News
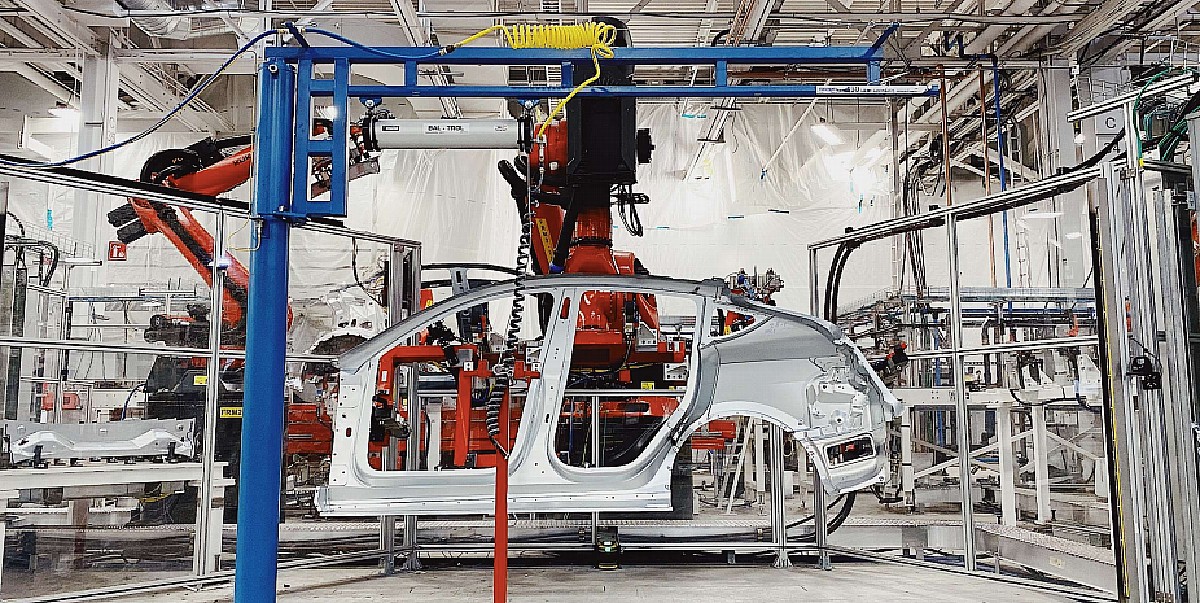
Tesla takes a step towards the Model Y’s single-piece cast with 410-ton machine purchase
When Elon Musk was interviewed in an episode of the Third Row Podcast earlier this year, he noted that the Model Y crossover’s rear underbody would eventually be built with a single-piece casting. This is quite a bold target, and one that can make the Model Y into one of the most cost-effective vehicles on the market today, electric or otherwise.
“The current version of Model Y has basically two big high-pressure diecast [HPDC] aluminum castings that are joined and there’s still a bunch of other bits that are attached. Later this year. We’ll transition to the rear underbody being a single-piece casting that also integrates the rear crash rails,” Musk remarked.
There are many advantages to using a single-piece cast for the Model Y. The vehicle could be built in a relatively simple manner by using fewer parts, helping the company optimize its production costs. Developing such a design only takes a lot of time and effort, as indicated by Elon Musk in the podcast.
“It gets better. The current castings, because you’ve got to interface with so many different things, we have to CNC-machine the interfaces and there’s a bunch of things that have to be joined; they have datums on them and that kind of thing. The single-piece casting has no CNC machining – it doesn’t even have datums. It took us a lot of iterations, by the way, to get there,” the CEO added.
