

News
SpaceX’s first batch of Starlink satellites already in Florida for launch debut
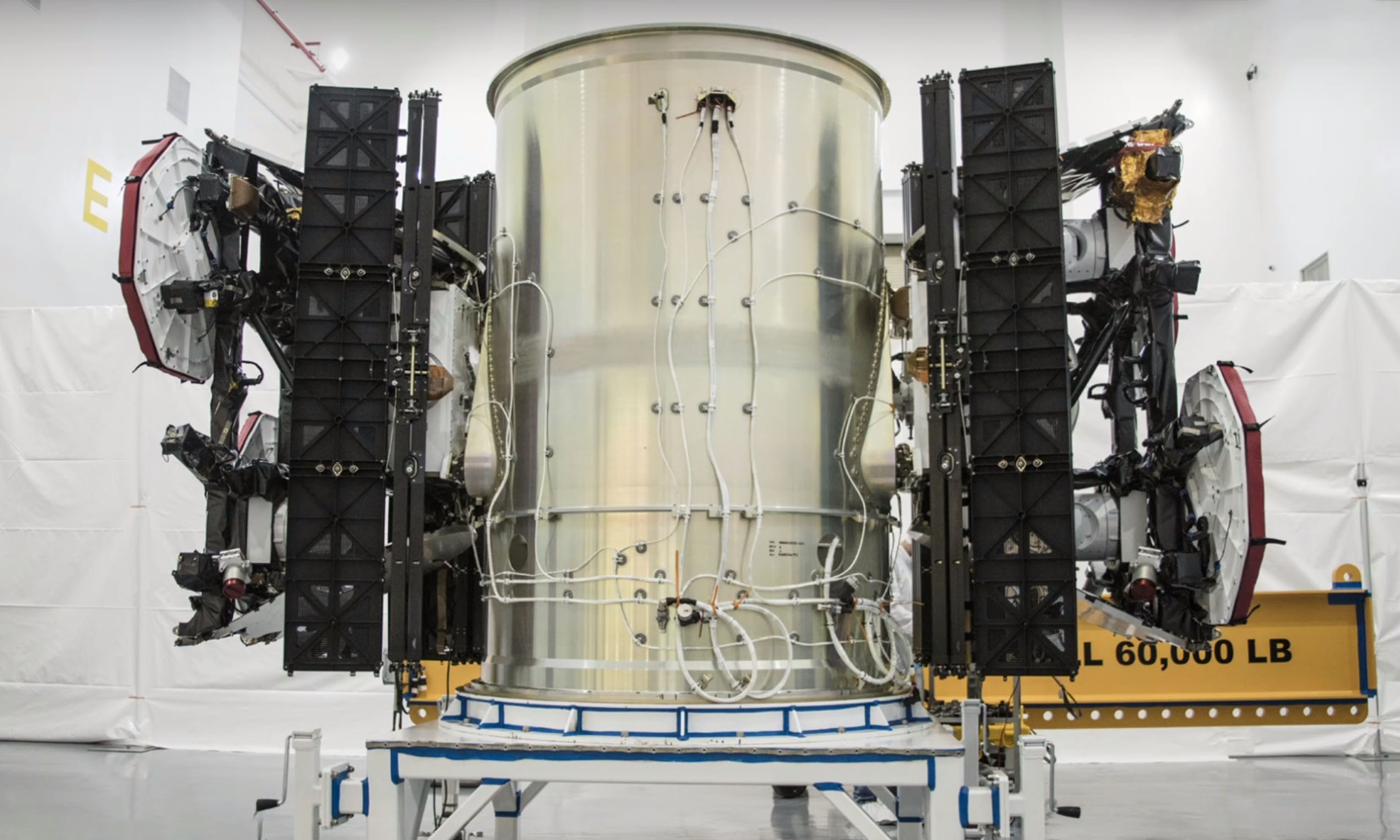
According to an official statement, SpaceX’s satellite mass production is “well underway” and the first batch of operational Starlink satellites are already in Florida for their May 2019 launch debut.
Simultaneously, the FCC has granted SpaceX’s request to modify the deployment of its first 1584 Starlink satellites, permitting the company to lower their orbit from approximately 1150 km to 550 km (715 mi to 340 mi). A lower insertion orbit should improve Falcon 9’s maximum Starlink payload, while the lower operational orbit will help to further minimize any risk posed by orbital debris that could be generated by failed SpaceX satellites.
