News
Tesla Roadster and ‘friends’ make history in newly-published log of 57k+ human objects in space
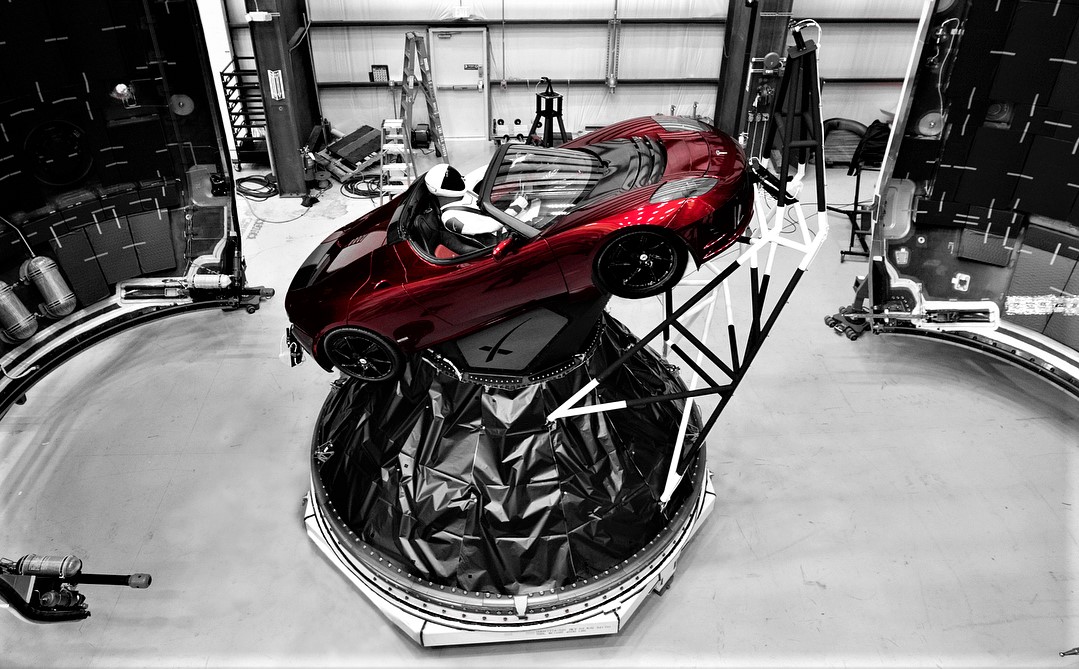
When the Tesla Roadster and its Starman occupant entered space aboard Falcon Heavy’s maiden voyage in 2018, it joined the ranks of one astronomer’s impressive database of human-made objects that have left Earth: The General Catalog of Artificial Space Objects (GCAT). It’s the most comprehensive collection of space object data available to the public, and its author recently published it in full for open-source use.
Jonathan McDowell, currently with the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, created GCAT as an endeavor that began about 40 years go during his Apollo-inspired childhood.
“It was hard for me growing up in England to get details about space because the media there weren’t as interested in it as the U.S. media, so in a slightly obsessive way I started making a list of rocket launches… Now I have the best list,” McDowell told VICE in recently published comments. Lack of information in his younger days seems to have only been the beginning of the challenges the astronomer was willing to take on for his project. As detailed to VICE, McDowell also traveled to international space agency locations to obtain their old rocket lists and even learned Russian to translate that country’s space object data.
Although McDowell has been collecting his Catalog data for decades, the push to finally put all of his work online was inspired by more recent events. The risks of COVID-19 and “imminent death” threatened the database’s purpose. “There’s no point if it dies with me,” he told VICE. Publishing the GCAT had been in his plans, however, the pandemic pushed its priority to the top of McDowell’s personal bucket list.
- Data from GCAT (J. McDowell, planet4589.org/space/gcat)
- Data from GCAT (J. McDowell, planet4589.org/space/gcat)
- Data from GCAT (J. McDowell, planet4589.org/space/gcat)
- Data from GCAT (J. McDowell, planet4589.org/space/gcat)
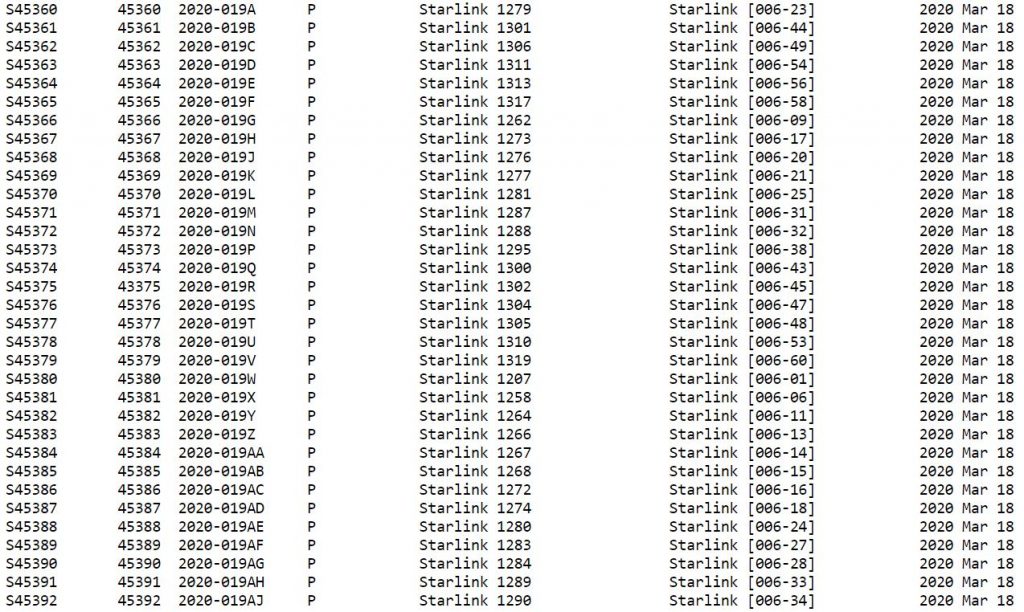
So, what exactly might one use the GCAT for? McDowell had his own suggestions, including the determination of how many working satellites are currently in space. Since the data is easy to export into software that allows sorting of tab-delimited files, one could perhaps also look at the amount of debris produced over the years to get a general picture for how active spaceflight operations were in the past or how they may be progressing. Plenty of information about each object’s origin and owner is included for this kind of research.
