News
SpaceX Falcon Heavy spied on the move ahead of test fire
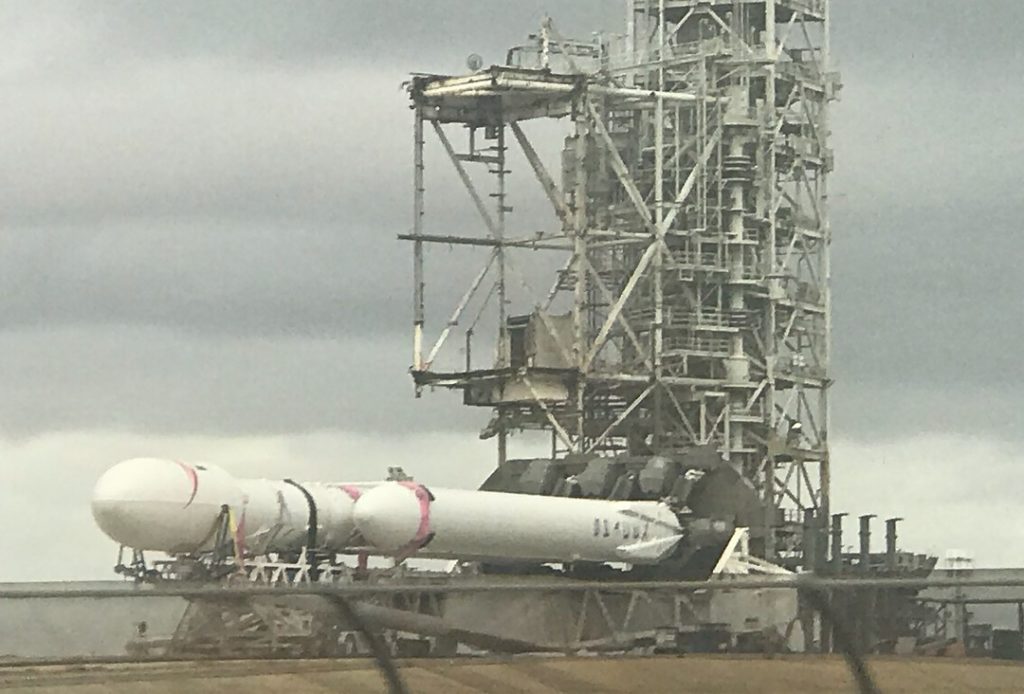
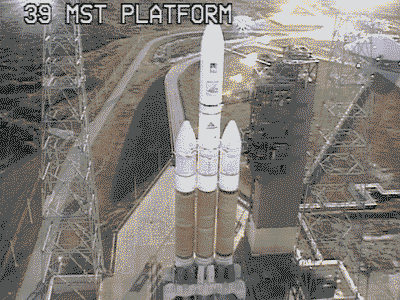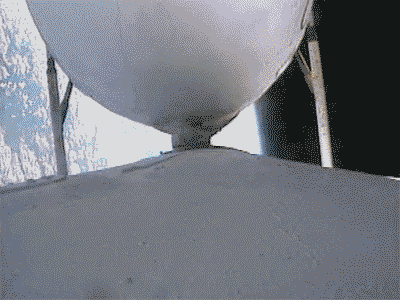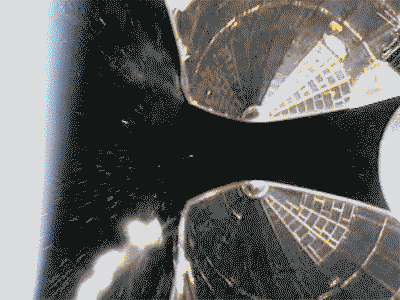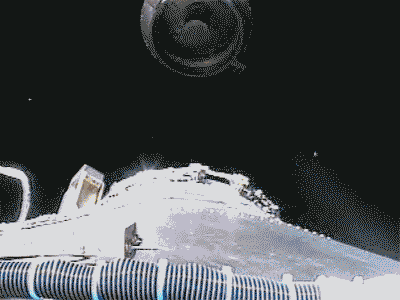
While touring Florida’s Kennedy Space Center by bus earlier this morning (January 8), several spaceflight fans captured SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rolling out to Pad 39A for the second time ever. Following a basic fit check and photo opportunity at the launch pad in the last week of 2017, the launch vehicle now appears to be prepped and ready for its first wet dress rehearsal (WDR) and static fire test.
