

News
SpaceX’s Starship explosion explained by Elon Musk
Shortly after a briefing following SpaceX’s flawless astronaut launch debut, CEO Elon Musk casually revealed the best explanation yet for why a Starship prototype violently exploded during testing on May 29th.
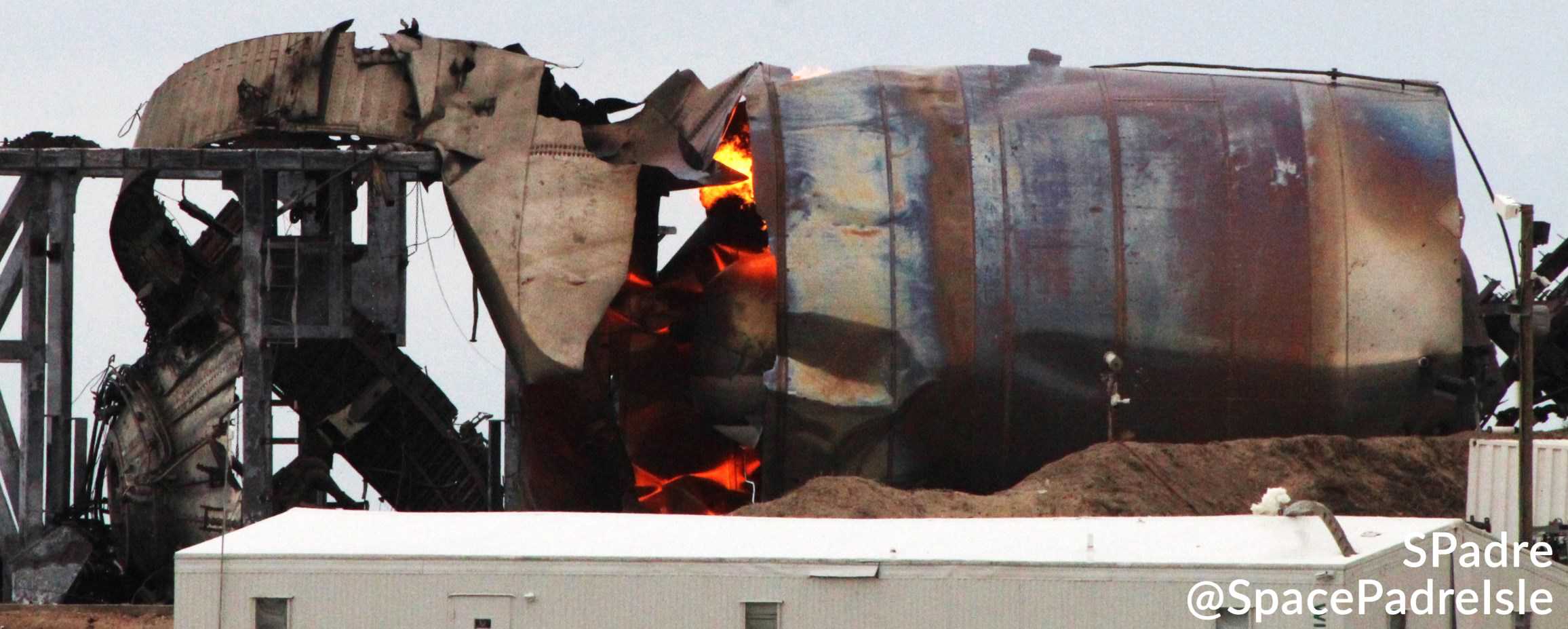
On that fated Saturday, SpaceX successfully completed the fifth static fire of a Raptor engine installed on a full-scale Starship prototype, preceded by about an hour and a half of vehicle checks and propellant loading. Unfortunately, around a minute after Raptor shut down, what was quickly identified as liquid methane began spurting out of a specific section at the base of Starship, rapidly creating a massive cloud as the cryogenic propellant boiled and turned into gas. The specific source is unclear but moments later, something under Starship SN4 provided the shock or spark needed to ignite the expanding fire hazard, producing a spectacularly large and violent explosion.