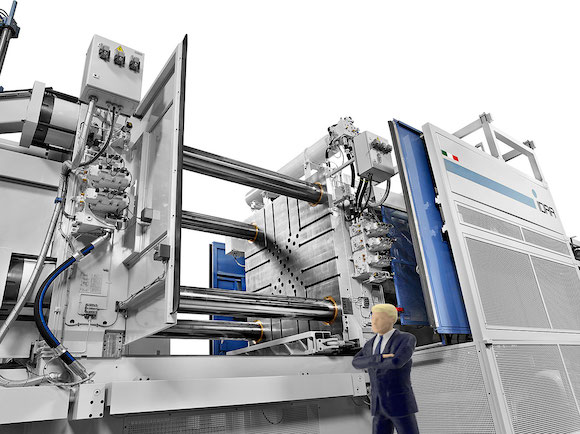
It appears that Tesla is now at a point where it is ready to pursue the Model Y’s single-piece cast. As indicated in a recent report on SAE Automotive Engineering, Tesla has purchased a machine from the IDRA Group, an Italian firm that makes HPDC equipment. What is rather interesting is that the machine that Tesla purchased is a gargantuan piece of equipment capable of producing the Model Y’s special components.
The machine that Tesla purchased, called the IDRA OL6100 CS, features an upgraded locking force that’s specially designed for the Model Y’s castings. Interestingly enough, the OL6100 CS is fondly dubbed as the “Giga Press” due to its size and power. The machine is 64 feet long and 17 feet high, and it weighs a whopping 410 tons. That’s roughly as heavy as five Space Shuttles.
Laurie Harbour, president at Harbour Results Inc., a manufacturing consultancy firm, noted that the new machine could effectively optimize the Model Y’s production process. With the Giga Press in use, Harbour estimates that Tesla could save about 20% on labor cost.
“Even with a big cycle time, you eliminate all the labor to assemble pieces and subcomponents. You’re saving on automation cells, you’re saving on people. It would be tough to put dollars to it, but think of multiple suppliers doing stampings, you could save maybe 20% on labor cost. And reduction in footprint is major. My guess is that it’s a net-net efficiency gain,” she said.
What is particularly interesting is that the Model Y was already highly optimized to begin with. Unlike the early production Model 3, which featured over 70 pieces in its rear underbody, early production Model Ys only had two large casts at the rear. This was confirmed by automotive teardown expert Sandy Munro, who conducted a thorough teardown of the Tesla Model Y from top to bottom.
Reflecting on the Model Y’s current casts, Munro noted that the vehicle had “two of the biggest castings we’ve ever seen in a car,” especially one in a consumer vehicle the size of the all-electric crossover. The teardown expert stated that other companies, such as BMW and Audi, have all used castings, but nothing comes close to the one that Tesla currently uses in the Model Y. And once Tesla moves to a single-piece casting system for the vehicle, Munro noted that the American electric car maker could “win the price.”
News
These Tesla, X, and xAI engineers were just poached by OpenAI
The news is the latest in an ongoing feud between Elon Musk and the Sam Altman-run firm OpenAI.
OpenAI, the xAI competitor for which Elon Musk previously served as a boardmember and helped to co-found, has reportedly poached high-level engineers from Tesla, along with others from xAI, X, and still others.
On Tuesday, Wired reported that OpenAI hired four high-level engineers from Tesla, xAI, and X, as seen in an internal Slack message sent by co-founder Greg Brockman. The engineers include Tesla Vice President of Software Engineering David Lau, X and xAI’s head of infrastructure engineering Uday Ruddarraju, and fellow xAI infrastructure engineer Mike Dalton. The hiring spree also included Angela Fan, an AI researcher from Meta.
“We’re excited to welcome these new members to our scaling team,” said Hannah Wong, an OpenAI spokesperson. “Our approach is to continue building and bringing together world-class infrastructure, research, and product teams to accelerate our mission and deliver the benefits of AI to hundreds of millions of people.”
Lau has been in his position as Tesla’s VP of Software Engineering since 2017, after previously working for the company’s firmware, platforms, and system integration divisions.
“It has become incredibly clear to me that accelerating progress towards safe, well-aligned artificial general intelligence is the most rewarding mission I could imagine for the next chapter of my career,” Lau said in a statement to Wired.
