

News
Tesla’s software fixes, the NHTSA’s status quo, and an impending need for updated recall terminologies
It is no secret that Tesla is a popular topic, so much so that the coverage around the company is immense. Couple this with CEO Elon Musk’s rockstar persona and you get a company whose vehicles are looked at under a microscope constantly. It might feel unfair for some, but it’s just the way it is. Tesla — by simply being Tesla — is newsworthy.
Tesla’s newsworthiness is a double-edged sword. A look at the coverage for the company’s vehicle recalls from the NHTSA would prove this point. So notable is Tesla’s news coverage that a mainstream newsreader would likely get the impression that Teslas get recalls frequently. The opposite is true. As evidenced by Reuters in the graphic below, data from January 1, 2020, through February 17, 2022, shows that Tesla actually recalls its vehicles less frequently than some of the market’s leading automakers. Tesla is also the only carmaker performing a large share of its vehicle recalls through over-the-air software updates.
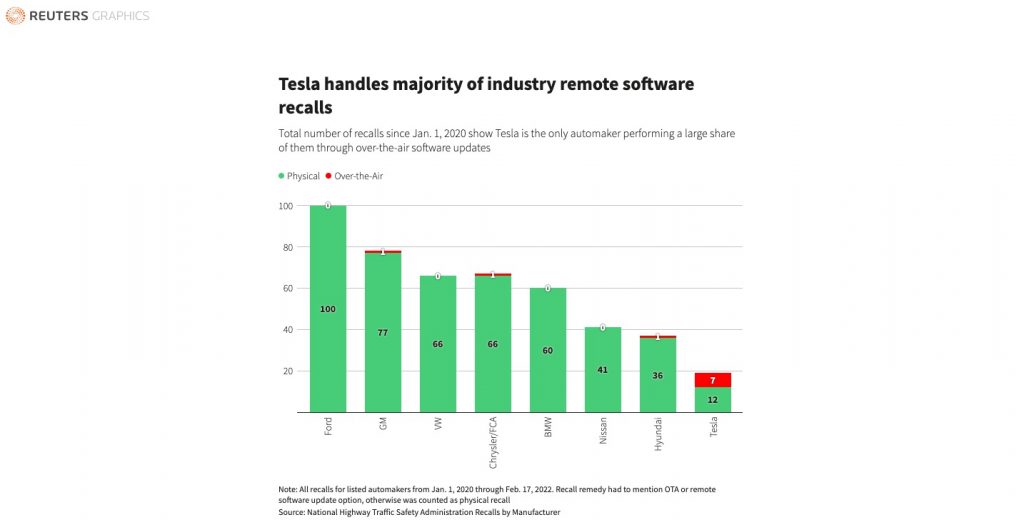
Tesla currently handles the majority of the industry’s remote software recalls, but it would soon not be the only one. New electric vehicle makers have used the idea of software updates as a means to promote their EVs’ capabilities. Rivian has performed OTA updates to its R1 vehicles, and those cars are only starting customer deliveries. Lucid is the same with its Air sedan, with the company rolling out features like Automatic Emergency Braking, Cross-Traffic Protection, Lane Departure Protection, Traffic Drive-Off Alert, and other features earlier this month through a software update. Ford has been rolling out updates called “Power-Ups” to the Mustang Mach-E as well.
Considering that software-based fixes are only bound to get more widespread over the coming years, one must then ask the question: Should software-based over-the-air fixes be dubbed and classified with the same terminologies as physical recalls, which typically involve the replacement of vehicle hardware?
A Vastly Different “Recall” Experience
Any car owner has likely experienced a recall for their vehicle at some point in their driving life. And more likely than not, one’s experience is probably not that pleasant. I certainly count myself among drivers who look at vehicle recalls with trepidation. My current vehicle, a Japanese-made van, was part of a minor fuel pump recall a couple of years ago, and even addressing that took a whole day out of my weekend. The dealer was overwhelmed with the number of cars it was fixing that day, and tempers among owners were flaring by the hour — all for a simple fuel pump replacement. I’ve been told that my experiences with vehicle recalls are not that unique.
In comparison, a software-based fix, such as the disabling of FSD Beta’s “rolling stops” feature, only required affected vehicles to be connected to the internet. There was no dealer visit, no forms to fill out, and no staff to argue with. The car was connected to the internet, a software fix was implemented, and the issue was resolved. One can argue that Tesla’s software fix to disable FSD Beta’s “rolling stops” feature was safety-related, and that’s true. But one could also argue that at least from a driver’s point of view, the experience related to software and hardware-based recalls is vastly different.
The Status Quo
Despite the different experiences involved when software and hardware-based vehicle recalls are addressed, it appears that the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) will, at least for now, keep the status quo. Teslarati reached out to the NHTSA to inquire if it was considering the adoption of updated terminologies for cars whose fixes are completed through OTA software updates, but the agency suggested that this would likely not be the case, at least for now. According to the NHTSA, vehicle manufacturers must initiate a recall for any repair that remedies a safety risk, regardless of whether the issue is fixed by software update or by hardware replacement.
“The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is committed to ensuring the highest safety standards on the nation’s roadways. NHTSA is empowered with robust tools and authorities to protect the public, to investigate potential safety issues, and to compel recalls when it finds evidence of noncompliance or an unreasonable risk to safety. Manufacturers are required to initiate a recall for any repair, including a software update, that remedies an unreasonable risk to safety. NHTSA recalls can include any required repair, which includes a software update, to remedy a potential safety risk. Manufacturers are also required to submit any communications to owners, dealers, and others about any software updates that address a defect, whether it is safety-related or not,” the NHTSA stated.
Product recall specialist and associate professor at the Indiana University Kelley School of Business Professor George Ball told Teslarati that while the NHTSA’s use of similar terminologies for software and hardware-based recalls is “definitely an example of regulators and industry moving at a different pace on technology,” the agency’s hesitation in adopting new terminologies for OTA fixes is understandable. Professor Ball further explained that using terms such as “soft recall” to refer to software-based vehicle fixes might imply a reduced level of risk, and this is something that the NHTSA would likely be unwilling to do.
“I believe NHTSA would resist ‘soft recall’ terminology because it implies a reduced level of customer hazard and allows the firm to be under less scrutiny by the press and public for quality corrections. While some updates are minor, some of the Tesla software upgrades are actually quite serious, and if not done, can allow a harmful defect to persist,” the recall specialist said.
But while the NHTSA’s stance on recall terminologies is completely understandable, one cannot deny the fact that the issues covered by vehicle recalls have a very wide range of risks. Take Tesla’s recall for 817,143 vehicles, which was announced earlier this month, for example. The recall was initiated since a software error may prevent a warning chime from activating even if drivers do not have their seat belts on. From a layman’s perspective, this recall seems grave as it affects over 800,000 Teslas on the road today. However, the issue was simply addressed through firmware release 2021.43.101.1 and later, which included a remedy for the seat belt chime error.
Compare this with General Motors’ recall last year of 400,000 pickup trucks in the US. Granted, it only affected about half as many vehicles as Tesla’s seat belt chime recall, but its hardware-based nature suggested that the risk presented by the issue was great. The recall covered certain 2015 and 2016 Chevrolet and GMC Sierra 1500, 2500, and 3500 trucks, and it involved a faulty airbag inflator that may rupture without warning. To fix the issue, owners of the affected trucks were required to head to a dealer so that they could get their airbag modules replaced. Since parts were in short supply last year, however, owners were notified with a letter to inform them when their trucks’ replacement parts were available.
What Can Be Done
While the NHTSA will likely continue to maintain the status quo with its recall terminologies for the foreseeable future, Professor Ball told Teslarati that the agency can actually implement some adjustments now that can make distinguishing safety fixes and issues clearer. This would likely be extremely important in the near future as more connected cars are rolled out and software updates become the norm.
“If I were to provide advice to the NHTSA, I would recommend that they get out ahead of this issue before every car maker starts updating cars like Tesla. One way to do it is to require the automaker to send all auto updates to NHTSA when pushed out, and to classify updates as ‘minor’ or ‘major.’ Any major update that impacts customer safety would be classified as a recall. Automakers won’t like this, but it will help keep the safety fixes transparent for all, especially consumers. By sending all updates to NHSTA, the agency could assign qualified people to audit the classifications assigned by the manufacturer, to ensure they are making good decisions there.
“I think any language that de-emphasizes the importance of a safety recall is not likely to be supported by NHTSA, and it doesn’t likely help customer safety. A clear distinction needs to be made between minor updates and major updates that influence safety. Those major updates should be classified as a recall, and NHTSA needs to get their arms around these updates and keep on top of them soon, or they will fall way behind the industry,” the recall specialist said.
Recalls can affect the perception of a company to the public. Software fixes should be one of the factors that are considered an edge for automakers like Tesla, not the other way around. Gary Black, Managing Partner of The Future Fund LLC, explained this from the point of view of a Tesla investor. “Since every NHTSA recall so far has been quickly solvable via Tesla OTA updates, ‘recalls’ are noise to most investors. Tesla’s huge software edge highlights one of the key advantages of owning Tesla over every other EV manufacturer,” the Wall Street veteran told Teslarati.
OTA updates, including those related to vehicle safety, are coming. With automakers like Ford joining the group of carmakers embracing OTA updates, software-based fixes are inevitable. Ultimately, I am inclined to agree with the recall specialist. By refusing to adapt to the advent of software-based vehicle fixes, the NHTSA may risk being left behind by the automotive industry. And that’s a scenario that I believe no automaker — or government agency for that matter — would prefer.
Don’t hesitate to contact us with news tips. Just send a message to simon@teslarati.com to give us a heads up.
News
Tesla Robotaxi has already surpassed Waymo in this key metric
Tesla Robotaxi has already overtaken Waymo in Austin in one key metric, but there’s still more work to do.