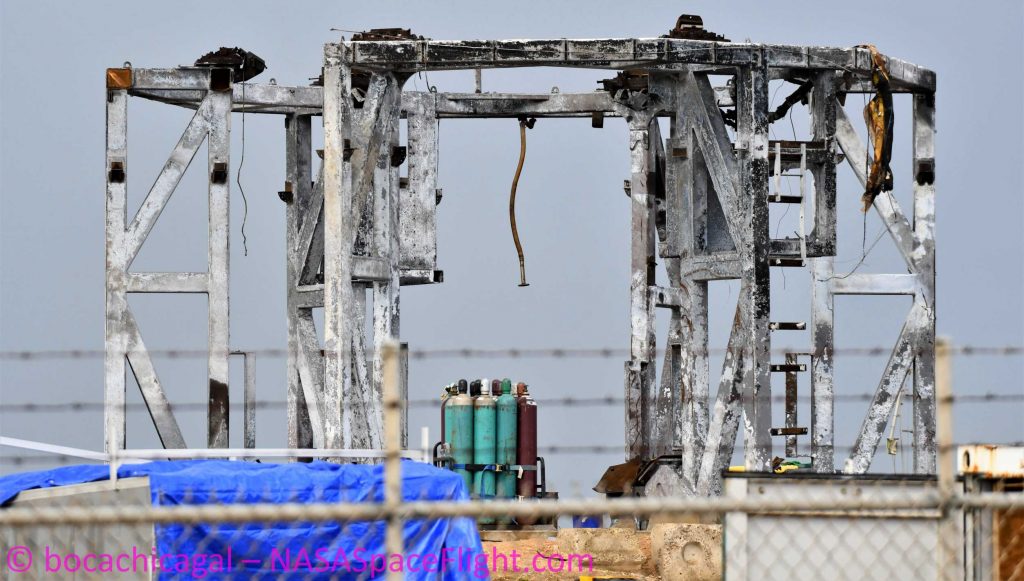
Unsurprisingly, the accidental fuel-air explosion that was created obliterated Starship SN4 in the blink of an eye, shredding its lower (liquid oxygen) tank into steel confetti and immediately breaching the upper (liquid methane) tank, which fell to the ground and subsequently exploded again. The launch mount Starship was staged on was also damaged beyond repair and has been fully dismantled and scrapped in the two days since the anomaly. Thankfully, however, SpaceX already has replacement mounts and ships well on their way to carrying Starship SN4’s torch forward and Elon Musk already seems to understand what caused the prototype’s demise.
Shortly after a post-launch briefing celebrating and discussing SpaceX’s inaugural astronaut launch on May 30th, Reuters reporter Joey Roulette was able to ask Musk about Starship SN4’s spectacular demise the day prior. The SpaceX CEO was quoted saying that “what we thought was going to be a minor test of a quick disconnect ended up being a big problem”, confirming suspicions based on careful analysis of public views of the explosion that it was caused by issues with Starship’s ground support equipment (GSE).
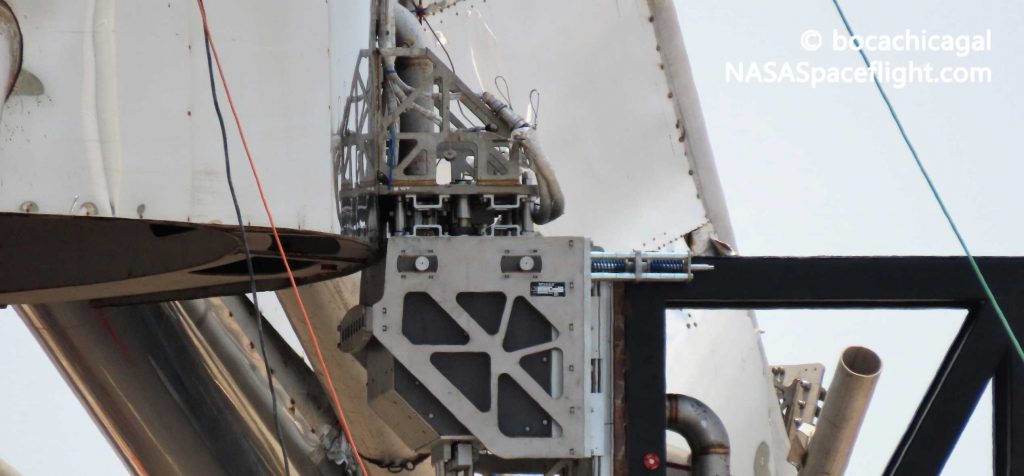

In Musk’s statement, “quick disconnect” (QD) refers to an umbilical port that connects a launch vehicle to GSE, enabling the loading and offloading of propellant and fluids, clamping down the rocket, and providing a wired telemetry and communications link for ground controllers. QDs must perform all those tasks while also being able to rapidly release and disconnect, allowing the rocket to lift off while still protecting its sensitive ports for ease of reuse.