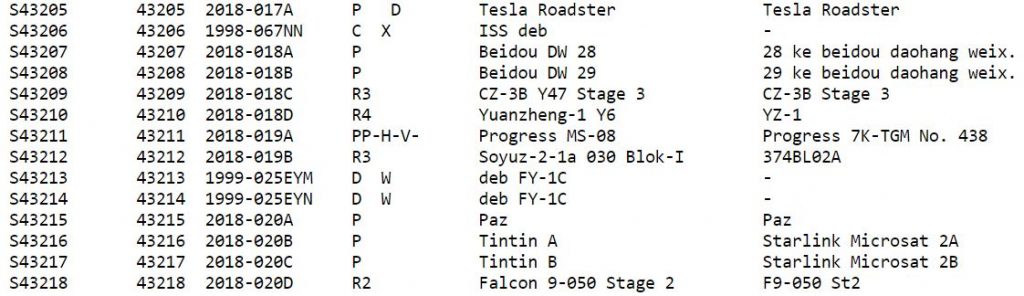
One of the GCAT data sets tracks failed objects that would have otherwise made it to orbit. As an example, looking at the number of items from failed launch attempts in 1958 (52) gives a hint as to how intense the space race between the US and the Soviet Union was at the time. Data browsing could be used for general historical inquiry as well. For instance, Sputnik 1, launched by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957, is object 00001; the Eagle lander still on the Moon from Apollo 11’s mission is object #04041; and the Tesla Roadster is object #43205.
Some of the data can inspire more historical awareness such as the listing of tools lost during on-orbit construction of the Soviets’ Mir Space Station in 1986. Of course, reminders of significant spaceflight misfortunes are also included like the Challenger Space Shuttle explosion in 1986 and SpaceX’s CRS-7 ISS resupply mission failure in 2015.
- Data from GCAT (J. McDowell, planet4589.org/space/gcat)
- Data from GCAT (J. McDowell, planet4589.org/space/gcat)
- Data from GCAT (J. McDowell, planet4589.org/space/gcat)
Since GCAT is inclusive of both functional items and notorious bits of space junk logged from decades of data digging, the Tesla Roadster and its 57,000+ “friends” are poised to help with some serious research now and in the far future.
“My audience is the historian 1,000 years from now,” McDowell explained. “I’m imagining that 1,000 years from now there will be more people living off Earth than on, and that they will look back to this moment in history as critically important.” For fans of Star Trek, this type of record keeping certainly seems to be relevant to future humans more often than not (away mission, anyone?). Perhaps that type of science fiction storyline will transpire into reality, just as so many of SpaceX’s achievements have done already.
Interestingly enough, McDowell is working on another project to track deep space objects beyond Earth’s orbit. Will space debris take center stage around Mars and beyond like it does around our own planet? Seeing the progress in one comprehensive database will certainly be an interesting way to show just how far humans have come since object #00001.
News
Tesla Robotaxi has already surpassed Waymo in this key metric
Tesla Robotaxi has already overtaken Waymo in Austin in one key metric, but there’s still more work to do.

Tesla Robotaxi has already surpassed Waymo in one extremely important key metric: size of service area.
Tesla just expanded its service area in Austin on Monday morning, pushing the boundaries of its Robotaxi fleet in an interesting fashion with new capabilities to the north. Yes, we know what it looks like:
🚨 Tesla’s new Robotaxi geofence is…
Finish the sentence 🥸 pic.twitter.com/3bjhMqsRm5
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 14, 2025
The expansion doubled Tesla Robotaxi’s potential travel locations, which now include the University of Texas at Austin, a school with over 53,000 students.
The doubling of the service area by Tesla has already made its travel area larger than Waymo’s, which launched driverless rides in October 2024. It became available to the public in March 2025.
According to Grok, the AI agent on X, Tesla Robotaxi’s current service area spans 42 square miles, which is five square miles larger than Waymo’s service area of 37 square miles.
Tesla Robotaxi (red) vs. Waymo geofence in Austin.
Much can be said about the shape… but the Robotaxi area is now ~3.9 mi² (10 km²) larger than Waymo’s!! pic.twitter.com/dVfh2ODxJC
— Robin (@xdNiBoR) July 14, 2025
The service area is one of the most important metrics in determining how much progress a self-driving ride-hailing service is making. Safety is the priority of any company operating a ride-hailing network, especially ones that are making it a point to use autonomy to deploy it.
However, these companies are essentially racing for a larger piece of the city or cities they are in. Waymo has expanded to several different regions around the United States, including Arizona and Los Angeles.
Tesla is attempting to do the same in the coming months as it has already filed paperwork in both California and Arizona to deploy its Robotaxi fleet in states across the U.S.
As the platform continues to show more prowess and accuracy in its operation, Tesla will begin to expand to new areas, eventually aiming for a global rollout of its self-driving service.
News
Tesla Megapacks arrive for massive battery replacing coal plant
Tesla Megapacks have started arriving on-site to the Stanwell Battery Project, just as Queensland prepares to wind down the Stanwell coal plant.

The first of over 300 Tesla Megapacks have arrived to the site of a massive battery energy storage system (BESS) being built in Australia, dubbed the Stanwell Battery Project after a coal plant it’s set to replace.
In a press release last week, the Stanwell Battery Project announced that the first Tesla Megapack 2XL units had arrived to the site, which is located outside of Rockhampton in Queensland, Australia. The project will eventually feature 324 Megapack units, set to arrive in the coming months, in order to support the 300MW/1,200MWh battery project.
“The Stanwell Battery is part of the diversification of our portfolio, to include cleaner and more flexible energy solutions,” said Angie Zahra, Stanwell Central Generation General Manager. “It is just one part of the 800 MW of battery energy storage capacity we have in our pipeline.
“Capable of discharging 300 MW of energy for up to four hours (1,200 MWh), our mega battery will be one of the largest in Queensland.”
