

News
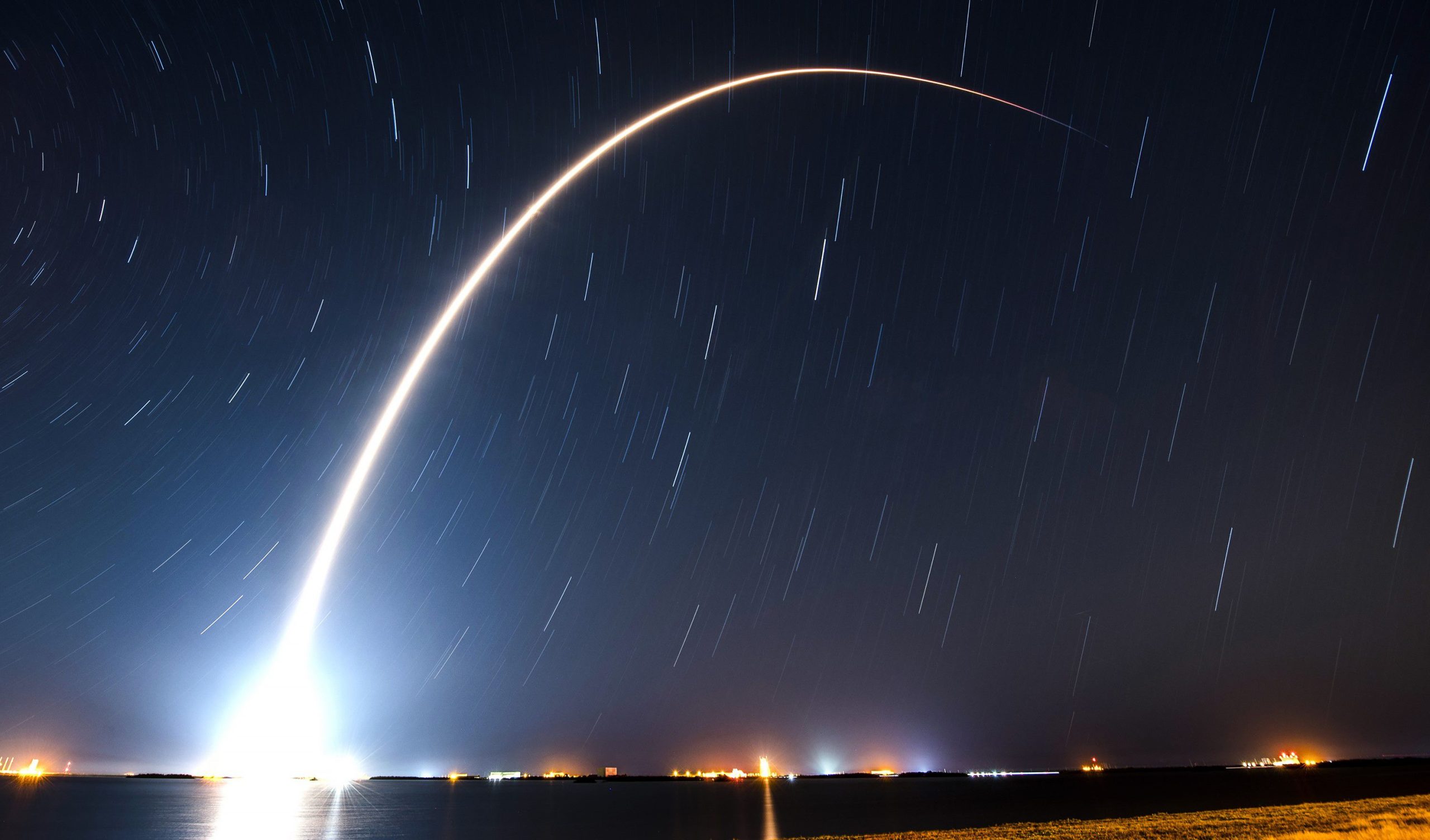
SpaceX aces 60th orbital launch of 2022
SpaceX has completed its 60th orbital launch of 2022, marking the first time the company has fully hit a public cadence target set by one of its executives.