In theory, Starship’s quick-disconnect umbilical panel is even more complex, as it will have to simultaneously enable the ship to be fueled and controlled while sitting on top of a Super Heavy booster and permit in-orbit docking and refueling. Given that Starships are currently being tested independently on spartan launch mounts, it’s unclear if the current generation of prototypes has been outfitted with advanced QD panels. More likely, Musk was referring to a test of a less advanced QD panel similar to the rough version used on Starhopper last year, and SpaceX simply wanted to test its ability to disconnect and reconnect to Starship on command.
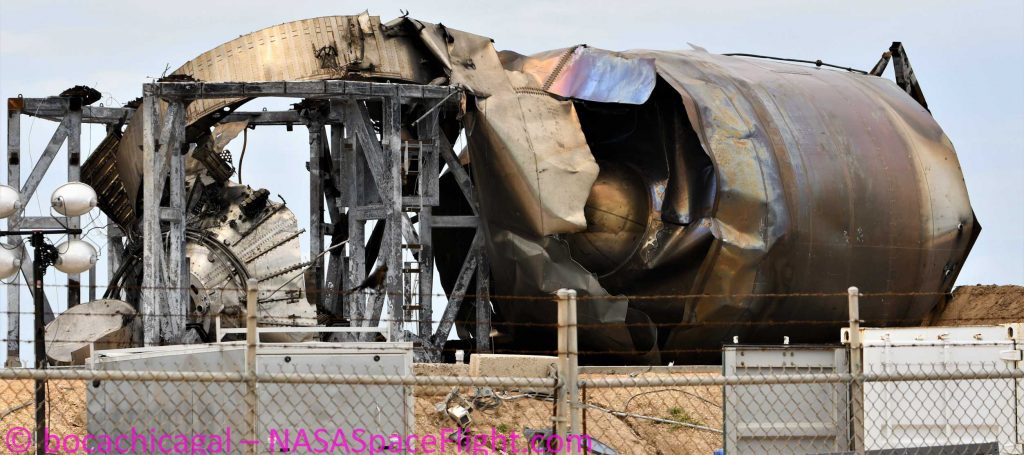


If that’s the case, the likeliest explanation for SN4’s explosion is that that quick disconnect was unable to fully reconnect after the test, resulting in a leak from the liquid methane port when SpaceX began to detank the rocket. Instead of the highly-pressurized fluid flowing smoothly back to ground storage tanks, the liquid methane sprayed wildly, akin to the effect one might observe when attempting to block off an active water source with an open palm.


Compared to the many possible ways a fueled Starship could fail, a propellant leak started by a faulty umbilical panel is about as convenient as they come. Starship SN4 may have been violently destroyed as a result, turning a relatively small error into exceptionally painful lesson but SpaceX has already had some success building full-scale prototypes at an almost unbelievably low cost – likely less than $10M apiece. Starship SN5 appears to be just shy of ready to take SN4’s place on the launch mount, although SpaceX will have to build an entirely new launch mount before it can resume testing.
At the same time, Starship SN5’s successor – SN6 – is just one stacking event away from reaching a level of completion similar to SN4 and SN5. All told, Starship SN4’s demise is just another part of the process of developing a new kind of rocket by building and testing hardware – failure can be a valuable tool when managed properly. Based on past observations, SpaceX could be ready to continue testing (and hopefully flying) Starship prototypes before the end of the month.
Check out Teslarati’s Marketplace! We offer Tesla accessories, including for the Tesla Cybertruck and Tesla Model 3.
News
These Tesla, X, and xAI engineers were just poached by OpenAI
The news is the latest in an ongoing feud between Elon Musk and the Sam Altman-run firm OpenAI.