Tesla Robotaxi has already surpassed Waymo in one extremely important key metric: size of service area.
Tesla just expanded its service area in Austin on Monday morning, pushing the boundaries of its Robotaxi fleet in an interesting fashion with new capabilities to the north. Yes, we know what it looks like:
🚨 Tesla’s new Robotaxi geofence is…
Finish the sentence 🥸 pic.twitter.com/3bjhMqsRm5
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) July 14, 2025
The expansion doubled Tesla Robotaxi’s potential travel locations, which now include the University of Texas at Austin, a school with over 53,000 students.
The doubling of the service area by Tesla has already made its travel area larger than Waymo’s, which launched driverless rides in October 2024. It became available to the public in March 2025.
According to Grok, the AI agent on X, Tesla Robotaxi’s current service area spans 42 square miles, which is five square miles larger than Waymo’s service area of 37 square miles.
Tesla Robotaxi (red) vs. Waymo geofence in Austin.
Much can be said about the shape… but the Robotaxi area is now ~3.9 mi² (10 km²) larger than Waymo’s!! pic.twitter.com/dVfh2ODxJC
— Robin (@xdNiBoR) July 14, 2025
The service area is one of the most important metrics in determining how much progress a self-driving ride-hailing service is making. Safety is the priority of any company operating a ride-hailing network, especially ones that are making it a point to use autonomy to deploy it.
However, these companies are essentially racing for a larger piece of the city or cities they are in. Waymo has expanded to several different regions around the United States, including Arizona and Los Angeles.
Tesla is attempting to do the same in the coming months as it has already filed paperwork in both California and Arizona to deploy its Robotaxi fleet in states across the U.S.
As the platform continues to show more prowess and accuracy in its operation, Tesla will begin to expand to new areas, eventually aiming for a global rollout of its self-driving service.
News
Tesla Megapacks arrive for massive battery replacing coal plant
Tesla Megapacks have started arriving on-site to the Stanwell Battery Project, just as Queensland prepares to wind down the Stanwell coal plant.