By every possible measure, 2022 has been a groundbreaking year for SpaceX even when considering the vast list of achievements it’s racked up over the last half-decade. It owns and operates the largest satellite constellation in history by an order of magnitude. Its Starlink satellite internet service has secured more than a million subscribers less than two years after entering beta. It operates the only routinely reusable orbital-class rockets and orbital spacecraft currently in service. Its Falcon 9 workhorse has launched more in one year than any other single rocket in history. It’s regularly launching at a pace that hasn’t been sustained by any one country – let alone a single company – in 40 years. It’s managing that near-historic cadence while simultaneously recovering and reusing boosters and fairings that represent some 70% of the value of almost every rocket it launches.
And now, SpaceX can also proudly show that it was able to hit a launch cadence target that seemed impossibly ambitious when CEO Elon Musk first shared it nine months ago.
The update that's rolling out to the fleet makes full use of the front and rear steering travel to minimize turning circle. In this case a reduction of 1.6 feet just over the air— Wes (@wmorrill3) April 16, 2024
Exactly nine months later, SpaceX has just completed its 60th launch of 2022. 69 days after its last orbital-class launch, Falcon 9 booster lifted off for the 11th time with a somewhat mysterious batch of 54 Starlink satellites. A bit less than nine minutes after liftoff, B1062 touched down 660 kilometers (410 mi) downrange on SpaceX drone ship A Shortfall Of Gravitas (ASOG). Seconds prior, Falcon 9’s expendable upper stage reached orbit, shut down its lone Merlin Vacuum engine, and began slowly spinning itself end over end.
Nineteen minutes after leaving the ground, the stack of 54 Starlink satellites was released all at once, slowly spreading out like a splayed deck of cards. Over the coming hours, days, and weeks, those satellites will naturally spread out, deploy solar arrays, stabilize their attitudes, test their payloads, and begin climbing toward an operational orbit somewhere between 480 and 580 kilometers (300-360 mi) above Earth’s surface.
As previously discussed, SpaceX’s so-called “Starlink 5-1” mission raises a number of questions that the company’s launch webcast and communications unfortunately failed to answer. First and foremost, the “5-1” name is nonsensical. The only information SpaceX did disclose about the mission is that it’s the “first [launch] of Starlink’s upgraded network…under [a] new license,” implying – but not actually confirming – that “Starlink 5-1” is the first launch for the Starlink Gen2 constellation.
The orbit the launch targeted only matches one of the Gen2 ‘shells’ the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) recently approved. Using a naming scheme that’s been consistent for a year and a half, “5-1” implies that the mission is the first launch of Starlink Gen1’s fifth ‘shell’ or group, which the orbit it was actually launched to explicitly makes impossible. It’s very odd that SpaceX did not explicitly call the mission what it actually is: the first launch of an entirely new Starlink Gen2 constellation. The name ultimately doesn’t matter much, but is now likely to create confusion given that SpaceX’s Starlink Gen1 constellation has a fifth shell that may begin launches in the near future.
Additionally, outside of a single obscure FCC filing submitted two months ago, it’s long been stated and implied that the Starlink Gen2 constellation’s main advantage over Gen1 was the much larger size of the Gen2/V2 satellites. But the satellites launched on “Starlink 5-1” appear to be virtually identical to all recent Starlink V1.5 satellites, which CEO Elon Musk once suggested were so cost-inefficient that they could risk bankrupting SpaceX in November 2021.

There is one obvious explanation for why SpaceX would launch ordinary Starlink V1.5 satellites in place of the larger V2 variants that will supposedly make the internet constellation more financially sustainable: a desire to add new customers as quickly as possible, no matter the relative cost. While a much smaller V1.5 satellite likely offers around 3-8 times less usable bandwidth than one of the larger V2 variants SpaceX is developing, it may still be true that a V1.5 satellite is better than nothing while larger V2 satellites are stuck behind development delays or waiting on SpaceX’s next-generation Starship rocket.