If all goes well during the wet dress rehearsal’s propellant loading tests, an admittedly less than guaranteed outcome, then the WDR will likely translate into a momentous occasion for the massive rocket: the first-ever simultaneous ignition of all three of its integrated first stages and their 27 Merlin 1D engines. While relatively unique to SpaceX, the company has made a habit of testing each and every new Falcon 9 first stage with two full-up static fire ignitions, one at McGregor, Texas and the other at the vehicle’s given launch pad. Following the destructive failure of Falcon 9 during a September 2016 static fire test, SpaceX further upped their cautious procedures by removing the payload for all future static fires, lest the customer request that it remain integrated for the sake of time savings.
Unsurprisingly, no customers have since chosen to bypass SpaceX’s new risk-reducing procedures. Falcon Heavy will clearly be a return to older methods, delineated by the clear presence of the second stage and Tesla Roadster payload at its top, although this decision was almost undoubtedly driven by the fact that the payload is in no real way valuable or even important for the “customer,” SpaceX itself. The Tesla Roadster is more or less a stand-in for the traditional boilerplate satellite (read: hunk of dead metal) often launched during the inaugural flights of new rockets. The best recent example is the 2004 inaugural launch of Boeing’s Delta IV Heavy rocket, similar to Falcon Heavy in the sense that it also features a triple-core first stage. Its first launch carried a payload that was quite literally a 6000 kg (13500 lb) piece of metal paired with a number of sensors used to gather vibrational data.
- A GIF of Delta IV Heavy’s inaugural 2004 launch. The mission was a partial failure. (ULA)
- The mission’s DemoSat, a 6100kg hunk of metal (and two DoD nanosats). (ULA)
Somewhat fittingly, Delta IV Heavy is aiming to conduct its own launch within the next week or so, providing the East Coast with back to back launches of the world’s two largest operational rockets. Still, as SpaceX and Elon Musk have repeatedly mentioned, Falcon Heavy is far more capable than even Delta IV Heavy: while Falcon Heavy is noticeably shorter, narrower, and thinner than Delta, it weighs almost twice as much and will sport nearly 2.5 times the thrust at liftoff.
Delta IV Heavy’s launches are undoubtedly spectacles to behold, particularly given explosive launch procedures, but the vehicle is entirely expendable, whereas Falcon Heavy will attempt recovery of all three of its first stages, and may eventually allow SpaceX to test technology that will enable second stage recovery, as well.
Falcon Heavy will launch a somewhat livelier version of Delta IV Heavy’s boilerplate mass-simulator with the Tesla Roadster, and the main goal is quite clearly to test the vehicle’s ability to send a payload into a trans-Martian injection (TMI) orbit, albeit likely without an actual injection into orbit around Mars at the other end. Even if the payload is somewhat silly, a successful launch to TMI would be the most literal step yet made by the commercial space company along its path to Mars. If this week’s propellant loading and static fire go as planned, launch will likely follow within a week or so – maybe two weeks given the new and unpredictable nature of testing what is more or less a prototype rocket.
Falcon Heavy goes vertical pic.twitter.com/uG1k0WISv1
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 5, 2018
Falcon Heavy can be expected to go vertical at the pad within the next 12-24 hours at most, and static fire will follow soon after. After a highly successful evening photographing the January 7 launch of Falcon 9 with Zuma, Teslarati’s launch photographer Tom Cross will be attempting to photograph the momentous test fire as it happens, and you can follow along live on Teslarati’s Instagram.
News
Tesla cleared in Canada EV rebate investigation
Tesla has been cleared in an investigation into the company’s staggering number of EV rebate claims in Canada in January.
Canadian officials have cleared Tesla following an investigation into a large number of claims submitted to the country’s electric vehicle (EV) rebates earlier this year.
Transport Canada has ruled that there was no evidence of fraud after Tesla submitted 8,653 EV rebate claims for the country’s Incentives for Zero-Emission Vehicles (iZEV) program, as detailed in a report on Friday from The Globe and Mail. Despite the huge number of claims, Canadian authorities have found that the figure represented vehicles that had been delivered prior to the submission deadline for the program.
According to Transport Minister Chrystia Freeland, the claims “were determined to legitimately represent cars sold before January 12,” which was the final day for OEMs to submit these claims before the government suspended the program.
Upon initial reporting of the Tesla claims submitted in January, it was estimated that they were valued at around $43 million. In March, Freeland and Transport Canada opened the investigation into Tesla, noting that they would be freezing the rebate payments until the claims were found to be valid.