Above all else, SpaceX’s confirmation that the first batch of Starlink satellites are already in Florida drives home the reality that the company’s internet satellite constellation is about to become very real. Said constellation has long been the subject of endless skepticism and criticism, dominated by a general atmosphere of dismissal. There is no doubt that Starlink, as proposed, is an extraordinarily ambitious program that will cost billions of dollars to even begin to realize. SpaceX will have to find ways to affordably manufacture and launch ~11,900 satellites – together weighing something like 500 metric tons (1.1 million lbs) – in as few as nine years, start to finish.
As of November 2018, there are roughly 2000 satellites operating in Earth orbit, meaning that SpaceX’s full Starlink constellation would increase the number of functional satellites in orbit by a factor of almost seven. Just the first phase of Starlink (4409 satellites) would more than triple the number of working satellites in orbit. To meet the contractual requirement that SpaceX launch at least half of Starlink’s licensed satellites within six years of the FCC granting the constellation license, the company will need to launch an average of ~37 satellites per month between now and April 2024. By April 2027, SpaceX will either have to launch all ~2200 remaining Phase 1 satellites or risk forfeiture of its Starlink constellation license. Same goes for the ~7500 very low Earth orbit (VLEO) satellites making up Starlink’s second phase, albeit with their launch deadlines instead in November of 2024 and 2027.

In fact, if SpaceX wants to preserve the separate FCC license for its VLEO Starlink segment, it will actually need to build and launch an average of 100 satellites per month – 20+ per week – for the next five years. In no way, shape, or form is the monthly production of 100 complex pieces of machinery unprecedented. It is, however, entirely unprecedented – and by a factor of no less than 10 – in the spaceflight and satellite industries. Accomplishing that feat will require numerous paradigm shifts in satellite design, manufacturing, and operations. It’s hard to think of anyone more up to the challenge than SpaceX but it will still be an immensely difficult and expensive undertaking.
“Baby” steps
According to SpaceX, the first 75 operational Starlink satellites will be significantly less refined than those that will follow. Most notably, they will eschew dual-band (Ku and Ka) phased array antennas, instead relying solely on Ka-band communications. The second main difference between relates to “demisability”, referring to characteristics exhibited during reentry. The first 75 spacecraft will be less refined and thus feature a handful of components that are expected to survive the rigors of reentering Earth’s atmosphere, creating a truly miniscule risk of property damage and/or human injuries. Subsequent Starlink vehicles will incorporate design changes to ensure that 100% of each satellite is incinerated during reentry, thus posing a ~0% risk on the ground.
In a sense, the first 75 Starlink satellites will be an in-depth demonstration of SpaceX’s proposed constellation. Depending on how the satellites are deployed in orbit, SpaceX’s development team could potentially have uninterrupted access to the orbiting mini-constellation. There will also be constant opportunities to thoroughly test SpaceX’s network architecture for real, including general downlink/uplink traffic, surge management, satellite handoffs, and the laser interlinks meant to join all Starlink satellites into one giant mesh network.

SpaceX has yet to announce the precise number of Starlink satellites that will be aboard Falcon 9 on the rocket’s first dedicated internal launch. More likely than not, the constraining factor will be the usable volume of SpaceX’s payload fairing, measuring 5.2m (17 ft) in diameter. For Flight 1, 10-20 satellites is a reasonable estimate. Likely to weigh around 10,000 kg (22,000 lb) total, the first Starlink payload will be delivered to a parking orbit of ~350 km (220 mi), easily allowing Falcon 9 to return to SpaceX’s Florida Landing Zone or perform a gentle landing aboard drone ship Of Course I Still Love You (OCISLY). The satellites will use their own electric Hall thrusters to reach their final destination (550 km).
According to SpaceX CEO Elon Musk, the first Falcon 9 fairing reuse may also happen during an internal Starlink launch, although it’s unclear if he was referring to Starlink Launch 1 (Starlink-1) or a follow-up mission later this year.
For now, SpaceX is targeting a mid-May for its first dedicated Starlink mission, set to launch from Launch Complex 40 (LC-40). Up next for LC-40 is SpaceX’s 17th operational Cargo Dragon launch (CRS-17), delayed from April 26th and April 30th to May 3rd.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.