🚨Optimistic projections point to xAI possibly attaining profitability by 2027, according to Bloomberg's sources.
If accurate, this would be quite a feat for xAI. OpenAI, its biggest rival, is still looking at 2029 as the year it could become cash flow positive.💰 https://t.co/pE5Z9daez8
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) June 18, 2025
READ MORE ON OPENAI: Elon Musk’s OpenAI lawsuit clears hurdle as trial looms
At xAI, Ruddarraju and Dalton both played a large role in developing the Colossus supercomputer, which is comprised of over 200,000 GPUs. One of the major ongoing projects at OpenAI is the company’s Stargate program,
“Infrastructure is where research meets reality, and OpenAI has already demonstrated this successfully,” Ruddarraju told Wired in another statement. “Stargate, in particular, is an infrastructure moonshot that perfectly matches the ambitious, systems-level challenges I love taking on.”
Elon Musk is currently in the process of suing OpenAI for shifting toward a for-profit model, as well as for accepting an investment of billions of dollars from Microsoft. OpenAI retaliated with a counterlawsuit, in which it alleges that Musk is interfering with the company’s business and engaging in unfair competition practices.
Elon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
News
SpaceX share sale expected to back $400 billion valuation
The new SpaceX valuation would represent yet another record-high as far as privately-held companies in the U.S. go.

A new report this week suggests that Elon Musk-led rocket company SpaceX is considering an insider share sale that would value the company at $400 billion.
SpaceX is set to launch a primary fundraising round and sell a small number of new shares to investors, according to the report from Bloomberg, which cited people familiar with the matter who asked to remain anonymous due to the information not yet being public. Additionally, the company would sell shares from employees and early investors in a follow-up round, while the primary round would determine the price for the secondary round.
The valuation would represent the largest in history from a privately-owned company in the U.S., surpassing SpaceX’s previous record of $350 billion after a share buyback in December. Rivaling company valuations include ByteDance, the parent company of TikTok, as well as OpenAI.
Bloomberg went on to say that a SpaceX representative didn’t respond to a request for comment at the time of publishing. The publication also notes that the details of such a deal could still change, especially depending on interest from the insider sellers and share buyers.
Axiom’s Ax-4 astronauts arriving to the ISS! https://t.co/WQtTODaYfj
— TESLARATI (@Teslarati) June 26, 2025
READ MORE ON SPACEX: SpaceX to decommission Dragon spacecraft in response to Pres. Trump war of words with Elon Musk
SpaceX’s valuation comes from a few different key factors, especially including the continued expansion of the company’s Starlink satellite internet company. According to the report, Starlink accounts for over half of the company’s yearly revenue. Meanwhile, the company produced its 10 millionth Starlink kit last month.
The company also continues to develop its Starship reusable rocket program, despite the company experiencing an explosion of the rocket on the test stand in Texas last month.
The company has also launched payloads for a number of companies and government contracts. In recent weeks, SpaceX launched Axiom’s Ax-4 mission, sending four astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS) for a 14-day stay to work on around 60 scientific experiments. The mission was launched using the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and a new Crew Dragon capsule, while the research is expected to span a range of fields including biology, material and physical sciences, and demonstrations of specialized technology.
News
Tesla Giga Texas continues to pile up with Cybercab castings
Tesla sure is gathering a lot of Cybercab components around the Giga Texas complex.
