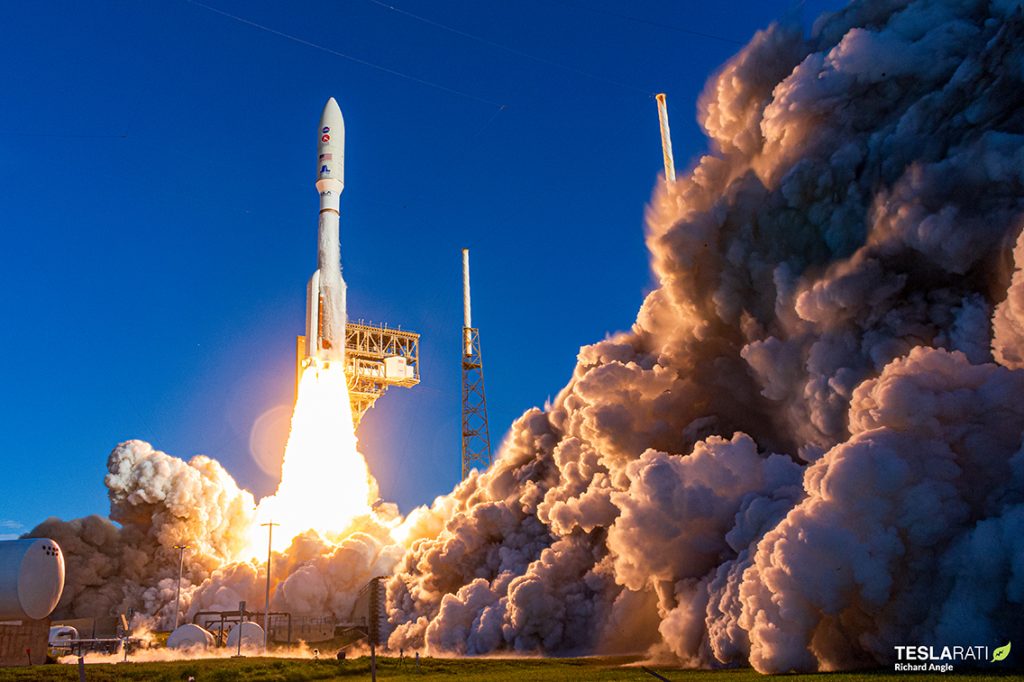

On July 30, 2020, NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance mission launched aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Base. Aboard that rocket was NASA’s most ambitious Mars mission to date. The launch phase of the mission suffered a few minor delays ultimately shifting the launch date from July 18, 2020 to July 30, 2020. However, ULA’s Atlas V first stage rocket and Centaur upper stage delivered NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance mission into such an accurate trajectory that the 2,260 lb (1,025 kg) rover landed on its specified February 18 landing date despite the delays in the launch timeline.
In total, three missions to Mars – China’s Tianwen-1, the United Arab Emirates Hope Probe, and NASA’s Perseverance – left Earth in the summer of 2020. All three missions targeted to leave Earth prior to August to best take advantage of the minimal distance between the planets during what is called opposition. The opposition between Earth and Mars only occurs once every 22 months. If the Perseverance mission had missed its launch date it would’ve had to wait until 2022 for a chance to travel to the Red Planet.
