
News
SpaceX to launch one of its last old-gen Falcon 9s in upcoming launch
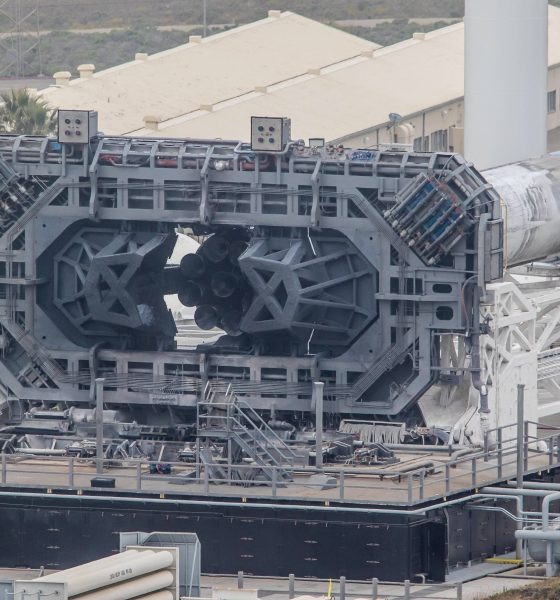
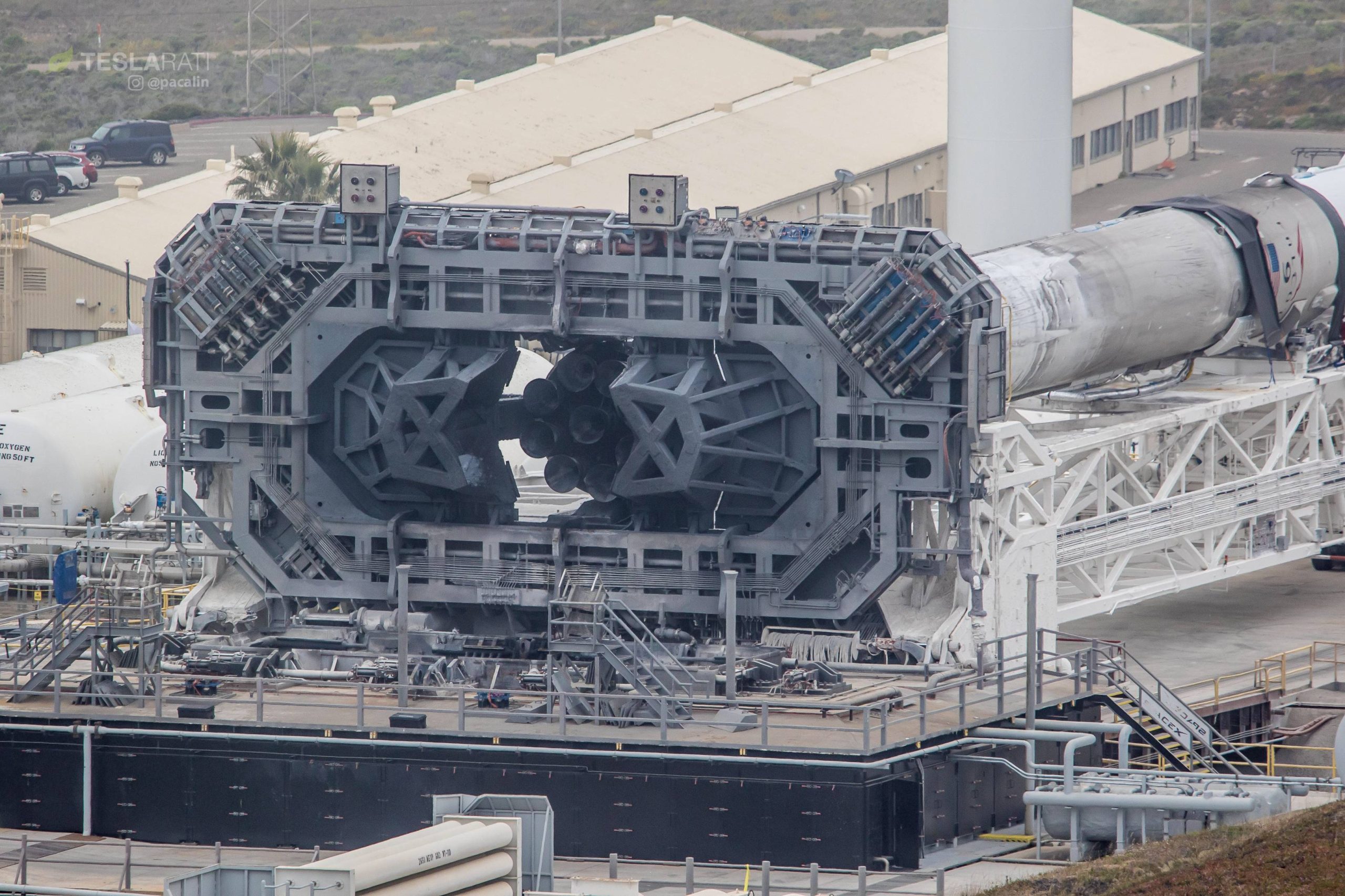
One of SpaceX’s rapidly shrinking fleet of older Falcon 9 launch vehicles has rolled out to the company’s California launch pad ahead of an expendable launch and fairing recovery attempt scheduled for no earlier than Tuesday (NET) 12:47 pm PST/19:47 UTC May 22.