News
Tesla Cybercab spotted with interesting charging solution, stimulating discussion
The port is located in the rear of the vehicle and features a manual door and latch for plug-in, and the video shows an employee connecting to a Tesla Supercharger.
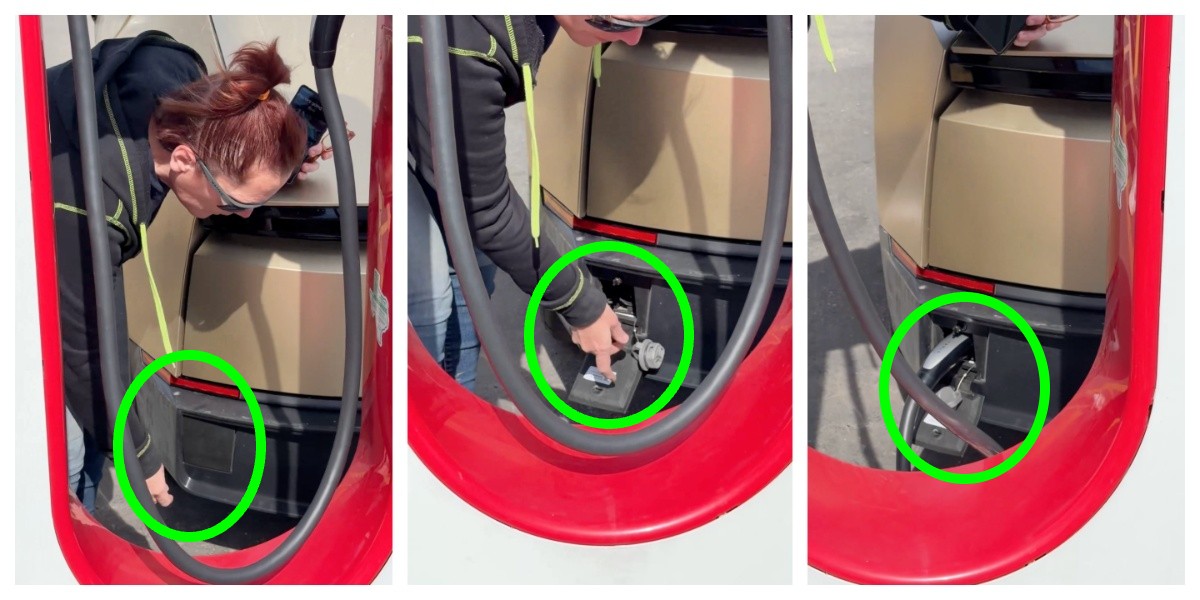
Tesla Cybercab units are being tested publicly on roads throughout various areas of the United States, and a recent sighting of the vehicle’s charging port has certainly stimulated some discussions throughout the community.
The Cybercab is geared toward being a fully-autonomous vehicle, void of a steering wheel or pedals, only operating with the use of the Full Self-Driving suite. Everything from the driving itself to the charging to the cleaning is intended to be operated autonomously.
But a recent sighting of the vehicle has incited some speculation as to whether the vehicle might have some manual features, which would make sense, but let’s take a look:
🚨 Tesla Cybercab charging port is in the rear of the vehicle!
Here’s a great look at plugging it in!!
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) January 29, 2026
The port is located in the rear of the vehicle and features a manual door and latch for plug-in, and the video shows an employee connecting to a Tesla Supercharger.
Now, it is important to remember these are prototype vehicles, and not the final product. Additionally, Tesla has said it plans to introduce wireless induction charging in the future, but it is not currently available, so these units need to have some ability to charge.
However, there are some arguments for a charging system like this, especially as the operation of the Cybercab begins after production starts, which is scheduled for April.
Wireless for Operation, Wired for Downtime
It seems ideal to use induction charging when the Cybercab is in operation. As it is for most Tesla owners taking roadtrips, Supercharging stops are only a few minutes long for the most part.
The Cybercab would benefit from more frequent Supercharging stops in between rides while it is operating a ride-sharing program.
Tesla wireless charging patent revealed ahead of Robotaxi unveiling event
However, when the vehicle rolls back to its hub for cleaning and maintenance, standard charging, where it is plugged into a charger of some kind, seems more ideal.
In the 45-minutes that the car is being cleaned and is having maintenance, it could be fully charged and ready for another full shift of rides, grabbing a few miles of range with induction charging when it’s out and about.