READ MORE ON ELECTRIC VEHICLES: EVs getting cleaner more quickly than expected in Europe: study
Huw Williams, Canadian Automobile Dealers Association Public Affairs Director, accepted the results of the investigation, while also questioning how Tesla knew to submit the claims that weekend, just before the program ran out.
“I think there’s a larger question as to how Tesla knew to run those through on that weekend,” Williams said. “It doesn’t appear to me that we have an investigation into any communication between Transport Canada and Tesla, between officials who may have shared information inappropriately.”
Tesla sales have been down in Canada for the first half of this year, amidst turmoil between the country and the Trump administration’s tariffs. Although Elon Musk has since stepped back from his role with the administration, a number of companies and officials in Canada were calling for a boycott of Tesla’s vehicles earlier this year, due in part to his association with Trump.
News
Tesla Semis to get 18 new Megachargers at this PepsiCo plant
PepsiCo is set to add more Tesla Semi Megachargers, this time at a facility in North Carolina.
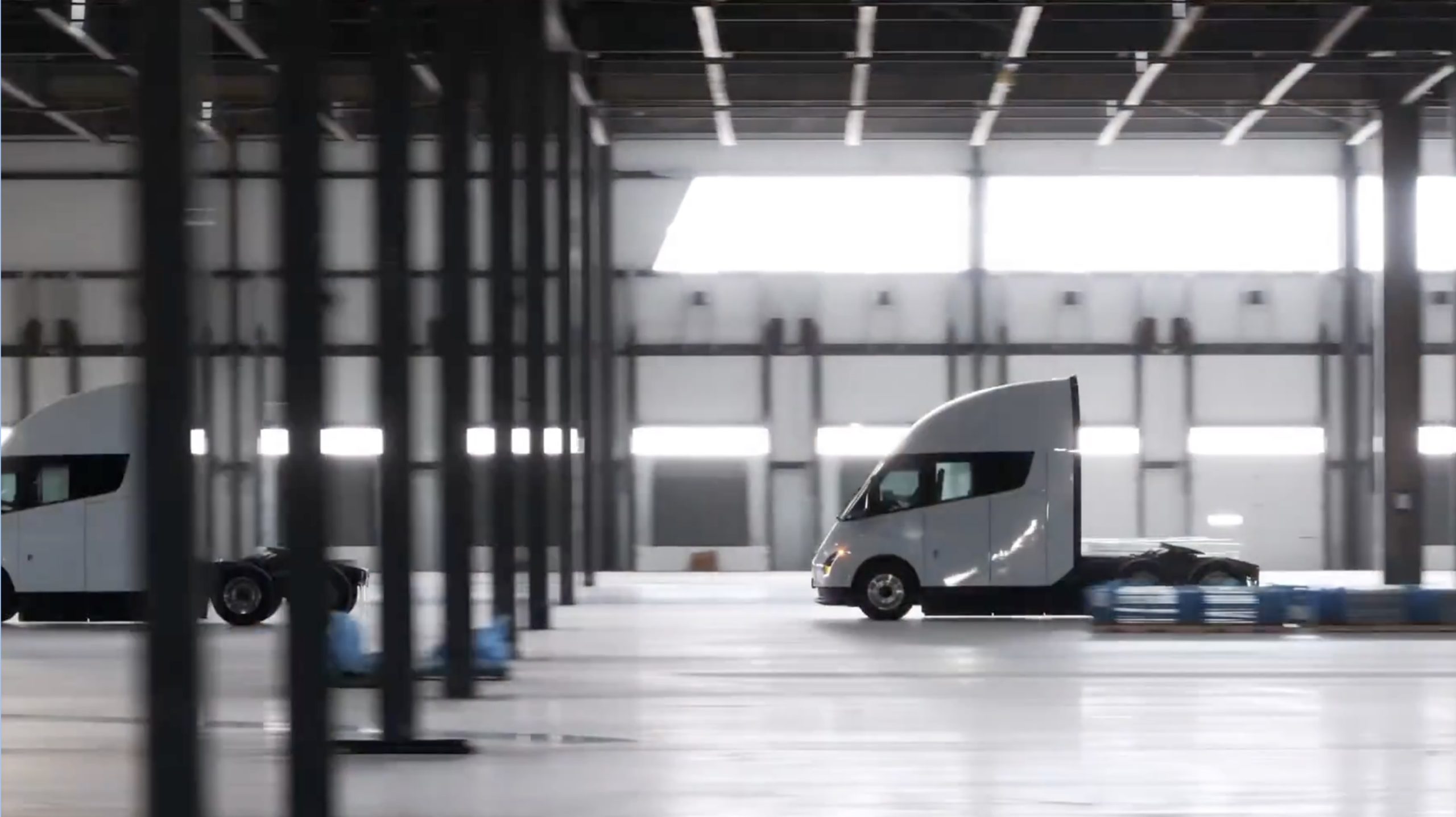

Tesla partner PepsiCo is set to build new Semi charging stations at one of its manufacturing sites, as revealed in new permitting plans shared this week.