Although SpaceX may have inaugurated a new era of truly reusable rocketry with the debut of Falcon 9 Block 5 earlier this month, there are still a number of older Falcon 9 boosters (all flight-proven) awaiting their second and final flights. At the moment, a minimum of four cores remain, including the sooty Falcon 9 first stage captured earlier this evening by Teslarati photographer Pauline Acalin.
Foreshadowing its imminent watery demise with a lack of landing legs, this particular booster (B1043) previously launched the mysterious and controversial Zuma mission in January 2018, a classified payload claimed (sans convincing evidence) to have failed and reentered Earth’s atmosphere mere hours after reaching orbit. While it’s possible that the mission was a failure, at the moment unsteadily blamed on the failure of a Northrop Grumman-designed payload adapter and deployment mechanism, it’s far more probable that the apparently wildly-expensive satellite is still in orbit.
- Falcon 9 B1043 lifts off for the first time with Zuma on January 7. (Tom Cross/Teslarati)
- After landing at LZ-1, B1043 was refurbished in approximately four months. (SpaceX)
- On May 21, the rocket was rolled out to SLC-4E on the opposite coast of its first launch, ready for one final flight. (Pauline Acalin)
Checking the pulse of Earth’s gravity
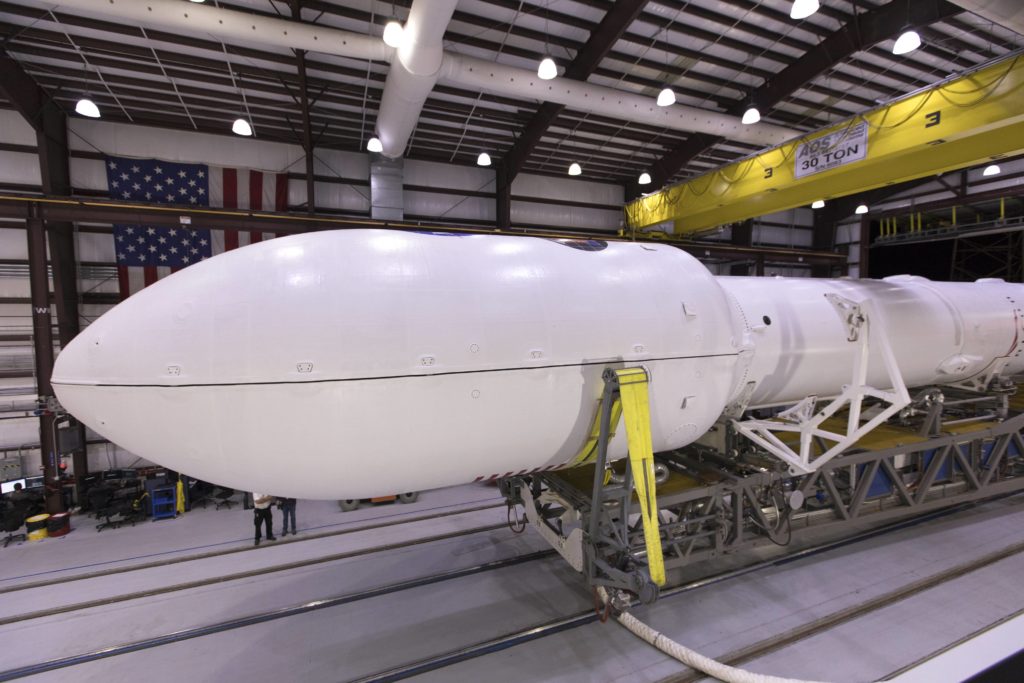
Regardless, the same SpaceX rocket booster responsible for lifting Zuma and the Falcon 9 upper stage out of the atmosphere is now ready to launch a new payload at SLC-4E, a launch pad stationed in Vandenberg Air Force Base. B1043’s second orbit-destined payload is a compliment of seven satellites: five are of the Iridium NEXT variety and the remaining satellites make up a scientific mission and technology demonstrator known as GRACE-FO (FO for Follow-On).