SpaceX will almost certainly want to replace any V1.5 satellites with V2 satellites when the opportunity arises, but in the meantime, V1.5 satellites launched as part of the Gen2 constellation may technically allow SpaceX to temporarily double the amount of bandwidth available where most people (and Starlink customers) live. Ultimately, that means that it makes a lot of sense for SpaceX to prioritize Gen2 launches. It doesn’t appear that SpaceX will go that far, but the Starlink Gen1 constellation is so far along that the company could easily leave the constellation as-is and prioritize Gen2 Falcon 9 launches for all of 2023 without risking an FCC penalty. SpaceX simply needs to finish its Gen1 constellation before April 2027 to avoid breaking those rules.
Instead, it looks like SpaceX will roughly split its launch and V1.5 satellite manufacturing capacity between Starlink Gen1 and Gen2 moving forward. That will let SpaceX significantly expand bandwidth where most customers live while also finishing the polar-orbiting Gen1 shells that will let the older constellation better serve maritime and aviation subscribers, and reach Starlink’s most remote customers.
News
Tesla cleared in Canada EV rebate investigation
Tesla has been cleared in an investigation into the company’s staggering number of EV rebate claims in Canada in January.
Canadian officials have cleared Tesla following an investigation into a large number of claims submitted to the country’s electric vehicle (EV) rebates earlier this year.
Transport Canada has ruled that there was no evidence of fraud after Tesla submitted 8,653 EV rebate claims for the country’s Incentives for Zero-Emission Vehicles (iZEV) program, as detailed in a report on Friday from The Globe and Mail. Despite the huge number of claims, Canadian authorities have found that the figure represented vehicles that had been delivered prior to the submission deadline for the program.
According to Transport Minister Chrystia Freeland, the claims “were determined to legitimately represent cars sold before January 12,” which was the final day for OEMs to submit these claims before the government suspended the program.
Upon initial reporting of the Tesla claims submitted in January, it was estimated that they were valued at around $43 million. In March, Freeland and Transport Canada opened the investigation into Tesla, noting that they would be freezing the rebate payments until the claims were found to be valid.
READ MORE ON ELECTRIC VEHICLES: EVs getting cleaner more quickly than expected in Europe: study
Huw Williams, Canadian Automobile Dealers Association Public Affairs Director, accepted the results of the investigation, while also questioning how Tesla knew to submit the claims that weekend, just before the program ran out.
“I think there’s a larger question as to how Tesla knew to run those through on that weekend,” Williams said. “It doesn’t appear to me that we have an investigation into any communication between Transport Canada and Tesla, between officials who may have shared information inappropriately.”
Tesla sales have been down in Canada for the first half of this year, amidst turmoil between the country and the Trump administration’s tariffs. Although Elon Musk has since stepped back from his role with the administration, a number of companies and officials in Canada were calling for a boycott of Tesla’s vehicles earlier this year, due in part to his association with Trump.
News
Tesla Semis to get 18 new Megachargers at this PepsiCo plant
PepsiCo is set to add more Tesla Semi Megachargers, this time at a facility in North Carolina.