The first of over 300 Tesla Megapacks have arrived to the site of a massive battery energy storage system (BESS) being built in Australia, dubbed the Stanwell Battery Project after a coal plant it’s set to replace.
In a press release last week, the Stanwell Battery Project announced that the first Tesla Megapack 2XL units had arrived to the site, which is located outside of Rockhampton in Queensland, Australia. The project will eventually feature 324 Megapack units, set to arrive in the coming months, in order to support the 300MW/1,200MWh battery project.
“The Stanwell Battery is part of the diversification of our portfolio, to include cleaner and more flexible energy solutions,” said Angie Zahra, Stanwell Central Generation General Manager. “It is just one part of the 800 MW of battery energy storage capacity we have in our pipeline.
“Capable of discharging 300 MW of energy for up to four hours (1,200 MWh), our mega battery will be one of the largest in Queensland.”
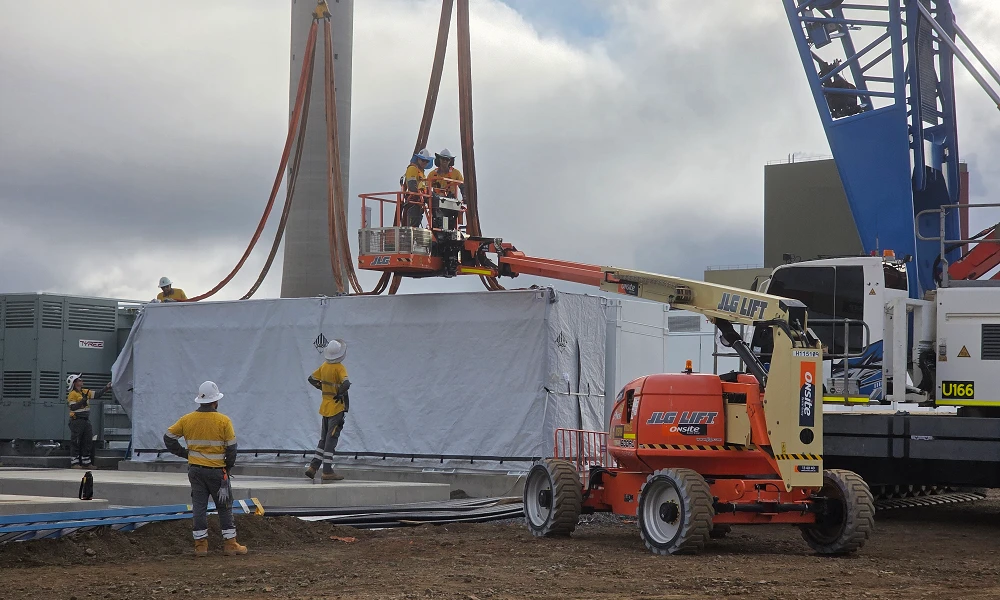

Credit: Stanwell
Did you know Tesla’s Lathrop facility churns out a Megapack every 68 minutes? That’s enough energy to power 3,600 homes for an hour per unit! ⚡️ pic.twitter.com/bG6fpHkB9O
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) June 11, 2025
READ MORE ON TESLA MEGAPACKS: Tesla Lathrop Megafactory celebrates massive Megapack battery milestone
The state is working with government-owned company Yurika to facilitate construction, and the process is expected to create roughly 80 jobs. The project is expected to come fully online in May 2027, with initial commissioning of the Megapacks aiming for November 2025.
The Stanwell Battery is set to replace the nearby Stanwell coal generation plant, which the government is planning to wind down starting in 2026 as part of efforts to reach an 80 percent renewable energy generation ratio by 2035. Meanwhile, the government is also set to begin winding down the Tarong and Callide coal plants, while several other Megapack projects are being built or coming online. o ya
Tesla currently has two Megapack production facilities, located in Lathrop, California, in the U.S. and another that came online earlier this year in Shanghai, China. The Shanghai Megafactory shipped its first units to Australia in March, while both factories are expected to be capable of producing 10,000 Megapack units per year upon reaching volume production.
News
The Tesla Diner is basically finished—here’s what it looks like
The company first broke ground on the Diner, Drive-in, and Supercharger location in September 2023. Now, it has served one of its first internal customers.
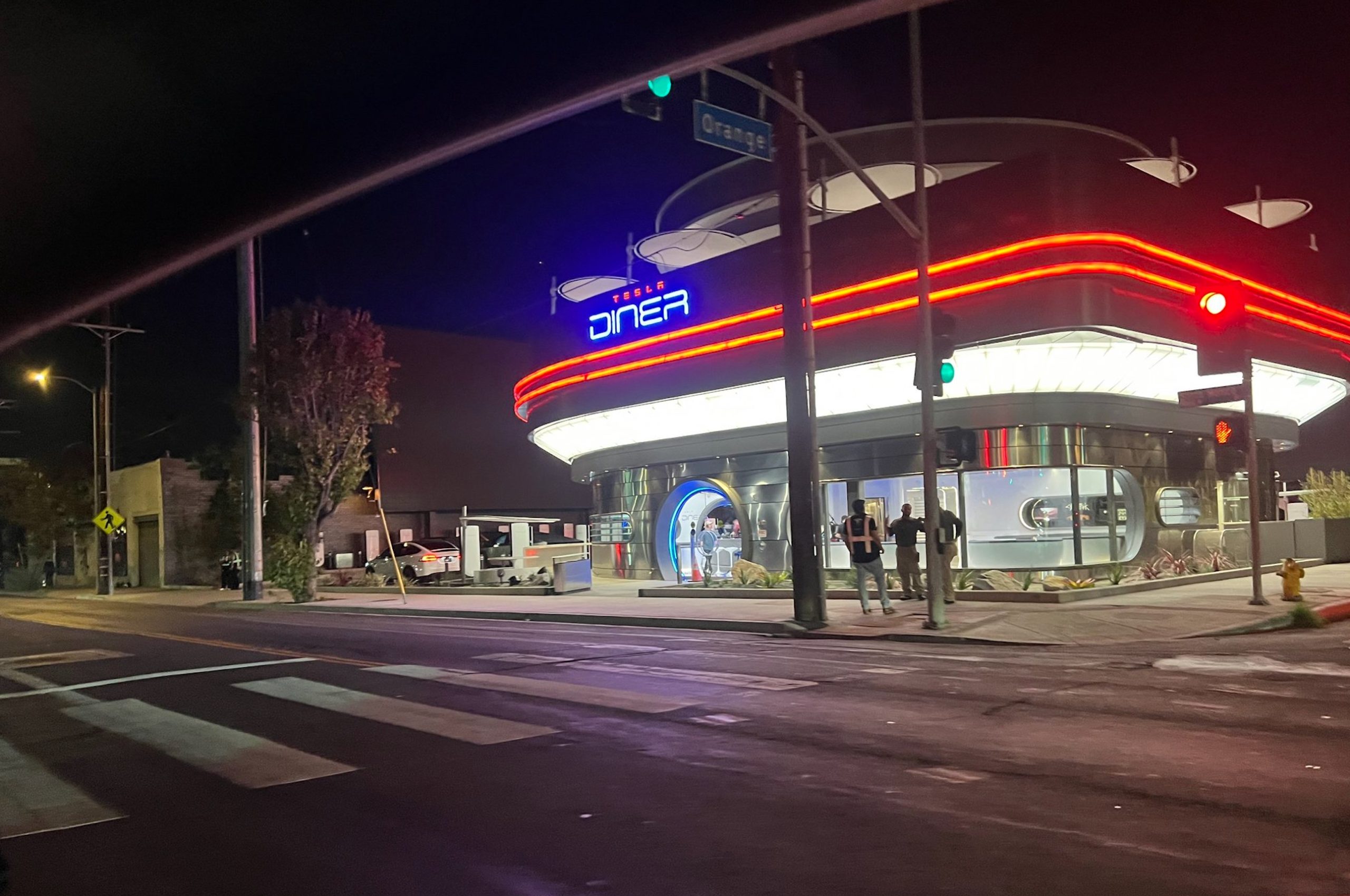