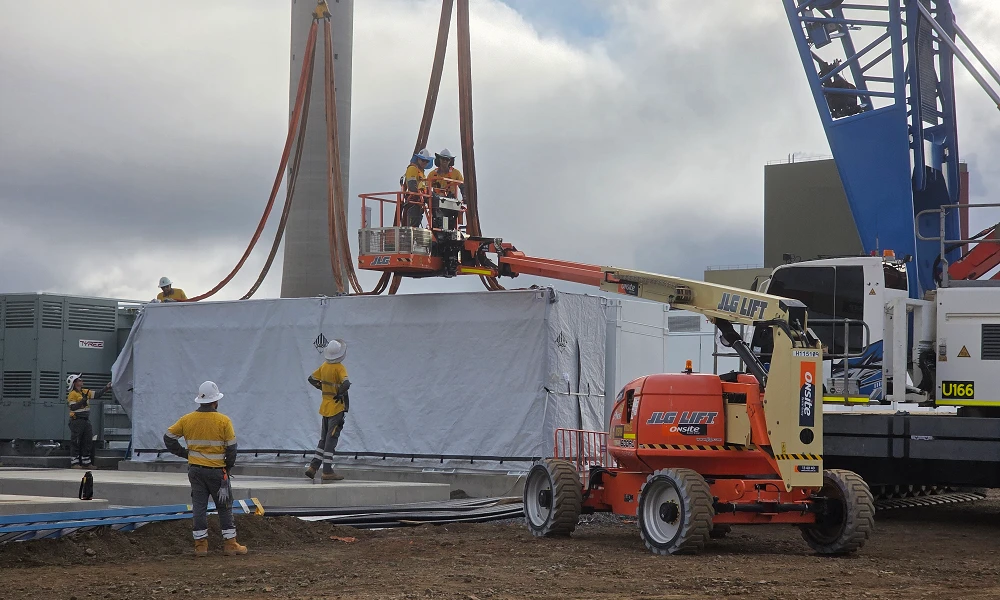

Credit: Stanwell
Did you know Tesla’s Lathrop facility churns out a Megapack every 68 minutes? That’s enough energy to power 3,600 homes for an hour per unit! ⚡️ pic.twitter.com/bG6fpHkB9O
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) June 11, 2025
READ MORE ON TESLA MEGAPACKS: Tesla Lathrop Megafactory celebrates massive Megapack battery milestone
The state is working with government-owned company Yurika to facilitate construction, and the process is expected to create roughly 80 jobs. The project is expected to come fully online in May 2027, with initial commissioning of the Megapacks aiming for November 2025.
The Stanwell Battery is set to replace the nearby Stanwell coal generation plant, which the government is planning to wind down starting in 2026 as part of efforts to reach an 80 percent renewable energy generation ratio by 2035. Meanwhile, the government is also set to begin winding down the Tarong and Callide coal plants, while several other Megapack projects are being built or coming online. o ya
Tesla currently has two Megapack production facilities, located in Lathrop, California, in the U.S. and another that came online earlier this year in Shanghai, China. The Shanghai Megafactory shipped its first units to Australia in March, while both factories are expected to be capable of producing 10,000 Megapack units per year upon reaching volume production.
News
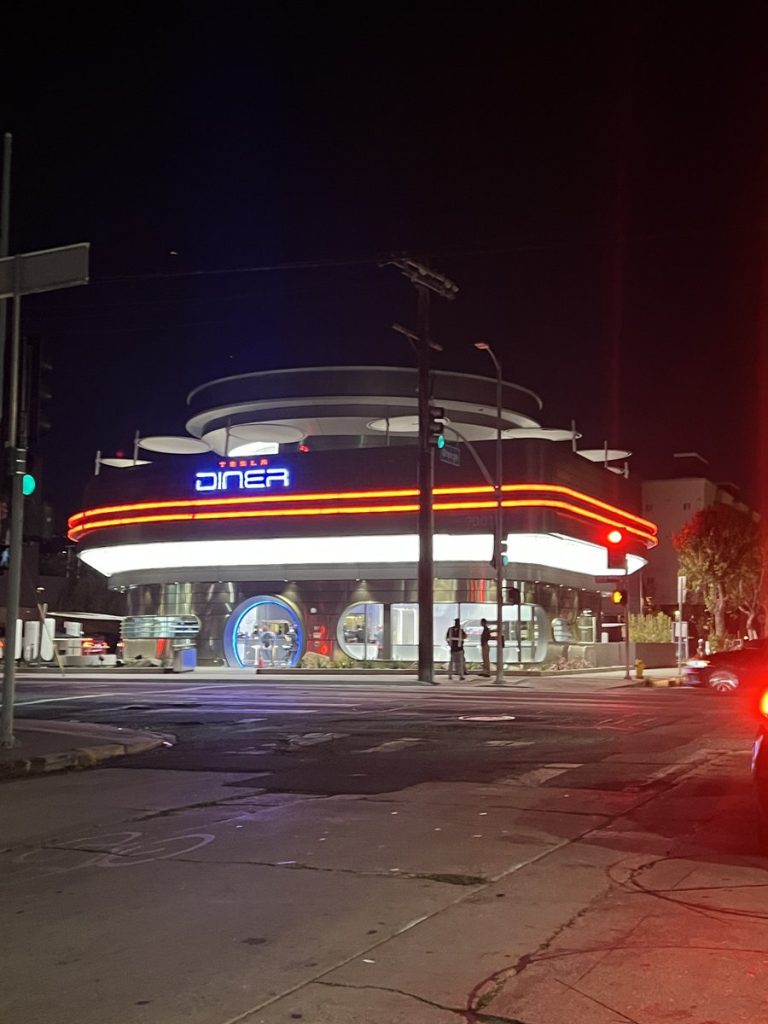
The Tesla Diner is basically finished—here’s what it looks like
The company first broke ground on the Diner, Drive-in, and Supercharger location in September 2023. Now, it has served one of its first internal customers.