On Friday, Tesla charging station scout MarcoRP shared plans on X for 18 Semi Megacharging stalls at PepsiCo’s facility in Charlotte, North Carolina, coming as the latest update plans for the company’s increasingly electrified fleet. The stalls are set to be built side by side, along with three Tesla Megapack grid-scale battery systems.
The plans also note the faster charging speeds for the chargers, which can charge the Class 8 Semi at speeds of up to 1MW. Tesla says that the speed can charge the Semi back to roughly 70 percent in around 30 minutes.
You can see the site plans for the PepsiCo North Carolina Megacharger below.
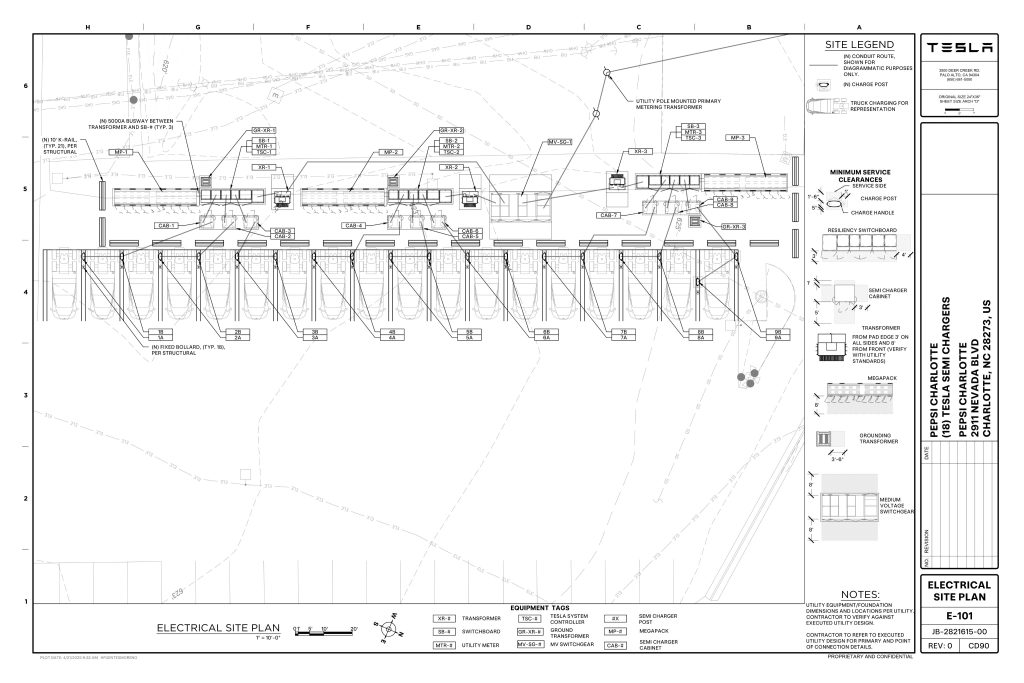
Credit: PepsiCo (via MarcoRPi1 on X)
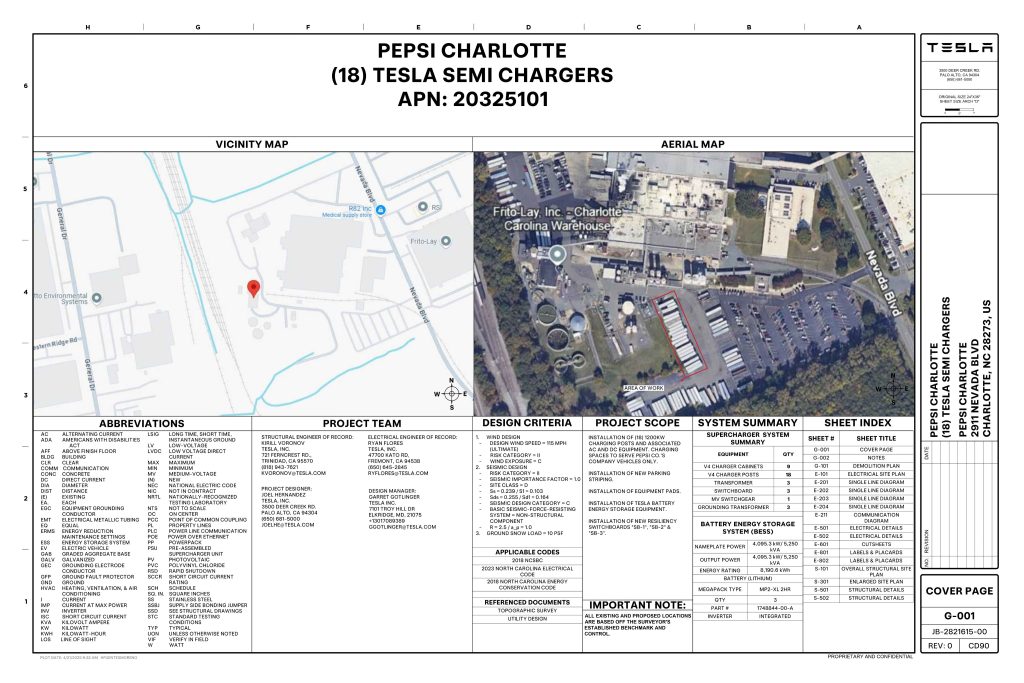
Credit: PepsiCo (via MarcoRPi1 on X)
READ MORE ON THE TESLA SEMI: Tesla to build Semi Megacharger station in Southern California
PepsiCo’s Tesla Semi fleet, other Megachargers, and initial tests and deliveries
PepsiCo was the first external customer to take delivery of Tesla’s Semis back in 2023, starting with just an initial order of 15. Since then, the company has continued to expand the fleet, recently taking delivery of an additional 50 units in California. The PepsiCo fleet was up to around 86 units as of last year, according to statements from Semi Senior Manager Dan Priestley.
Additionally, the company has similar Megachargers at its facilities in Modesto, Sacramento, and Fresno, California, and Tesla also submitted plans for approval to build 12 new Megacharging stalls in Los Angeles County.
