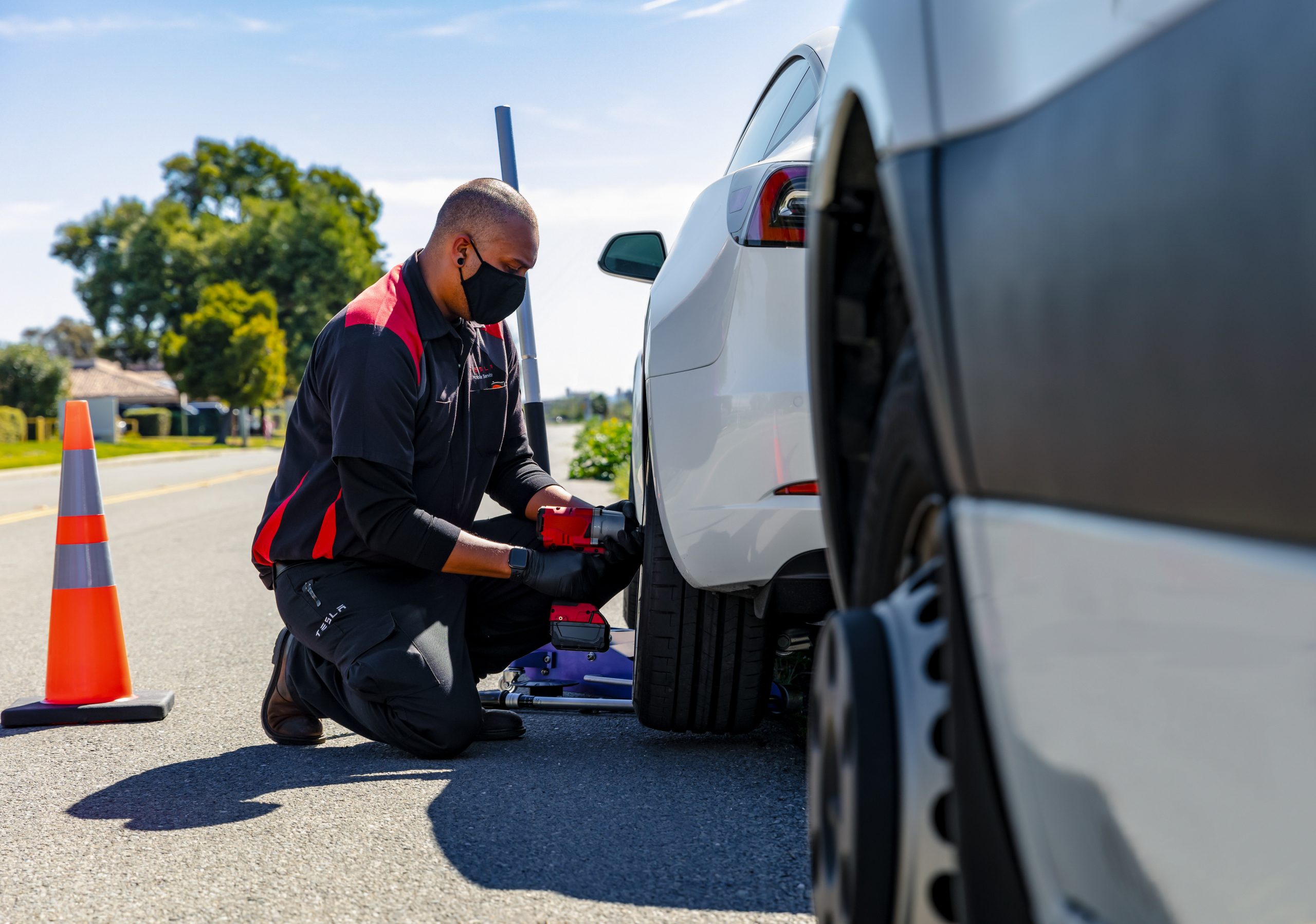
Last week, Elon Musk tweeted in a series of updates that Tesla would be attempting to service two-thirds of customer requests “same day.”
One of the many benefits of owning an electric vehicle is the lack of service required. According to Autoblog, of the top 5 most common car repairs – oxygen sensor replacement, inspection of loose fuel cap causing engine light, catalytic converter replacement, mass airflow sensor replacement, and spark plug replacement – none of them are even possible on an electric vehicle. Nonetheless, due to a range of issues, Tesla has had a consistent problem with servicing its ever-growing group of customers’ needs. Musk is set out to change this, and owners should have many reasons to be optimistic!
Working on Tesla North American service.
Goal is 2/3 of cars receive same-day service, no wait.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) June 4, 2022
Looking at Tesla’s service problem, it is multifaceted and often self-feeding in nature. To start off, quality control at Tesla has been a known problem, with customers experiencing everything from missing badges to paint issues to panel gaps. All of these issues must be serviced, and much of this service will be done at one of the company’s service centers.
Quality control (QC) service requests, when combined with normal service load, mean that Tesla service centers’ availability is often impaired. Tesla Motors Club forum even has a thread dedicated for service center wait times. This means that customers may be forced to wait longer periods before service, and if the service is not done 100% correctly the first time, the service center doesn’t have the capacity to bring them back immediately.
This lack of availability is compounded by Tesla’s lack of service centers as a whole, some states having only single-digit numbers of service centers available. This means that the service centers that do exist are responsible for a larger number of vehicles. And while independent service centers exist commonly throughout the US, many refuse to work on Tesla products or any electric vehicles for that matter, even when they have the capability to do the work. Once again, this forces more service requests to Tesla service centers.