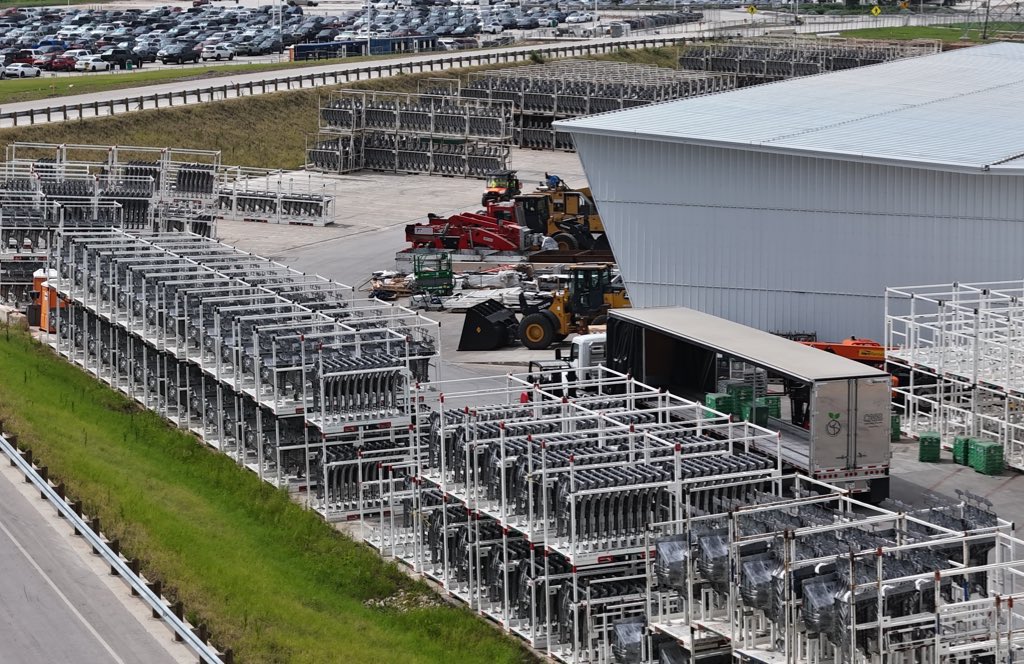

Tesla may be extremely tight-lipped about the new affordable models that it was expected to start producing in the first half of the year, but the company sure is gathering a lot of Cybercab castings around the Giga Texas complex. This is, at least, as per recent images taken of the facility.
Cybercab castings galore
As per longtime drone operator Joe Tegtmeyer, who has been chronicling the developments around the Giga Texas complex for several years now, the electric vehicle maker seems to be gathering hundreds of Cybercab castings around the factory.
Based on observations from industry watchers, the drone operator appears to have captured images of about 180 front and 180 rear Cybercab castings in his recent photos.
Considering the number of castings that were spotted around Giga Texas, it would appear that Tesla may indeed be preparing for the vehicle’s start of trial production sometime later this year. Interestingly enough, large numbers of Cybercab castings have been spotted around the Giga Texas complex in the past few months.
Cybercab production
The Cybercab is expected to be Tesla’s first vehicle that will adopt the company’s “unboxed” process. As per Tesla’s previous update letters, volume production of the Cybercab should start in 2026. So far, prototypes of the Cybercab have been spotted testing around Giga Texas, and expectations are high that the vehicle’s initial trial production should start this year.
With the start of Tesla’s dedicated Robotaxi service around Austin, it might only be a matter of time before the Cybercab starts being tested on public roads as well. When this happens, it would be very difficult to deny the fact that Tesla really does have a safe, working autonomous driving system, and it has the perfect vehicle for it, too.
-

 Elon Musk1 week ago
Elon Musk1 week agoTesla investors will be shocked by Jim Cramer’s latest assessment
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoTesla Robotaxi’s biggest challenge seems to be this one thing
-

 Elon Musk1 day ago
Elon Musk1 day agoElon Musk confirms Grok 4 launch on July 9 with livestream event
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoWatch the first true Tesla Robotaxi intervention by safety monitor
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoTesla Model 3 ranks as the safest new car in Europe for 2025, per Euro NCAP tests
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoA Tesla just delivered itself to a customer autonomously, Elon Musk confirms
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoxAI welcomes Memphis pollution results, environmental groups push back
-

 Elon Musk2 weeks ago
Elon Musk2 weeks agoElon Musk confirms Tesla Optimus V3 already uses Grok voice AI