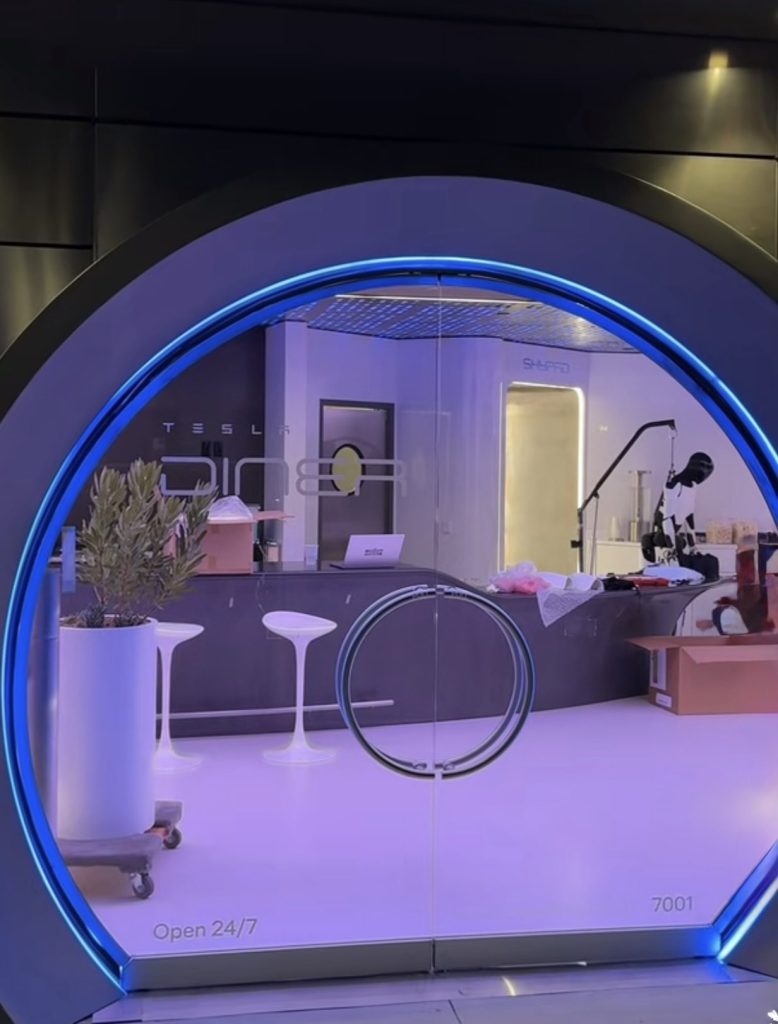
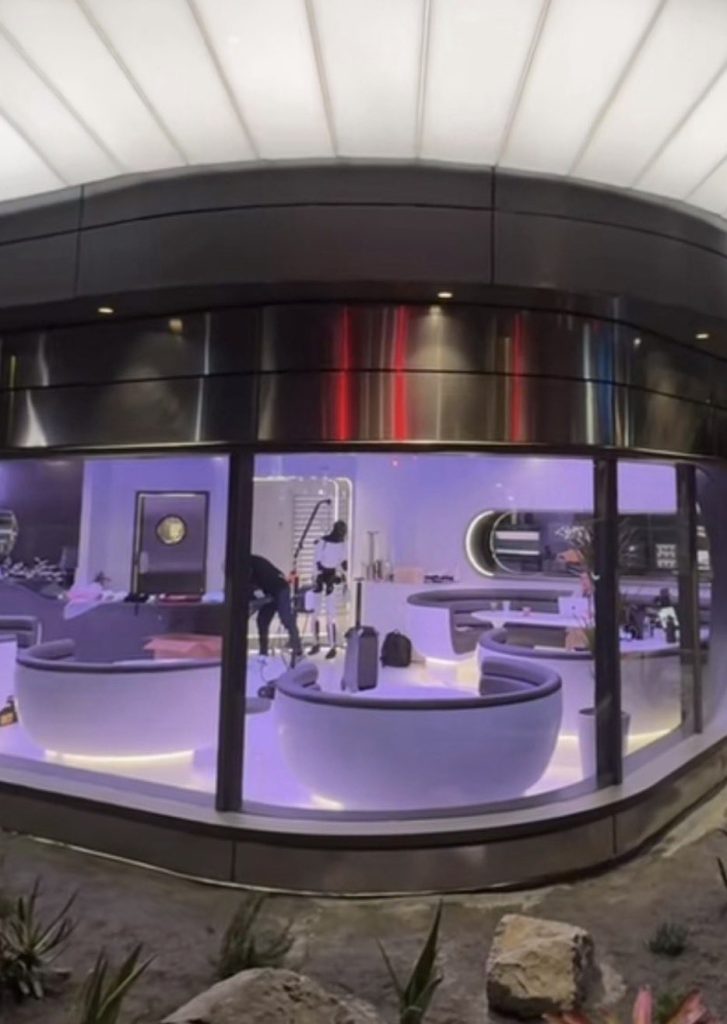
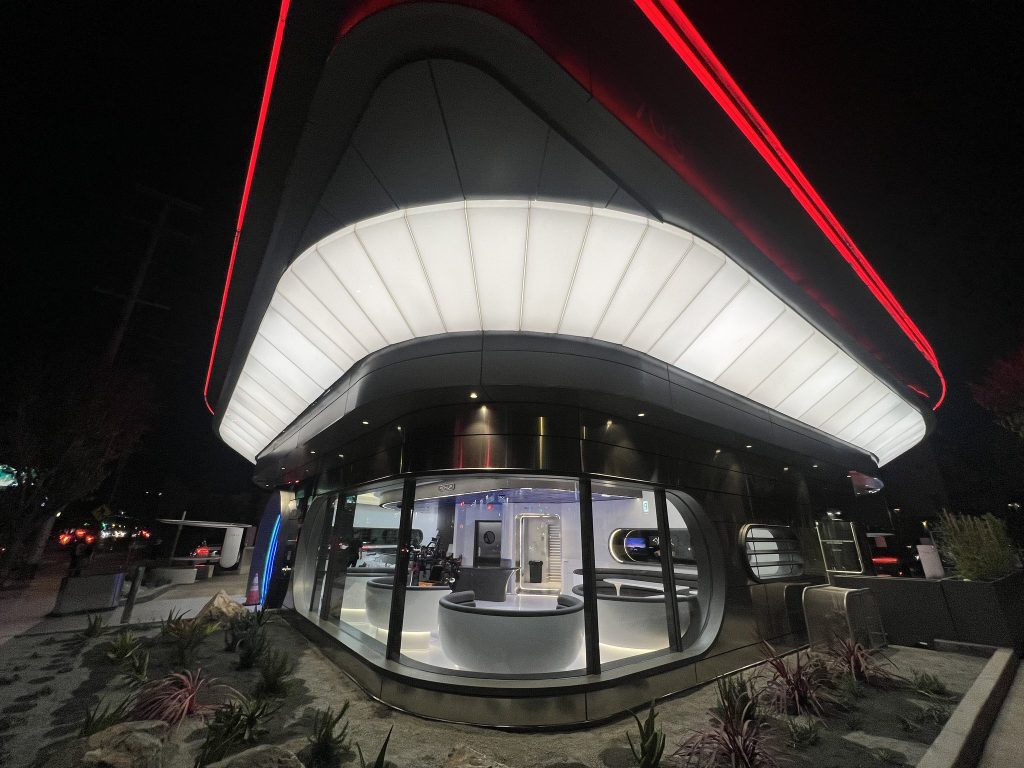
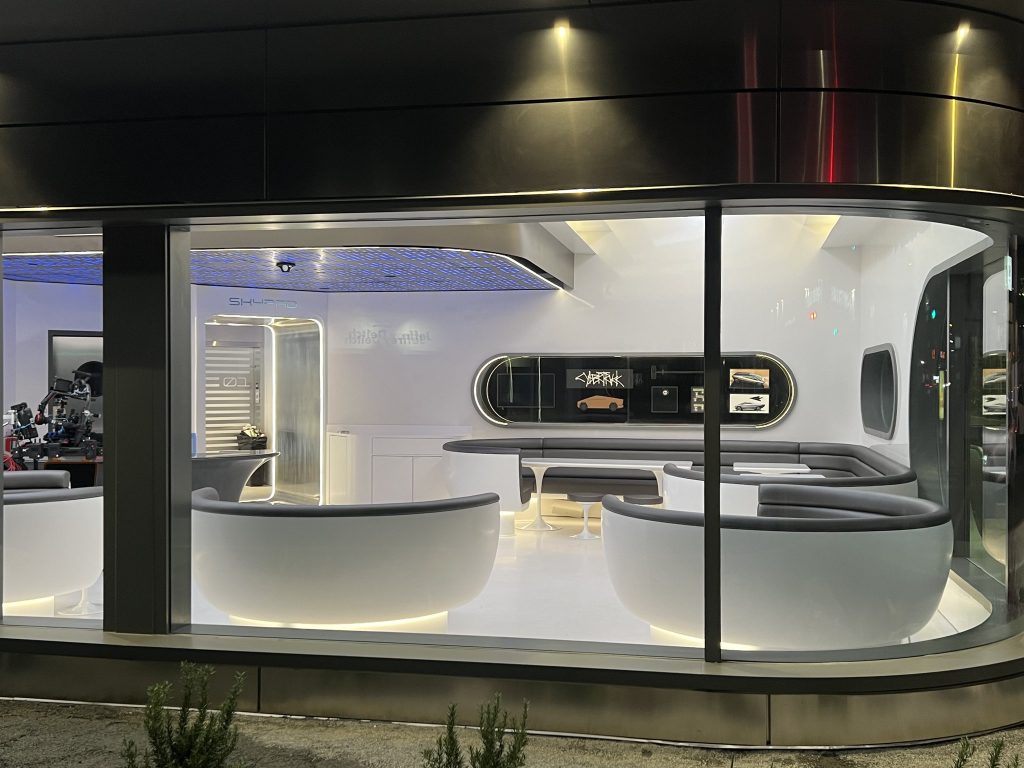
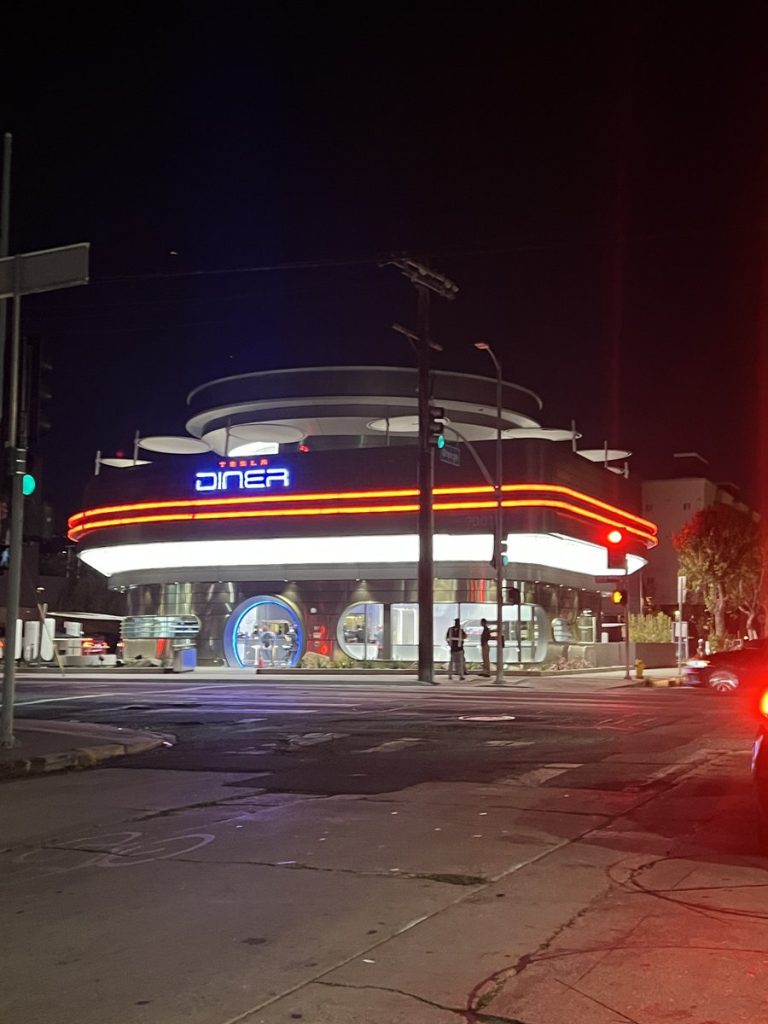
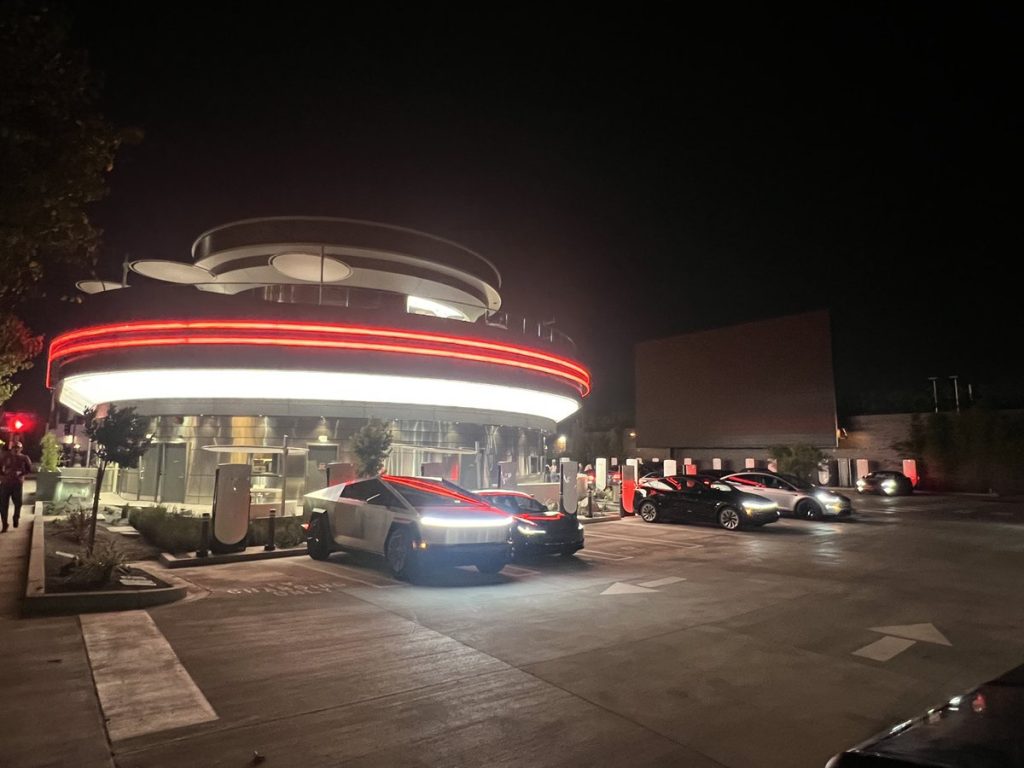
Tesla has finally completed the construction of its highly anticipated Diner, Drive-in, and Supercharger in Los Angeles, and recent photos of the interior’s “retro-futuristic” style are making their way around the internet.
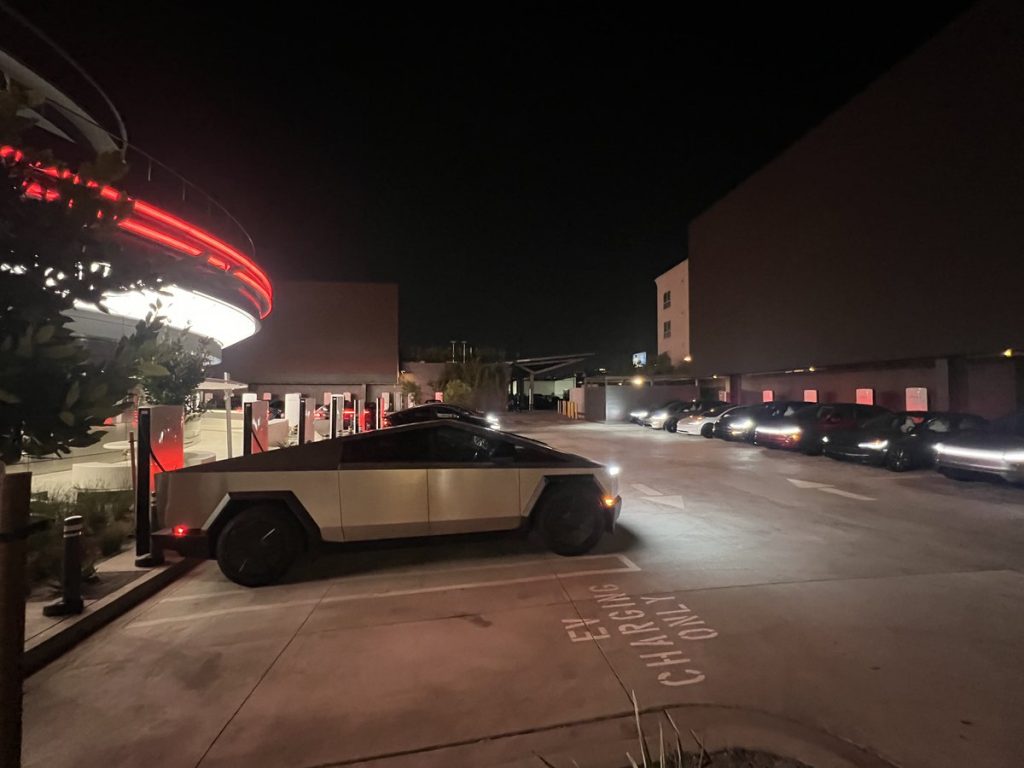
X user Brad Goldberg shared photos from the Tesla Diner site last Tuesday, depicting some of the Supercharger stalls, indoor and outdoor seating areas, multiple neon lights, and even an Optimus robot. Goldberg also noted that there had been a “flurry of activity on site” while he was snapping the photos last week, suggesting that the restaurant location could be getting close to opening.
The Tesla Diner also served one of its first internal customers in the past few days, as Elon Musk posted on X on early Monday morning that he had just finished up eating a meal at the site:
I just had dinner at the retro-futuristic Tesla diner and Supercharger.
Team did great work making it one of the coolest spots in LA!
The photos also show that the site is pretty much done, with some of them even showing vehicles charging at the charging stalls.
You can see some of the latest photos of the Tesla Diner below.
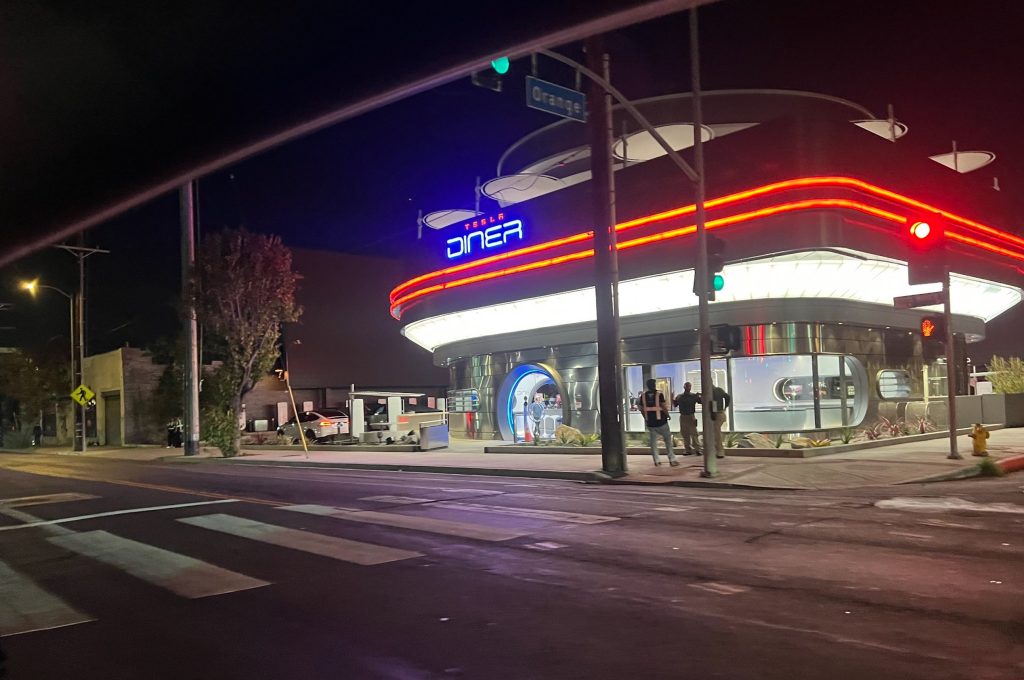