Induction Charging Challenges
Induction charging is still something that presents many challenges for companies that use it for anything, including things as trivial as charging cell phones.
While it is convenient, a lot of the charge is lost during heat transfer, which is something that is common with wireless charging solutions. Even in Teslas, the wireless charging mat present in its vehicles has been a common complaint among owners, so much so that the company recently included a feature to turn them off.
Production Timing and Potential Challenges
With Tesla planning to begin Cybercab production in April, the real challenge with the induction charging is whether the company can develop an effective wireless apparatus in that short time frame.
It has been in development for several years, but solving the issue with heat and energy loss is something that is not an easy task.
In the short-term, Tesla could utilize this port for normal Supercharging operation on the Cybercab. Eventually, it could be phased out as induction charging proves to be a more effective and convenient option.
News
Tesla confirms that it finally solved its 4680 battery’s dry cathode process
The suggests the company has finally resolved one of the most challenging aspects of its next-generation battery cells.
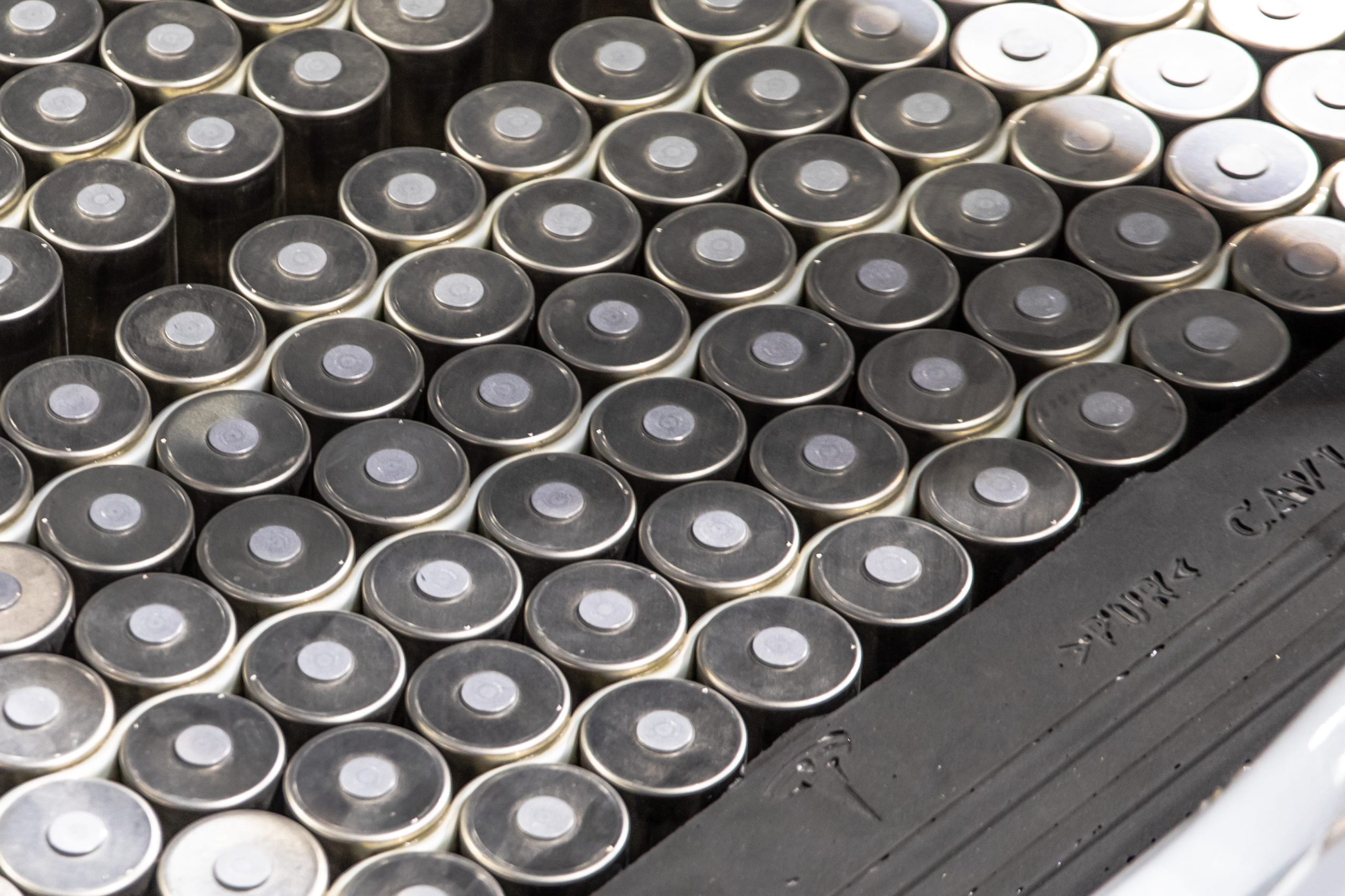

Tesla has confirmed that it is now producing both the anode and cathode of its 4680 battery cells using a dry-electrode process, marking a key breakthrough in a technology the company has been working to industrialize for years.