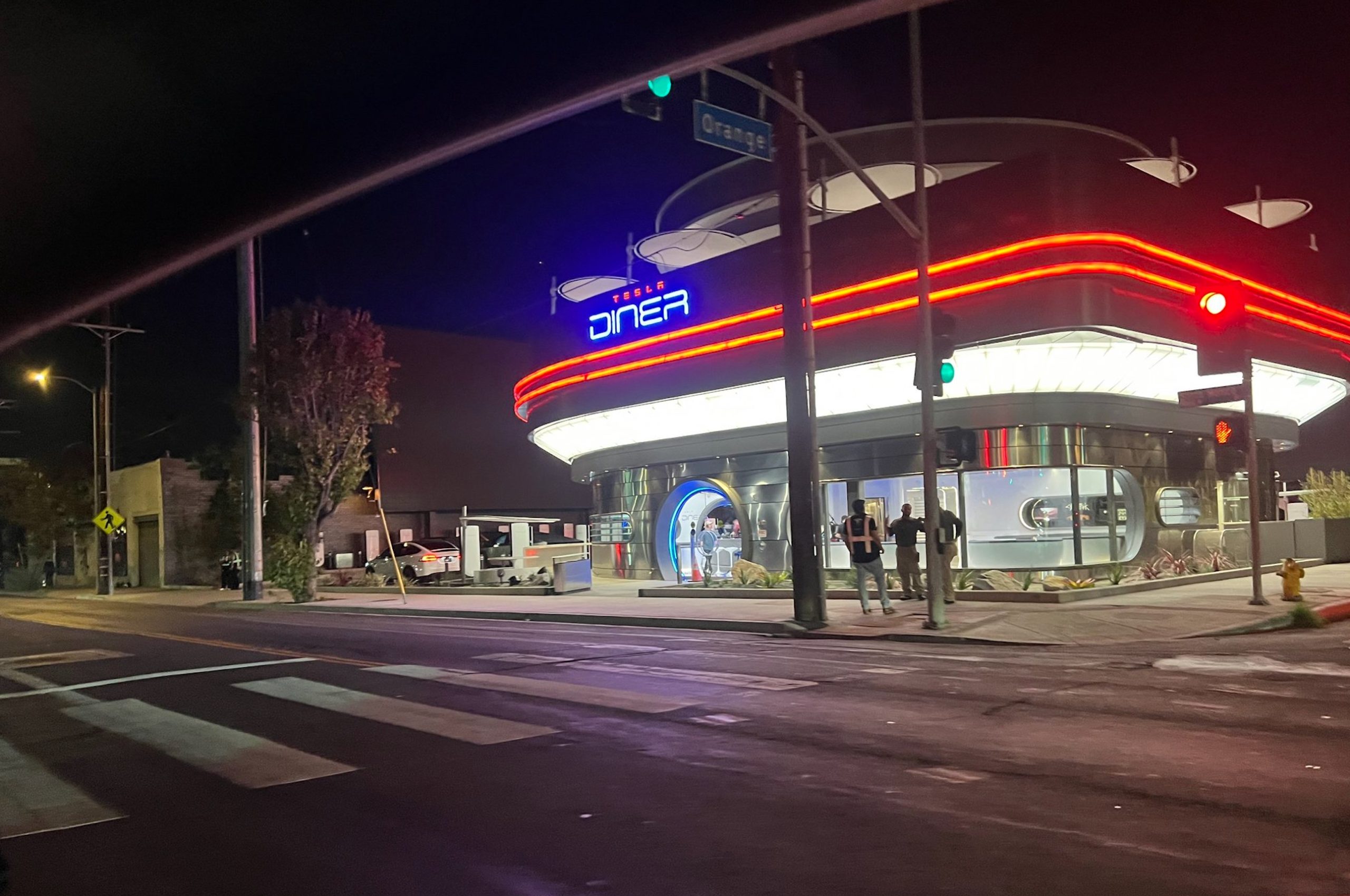

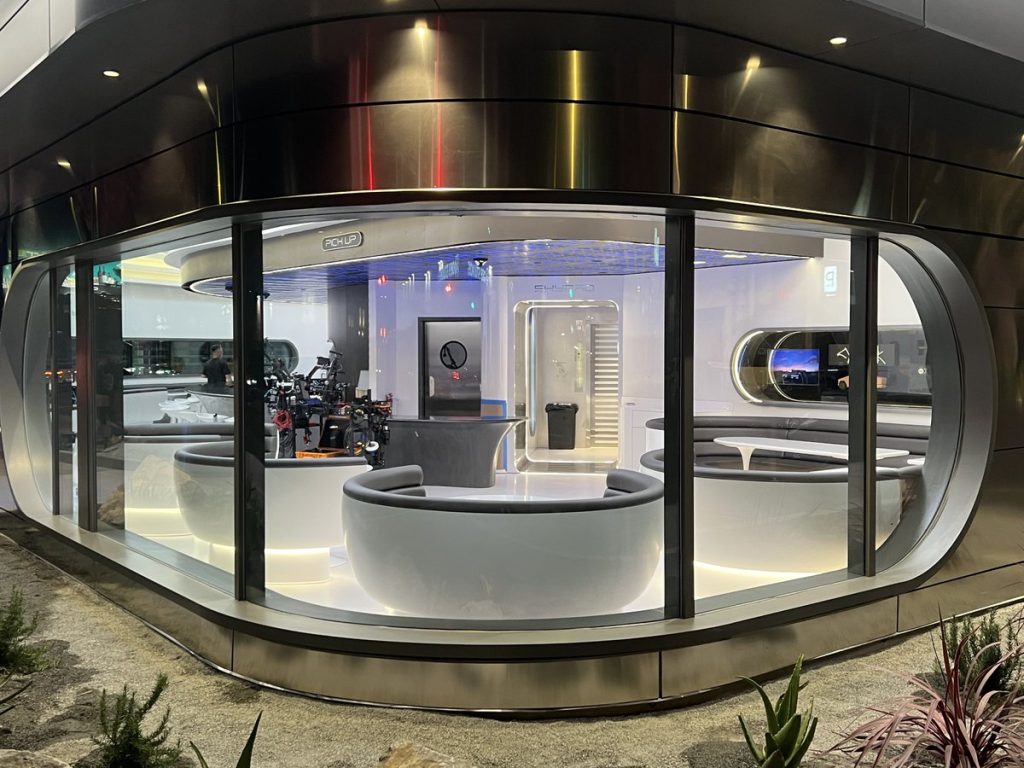
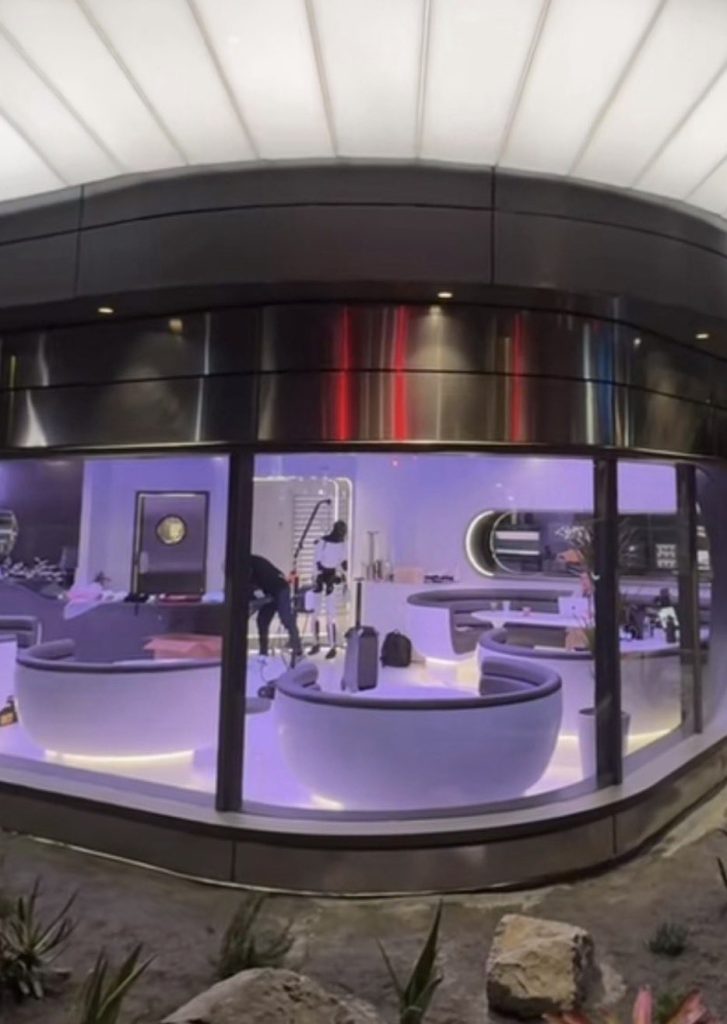
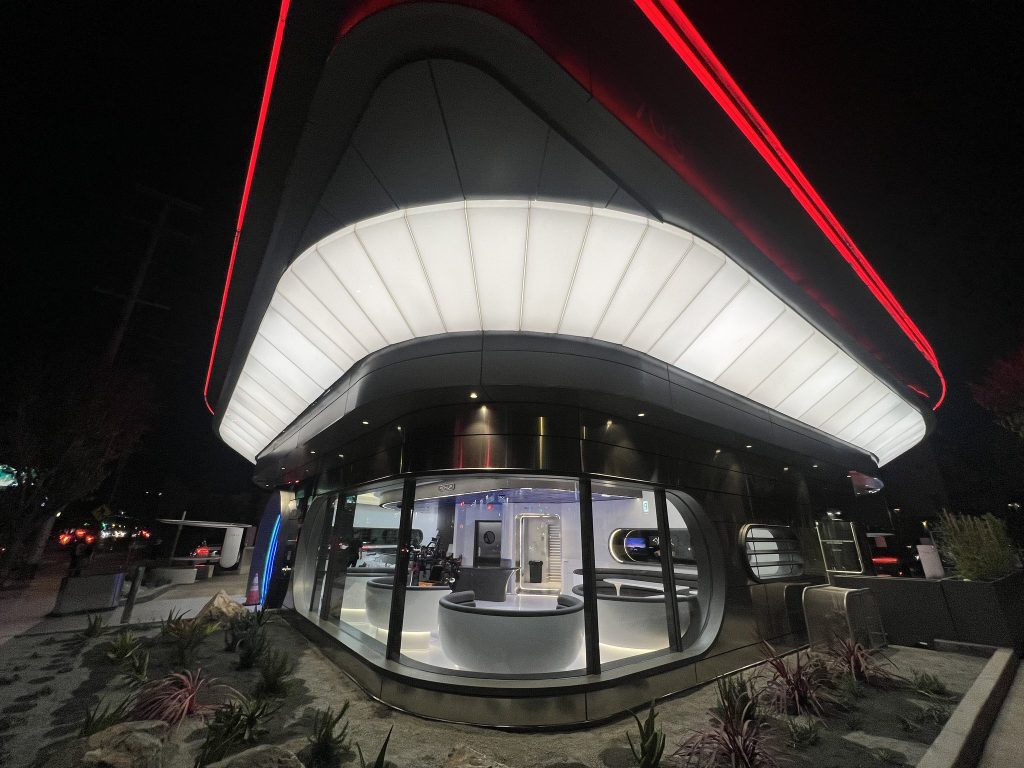