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X
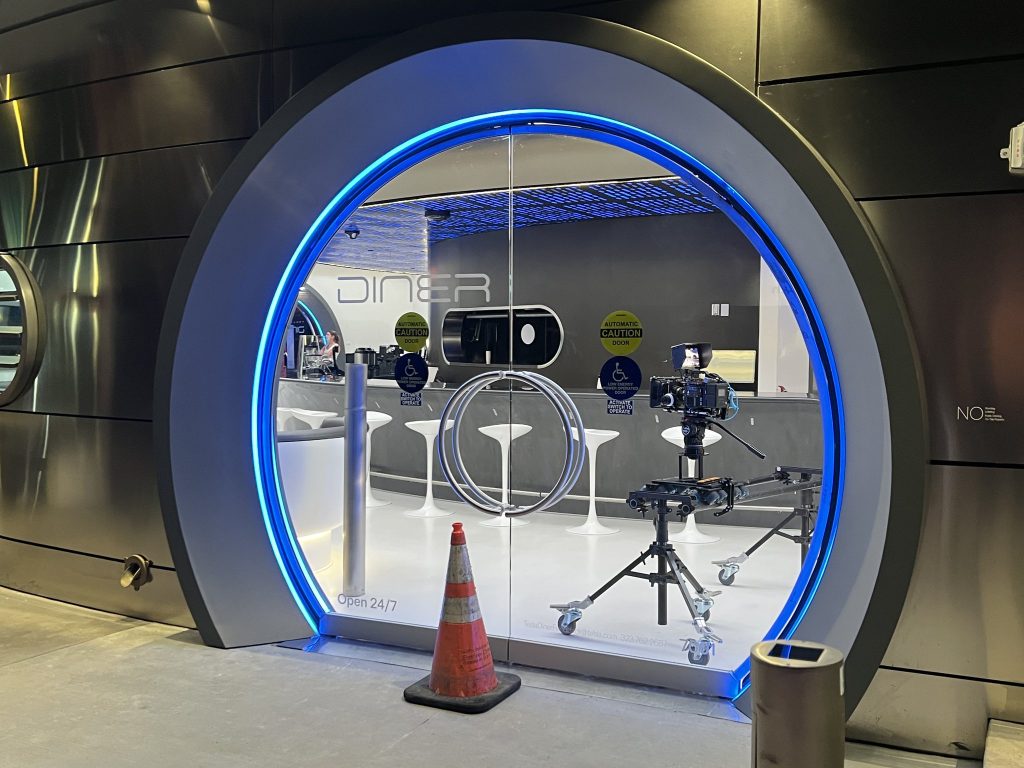