- The two GRACE-FO satellites are stacked atop five Iridium NEXT communications satellites. (NASA)
- (NASA)
- (NASA)
- SpaceX is already fairly experienced with launching multi-satellite missions and building custom payload adapters. (NASA)
- A combination of scientific satellites and five Iridium NEXT communications satellites preparing for launch in May 2018. (NASA)
- During a normal Iridium NEXT launch, two groups of five satellites are stacked on top of each other. Here, the top stack was replaced by NASA/DLR’s GRACE-FO spacecraft. (NASA)
Following in the footsteps of the original GRACE’s (Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment) 15 year orbital tenure, GRACE-FO is effectively the same mission with significantly upgraded hardware – the biggest experimental component is actually an advanced laser interferometer designed to measure the distance between the two satellites (roughly equivalent to the distance between LA and San Diego) with the precision of a single micrometer (10-100x smaller than the width of a human hair). At that level of precision, the pair of satellites can detect minute changes in Earth’s gravity, to the extent that they can actually observe droughts, floods, and ice melt through the change in gravity caused by the movement of large (i.e. heavy) quantities of water. If the experimental laser ranging technology works as intended, it will be at least ten times more accurate than the microwave-ranging technology also installed on the follow-on satellites.
SpaceX’s rocket fleet makes way for Block 5
On the SpaceX side of things, Falcon 9 B1043 will be expended after dutifully completing the launch of Iridium-6/GRACE-FO, although the presence of grid fins on the rocket indicates that SpaceX will likely continue a regime of soft-landing recovery tests to optimize and flesh out the limits of Falcon 9’s capabilities. At first glance, the tradeoff of expending entire rocket boosters able to be (relatively inefficiently) refurbished for considerably more than two flights seems extreme and inadvisable. However, SpaceX is presumably ravenous for data on the survivable envelope of Falcon 9 performance – particularly reuse – in advance of the complete transition to the rocket’s Block 5 iteration, a significant upgrade likely to come hand in hand with a more pronounced aversion to expendable missions given each booster’s design lifespan of 10 to 100 missions. At that level of reusability, expending Falcon 9 Block 5s would truly become comparable with the absurdity of trashing an airliner after one or a handful of flights, an (in)famous talking point used by Elon Musk over his years of public SpaceX discussions.
Thus, if SpaceX can gather data that might enable future Falcon 9 Block 5 recoveries by expending much less valuable Block 3 and 4 boosters, the payoff would be irresistible once examined with a long-term outlook. In the sense that Block 5 may be capable of magnitudes more flights with considerably cheaper refurbishment, the literal elemental value of the hardware – in the likely event that Block 5 production is more capital-intensive than Block 3/4 – is more or less irrelevant for an aversion to expending Block 5 boosters.
Rather, what is lost alongside an expendable Block 5 mission is instead the comparatively vast amount of revenue locked within dozens of additional highly-profitable launches each expended booster could have supported. From that perspective, expending Block 3s and 4s to gather data might be accurately compared to destroying single-pilot Cessnas to improve the utility of a 747 airliner.
After B1043 is expended, only three obvious flightworthy cores will remain outside of the gradually growing Falcon 9 Block 5 fleet (just two boosters, currently). In order of anticipated launch, these three missions are SES-12 (NET May 31), CRS-15 (NET June 28), and the Crew Dragon in-flight abort test (NET Q4 2018). Barring the unexpected refurbishment of an older flight-proven core for a third mission, these final three missions will bring to a close the inherently temporary era of partially-reusable SpaceX rockets – in the words of Elon Musk, Block 5 would thus signify that SpaceX has moved from “the dog that caught the bus” to, perhaps, the dog that caught the bus and then learned how to drive and maintain it. Somewhere in the middle of those final throes of old-guard Falcons will be an ever-increasing cadence of Block 5 launches and re-launches, likely including the first manifest-necessitated reuse of a Block 5 booster sometime this summer.