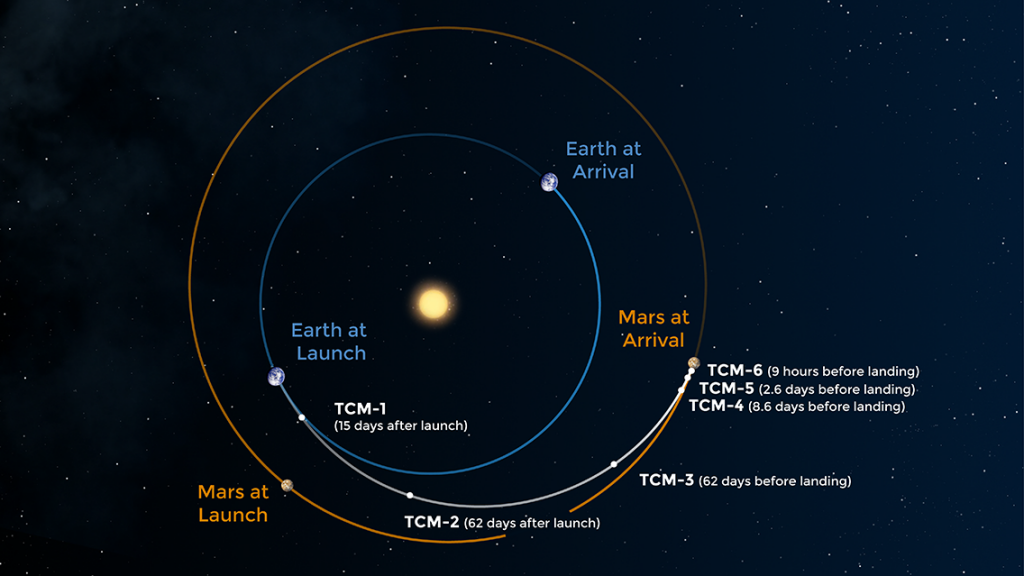
Entry, Descent, and Landing – a controlled disassembly
As Perseverance descended into the Martian atmosphere the Cruise Phase – hardware that propelled the spacecraft through space for seven months – was jettisoned. The Perseverance rover safely tucked inside the aeroshell and protected by a robust heat shield soared through the thin Martian atmosphere enduring an extreme amount of friction that produced heat energy that reached up to 2,370 degrees Fahrenheit (about 1,300 degrees Celsius).
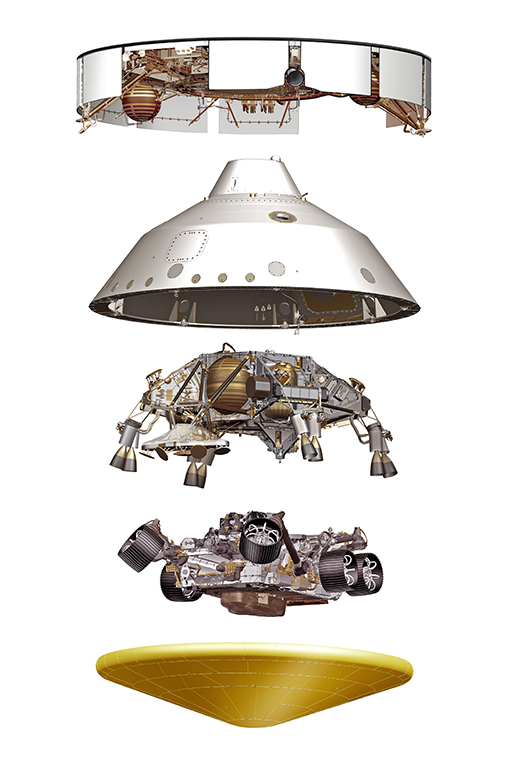

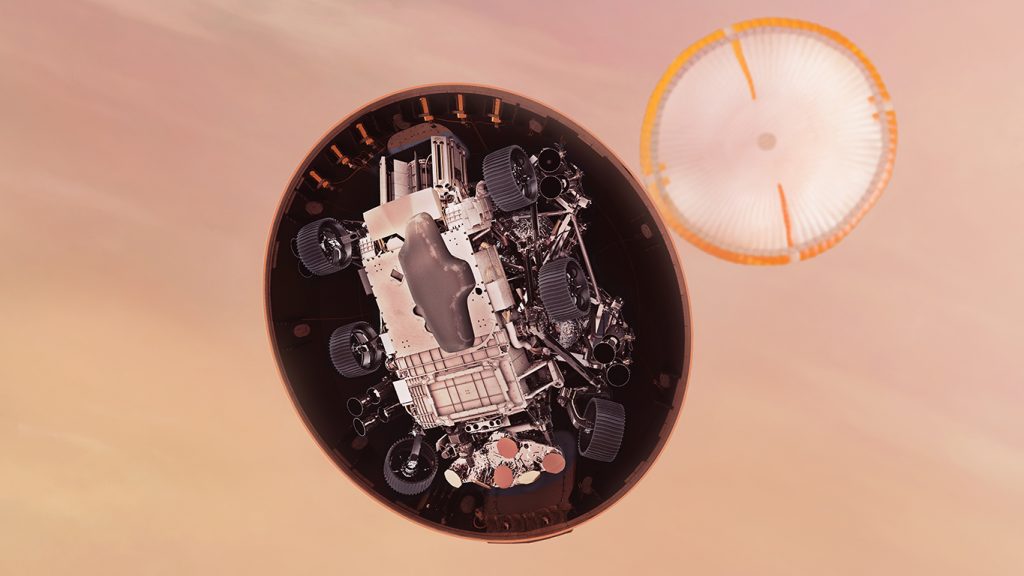
Once through the period of peak heating the heat shield was jettisoned exposing Perseverance to the Martian environment for the first time. Then about 7 miles (11 kilometers) from the surface the largest supersonic parachute NASA has ever sent to another planet – 70.5 feet (21.5 meters) in diameter – was deployed drastically slowing the spacecraft.