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X
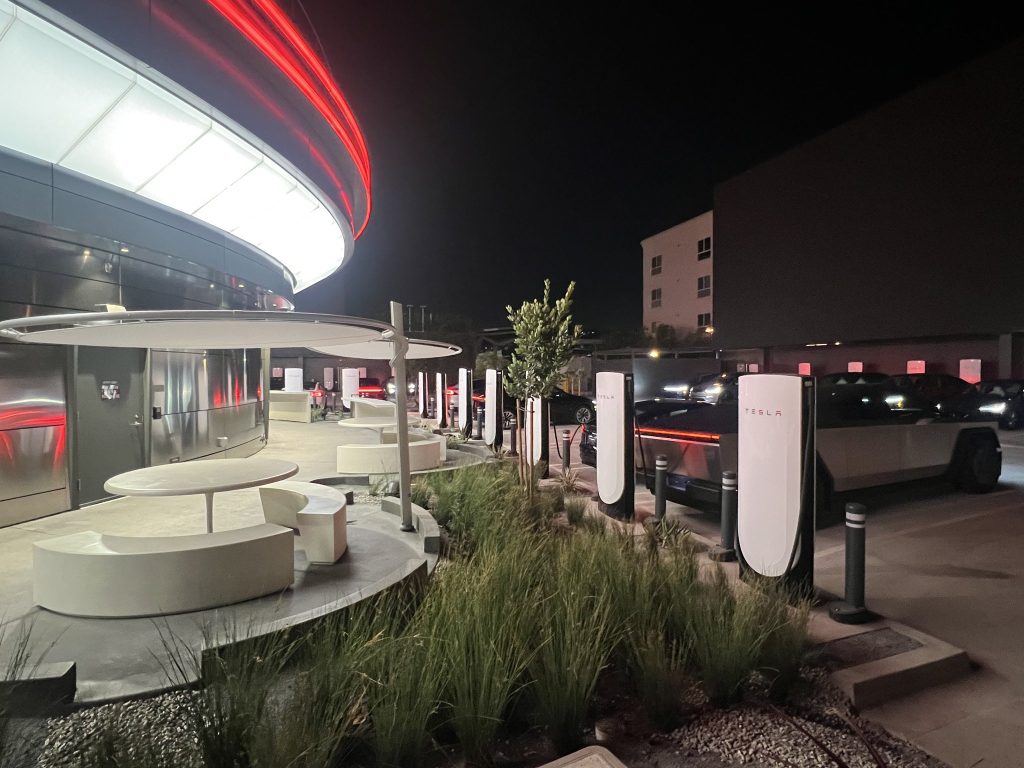