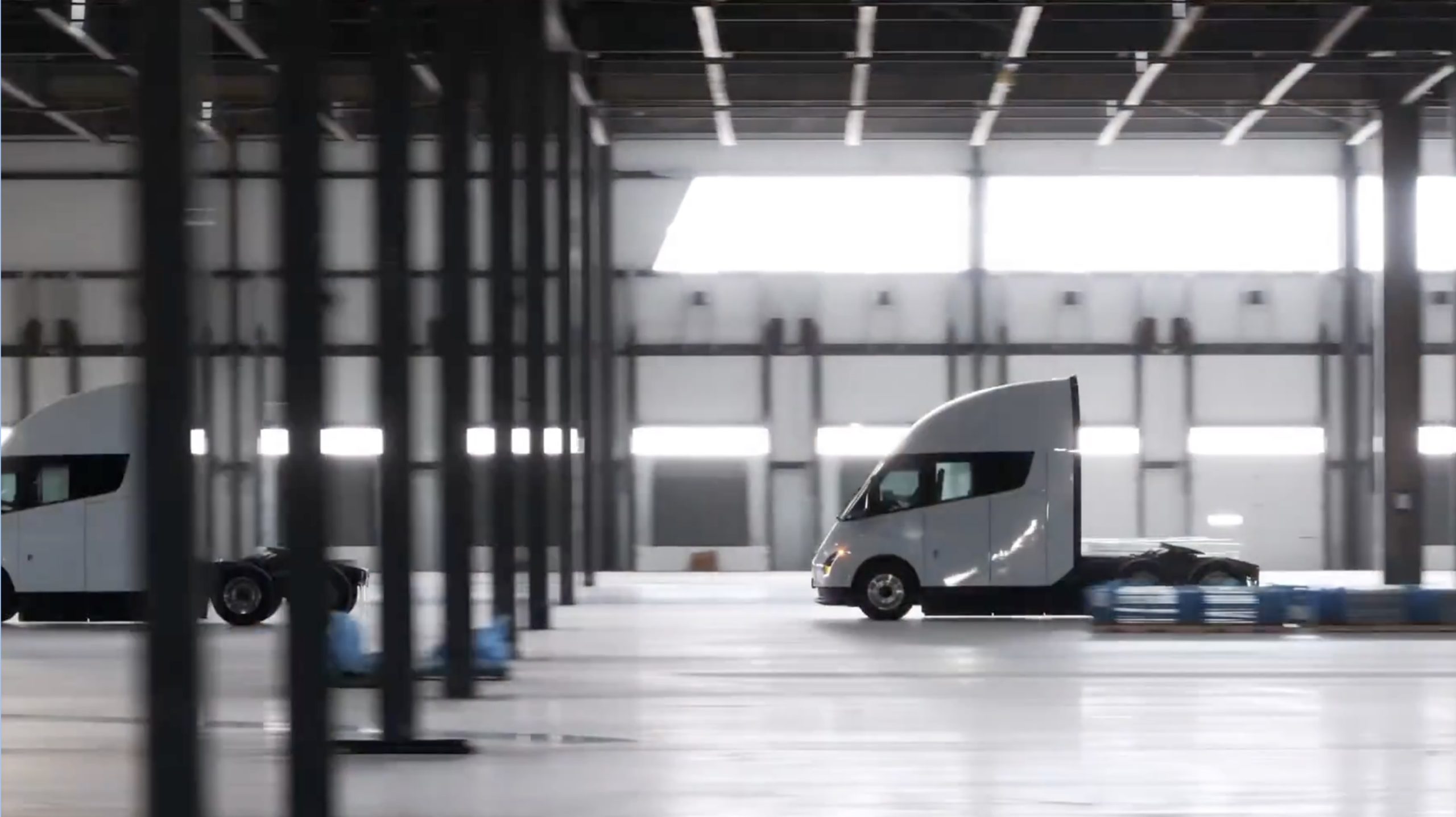

Tesla partner PepsiCo is set to build new Semi charging stations at one of its manufacturing sites, as revealed in new permitting plans shared this week.
On Friday, Tesla charging station scout MarcoRP shared plans on X for 18 Semi Megacharging stalls at PepsiCo’s facility in Charlotte, North Carolina, coming as the latest update plans for the company’s increasingly electrified fleet. The stalls are set to be built side by side, along with three Tesla Megapack grid-scale battery systems.
The plans also note the faster charging speeds for the chargers, which can charge the Class 8 Semi at speeds of up to 1MW. Tesla says that the speed can charge the Semi back to roughly 70 percent in around 30 minutes.
You can see the site plans for the PepsiCo North Carolina Megacharger below.