- Falcon 9 B1045 shows off its own Fairing 2.0 ahead of the launch of TESS. (NASA)
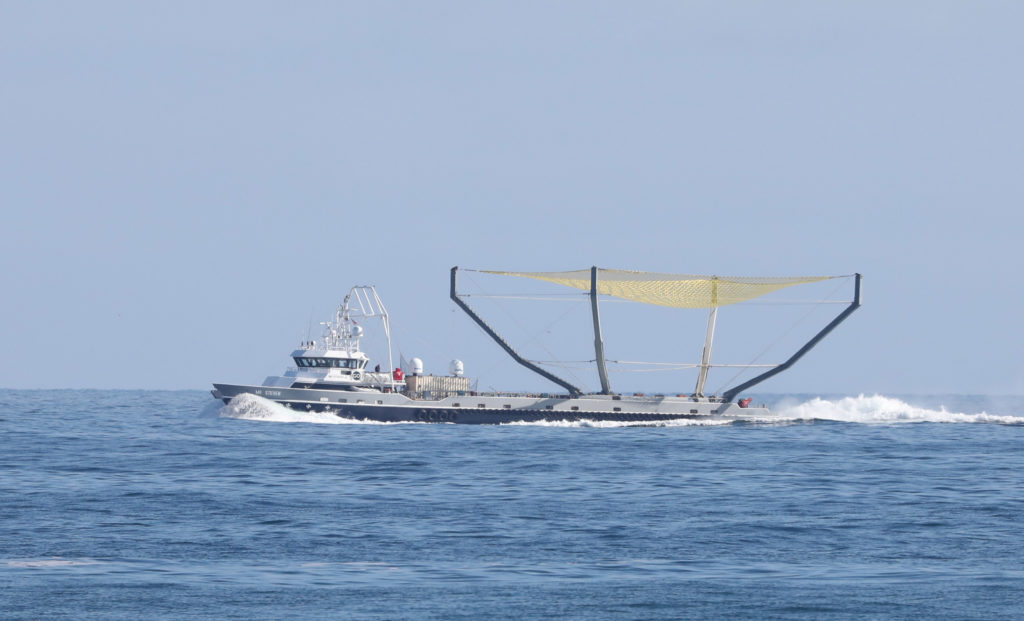
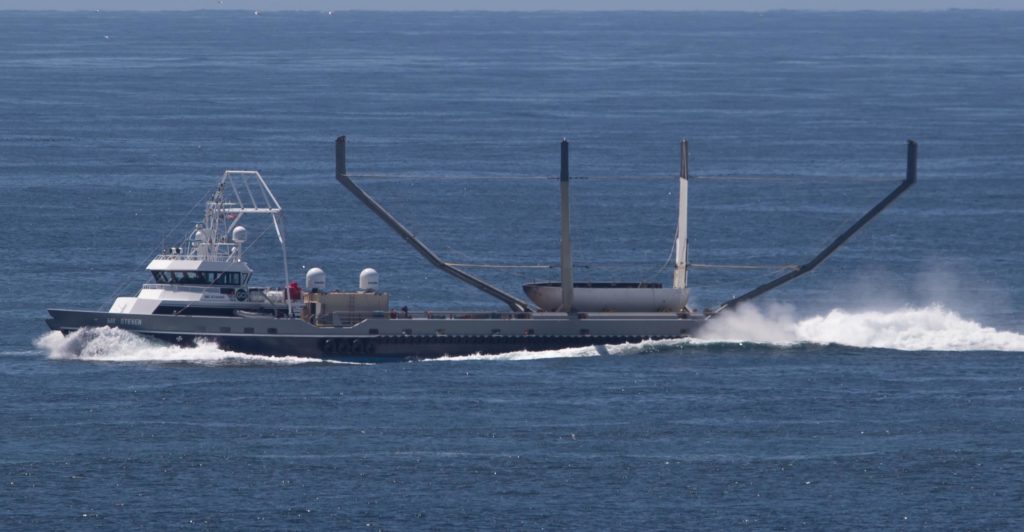
- Chuck Bennett captured Mr Steven conducting high-speed maneuvers with its new, yellow net installed, May 17. (Charles Bennett/@chuckbennett)
- Not nearly enough net, as it turned out. (Pauline Acalin, May 2018)
Meanwhile, despite the sealed fate of the rocket’s booster, tomorrow’s launch will debut fairing-catcher Mr Steven’s new and improved net. With the introduction of an upgraded net and what can only be described as back-to-back days of relentless ocean-going practice over the last two weeks, it’s entirely possible that Iridium-6/GRACE-FO will be able to lay claim to the first successful catch of a payload fairing following an orbital rocket launch. Fingers crossed.