While still descending, the controlled descent module – called the sky crane – separated from the backshell about 1.3 miles (2.1 kilometers) above the surface to free-fly in the Martian atmosphere. The descent module used a new landing technology called Terrain-Relative Navigation used a constant stream of visual input and guidance collected from the Vision Compute Element and Rover Compute Element to determine the safest reachable landing site.

The throttleable rockets on the powered descent module steered the rover to its landing spot in Mars’ Jezero Crater and slowed to approximately 1.7 mph (2.7 kph) about 66 feet (20 meters) above the Martian surface. Perseverance was then lowered using a system of Nylon cords which were autonomously severed upon touchdown. The final stage of the controlled disassembly was for the sky crane to throttle its rockets back up and fly away for a crash landing a safe distance from the rover.
Ultimately, the Perseverance rover landed about a kilometer south of the intended delta of the Jezero Crater.
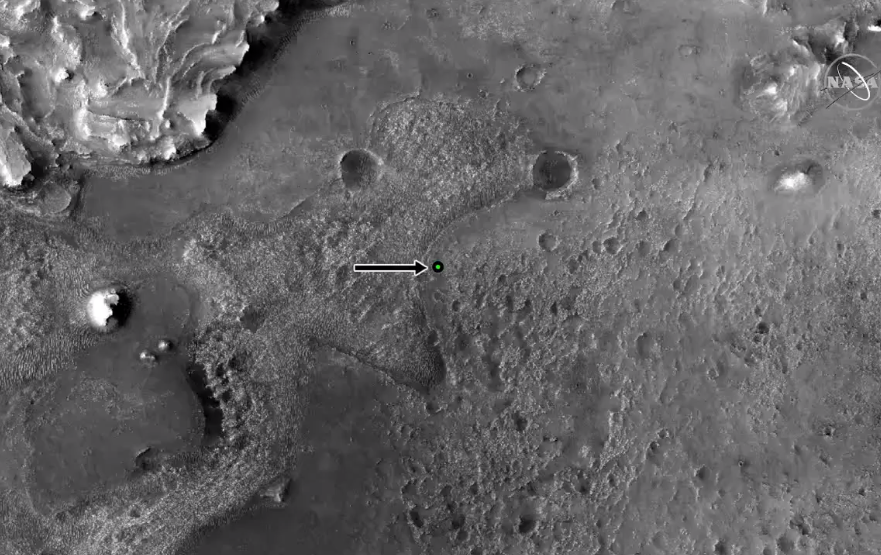

Perseverance made it to Mars, now what?