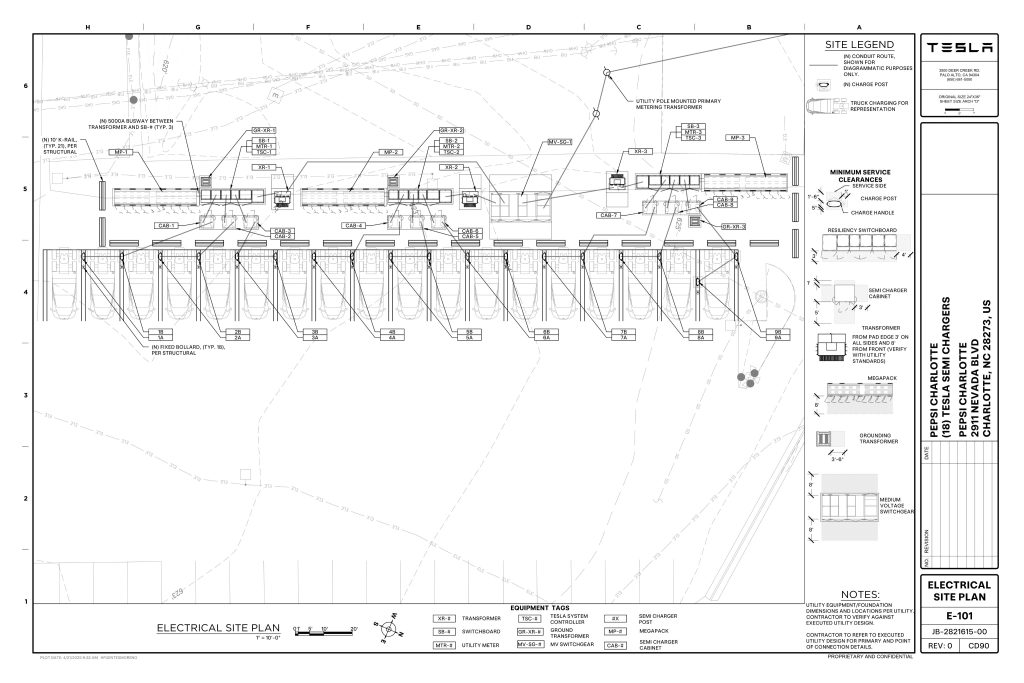
Credit: PepsiCo (via MarcoRPi1 on X)
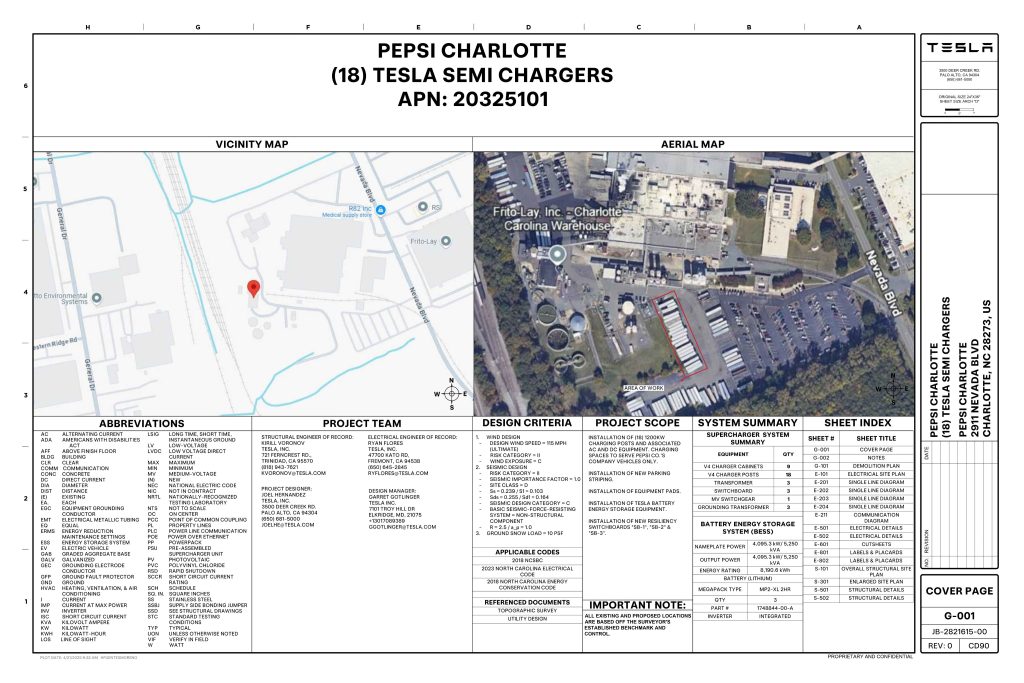
Credit: PepsiCo (via MarcoRPi1 on X)
READ MORE ON THE TESLA SEMI: Tesla to build Semi Megacharger station in Southern California
PepsiCo’s Tesla Semi fleet, other Megachargers, and initial tests and deliveries
PepsiCo was the first external customer to take delivery of Tesla’s Semis back in 2023, starting with just an initial order of 15. Since then, the company has continued to expand the fleet, recently taking delivery of an additional 50 units in California. The PepsiCo fleet was up to around 86 units as of last year, according to statements from Semi Senior Manager Dan Priestley.
Additionally, the company has similar Megachargers at its facilities in Modesto, Sacramento, and Fresno, California, and Tesla also submitted plans for approval to build 12 new Megacharging stalls in Los Angeles County.
Over the past couple of years, Tesla has also been delivering the electric Class 8 units to a number of other companies for pilot programs, and Priestley shared some results from PepsiCo’s initial Semi tests last year. Notably, the executive spoke with a handful of PepsiCo workers who said they really liked the Semi and wouldn’t plan on going back to diesel trucks.