Follow the mission live on SpaceX’s webcast at 12:30 pm PST on Tuesday, May 22, and make sure to check back at Teslarati over the course of the week as photographer Pauline Acalin covers Mr Steven’s return to Port of San Pedro.
Follow us for live updates, behind-the-scenes sneak peeks, and a sea of beautiful photos from our East and West coast photographers.
Teslarati – Instagram – Twitter
Tom Cross – Twitter
Pauline Acalin – Twitter
Eric Ralph – Twitter

Elon Musk
Brazil Supreme Court orders Elon Musk and X investigation closed
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.

Brazil’s Supreme Federal Court has ordered the closure of an investigation involving Elon Musk and social media platform X. The inquiry had been pending for about two years and examined whether the platform was used to coordinate attacks against members of the judiciary.
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.
According to a report from Agencia Brasil, the investigation conducted by the Federal Police did not find evidence that X deliberately attempted to attack the judiciary or circumvent court orders.
Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet concluded that the irregularities identified during the probe did not indicate fraudulent intent.
Justice Moraes accepted the prosecutor’s recommendation and ruled that the investigation should be closed. Under the ruling, the case will remain closed unless new evidence emerges.
The inquiry stemmed from concerns that content on X may have enabled online attacks against Supreme Court justices or violated rulings requiring the suspension of certain accounts under investigation.
Justice Moraes had previously taken several enforcement actions related to the platform during the broader dispute involving social media regulation in Brazil.
These included ordering a nationwide block of the platform, freezing Starlink accounts, and imposing fines on X totaling about $5.2 million. Authorities also froze financial assets linked to X and SpaceX through Starlink to collect unpaid penalties and seized roughly $3.3 million from the companies’ accounts.
Moraes also imposed daily fines of up to R$5 million, about $920,000, for alleged evasion of the X ban and established penalties of R$50,000 per day for VPN users who attempted to bypass the restriction.
Brazil remains an important market for X, with roughly 17 million users, making it one of the platform’s larger user bases globally.
The country is also a major market for Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite internet service, which has surpassed one million subscribers in Brazil.
Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Energy
Tesla Energy gains UK license to sell electricity to homes and businesses
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.

Tesla Energy has received a license to supply electricity in the United Kingdom, opening the door for the company to serve homes and businesses in the country.
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.
According to Ofgem, the license took effect at 6 p.m. local time on Wednesday and applies to Great Britain.
The approval allows Tesla’s energy business to sell electricity directly to customers in the region, as noted in a Bloomberg News report.
Tesla has already expanded similar services in the United States. In Texas, the company offers electricity plans that allow Tesla owners to charge their vehicles at a lower cost while also feeding excess electricity back into the grid.
Tesla already has a sizable presence in the UK market. According to price comparison website U-switch, there are more than 250,000 Tesla electric vehicles in the country and thousands of Tesla home energy storage systems.
Ofgem also noted that Tesla Motors Ltd., a separate entity incorporated in England and Wales, received an electricity generation license in June 2020.
The new UK license arrives as Tesla continues expanding its global energy business.
Last year, Tesla Energy retained the top position in the global battery energy storage system (BESS) integrator market for the second consecutive year. According to Wood Mackenzie’s latest rankings, Tesla held about 15% of global market share in 2024.
The company also maintained a dominant position in North America, where it captured roughly 39% market share in the region.
At the same time, competition in the energy storage sector is increasing. Chinese companies such as Sungrow have been expanding their presence globally, particularly in Europe.





