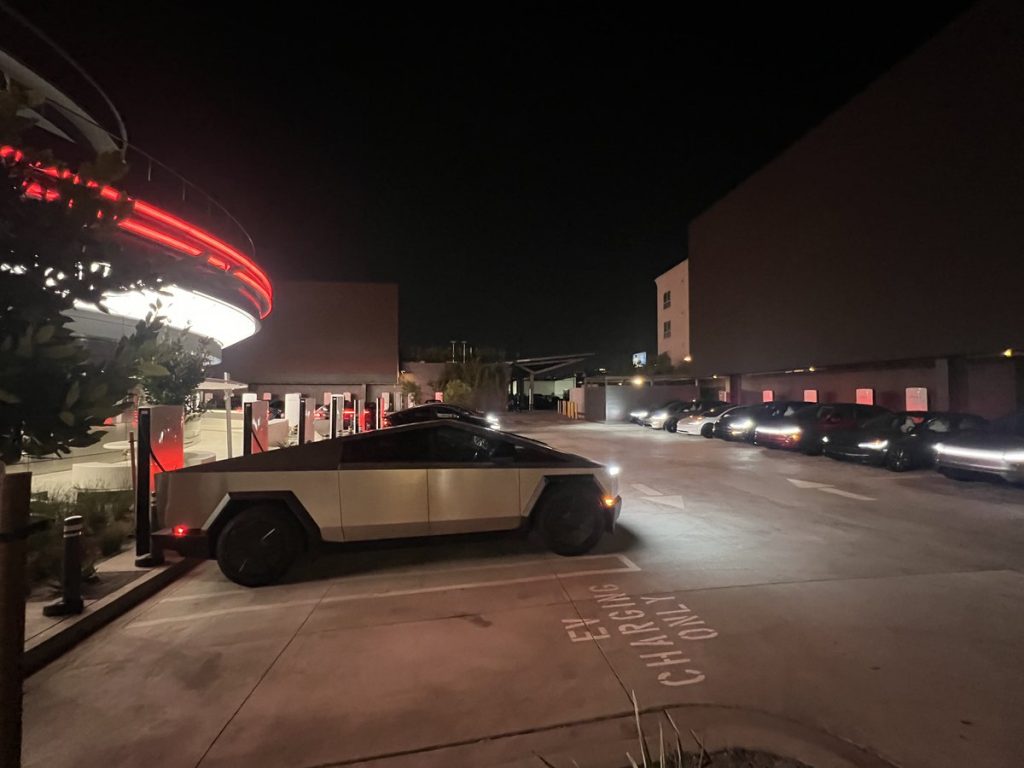
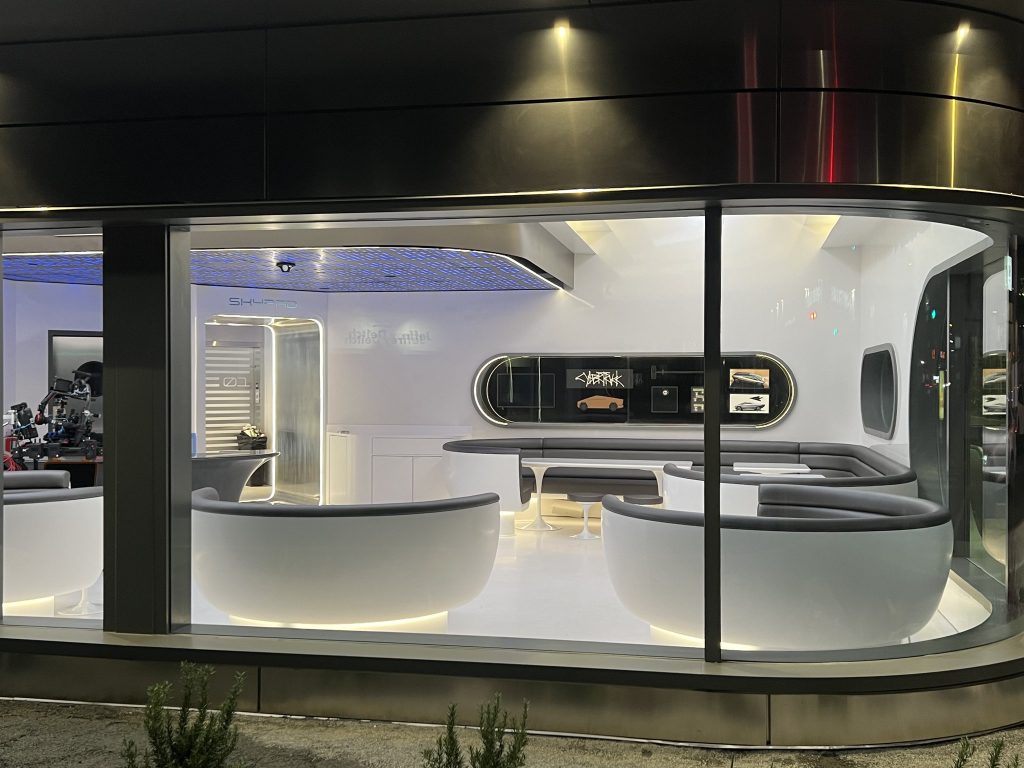
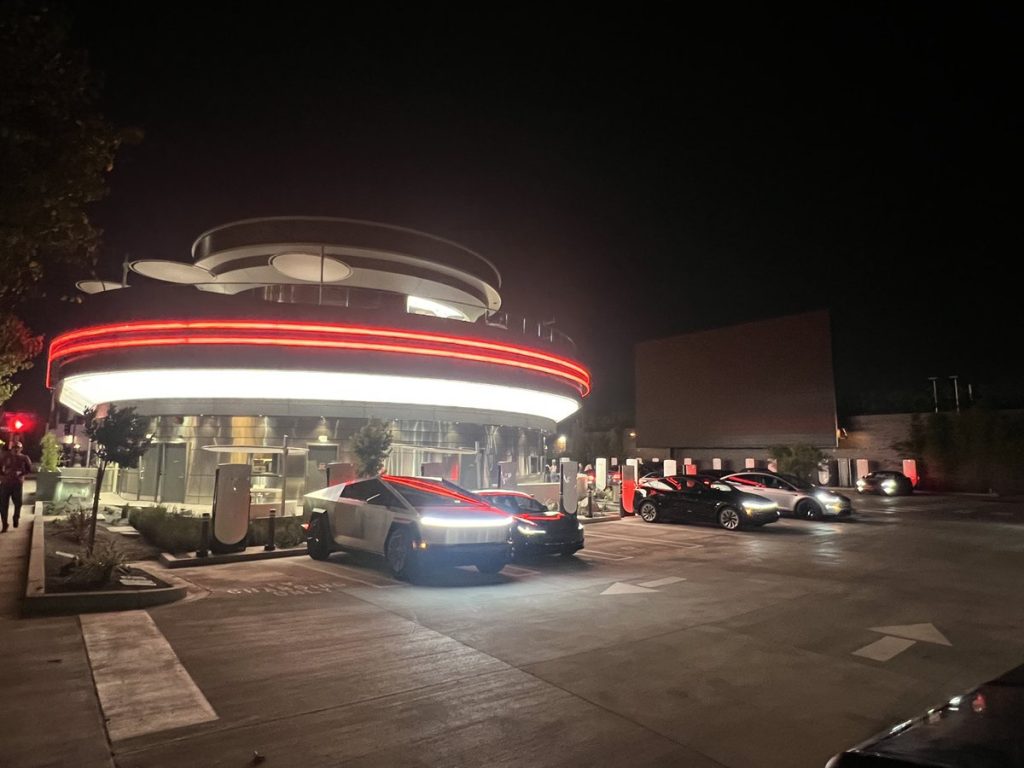
Tesla has finally completed the construction of its highly anticipated Diner, Drive-in, and Supercharger in Los Angeles, and recent photos of the interior’s “retro-futuristic” style are making their way around the internet.