The company is also nearing completion of a higher-volume Semi plant at its Gigafactory in Nevada, which is expected to eventually have an annual production capacity of 50,000 Semi units.
Tesla executive teases plan to further electrify supply chain
News
Tesla sales soar in Norway with new Model Y leading the charge
Tesla recorded a 54% year-over-year jump in new vehicle registrations in June.
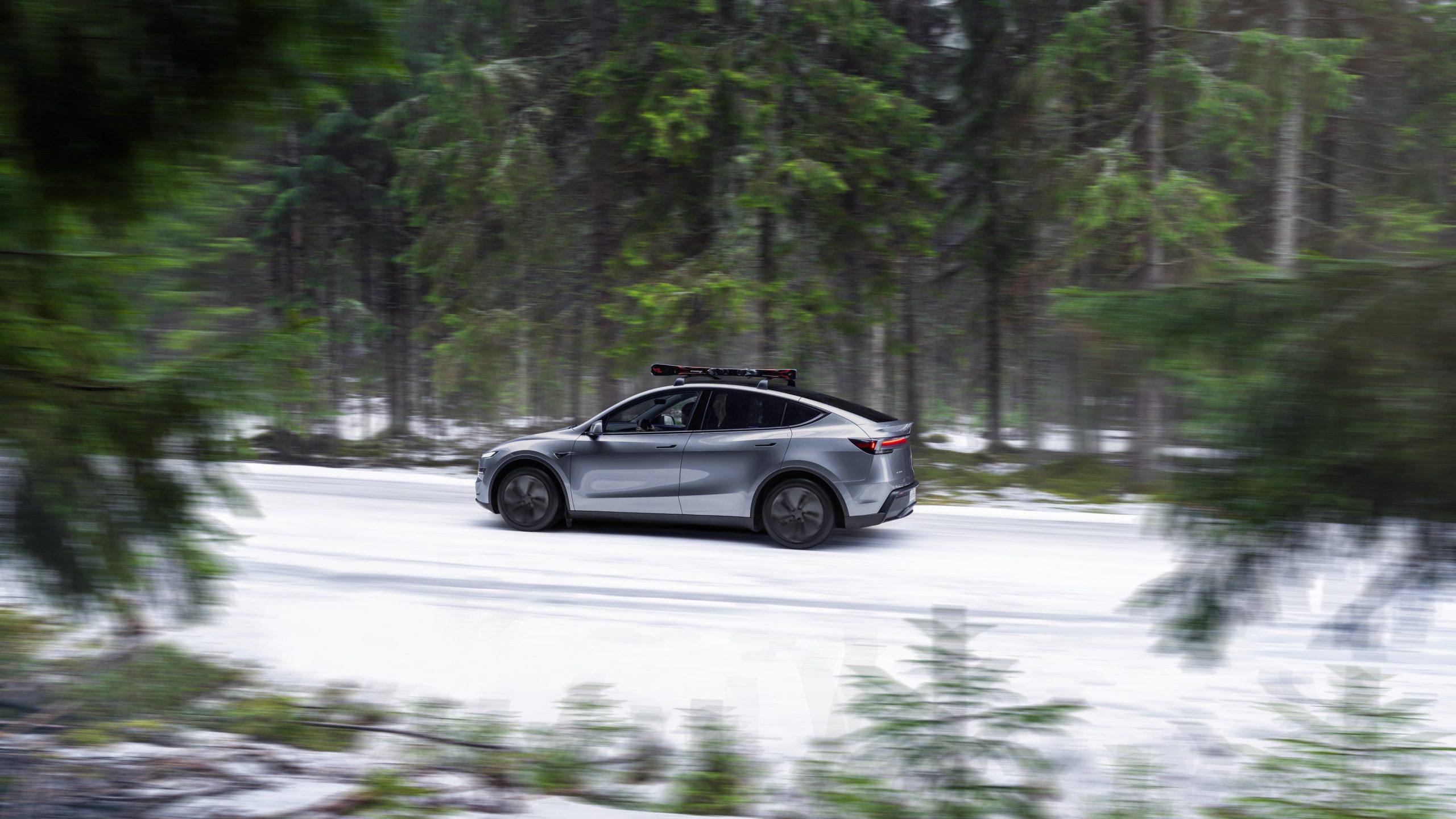

Tesla is seeing strong momentum in Norway, with sales of the new Model Y helping the company maintain dominance in one of the world’s most electric vehicle-friendly markets.
Model Y upgrades and consumer preferences
According to the Norwegian Road Federation (OFV), Tesla recorded a 54% year-over-year jump in new vehicle registrations in June. The Model Y led the charge, posting a 115% increase compared to the same period last year. Tesla Norway’s growth was even more notable in May, with sales surging a whopping 213%, as noted in a CNBC report.
Christina Bu, secretary general of the Norwegian EV Association (NEVA), stated that Tesla’s strong market performance was partly due to the updated Model Y, which is really just a good car, period.
“I think it just has to do with the fact that they deliver a car which has quite a lot of value for money and is what Norwegians need. What Norwegians need, a large luggage space, all wheel drive, and a tow hitch, high ground clearance as well. In addition, quite good digital solutions which people have gotten used to, and also a charging network,” she said.
Tesla in Europe
Tesla’s success in Norway is supported by long-standing government incentives for EV adoption, including exemptions from VAT, road toll discounts, and access to bus lanes. Public and home charging infrastructure is also widely available, making the EV ownership experience in the country very convenient.
Tesla’s performance in Europe is still a mixed bag, with markets like Germany and France still seeing declines in recent months. In areas such as Norway, Spain, and Portugal, however, Tesla’s new car registrations are rising. Spain’s sales rose 61% and Portugal’s sales rose 7% last month. This suggests that regional demand may be stabilizing or rebounding in pockets of Europe.
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk4 days ago
Elon Musk4 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla sees explosive sales growth in UK, Spain, and Netherlands in June

