Getting to Mars was only the first of many milestones that Perseverance is expected to achieve during its projected one Mars year-long mission – about 687 Earth days. Now that the rover has touched down the science will begin.
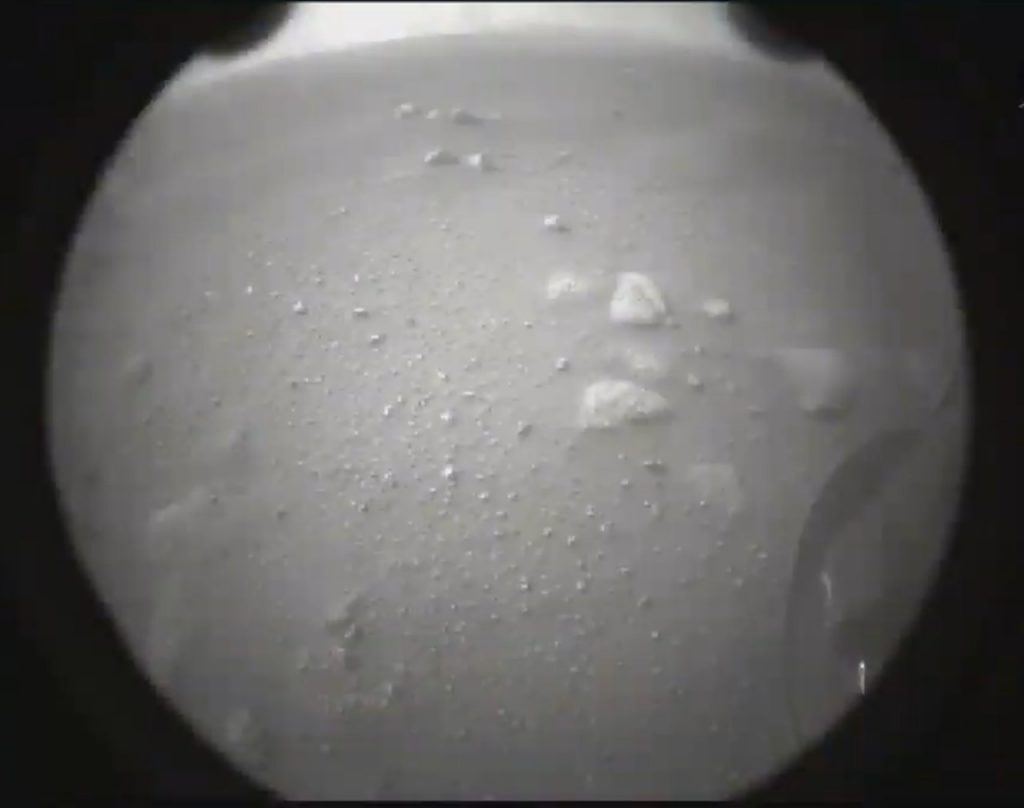
First and foremost once Perseverance stretched its legs, so to speak, the first event took place just minutes after landing. Perseverance captured photos of the Martian surface with a pair of engineering cameras called Hazard Cameras mounted to the front and back of the rover.
The upgraded Navigation and Hazard cameras feature the capability to capture imagery of the Martian surface in 20 megapixel high-definition resolution for the first time. In the coming days, more images will be relayed back to Earth taken with the rover’s Navigation cameras and Mastcam-Z.