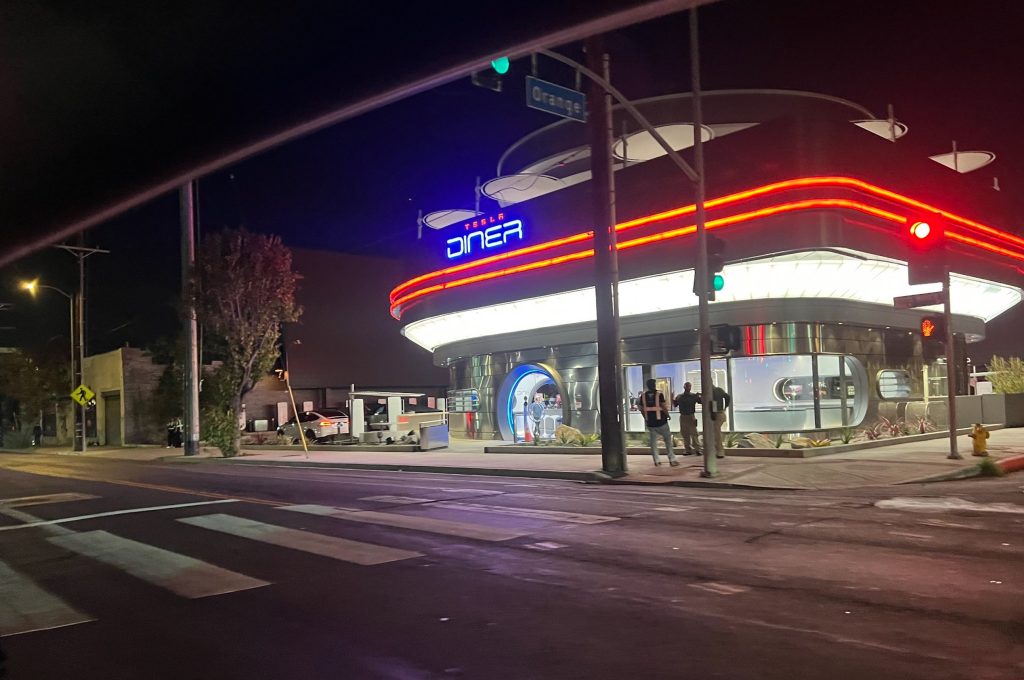
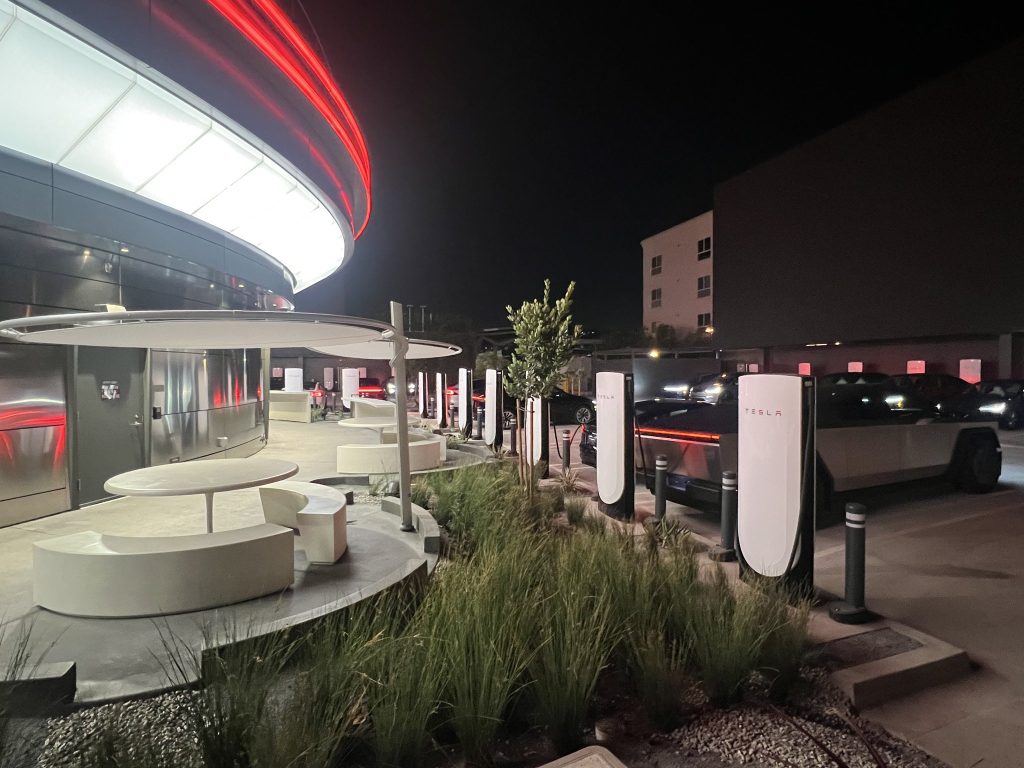
X user Brad Goldberg shared photos from the Tesla Diner site last Tuesday, depicting some of the Supercharger stalls, indoor and outdoor seating areas, multiple neon lights, and even an Optimus robot. Goldberg also noted that there had been a “flurry of activity on site” while he was snapping the photos last week, suggesting that the restaurant location could be getting close to opening.
The Tesla Diner also served one of its first internal customers in the past few days, as Elon Musk posted on X on early Monday morning that he had just finished up eating a meal at the site:
I just had dinner at the retro-futuristic Tesla diner and Supercharger.
Team did great work making it one of the coolest spots in LA!
The photos also show that the site is pretty much done, with some of them even showing vehicles charging at the charging stalls.
You can see some of the latest photos of the Tesla Diner below.