The update, disclosed in Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 update letter, suggests the company has finally resolved one of the most challenging aspects of its next-generation battery cells.
Dry cathode 4680 cells
In its Q4 and FY 2025 update letter, Tesla stated that it is now producing 4680 cells whose anode and cathode were produced during the dry electrode process. The confirmation addresses long-standing questions around whether Tesla could bring its dry cathode process into sustained production.
The disclosure was highlighted on X by Bonne Eggleston, Tesla’s Vice President of 4680 batteries, who wrote that “both electrodes use our dry process.”
Tesla first introduced the dry-electrode concept during its Battery Day presentation in 2020, pitching it as a way to simplify production, reduce factory footprint, lower costs, and improve energy density. While Tesla has been producing 4680 cells for some time, the company had previously relied on more conventional approaches for parts of the process, leading to questions about whether a full dry-electrode process could even be achieved.
4680 packs for Model Y
Tesla also revealed in its Q4 and FY 2025 Update Letter that it has begun producing battery packs for certain Model Y vehicles using its in-house 4680 cells. As per Tesla:
“We have begun to produce battery packs for certain Model Ys with our 4680 cells, unlocking an additional vector of supply to help navigate increasingly complex supply chain challenges caused by trade barriers and tariff risks.”
The timing is notable. With Tesla preparing to wind down Model S and Model X production, the Model Y and Model 3 are expected to account for an even larger share of the company’s vehicle output. Ensuring that the Model Y can be equipped with domestically produced 4680 battery packs gives Tesla greater flexibility to maintain production volumes in the United States, even as global battery supply chains face increasing complexity.
Elon Musk
Tesla Giga Texas to feature massive Optimus V4 production line
This suggests that while the first Optimus line will be set up in the Fremont Factory, the real ramp of Optimus’ production will happen in Giga Texas.

Tesla will build Optimus 4 in Giga Texas, and its production line will be massive. This was, at least, as per recent comments by CEO Elon Musk on social media platform X.
Optimus 4 production
In response to a post on X which expressed surprise that Optimus will be produced in California, Musk stated that “Optimus 4 will be built in Texas at much higher volume.” This suggests that while the first Optimus line will be set up in the Fremont Factory, and while the line itself will be capable of producing 1 million humanoid robots per year, the real ramp of Optimus’ production will happen in Giga Texas.
This was not the first time that Elon Musk shared his plans for Optimus’ production at Gigafactory Texas. During the 2025 Annual Shareholder Meeting, he stated that Giga Texas’ Optimus line will produce 10 million units of the humanoid robot per year. He did not, however, state at the time that Giga Texas would produce Optimus V4.
“So we’re going to launch on the fastest production ramp of any product of any large complex manufactured product ever, starting with building a one-million-unit production line in Fremont. And that’s Line one. And then a ten million unit per year production line here,” Musk stated.
How big Optimus could become
During Tesla’s Q4 and FY 2025 earnings call, Musk offered additional context on the potential of Optimus. While he stated that the ramp of Optimus’ production will be deliberate at first, the humanoid robot itself will have the potential to change the world.
“Optimus really will be a general-purpose robot that can learn by observing human behavior. You can demonstrate a task or verbally describe a task or show it a task. Even show it a video, it will be able to do that task. It’s going to be a very capable robot. I think long-term Optimus will have a very significant impact on the US GDP.
“It will actually move the needle on US GDP significantly. In conclusion, there are still many who doubt our ambitions for creating amazing abundance. We are confident it can be done, and we are making the right moves technologically to ensure that it does. Tesla, Inc. has never been a company to shy away from solving the hardest problems,” Musk stated.