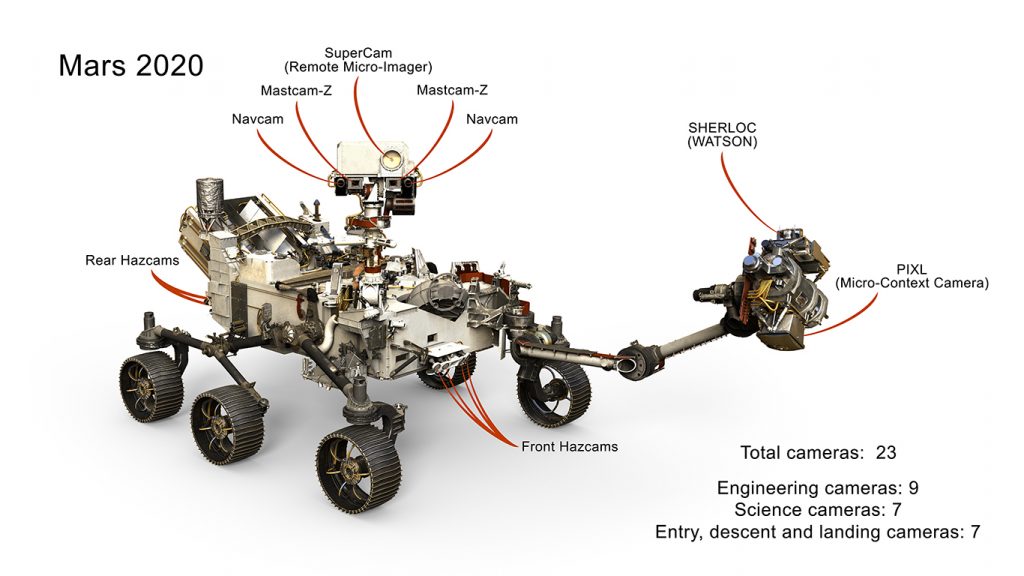
Once on Mars, the control of the Perseverance rover was transitioned from NASA JPL’s EDL team to the Perseverance Surface team. The Surface Phase of the Mars 2020 mission – or the phase of the mission that consists of the four main science objectives – began about twenty minutes after the touchdown.
Perseverance was sent to Mars to determine whether life ever existed on Mars, characterize the climate, characterize the geology, and prepare for the eventual human exploration of Mars. To achieve these massive science goals, the robotic astrobiologist was sent with an impressive suite of scientific research tools. Over the next 30 Martian days – called sols – the rover will begin to unfurl and begin testing the various pieces of hardware in preparation for exploring the delta of Jezero Crater.
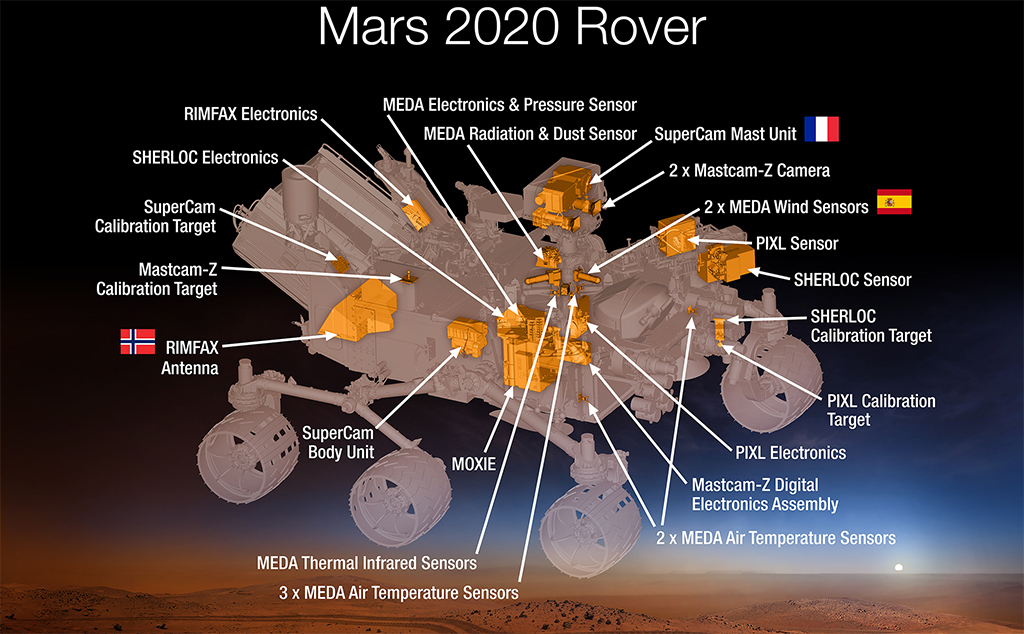
Deploying the stowaway
Perseverance not only took a roving science lab to Mars, but it also took the first rotorcraft helicopter to be deployed to another planet dubbed Ingenuity. Ingenuity is a small double-bladed rotorcraft weighing only about 4 pounds (1.8 kilograms).