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X

Credit: TeslaKing420 | X

Credit: TeslaKing420 | X

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)
READ MORE ON TESLA’S LA DINER: Tesla readies Drive-In Diner Supercharger for launch with app inclusion
When will the Tesla Diner open to external customers?
While it’s still not open to external customers yet, the news again suggests that the company could be close to an official opening date. Tesla first broke ground on the Diner in September 2023, after receiving a wave of building permit approvals throughout that year. Teslarati also covered much of the construction progress throughout last year, including when crews installed the first and second drive-in screens.
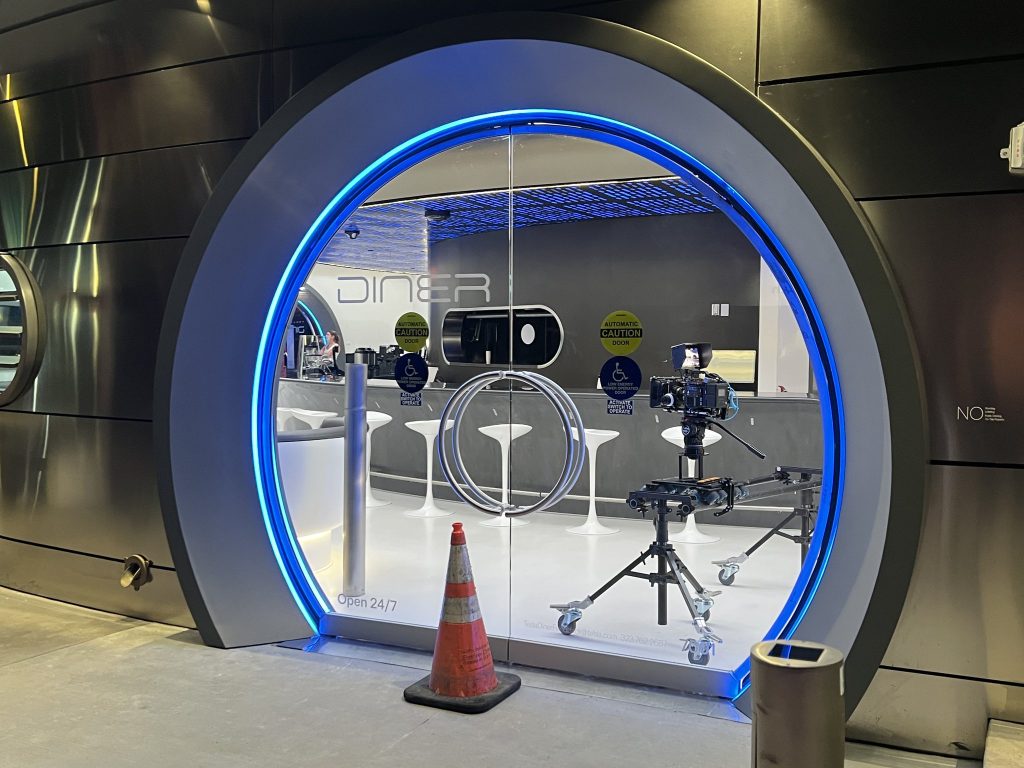
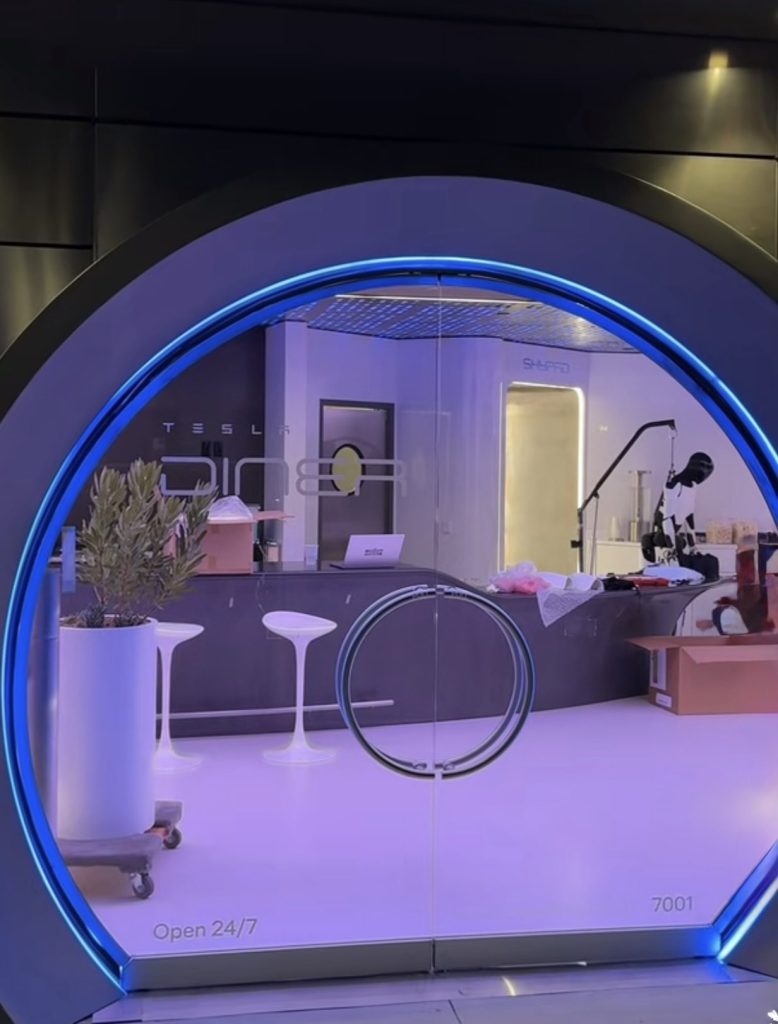
Located at 7001 West Santa Monica Boulevard, the idea was first discussed in 2018 by Musk and a few others on Twitter, featuring 1950s rock and roll, waiters on roller skates, and drive-in movie theater screens playing clips from some of history’s best movies. Notably, the photos of the front doors also show that the site will be open 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, whenever it does end up opening.
Tesla’s progress on Supercharger with diner, drive-in seen in aerial footage
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoTesla debuts hands-free Grok AI with update 2025.26: What you need to know
-

 Elon Musk4 days ago
Elon Musk4 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk6 days ago
Elon Musk6 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoTesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales