

Energy
Tesla says its SA battery response time is too fast for utility billing system
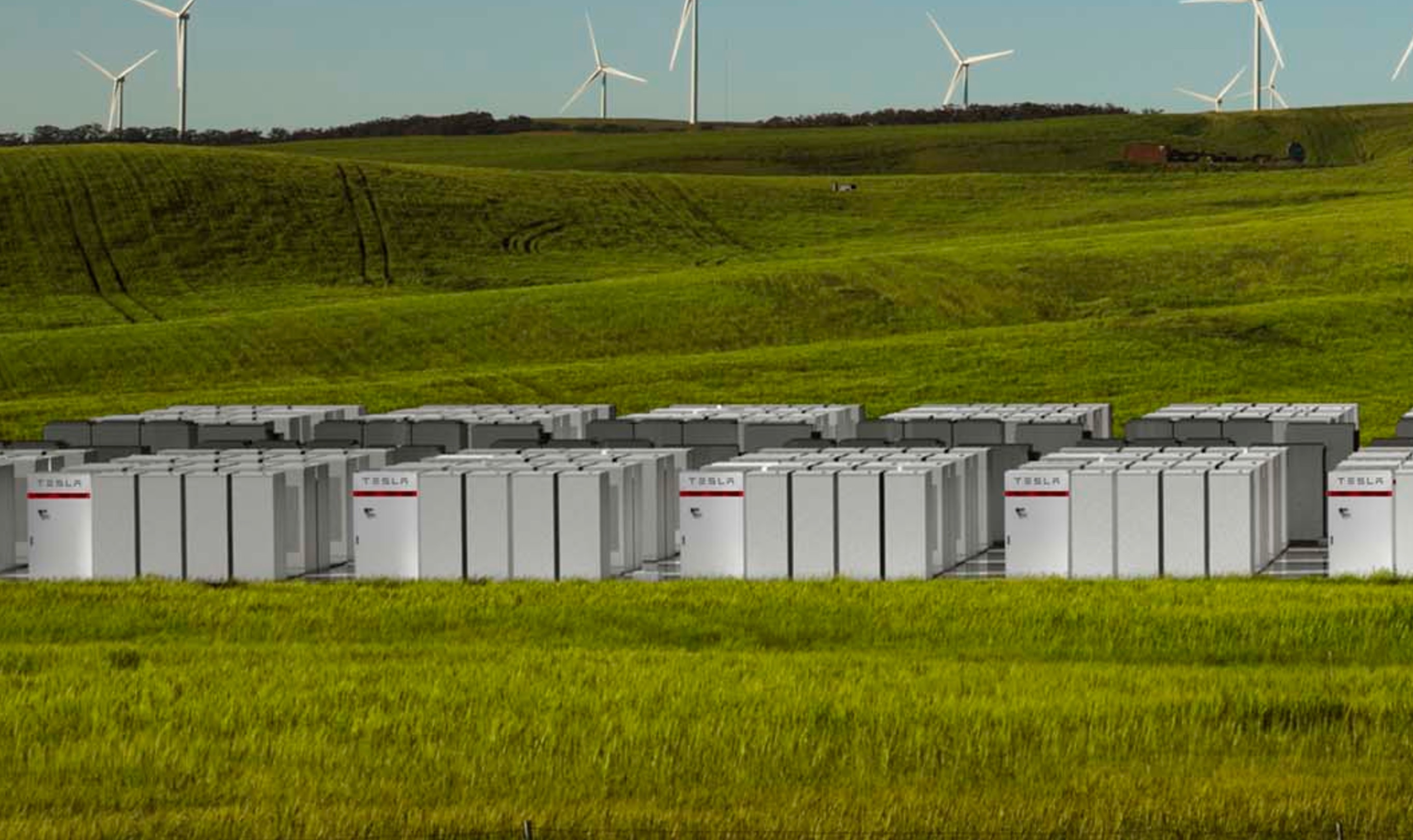
Tesla’s 100 MW/129MWh Powerpack system near Jamestown in South Australia is proving to be so quick in providing backup power to the energy grid that 30-40% of the services it provides end up unpaid. The electric car and energy company claims that this is due to SA’s legacy utility billing system not being optimized for the big battery’s response time.
Tesla’s earnings from its big battery installation currently follow the standards set by the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO), which breaks down a power provider’s response time into 6 seconds, 1 minute, and 5 minutes for energy to be fed into the grid. Tesla’s SA Powerpack farm near Jamestown, however, has been providing backup energy in as quick as 200 milliseconds. Thus, any amount of energy sent from Tesla’s battery into the grid that lasts between 200 milliseconds and 6 seconds is just too quick to be registered according to AEMO’s current specifications.
In a statement to The Sydney Morning Herald, Tesla stated that around 30%-40% of services provided by the SA big battery ended up unpaid due to the system’s quick response time. Tesla further asserted that AEMO’s standards are currently designed for fossil fuel-based backup systems, which respond to energy grid instabilities far slower than the industry-grade Powerpack batteries.
“Tesla estimates that the Hornsdale Power Reserve battery has delivered 30 to 40% of its services to frequency markets without being paid due to existing AEMO technical specifications being written based on fossil fuel generation assets.
“Current standards compensate batteries for their capacity based on fossil generator response rates, despite the ability to provide a faster ramp time. This makes it difficult for the full value of fast-responding technologies to be recognized in the current contingency FCAS markets.”
Over the past few months, Tesla’s SA Powerpack farm, which currently stands as the largest lithium-ion battery installation in the world, has been pivotal in stabilizing the energy grid in South Australia. Last December alone, Tesla’s 100 MW/129MWh installation accomplished a huge feat, keeping the region’s energy stable amidst the unexpected failure of the coal-powered Loy Yang A power plant in Victoria. During that time, Tesla’s Powerpacks backed up the grid within 0.14 seconds after the unexpected breakdown of the coal-powered plant. The system also supported the grid hundreds of times over the course of the month.
The performance of Tesla’s big battery in South Australia was recently examined by energy expert Hugh Saddler, who studied the charge and discharge patterns of the installation. Over the course of his tests, Saddler noted that the Powerpack farm exhibited great efficiency, with 30% of the battery’s 100MW capacity being allocated to the system’s daily charge and discharge cycles, and the rest being allotted to keep the energy grid’s frequency at a steady 50 Hz and 240 volts.
Tesla’s energy initiatives in South Australia recently met a series of roadblocks, however, with South Australia resource minister Matt Canavan mocking the SA Powerpack farm by calling it the “Kardashian” of the energy industry and alleging that the installation is simply “famous for being famous.” Newly-elected South Australia premier Steven Marshall has also gone on the offensive against the Elon Musk-led company’s projects, stating that his government would not be supporting Tesla’s proposal of building a 250 MW/650 MWh virtual power plant from 50,000 low-income residential units and home Powerwall 2 systems.
Energy
Tesla Lathrop Megafactory celebrates massive Megapack battery milestone
The Tesla Megapack is the backbone of Tesla Energy’s battery deployments.
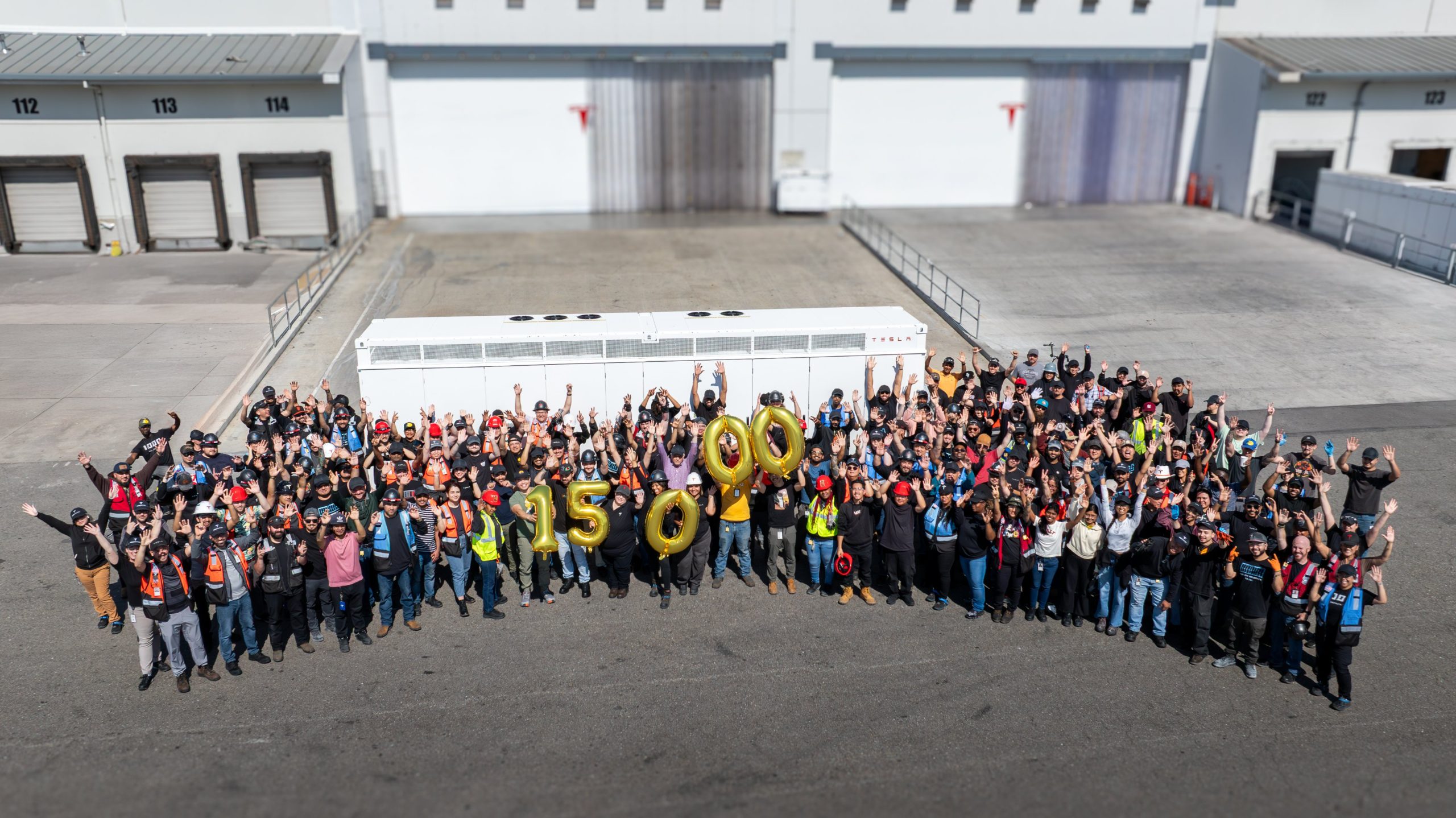

The Tesla Lathrop Megafactory recently achieved a new milestone. As per the official Tesla Megapack account on X, the Lathrop Megafactory has produced its 15,000th Megapack 2 XL battery.
15,000 Megapack Batteries
Tesla celebrated the milestone with a photo of the Lathrop Megafactory team posing with a freshly produced Megapack battery. To commemorate the event, the team held balloons that spelled out “15,000” as they posed for the photo.
The Tesla Megapack is the backbone of Tesla Energy’s battery deployments. Designed for grid-scale applications, each Megapack offers 3.9 MWh of energy and 1.9 MW of power. The battery is extremely scalable, making it perfect for massive energy storage projects.
More Megafactories
The Lathrop Megafactory is Tesla’s first dedicated facility for its flagship battery storage system. It currently stands as the largest utility-scale battery factory in North America. The facility is capable of producing 10,000 Megapack batteries every year, equal to 40 GWh of clean energy storage.
Thanks to the success of the Megapack, Tesla has expanded its energy business by building and launching the Shanghai Megafactory, which is also expected to produce 40 GWh of energy storage per year. The ramp of the Shanghai Megafactory is quite impressive, with Tesla noting in its Q1 2025 Update Letter that the Shanghai Megafactory managed to produce over 100 Megapack batteries in the first quarter alone.
Tesla Energy’s Potential
During the first quarter earnings call, CEO Elon Musk stated that the Megapack is extremely valuable to the energy industry.
“The Megapack enables utility companies to output far more total energy than would otherwise be the case… This is a massive unlock on total energy output of any given grid over the course of a year. And utility companies are beginning to realize this and are buying in our Megapacks at scale,” Musk said.
Energy
Tesla Megapacks powers the xAI Colossus supercomputer
Tesla Megapacks step in to stabilize xAI’s Colossus supercomputer, replacing natural gas turbines. Musk’s ventures keep intertwining.
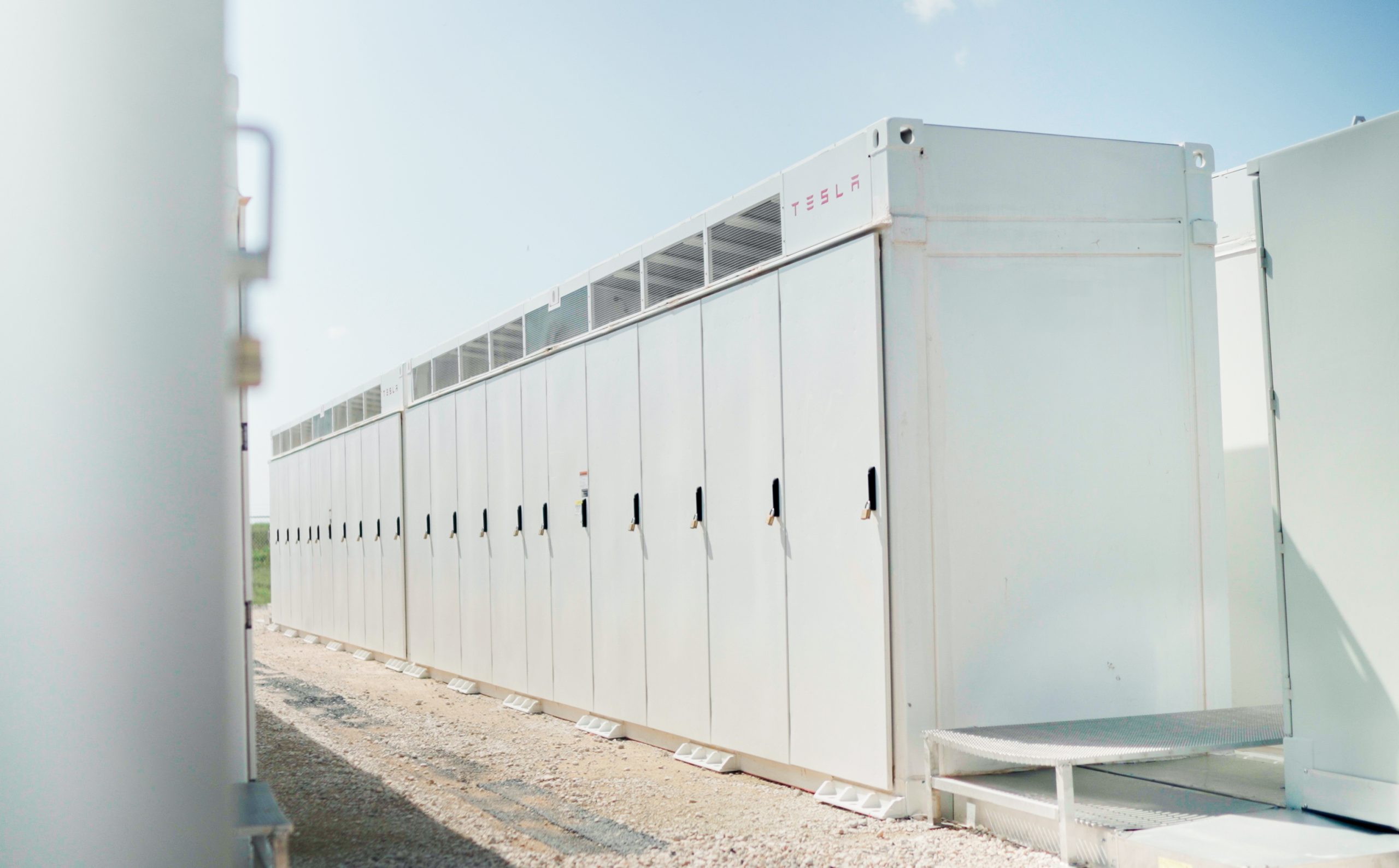

Tesla Megapack batteries will power the xAI Colossus supercomputer in Memphis to ensure power stability. The collaboration between Tesla and xAI highlights the synergy among Elon Musk’s ventures.
The artificial intelligence startup has integrated Tesla Megapacks to manage outages and demand surges, bolstering the facility’s reliability. The Greater Memphis Chamber announced that Colossus, recently connected to a new 150-megawatt electric substation, is completing its first construction phase. This transition addresses criticism from environmental justice groups over the initial use of natural gas turbines.
“The temporary natural gas turbines that were being used to power the Phase I GPUs prior to grid connection are now being demobilized and will be removed from the site over the next two months.
“About half of the operating turbines will remain operating to power Phase II GPUs of xAI until a second substation (#22) already in construction is completed and connected to the electric grid, which is planned for the Fall of 2025, at which time the remaining turbines will be relegated to a backup power role,” the Chamber stated.
xAI’s rapid development of Colossus reflects its ambition to advance AI capabilities, but the project has faced scrutiny for environmental impacts. The shift to Megapacks and grid power aims to mitigate these concerns while ensuring operational continuity.
The Megapack deployment underscores the collaboration among Musk’s companies, including Tesla, SpaceX, Neuralink, and The Boring Company. Tesla appears to be the common link between all of Musk’s companies. For example, The Boring Company built a tunnel in Giga, Texas. In addition, Musk has hinted at a potential collaboration between the Tesla Optimus Bot and Neuralink. And from January 2024 to February 2025, xAI invested $230 million in Megapacks, per a Tesla filing.
Tesla Energy reported a 156% year-over-year increase in Q1 2025, deploying 10.4 GWh of storage products, including Megapacks and Powerwalls. Tesla’s plans for a new Megapack factory in Waller County, Texas, which is expected to create 1,500 jobs in the area, further signal its commitment to scaling energy solutions.
As xAI leverages Tesla’s Megapacks to power Colossus, the integration showcases Musk’s interconnected business ecosystem. The supercomputer’s enhanced stability positions xAI to drive AI innovation, while Tesla’s energy solutions gain prominence, setting the stage for broader technological and economic impacts.
Energy
Tesla Energy celebrates one decade of sustainability
Tesla Energy has gone far since its early days, and it is now becoming a progressively bigger part of the company.

Tesla Energy recently celebrated its 10th anniversary with a dedicated video showcasing several of its milestones over the past decade.
Tesla Energy has gone far since its early days, and it is now becoming a progressively bigger part of the company.
Tesla Energy Early Days
When Elon Musk launched Tesla Energy in 2015, he noted that the business is a fundamental transformation of how the world works. To start, Tesla Energy offered the Powerwall, a 7 kWh/10 kWh home battery system, and the Powerpack, a grid-capable 100 kWh battery block that is designed for scalability. A few days after the products’ launch, Musk noted that Tesla had received 38,000 reservations for the Powerwall and 2,500 reservations for the Powerpack.
Tesla Energy’s beginnings would herald its quiet growth, with the company later announcing products like the Solar Roof tile, which is yet to be ramped, and the successor to the Powerwall, the 13.5 kWh Powerwall 2. In recent years, Tesla Energy also launched its Powerwall 3 home battery and the massive Megapack, a 3.9 MWh monster of a battery unit that has become the backbone for energy storage systems across the globe.
Key Milestones
As noted by Tesla Energy in its recent video, it has now established facilities that allow the company to manufacture 20,000 units of the Megapack every year, which should help grow the 23 GWh worth of Megapacks that have already been deployed globally.
The Powerwall remains a desirable home battery as well, with more than 850,000 units installed worldwide. These translate to 12 GWh of residential entry storage delivered to date. Just like the Megapack, Tesla is also ramping its production of the Powerwall, allowing the division to grow even more.
Tesla Energy’s Role
While Tesla Energy does not catch as much headlines as the company’s electric vehicle businesses, its contributions to the company’s bottom line have been growing. In the first quarter of 2025 alone, Tesla Energy deployed 10.4 GWh of energy storage products. Powerwall deployments also crossed 1 GWh in one quarter for the first time. As per Tesla in its Q1 2025 Update Letter, the gross margin for the Energy division has improved sequentially as well.
-

 Elon Musk4 days ago
Elon Musk4 days agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-
 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
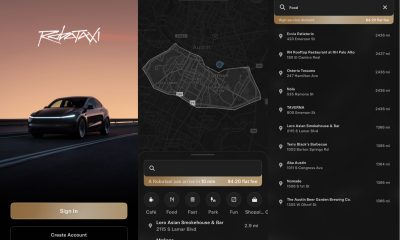
Elon Musk2 weeks agoFirst Look at Tesla’s Robotaxi App: features, design, and more
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoWatch Tesla’s first driverless public Robotaxi rides in Texas
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoSpaceX and Elon Musk share insights on Starship Ship 36’s RUD
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoWatch the first true Tesla Robotaxi intervention by safety monitor
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla has started rolling out initial round of Robotaxi invites
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla to launch in India in July with vehicles already arriving: report





