After the initial 30 Ssls of stretching its legs, Perseverance will travel a short distance to find a flat area of the Martian surface to deploy the Ingenuity helicopter. Once deployed, the Ingenuity team will have a technology demonstration window of approximately 30 sols to complete the first flight test of Ingenuity – the first time powered, controlled flight will be attempted on another planet.
Landing is just the beginning
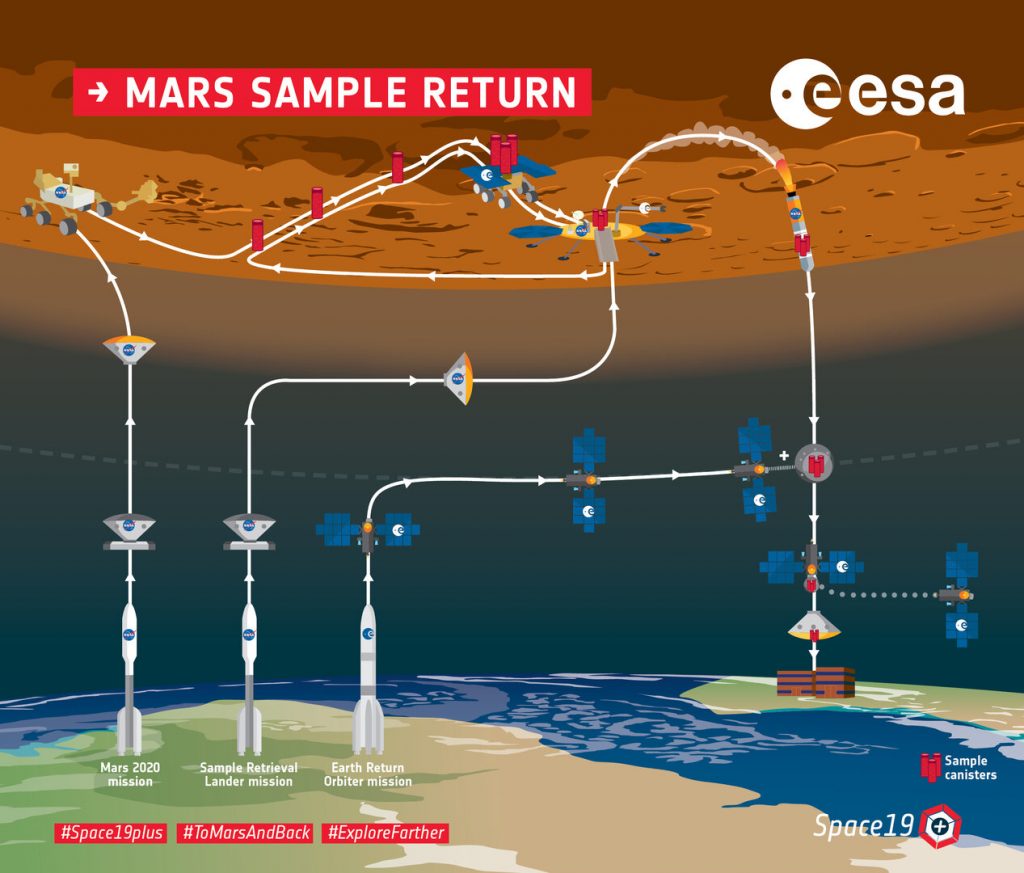
As exciting as landing on Mars was, it is only the beginning for the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover. The nuclear-powered astrobiology robot will spend the next Martian year excavating the surface of a very rich delta in the Jezero crater searching for the first evidence of ancient, microbial life.