OpenAI, the xAI competitor for which Elon Musk previously served as a boardmember and helped to co-found, has reportedly poached high-level engineers from Tesla, along with others from xAI, X, and still others.
On Tuesday, Wired reported that OpenAI hired four high-level engineers from Tesla, xAI, and X, as seen in an internal Slack message sent by co-founder Greg Brockman. The engineers include Tesla Vice President of Software Engineering David Lau, X and xAI’s head of infrastructure engineering Uday Ruddarraju, and fellow xAI infrastructure engineer Mike Dalton. The hiring spree also included Angela Fan, an AI researcher from Meta.
“We’re excited to welcome these new members to our scaling team,” said Hannah Wong, an OpenAI spokesperson. “Our approach is to continue building and bringing together world-class infrastructure, research, and product teams to accelerate our mission and deliver the benefits of AI to hundreds of millions of people.”
Lau has been in his position as Tesla’s VP of Software Engineering since 2017, after previously working for the company’s firmware, platforms, and system integration divisions.
“It has become incredibly clear to me that accelerating progress towards safe, well-aligned artificial general intelligence is the most rewarding mission I could imagine for the next chapter of my career,” Lau said in a statement to Wired.
🚨Optimistic projections point to xAI possibly attaining profitability by 2027, according to Bloomberg's sources.
If accurate, this would be quite a feat for xAI. OpenAI, its biggest rival, is still looking at 2029 as the year it could become cash flow positive.💰 https://t.co/pE5Z9daez8
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) June 18, 2025
READ MORE ON OPENAI: Elon Musk’s OpenAI lawsuit clears hurdle as trial looms
At xAI, Ruddarraju and Dalton both played a large role in developing the Colossus supercomputer, which is comprised of over 200,000 GPUs. One of the major ongoing projects at OpenAI is the company’s Stargate program,
“Infrastructure is where research meets reality, and OpenAI has already demonstrated this successfully,” Ruddarraju told Wired in another statement. “Stargate, in particular, is an infrastructure moonshot that perfectly matches the ambitious, systems-level challenges I love taking on.”
Elon Musk is currently in the process of suing OpenAI for shifting toward a for-profit model, as well as for accepting an investment of billions of dollars from Microsoft. OpenAI retaliated with a counterlawsuit, in which it alleges that Musk is interfering with the company’s business and engaging in unfair competition practices.
Elon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
News
SpaceX share sale expected to back $400 billion valuation
The new SpaceX valuation would represent yet another record-high as far as privately-held companies in the U.S. go.

A new report this week suggests that Elon Musk-led rocket company SpaceX is considering an insider share sale that would value the company at $400 billion.
SpaceX is set to launch a primary fundraising round and sell a small number of new shares to investors, according to the report from Bloomberg, which cited people familiar with the matter who asked to remain anonymous due to the information not yet being public. Additionally, the company would sell shares from employees and early investors in a follow-up round, while the primary round would determine the price for the secondary round.
The valuation would represent the largest in history from a privately-owned company in the U.S., surpassing SpaceX’s previous record of $350 billion after a share buyback in December. Rivaling company valuations include ByteDance, the parent company of TikTok, as well as OpenAI.
Bloomberg went on to say that a SpaceX representative didn’t respond to a request for comment at the time of publishing. The publication also notes that the details of such a deal could still change, especially depending on interest from the insider sellers and share buyers.
Axiom’s Ax-4 astronauts arriving to the ISS! https://t.co/WQtTODaYfj
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) June 26, 2025
READ MORE ON SPACEX: SpaceX to decommission Dragon spacecraft in response to Pres. Trump war of words with Elon Musk
SpaceX’s valuation comes from a few different key factors, especially including the continued expansion of the company’s Starlink satellite internet company. According to the report, Starlink accounts for over half of the company’s yearly revenue. Meanwhile, the company produced its 10 millionth Starlink kit last month.
The company also continues to develop its Starship reusable rocket program, despite the company experiencing an explosion of the rocket on the test stand in Texas last month.
The company has also launched payloads for a number of companies and government contracts. In recent weeks, SpaceX launched Axiom’s Ax-4 mission, sending four astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS) for a 14-day stay to work on around 60 scientific experiments. The mission was launched using the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and a new Crew Dragon capsule, while the research is expected to span a range of fields including biology, material and physical sciences, and demonstrations of specialized technology.