Over the past couple of years, Tesla has also been delivering the electric Class 8 units to a number of other companies for pilot programs, and Priestley shared some results from PepsiCo’s initial Semi tests last year. Notably, the executive spoke with a handful of PepsiCo workers who said they really liked the Semi and wouldn’t plan on going back to diesel trucks.
The company is also nearing completion of a higher-volume Semi plant at its Gigafactory in Nevada, which is expected to eventually have an annual production capacity of 50,000 Semi units.
Tesla executive teases plan to further electrify supply chain
News
Tesla sales soar in Norway with new Model Y leading the charge
Tesla recorded a 54% year-over-year jump in new vehicle registrations in June.
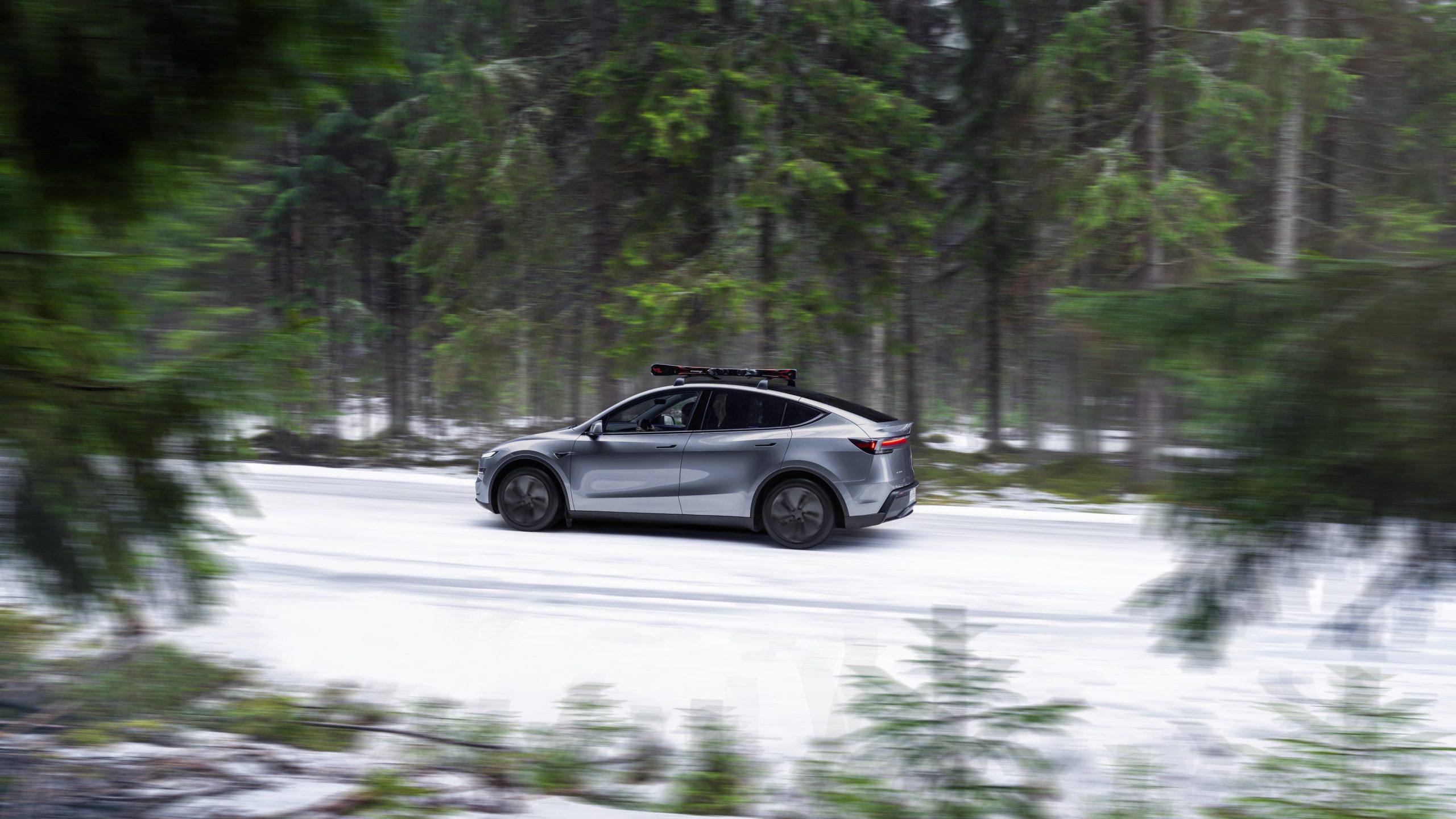

Tesla is seeing strong momentum in Norway, with sales of the new Model Y helping the company maintain dominance in one of the world’s most electric vehicle-friendly markets.
Model Y upgrades and consumer preferences
According to the Norwegian Road Federation (OFV), Tesla recorded a 54% year-over-year jump in new vehicle registrations in June. The Model Y led the charge, posting a 115% increase compared to the same period last year. Tesla Norway’s growth was even more notable in May, with sales surging a whopping 213%, as noted in a CNBC report.
Christina Bu, secretary general of the Norwegian EV Association (NEVA), stated that Tesla’s strong market performance was partly due to the updated Model Y, which is really just a good car, period.
“I think it just has to do with the fact that they deliver a car which has quite a lot of value for money and is what Norwegians need. What Norwegians need, a large luggage space, all wheel drive, and a tow hitch, high ground clearance as well. In addition, quite good digital solutions which people have gotten used to, and also a charging network,” she said.
Tesla in Europe
Tesla’s success in Norway is supported by long-standing government incentives for EV adoption, including exemptions from VAT, road toll discounts, and access to bus lanes. Public and home charging infrastructure is also widely available, making the EV ownership experience in the country very convenient.
Tesla’s performance in Europe is still a mixed bag, with markets like Germany and France still seeing declines in recent months. In areas such as Norway, Spain, and Portugal, however, Tesla’s new car registrations are rising. Spain’s sales rose 61% and Portugal’s sales rose 7% last month. This suggests that regional demand may be stabilizing or rebounding in pockets of Europe.
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 Elon Musk2 days ago
Elon Musk2 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk4 days ago
Elon Musk4 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoXiaomi CEO congratulates Tesla on first FSD delivery: “We have to continue learning!”
-

 Investor's Corner2 weeks ago
Investor's Corner2 weeks agoTesla gets $475 price target from Benchmark amid initial Robotaxi rollout