Even more exciting is that Perseverance is only the first phase of a larger mission called the Mars Sample Return mission that will someday bring the excavated samples that Perseverance collects back to Earth in a joint effort between NASA and the European Space Agency.
Although the Perseverance mission is only intended to last one Martian year, Perseverance has the capacity to extend its mission to nearly 15 years thanks to its power source, a Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) which produces a steady stream of electricity provided by the radioactive decay of plutonium-238. Perseverance could potentially outlast all of NASA’s other Mars missions.

Elon Musk
Brazil Supreme Court orders Elon Musk and X investigation closed
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.

Brazil’s Supreme Federal Court has ordered the closure of an investigation involving Elon Musk and social media platform X. The inquiry had been pending for about two years and examined whether the platform was used to coordinate attacks against members of the judiciary.
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.
According to a report from Agencia Brasil, the investigation conducted by the Federal Police did not find evidence that X deliberately attempted to attack the judiciary or circumvent court orders.
Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet concluded that the irregularities identified during the probe did not indicate fraudulent intent.
Justice Moraes accepted the prosecutor’s recommendation and ruled that the investigation should be closed. Under the ruling, the case will remain closed unless new evidence emerges.
The inquiry stemmed from concerns that content on X may have enabled online attacks against Supreme Court justices or violated rulings requiring the suspension of certain accounts under investigation.
Justice Moraes had previously taken several enforcement actions related to the platform during the broader dispute involving social media regulation in Brazil.
These included ordering a nationwide block of the platform, freezing Starlink accounts, and imposing fines on X totaling about $5.2 million. Authorities also froze financial assets linked to X and SpaceX through Starlink to collect unpaid penalties and seized roughly $3.3 million from the companies’ accounts.
Moraes also imposed daily fines of up to R$5 million, about $920,000, for alleged evasion of the X ban and established penalties of R$50,000 per day for VPN users who attempted to bypass the restriction.
Brazil remains an important market for X, with roughly 17 million users, making it one of the platform’s larger user bases globally.
The country is also a major market for Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite internet service, which has surpassed one million subscribers in Brazil.
Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Energy
Tesla Energy gains UK license to sell electricity to homes and businesses
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.

Tesla Energy has received a license to supply electricity in the United Kingdom, opening the door for the company to serve homes and businesses in the country.
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.
According to Ofgem, the license took effect at 6 p.m. local time on Wednesday and applies to Great Britain.
The approval allows Tesla’s energy business to sell electricity directly to customers in the region, as noted in a Bloomberg News report.
Tesla has already expanded similar services in the United States. In Texas, the company offers electricity plans that allow Tesla owners to charge their vehicles at a lower cost while also feeding excess electricity back into the grid.
Tesla already has a sizable presence in the UK market. According to price comparison website U-switch, there are more than 250,000 Tesla electric vehicles in the country and thousands of Tesla home energy storage systems.
Ofgem also noted that Tesla Motors Ltd., a separate entity incorporated in England and Wales, received an electricity generation license in June 2020.
The new UK license arrives as Tesla continues expanding its global energy business.
Last year, Tesla Energy retained the top position in the global battery energy storage system (BESS) integrator market for the second consecutive year. According to Wood Mackenzie’s latest rankings, Tesla held about 15% of global market share in 2024.
The company also maintained a dominant position in North America, where it captured roughly 39% market share in the region.
At the same time, competition in the energy storage sector is increasing. Chinese companies such as Sungrow have been expanding their presence globally, particularly in Europe.