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X
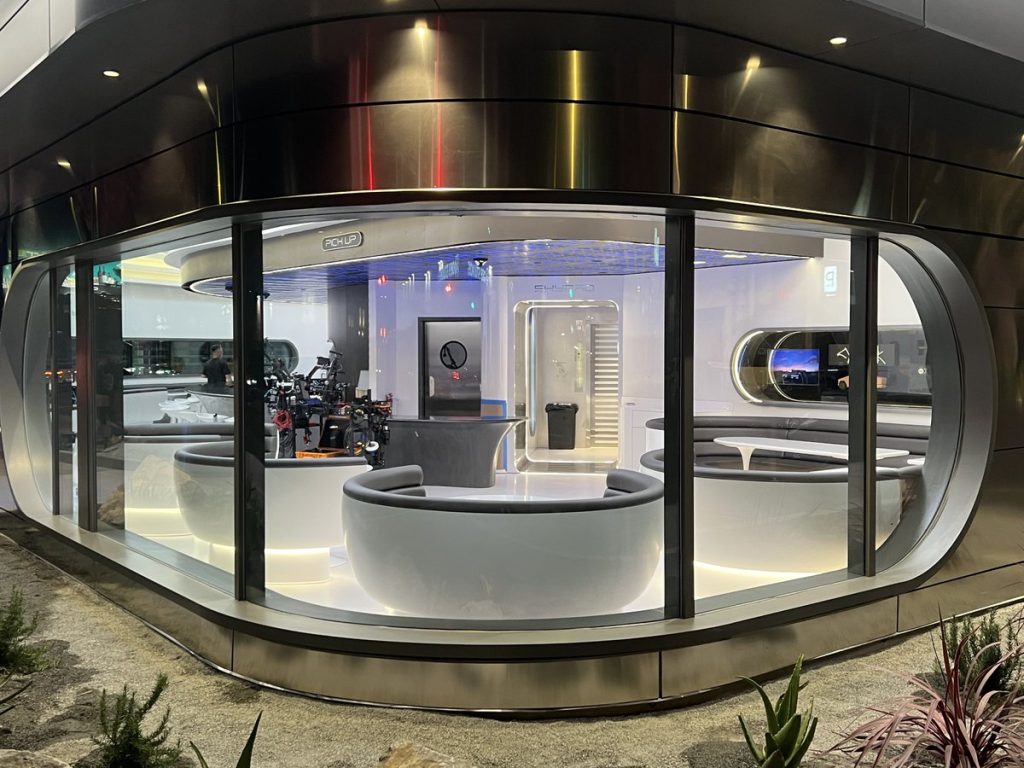