Credit: Tesla
Finally, because new car QC requests are often covered by Tesla at no cost, this incentivizes customers to go to service centers for free work instead of going to independent shops that may be able to help them.
These problems have not been ignored by Elon Musk, and since 2018, Tesla has addressed many of these concerns. Most predominantly, since 2018, the number of service centers and the area that they cover has increased drastically. Looking at a map of 2018 and comparing it to now, areas such as New England, the Pacific Northwest, and the South have all seen massive increases in capacity. Tesla aimed to open one new Service Center per week in 2021, and, in general, the automaker has experimented with many different specialized service programs.
- Map of Tesla service centers in the US as of 2018.
- Map of Tesla service centers in the US in 2022
This is combined with an increase in capacity in Tesla’s mobile repair teams, who can often address service requests before the customer has to come to a service center. And in more recent news, Tesla has even made their repair manual free for customers to access, allowing more repairs to be done outside of service centers.
Another obvious change consumers have seen is an improvement in QC. Even according to JD Power’s rankings of brands by initial quality, from 2020 to 2021, Tesla has reduced the number of “problems per 100 vehicles” from 250 in 2020 to 231 in 2021, a number that is competitive with brands like Audi (240) and VW (213).
Service centers themselves have also been changed over the past 4 years with the inclusion of F1 style pit lanes that allow customers to be more quickly addressed and hence allow the service team to address more requests in a day.
Nonetheless, many have been concerned that these changes have not been enough to fix the Tesla service issue. Leading many to think about what could be done to improve the situation. A couple of options have been put forward by industry professionals and Twitter users alike. One such suggestion has been the expansion of the Tesla START program, a program that teaches individuals how to work on Teslas and then places them with a full-time job at a Service Center location across the country. Currently, the program is offered at eight colleges across the country: Rio Honda Community College in Los Angeles, Central Piedmont Community College in Charlotte, North Carolina, Shoreline Community College in Seattle, Evergreen Valley College in San Jose, California, Suffolk Community College in Selden, New York, Miami Dade College in Florida, Texas State Technical College in Waco, Texas, and Sinclair Community College in Dayton, Ohio.
Overall, the changes made in the past 4 years should give Tesla’s current and future customers much to be optimistic about. QC has improved, the speed of service operation has increased, service manuals are free and open to anyone, and the number of service centers has increased. The only question is, what is Elon Musk planning on implementing next to improve Tesla’s Service department?
What do you think of the article? Do you have any comments, questions, or concerns? Shoot me an email at william@teslarati.com. You can also reach me on Twitter @WilliamWritin. If you have news tips, email us at tips@teslarati.com

Elon Musk
Brazil Supreme Court orders Elon Musk and X investigation closed
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.