News
Tesla Giga Texas continues to pile up with Cybercab castings
Tesla sure is gathering a lot of Cybercab components around the Giga Texas complex.
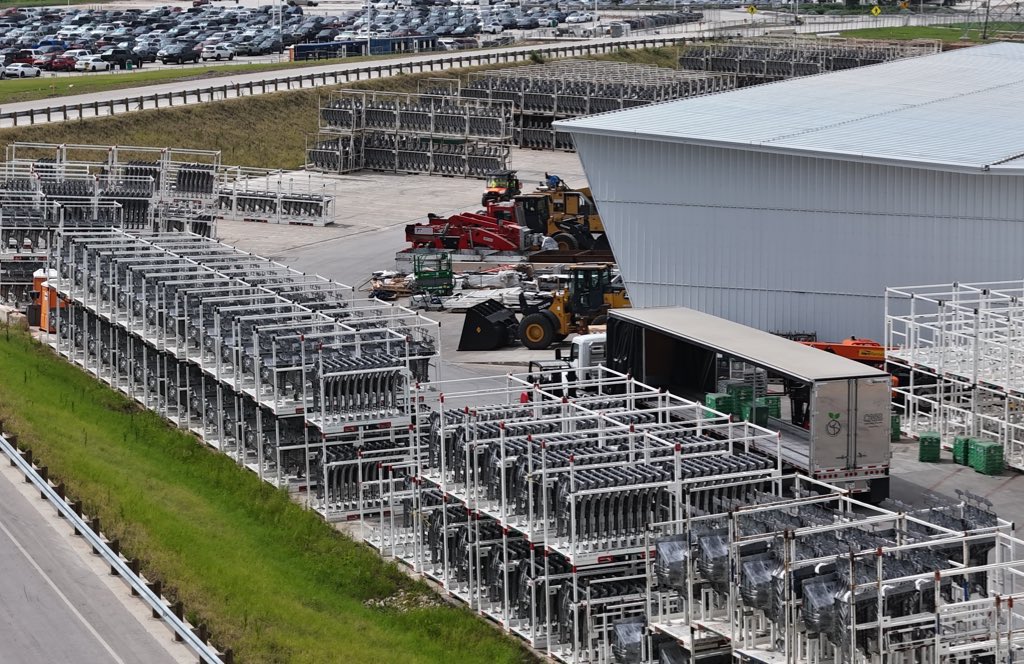

Tesla may be extremely tight-lipped about the new affordable models that it was expected to start producing in the first half of the year, but the company sure is gathering a lot of Cybercab castings around the Giga Texas complex. This is, at least, as per recent images taken of the facility.
Cybercab castings galore
As per longtime drone operator Joe Tegtmeyer, who has been chronicling the developments around the Giga Texas complex for several years now, the electric vehicle maker seems to be gathering hundreds of Cybercab castings around the factory.
Based on observations from industry watchers, the drone operator appears to have captured images of about 180 front and 180 rear Cybercab castings in his recent photos.
Considering the number of castings that were spotted around Giga Texas, it would appear that Tesla may indeed be preparing for the vehicle’s start of trial production sometime later this year. Interestingly enough, large numbers of Cybercab castings have been spotted around the Giga Texas complex in the past few months.
Cybercab production
The Cybercab is expected to be Tesla’s first vehicle that will adopt the company’s “unboxed” process. As per Tesla’s previous update letters, volume production of the Cybercab should start in 2026. So far, prototypes of the Cybercab have been spotted testing around Giga Texas, and expectations are high that the vehicle’s initial trial production should start this year.
With the start of Tesla’s dedicated Robotaxi service around Austin, it might only be a matter of time before the Cybercab starts being tested on public roads as well. When this happens, it would be very difficult to deny the fact that Tesla really does have a safe, working autonomous driving system, and it has the perfect vehicle for it, too.
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 Elon Musk1 day ago
Elon Musk1 day agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoWatch the first true Tesla Robotaxi intervention by safety monitor
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk confirms Tesla Optimus V3 already uses Grok voice AI
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI welcomes Memphis pollution results, environmental groups push back