Credit: BradGoldbergMD | X

Credit: TeslaKing420 | X

Credit: TeslaKing420 | X

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)

Credit: Brad Goldberg (via Sawyer Merritt on X)
READ MORE ON TESLA’S LA DINER: Tesla readies Drive-In Diner Supercharger for launch with app inclusion
When will the Tesla Diner open to external customers?
While it’s still not open to external customers yet, the news again suggests that the company could be close to an official opening date. Tesla first broke ground on the Diner in September 2023, after receiving a wave of building permit approvals throughout that year. Teslarati also covered much of the construction progress throughout last year, including when crews installed the first and second drive-in screens.
Located at 7001 West Santa Monica Boulevard, the idea was first discussed in 2018 by Musk and a few others on Twitter, featuring 1950s rock and roll, waiters on roller skates, and drive-in movie theater screens playing clips from some of history’s best movies. Notably, the photos of the front doors also show that the site will be open 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, whenever it does end up opening.
Tesla’s progress on Supercharger with diner, drive-in seen in aerial footage
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoTesla debuts hands-free Grok AI with update 2025.26: What you need to know
-

 Elon Musk4 days ago
Elon Musk4 days agoxAI launches Grok 4 with new $300/month SuperGrok Heavy subscription
-

 Elon Musk7 days ago
Elon Musk7 days agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI’s Memphis data center receives air permit despite community criticism
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoTesla begins Robotaxi certification push in Arizona: report
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoTesla scrambles after Musk sidekick exit, CEO takes over sales