Brazil’s Supreme Federal Court has ordered the closure of an investigation involving Elon Musk and social media platform X. The inquiry had been pending for about two years and examined whether the platform was used to coordinate attacks against members of the judiciary.
The decision was issued by Supreme Court Justice Alexandre de Moraes following a recommendation from Brazil’s Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet.
According to a report from Agencia Brasil, the investigation conducted by the Federal Police did not find evidence that X deliberately attempted to attack the judiciary or circumvent court orders.
Prosecutor-General Paulo Gonet concluded that the irregularities identified during the probe did not indicate fraudulent intent.
Justice Moraes accepted the prosecutor’s recommendation and ruled that the investigation should be closed. Under the ruling, the case will remain closed unless new evidence emerges.
The inquiry stemmed from concerns that content on X may have enabled online attacks against Supreme Court justices or violated rulings requiring the suspension of certain accounts under investigation.
Justice Moraes had previously taken several enforcement actions related to the platform during the broader dispute involving social media regulation in Brazil.
These included ordering a nationwide block of the platform, freezing Starlink accounts, and imposing fines on X totaling about $5.2 million. Authorities also froze financial assets linked to X and SpaceX through Starlink to collect unpaid penalties and seized roughly $3.3 million from the companies’ accounts.
Moraes also imposed daily fines of up to R$5 million, about $920,000, for alleged evasion of the X ban and established penalties of R$50,000 per day for VPN users who attempted to bypass the restriction.
Brazil remains an important market for X, with roughly 17 million users, making it one of the platform’s larger user bases globally.
The country is also a major market for Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite internet service, which has surpassed one million subscribers in Brazil.
Elon Musk
FCC chair criticizes Amazon over opposition to SpaceX satellite plan
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.

U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairman Brendan Carr criticized Amazon after the company opposed SpaceX’s proposal to launch a large satellite constellation that could function as an orbital data center network.
Carr made the remarks in a post on social media platform X.
Amazon recently urged the FCC to reject SpaceX’s application to deploy a constellation of up to 1 million low Earth orbit satellites that could serve as artificial intelligence data centers in space.
The company described the proposal as a “lofty ambition rather than a real plan,” arguing that SpaceX had not provided sufficient details about how the system would operate.
Carr responded by pointing to Amazon’s own satellite deployment progress.
“Amazon should focus on the fact that it will fall roughly 1,000 satellites short of meeting its upcoming deployment milestone, rather than spending their time and resources filing petitions against companies that are putting thousands of satellites in orbit,” Carr wrote on X.
Amazon has declined to comment on the statement.
Amazon has been working to deploy its Project Kuiper satellite network, which is intended to compete with SpaceX’s Starlink service. The company has invested more than $10 billion in the program and has launched more than 200 satellites since April of last year.
Amazon has also asked the FCC for a 24-month extension, until July 2028, to meet a requirement to deploy roughly 1,600 satellites by July 2026, as noted in a CNBC report.
SpaceX’s Starlink network currently has nearly 10,000 satellites in orbit and serves roughly 10 million customers. The FCC has also authorized SpaceX to deploy 7,500 additional satellites as the company continues expanding its global satellite internet network.
Energy
Tesla Energy gains UK license to sell electricity to homes and businesses
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.

Tesla Energy has received a license to supply electricity in the United Kingdom, opening the door for the company to serve homes and businesses in the country.
The license was granted to Tesla Energy Ventures Ltd. by UK energy regulator Ofgem after a seven-month review process.
According to Ofgem, the license took effect at 6 p.m. local time on Wednesday and applies to Great Britain.
The approval allows Tesla’s energy business to sell electricity directly to customers in the region, as noted in a Bloomberg News report.
Tesla has already expanded similar services in the United States. In Texas, the company offers electricity plans that allow Tesla owners to charge their vehicles at a lower cost while also feeding excess electricity back into the grid.
Tesla already has a sizable presence in the UK market. According to price comparison website U-switch, there are more than 250,000 Tesla electric vehicles in the country and thousands of Tesla home energy storage systems.
Ofgem also noted that Tesla Motors Ltd., a separate entity incorporated in England and Wales, received an electricity generation license in June 2020.
The new UK license arrives as Tesla continues expanding its global energy business.
Last year, Tesla Energy retained the top position in the global battery energy storage system (BESS) integrator market for the second consecutive year. According to Wood Mackenzie’s latest rankings, Tesla held about 15% of global market share in 2024.
The company also maintained a dominant position in North America, where it captured roughly 39% market share in the region.
At the same time, competition in the energy storage sector is increasing. Chinese companies such as Sungrow have been expanding their presence globally, particularly in Europe.